Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Different Position of Patient During
Uploaded by
Rizthie Reconalla ValeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Different Position of Patient During
Uploaded by
Rizthie Reconalla ValeCopyright:
Available Formats
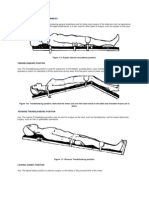
The usual position for surgery, called the dorsal recumbent position, is flat on the back.
One arm is positioned at the side of the table, with the hand placed palm down; the other is carefully positioned on an armboard to facilitate intravenous infusion of fluids, blood, or medications. This position is used for most abdominal surgeries except for surgery of the gallbladder and pelvis (see Fig. 19-3A).
The Trendelenburg position usually is used for surgery on the lower abdomen and pelvis to obtain good exposure by displacing the intestines into the upper abdomen. In this position, the head and body are lowered. The patient is held in position by padded shoulder braces (see Fig. 19-3B).
The lithotomy position is used for nearly all perineal, rectal, and vaginal surgical procedures (see Fig. 19-3C). The patient is positioned on the back with the legs and thighs flexed. The position is maintained by placing the feet in stirrups.
The Sims or lateral position is used for renal surgery. The patient is placed on the nonoperative side with an air pillow 12.5 to 15 cm (5 to 6 inches) thick under the loin, or on a table with a kidney or back lift (see Fig. 19-3D).
You might also like
- The Supine PositionDocument29 pagesThe Supine PositionKlaue Neiv CallaNo ratings yet
- تخدير نظري Lec 9Document8 pagesتخدير نظري Lec 969moctNo ratings yet
- PositionsDocument4 pagesPositionsMixsz LlhAdyNo ratings yet
- Surgical Positions: Surgical Positioning Is To Facilitate The Surgeon's Technical Approach While Balancing RiskDocument11 pagesSurgical Positions: Surgical Positioning Is To Facilitate The Surgeon's Technical Approach While Balancing RiskEinnel Nelmida0% (1)
- Operating Table2Document11 pagesOperating Table2Yhoyho Akhilun Dewa MimpiNo ratings yet
- Patient PositioningDocument4 pagesPatient PositioningAfifa Noori SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- PosicionesDocument12 pagesPosicioneshumberto paco jachoNo ratings yet
- Mobility 1Document47 pagesMobility 1Jan LagriaNo ratings yet
- NCMDocument2 pagesNCMDiana CaceresNo ratings yet
- Lithotomy Position V/s Lloyd Davis PositionDocument1 pageLithotomy Position V/s Lloyd Davis Positiondr_ella44No ratings yet
- Common Patient PositionsDocument26 pagesCommon Patient PositionsRonnel FranciaNo ratings yet
- Positions for Patient CareDocument26 pagesPositions for Patient CaresunielgowdaNo ratings yet
- Positions 140601013927 Phpapp01Document49 pagesPositions 140601013927 Phpapp01angelito cubeloNo ratings yet
- Hip and Knee Contractures PDFDocument19 pagesHip and Knee Contractures PDFreyNo ratings yet
- Positioning in NursingDocument6 pagesPositioning in NursingArsheen BalouchNo ratings yet
- POSITIONINGDocument25 pagesPOSITIONINGJhon Kenneth Magalong JuguilonNo ratings yet
- BSN1C Flores Ha (Rle) Ass2 PrelimsDocument11 pagesBSN1C Flores Ha (Rle) Ass2 PrelimsFrances Nicole FloresNo ratings yet
- Positioning PatientsDocument15 pagesPositioning Patientserica cucul.No ratings yet
- Goals of Patient Positioning: Patient Positions in BedDocument4 pagesGoals of Patient Positioning: Patient Positions in Bedjoanna sheenNo ratings yet
- Postural DrainageDocument7 pagesPostural DrainagemohtishimNo ratings yet
- Comfort MeasuresDocument7 pagesComfort MeasuresMary MenuNo ratings yet
- Body Mechanics GuideDocument5 pagesBody Mechanics GuideChrismon Arek KeneNo ratings yet
- eFAST MACDocument3 pageseFAST MACigd rssaNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomical TerminologyDocument11 pagesBasic Anatomical TerminologyJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Patient Positioning and NeuropathiesDocument57 pagesPatient Positioning and NeuropathiesAnangga AristantyoNo ratings yet
- Abdominal RadiographyDocument12 pagesAbdominal RadiographychidiogoNo ratings yet
- Group 41Document61 pagesGroup 41angelito cubeloNo ratings yet
- Patient Positioning: Complete Guide For Nurses: Marjo S. Malabanan, R.N.,M.NDocument43 pagesPatient Positioning: Complete Guide For Nurses: Marjo S. Malabanan, R.N.,M.NMercy Anne EcatNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris TK IiDocument5 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris TK IiNurharwati WanthyNo ratings yet
- Positions in NursingDocument3 pagesPositions in NursingAparna HarshanNo ratings yet
