Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Second Grade October Character Unit
Uploaded by
api-169447826Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Second Grade October Character Unit
Uploaded by
api-169447826Copyright:
Available Formats
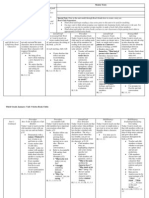
Second Grade October: Unit 3 Characters Face Bigger ChallengesMentor Texts: and So Do Readers Unit Objective: Students will
be able to walk in the characters shoes, role play, empathize with a character and predict while reading to increase fluency and intonation. Students will notice their characters settings, action, and Special note: Stop and jots can be in reading response journals or post it note form based on your teaching motivations. preference. Students will identify and analyze character traits and feelings. Students will think deeper and talk longer about the characters in their books. Part 1: Strategy/Skill Procedure Strategy/Skill Strategy/Skill Strategy/Skill Getting To Know Prediction Book Shopping Gathering Information Prediction Confirm/Revise Predictions Characters Wants Today I want to teach you that Today I want to teach you Today I want to teach you as Today I want to teach you that Today I want to teach you and Troubles we get to know the characters how readers find just right we read our books we add while reading we make that readers confirm and in the book well by paying books. new information to build an predictions about what will revise predictions about attention to their wants and P.54 understanding of who are happen to a character. characters as we read on. problems. One way we do characters are. P. 54,59 P. 54, 60 Five finger rule this is by looking at the title P. 54, 59 Think about the Determine if our Looking for interests and blurb on the back of the Think about the characters problem and predictions were Readability book before we begin reading. information we read ask: correct, confirm. If Using the blurb and P. 52-54, 59 from the blurb while What would I do not then revise and title. When reading the title or blurb reading the book. next if I were this read on with this Anchor Chart for readers ask themselves: character? new prediction. Add new information shopping. What kind of How would I try to about the setting and Star confirmed post Teacher can use problem will the work it out or get the characters lives. its and revise/edit book shopping lists. character face? what I want? unconfirmed Read on expecting to (making connections) What does the predictions. find the problem in character want? Paying close attentions the story. RL 2.10, 2.11 to the patterns in RL 2.1, 2.3, 2.7 Post it the new RL 2.1, 2.7 character behavior in information order to predict. Does collected. * Post its the character act in a will be saved and certain way over and used throughout the over again? What does unit. that make me think about RL 2.1, 2.3 how he/she will work out their problem? Look over previous stop and jots/Post its to locate patterns in character behaviors. RL 2.1, 2.3, 2.11
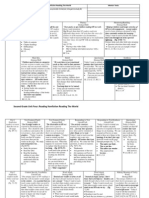
Second Grade October: Unit 3 Characters Face Bigger Challenges-and So Do Readers
Part 1: Getting To Know Characters Wants and Troubles
Literal/Craft Note-taking Today I want to teach you how to follow a characters wants and note how the character achieved them by marking their actions and decisions. P. 54-55 Model how to stop and post it important actions and decisions of the character during reading. RL 2.3
Literal/Craft Story Structure/Retelling Today I want to teach you how to keep track of our characters actions to make sure that we follow all that is happening in the story. P. 54-55,60 Model how to line up our previous post it notes in a sequential story arc to highlight the big things they are noticing about their character as well as to retell the bigger actions of the book. Story Arcs can be modeled/used here to introduce a 3rd grade skill. This helps students carry their thoughts throughout a text. After students put their post its in an arc they can reread their post-its and retell across them. RL 2.3, 2.5
Strategy/Skill Clarify/Monitor Today I want to teach you that when we read about a character we are on alert for scenes or details that dont fit with what we are expecting. P. 55,60 Model how stop and reread to clarify when something doesnt make sense in the story. RL 2.1
Procedure Partner Conversations Today I want to teach you how readers can talk with their partners about the books they have been reading. P. 55 Review anchor chart of partnership rules. Have partners retell their story to each other and discuss what they have noticed so far about their characters by using their notes and story arc. Teacher can use this time to conference with partnerships to notice the following: Transference of skills and strategies learned during read alouds and independent reading and the level of student conversations. SL 2.1, 2.4, 2.6 RL 2.3
Second Grade October: Unit 3 Characters Face Bigger Challenges-and So Do Readers
Part 2: Readers Think About Characters Traits and Feelings
Literal/Craft Character Traits Today I want to teach you that readers dont just make guesses about a character we refer to specific examples from the story to prove that a character is a certain way. P. 55, 60 Look for information about what kind of person a character is. Look for places in the text that show off that information and mark it! (Text based evidence) Model/push students to use specific language/words when describing their characters. For Ex. calling a character caring rather than nice. Create a character traits chart. Ex. T-Chart of Actions/Behaviors VS. Traits RL 2.3, 2.7
Literal/Craft Analyze Today I want to teach you that sometimes our characters act out of character. P. 56,60 Notice when characters act out of character. Readers can stop and say, Wait! Thats not like him/her. Student can stop and jot parts of the books where this might occur. RL 2.3, 2.6