- Incision Access UrologyDocument47 pagesIncision Access UrologyHafizur RashidNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Positions Guide for SurgeryDocument6 pagesAnatomy Positions Guide for SurgeryJee ShangNo ratings yet
- Positioning NCLEXDocument4 pagesPositioning NCLEXShazaNo ratings yet
- Common P Ositions For PatientsDocument40 pagesCommon P Ositions For PatientsHARI KRISHNA G LNo ratings yet
- Laparoscopic Anatomy of the Abdominal CavityDocument14 pagesLaparoscopic Anatomy of the Abdominal CavityUffie-Isabela GheNo ratings yet
- Complete Guide to Patient Positioning BasicsDocument13 pagesComplete Guide to Patient Positioning BasicsAbriann Vince ImpenioNo ratings yet
- Patient PositioningDocument35 pagesPatient PositioningMona DoriaNo ratings yet
- Proper positioning techniquesDocument47 pagesProper positioning techniquesMuhammad Al-azzizNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia PositionsDocument19 pagesAnesthesia Positionsnicolinna2000yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Pantorrillas LipofillingDocument9 pagesPantorrillas LipofillingAntonio CardenasNo ratings yet
- Body MechanicsDocument47 pagesBody MechanicsTimothy BaltasarNo ratings yet
- Positioning and Its ImportanceDocument22 pagesPositioning and Its ImportanceDeepika PatidarNo ratings yet
- OMT Workshop Techniques - HohnerDocument43 pagesOMT Workshop Techniques - Hohnerstudentdoc440100% (1)
- Volumen AbdomenDocument5 pagesVolumen AbdomenManuel AGNo ratings yet
- Common Surgical Positions For OtDocument6 pagesCommon Surgical Positions For Otdharshinib2020No ratings yet
- Part A: Introduction To The Surface Anatomy of The Thoracic SpineDocument11 pagesPart A: Introduction To The Surface Anatomy of The Thoracic SpineHammad -ullahNo ratings yet
- Mobilzation Upper Limb PracticalDocument25 pagesMobilzation Upper Limb PracticalthestaffforpediatricptNo ratings yet
- Patient PositioningDocument54 pagesPatient PositioningLea Jean Lobrigo OleaNo ratings yet
- Pronation Therapy: DR Ahmed Abdelhady MD Critical Care ICU ConsultantDocument30 pagesPronation Therapy: DR Ahmed Abdelhady MD Critical Care ICU Consultantlayla alyamiNo ratings yet
- Five Different Patient PositionDocument1 pageFive Different Patient Positionfanboiitsme20No ratings yet
- Positioning OkDocument23 pagesPositioning OkDencel BarramedaNo ratings yet
- Modified Direct Lateral Approach for Total Hip ArthroplastyDocument5 pagesModified Direct Lateral Approach for Total Hip ArthroplastyscribdfoaktNo ratings yet
- Body Positions For Physical Exam PDFDocument2 pagesBody Positions For Physical Exam PDFReifonAruseifu100% (2)
- Abdominal Incisions NewDocument45 pagesAbdominal Incisions Newankit ahirNo ratings yet
- PositionsDocument16 pagesPositionsdenver matonNo ratings yet
- 2014 172 0 Retroperitoneal and Retrograde Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy As A Standard Treatment in A Community Hospital 97 101 1Document5 pages2014 172 0 Retroperitoneal and Retrograde Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy As A Standard Treatment in A Community Hospital 97 101 1Sarah MuharomahNo ratings yet
- Los Terrybles Book TeamDocument6 pagesLos Terrybles Book TeamWildor Herrera GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Tight Hip Flexors: Comprehensive Guide on How to Efficiently Relieve All Kinds of Pain Associated with Tight Hip Flexors in less Than 5 minutes; Tight Hip Flexor Home/Gym Remedies (Beginner's Guide)From EverandTight Hip Flexors: Comprehensive Guide on How to Efficiently Relieve All Kinds of Pain Associated with Tight Hip Flexors in less Than 5 minutes; Tight Hip Flexor Home/Gym Remedies (Beginner's Guide)No ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Ultrasound for the Orthopaedic Surgeon OR, ER and Clinic, Volume 2From EverandMusculoskeletal Ultrasound for the Orthopaedic Surgeon OR, ER and Clinic, Volume 2No ratings yet
- Tips for Everyday Life and Sports With an Artificial Joint: Expert guidebook for dealing with a prosthesis for patients with a new hip or knee jointFrom EverandTips for Everyday Life and Sports With an Artificial Joint: Expert guidebook for dealing with a prosthesis for patients with a new hip or knee jointNo ratings yet
- Handouts AnemiaDocument2 pagesHandouts AnemiaRizthie Reconalla ValeNo ratings yet
- Nursing HistoryDocument1 pageNursing HistoryRizthie Reconalla ValeNo ratings yet
- Different Position of Patient DuringDocument2 pagesDifferent Position of Patient DuringRizthie Reconalla ValeNo ratings yet
- The Mode of Action of AnesthesiaDocument1 pageThe Mode of Action of AnesthesiaRizthie Reconalla ValeNo ratings yet