Literal/Craft Analyze Today I want to teach you another way to study you characters. Readers dont just think about the characters traits, we track their feelings too. We notice what they are feeling the beginning, middle and end of the book. P. 56, 61 Point out how most characters core traits do not change throughout the book but their feelings may depending on the situation. (See page 61 for example) Model how to make an emotional timeline for the character using post its or readers notebook. RL 2.3,2.5, 2.7
Procedure Partner Conversations Today I want to teach you how partners can compare and contrast the main characters in their books using accountable talk. Review anchor chart of partnership rules. Have partners discuss their characters using their emotional timeline. Monitor students use of character trait language (referring to class chart) Teacher can use this time to conference with partnerships to notice the following: Transference of skills and strategies learned during read alouds and independent reading and the level of student conversations. SL 2.1 RL 2.3
Second Grade October: Unit 3 Characters Face Bigger Challenges-and So Do Readers
Part 3: Readers Can Find Deeper Meanings in Our Books
Strategy/Skill Asking and Answering Questions Today I want to teach you that when partners are reading and talking with each other we dont just talk about our thinking we also listen carefully to each other and add on to or raise questions about what our partners said. P. 56-61 Readers can first ask these questions to themselves to prepare for partner talk: Why would this character do that? Would I have behaved the same way? Partners can challenge each other by questioning. Why would Why did Would you SL 2.1, 2.3, 2.6 RL 2.3
Literal/Craft Growing Big Ideas/Partner Conversations Today I want to teach you how readers grow big ideas in our books. One way that readers do this is to use those feelings that we have been noticing in our books to help us think about the bigger ideas that the story is showing or teaching us. P. 56,61 Model how to find places where characters show strong emotions and then ask, Is something big happening here? This will help students find the important parts in their books. Once important parts are located have partners talk long about those parts in order to grow bigger ideas about the book. SL 2.1, 2.4, RL 2.2, 2.4, 2.5
Literal/Craft Cause & Effect/Preparing for Partner Talk Today I want to teach you that readers prepare for partner talk: As you read your notes you will look over and compare, gather up all your thoughts before you meet with your partner. P.61 Model how characters feelings affect what the character does (actions) by creating a T-Chart of Feelings Vs. Actions to help demonstrate Cause/Effect. Ex. Mudge was feeling sad when he was lost in the woods so he starting whimpering and walking slowly. After modeling and guided practice students will practice this activity independently in their own books in order to prepare for partnership conversations. **Partners can begin talking about what they gathered on the same day as this lesson or you can extend it into the next day. SL 2.1, 2.4, RL 2.3, 2.7
Literal/Craft Synthesizing/Preparing for Partner Talk Today I want to teach you that readers prepare for partner talk: We can think about how two ideas we have on a post it fit together. P.62 Model how earlier events tie into later events following the sequence of the story by classifying post its. After modeling and guided practice students will practice this activity independently in their own books in order to prepare for partnership conversations. SL 2.1, 2.4, RL 2.2, 2.5, 2.7
Literal/Craft Evaluating/Preparing for Partner Talk Today I want to teach you that readers prepare for partner talk: We can think about why or how the information we have gathered is important to the story. P.62 Model how readers can use text-based evidence to support their thinking. After modeling and guided practice students will practice this activity independently in their own books in order to prepare for partnership conversations. SL 2.1, 2.4 RL 2.2, 2.5, 2.7
Second Grade October: Unit 3 Characters Face Bigger Challenges-and So Do Readers
Part 3: Readers Can Find Deeper Meanings in Our Books
Strategy/Skill Opinion/Preparing for Partner Talk Today I want to teach you that readers prepare for partner talk: We can think about our own opinions about what the characters did or how they behaved. P.62 We can tell our partners what we liked about our characters, or that we were shocked by our characters. We say why we feel that way, too. SL2.1, RL 2.1, 2.7
Literal/Craft Synthesizing/Character Change One thing readers expect is that characters might be different at the end of the story then they were at the beginning. Today I want to teach you that when we read we want to catch the changes and think, Hmm, whats different now? What is changing and why? P.57, 62 Model how to mark where the character changes and list why it is important to the story using post its. Look back at the post its from the beginning, middle, and end of the story and compare them. RL 2.1, 2.3, 2.5
Literal/Craft Central Message/Reflection Today I want to teach you that readers not only learn about characters we learn from characters too. As we come to the end of the book we can ask ourselves, Did this character learn something that I can use to help me think about my life? P. 57,62 Model how to use our post its to look across the text and discover life lessons that can be learned from our characters. Have students think about how they can apply these lessons to their own lives. (possibly respond in readers notebook) RL 2.2, 2.11
Celebration Idea: Pick a character youve read about and create a character timeline.
Second Grade October: Unit 3 Characters Face Bigger Challenges-and So Do Readers
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Falcon LetterDocument1 pageFalcon Letterapi-169447826No ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Marcos Maldonado Ci Statement of NeedsDocument2 pagesMarcos Maldonado Ci Statement of Needsapi-169447826No ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Ira MccrackenDocument1 pageIra Mccrackenapi-169447826No ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Response RedactedDocument4 pagesResponse Redactedapi-169447826No ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- First Grade February Unit 5 We Can Be Our Own Teachers When We Work Hard To Figure Out WordsDocument5 pagesFirst Grade February Unit 5 We Can Be Our Own Teachers When We Work Hard To Figure Out Wordsapi-169447826No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- September Third Grade Launching 6-17Document3 pagesSeptember Third Grade Launching 6-17api-169447826No ratings yet
- 3rd Grade January Unit 3 Series BooksDocument6 pages3rd Grade January Unit 3 Series Booksapi-169447826No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Third Grade February Unit 6 BiographyDocument3 pagesThird Grade February Unit 6 Biographyapi-169447826No ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Second Grade January - February Series BooksDocument4 pagesSecond Grade January - February Series Booksapi-169447826No ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Budget LetterDocument1 pageBudget Letterapi-169447826No ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Third Grade October Unit 2 CharacterDocument4 pagesThird Grade October Unit 2 Characterapi-169447826No ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- November-December Third Grade Unit 4Document3 pagesNovember-December Third Grade Unit 4api-169447826No ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- September Second Grade LaunchingDocument2 pagesSeptember Second Grade Launchingapi-169447826No ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- November-December First Grade Unit 3Document4 pagesNovember-December First Grade Unit 3api-169447826No ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- First Grade January Unit 4 Non-FictionDocument6 pagesFirst Grade January Unit 4 Non-Fictionapi-169447826No ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- October First GradeDocument4 pagesOctober First Gradeapi-169447826No ratings yet
- Fifth Grade November-January Unit 3 Non Fiction ReadingDocument4 pagesFifth Grade November-January Unit 3 Non Fiction Readingapi-169447826No ratings yet
- Second Grade November-December Unit 4 NFDocument3 pagesSecond Grade November-December Unit 4 NFapi-169447826No ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- K Unit 3 NovemberDocument5 pagesK Unit 3 Novemberapi-169447826No ratings yet
- K Unit 5 JanuaryDocument2 pagesK Unit 5 Januaryapi-169447826No ratings yet
- K Unit 6 February Mid-MarchDocument3 pagesK Unit 6 February Mid-Marchapi-169447826No ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Fifth Grade November-January Unit 4-Nonfiction Research ProjectsDocument2 pagesFifth Grade November-January Unit 4-Nonfiction Research Projectsapi-169447826100% (1)
- Fifth Grade October Reading CharacterDocument4 pagesFifth Grade October Reading Characterapi-169447826No ratings yet
- K Unit 4 DecemberDocument4 pagesK Unit 4 Decemberapi-169447826No ratings yet
- K Unit 2 OctoberDocument2 pagesK Unit 2 Octoberapi-169447826No ratings yet
- Fifth Grade Unit 5 Historical Fiction CurriculumDocument3 pagesFifth Grade Unit 5 Historical Fiction Curriculumapi-169447826No ratings yet
- K Unit 1 SeptemberDocument2 pagesK Unit 1 Septemberapi-169447826No ratings yet
- 5th Grade September Reading Launch 2013Document2 pages5th Grade September Reading Launch 2013api-169447826No ratings yet
- Fourth Grade January MapDocument4 pagesFourth Grade January Mapapi-169447826No ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- 1 HN 1 To 4000Document308 pages1 HN 1 To 4000K SachinNo ratings yet
- LCD DLP PDP ComparisonDocument27 pagesLCD DLP PDP Comparisonahmad_wazierNo ratings yet
- VirginDocument14 pagesVirginGururaj Prakash75% (4)
- Catalog Company PDFDocument3 pagesCatalog Company PDFBukhori IsakNo ratings yet
- TANCET Model Question Paper For Me EEE PDFDocument51 pagesTANCET Model Question Paper For Me EEE PDFsree ramNo ratings yet
- Basculas Con MIGO SAPDocument3 pagesBasculas Con MIGO SAPmizraimNo ratings yet
- Types of AssessmentDocument7 pagesTypes of AssessmentAisa karatuanNo ratings yet
- Oil Based Mud ThinnerDocument2 pagesOil Based Mud ThinnerjangriNo ratings yet
- Chemicals Zetag DATA Organic Coagulants Magnafloc LT 7985 - 0410Document2 pagesChemicals Zetag DATA Organic Coagulants Magnafloc LT 7985 - 0410PromagEnviro.comNo ratings yet
- Muhamad Azamudin ResumeDocument1 pageMuhamad Azamudin ResumeMuhamad AzamudinNo ratings yet
- Tolerances of A Polystyrene Film: 2.2.25. ABSORPTION Spectrophotometry, Ultraviolet and VisibleDocument3 pagesTolerances of A Polystyrene Film: 2.2.25. ABSORPTION Spectrophotometry, Ultraviolet and Visibleivan cuadradoNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Munsat, S. - ProcessDocument6 pagesMunsat, S. - ProcessBen FortisNo ratings yet
- FormworksDocument94 pagesFormworksLouie Zavalla LeyvaNo ratings yet
- QMGT Assignment QMGT2015Document3 pagesQMGT Assignment QMGT2015LiibanMaahirNo ratings yet
- Project Vetting Worksheet-9472538Document4 pagesProject Vetting Worksheet-9472538kovzsanNo ratings yet
- Crossword PuzzleDocument2 pagesCrossword PuzzleGege MendozaNo ratings yet
- FMEADocument10 pagesFMEAlibyanleopardNo ratings yet
- Non Probability SamplingDocument9 pagesNon Probability SamplingMary Grace Broqueza100% (1)
- Thermal Comfort Bioclimatic Architecture StrategiesDocument21 pagesThermal Comfort Bioclimatic Architecture StrategiesJayshree RokdeNo ratings yet
- Standard Operation Procedures.06 - Potentially Hazardous Foods - Date MarkingDocument3 pagesStandard Operation Procedures.06 - Potentially Hazardous Foods - Date MarkingJumadi SuburNo ratings yet
- A Comparative GrammarDocument503 pagesA Comparative GrammarXweuis Hekuos KweNo ratings yet
- Anti AgingDocument5 pagesAnti AgingsaturninojonesNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument4 pagesComputer NetworksMainul HossainNo ratings yet
- Tehreem Mohsin (FA18-BBAH-0003) Eraj Rehan (FA18-BBAH-0004) Mehwish Naeem (FA18-BBAH-0007) Ameer Hamza (FA18-BBAH-0010)Document4 pagesTehreem Mohsin (FA18-BBAH-0003) Eraj Rehan (FA18-BBAH-0004) Mehwish Naeem (FA18-BBAH-0007) Ameer Hamza (FA18-BBAH-0010)Eraj RehanNo ratings yet
- Costing 1 PDFDocument8 pagesCosting 1 PDFSamyNo ratings yet
- APMA 3100 Chapter 1-HandoutDocument10 pagesAPMA 3100 Chapter 1-HandoutMichael ChangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document62 pagesChapter 3Matthew AloNo ratings yet
- Model 9200-2123: 1 RS-422 Input/3 RS-422 Output ModuleDocument2 pagesModel 9200-2123: 1 RS-422 Input/3 RS-422 Output ModuleNisar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cri 201 Pre Compre ExaminationDocument6 pagesCri 201 Pre Compre ExaminationKyle Adrian FedranoNo ratings yet
- Pork Carcass ChillingDocument6 pagesPork Carcass ChillingDumitru PodgorneakNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: The Infographics EditionFrom EverandThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: The Infographics EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2475)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Becoming Supernatural: How Common People Are Doing The UncommonFrom EverandBecoming Supernatural: How Common People Are Doing The UncommonRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1476)
- Summary: Atomic Habits by James Clear: An Easy & Proven Way to Build Good Habits & Break Bad OnesFrom EverandSummary: Atomic Habits by James Clear: An Easy & Proven Way to Build Good Habits & Break Bad OnesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1631)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)