Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WB Answers 2t U1 14
Uploaded by
api-222703744Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
WB Answers 2t U1 14
Uploaded by
api-222703744Copyright:
Available Formats
ANSWERSHEET Questions CHAPTER 1
WB 1.1 Heart 1. Muscle / chambers / atria / ventricles / valves / right atrium / right ventricle / lungs / oxygen / left atrium / left ventricle / all organs 2. Worksheet heart 3. Only have to squeeze the blood into the ventricles 4. Blood pressure caused by ventricles contracting / to prevent the blood from flowing back 5. Left ventricle needs to pump harder: higher pressure needed for body circulation and lung circulation needs lower pressure (the slower the flow the more oxygen can be taken up and high pressure would lead to flow of fluid into the lungs) 6. Only have to squeeze the blood into the ventricles 7. a. The heart / is made of / cardiac / muscle tissue / which can / contract / to pump / the blood / through / your body b. The valves / are made of / connective tissue / and prevent / blood from / flowing back c. The natural pacemaker / is located / in the wall / of the right atrium / of the heart / it is the place / where / the contraction of / the heart / starts
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
WORKBOOK BIOLOGY
2 tto 2011
ANSWERSHEET
Lyceum Oudehoven
ANSWERSHEET Questions CHAPTER 1
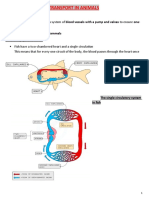
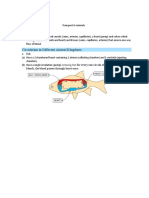
WB 1.2 Circulation 1. Oxygen / glucose / coronary / oxygenated / aorta / capillaries / exchange / nutrients / waste / CO2 / veins / inferior and superior vena cava 2. To allow exchange 3. To take up oxygen: it is hard to store oxygen 4. a. Coronary: to supply the heart / Pulmonary: to take up oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide / Systemic: to supply the organs b. Coronary can be considered to be part of Systemic 5. Worksheet circulation 6. See table below artery
carries blood from the heart very thick and muscular walls with elastic connective tissue
capillary
blood flows from the heart to the organs very thin walls (only one cell thick)
vein
carries blood to the heart thinner and not so very muscular with elastic connective tissue blood flows a bit faster no pulse valves to stop blood from flowing backwards
blood flows very fast blood flows slowly pulse no valves no pulse no valves
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
WORKBOOK BIOLOGY
2 tto 2011
ANSWERSHEET
Lyceum Oudehoven
ANSWERSHEET Questions CHAPTER 1
WB 1.3 Blood pressure and heart disease 1. a. pressure / arteries / pulse / wrist / neck b. measure / cuff / upper / stethoscope / brachial c. systole / pumping / heart (ventricle) /diastole / bounces / semi-lunar valves 2. It changes due to different needs (more exercise) or circumstances (falling in love, being nervous or angry): pumping harder means a higher pressure 3. Safer 4. Hypertension: (too) high blood pressure / atherosclerosis: cholesterol accumulates at the inside of arteries narrowing these / plaque: deposited fat becomes hard and stiff 5. Brain suffers from lack of oxygen because of blockage or rupture of a blood vessel 6. a. Balloon catheter inserted into an artery (arm or groin) and advanced into the narrowed (coronary) artery > inflated to widen it (stent to strengthen possible) b. medicines to solve clots or lower cholesterol, bypass operation, change in diet, extra exercise
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
WORKBOOK BIOLOGY
2 tto 2011
ANSWERSHEET
Lyceum Oudehoven
ANSWERSHEET Questions CHAPTER 1
WB 1.4 Blood
1. a. red / oxygen / nucleus / haemoglobin / white / phagocytes / engulfing / lymphocytes / specific / platelets / clotting / plasma b. heavier than waterl c. red blood cells 2. a. to leave capillaries and hug bacteria (deadly) b. dead white blood cells (with bacteria in them) 3. See table below
substance
oxygen carbondioxide glucose
entering organ
lungs all active tissues intestines / liver
leaving organ
all active tissues lungs all active tissues / liver all active tissues all active tissues all reacting tissues kidneys (sweating glands) all tissues / skin
minerals / vitamins / etc intestines water hormones waste heat intestines (exp. large) hormonal glands all active tissues all active tissues / liver
4. a. Producing the recipe for specific antibodies takes time. b. Antibodies are specific c. The recipe is DNA (specially designed by a cut-and-paste operation) d. The number of memory cells gradually decreases 5. When platelets / break open / in a wound / fibrinogen is changed / into fibrin. Sticky fibres / form a spider-like web / which traps blood cells / which stops the bleeding. Drying out / this clot forms a scab / which will fall off / as soon as enough / skin cells have been made / to heal the skin.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
WORKBOOK BIOLOGY
2 tto 2011
ANSWERSHEET
Lyceum Oudehoven
You might also like
- CAPEc 06Document30 pagesCAPEc 06Isheba Warren83% (6)
- CH 9 Animal Transport 2023Document46 pagesCH 9 Animal Transport 2023Mohamed AlyNo ratings yet
- 2015A&PIntro CardiovascularHandoutDocument16 pages2015A&PIntro CardiovascularHandoutMaggieHameedNo ratings yet
- 8 Transport in AnimalsDocument24 pages8 Transport in AnimalsMariam ShehabNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System PlanDocument95 pagesCirculatory System Plankirsten23No ratings yet
- Transport in ManDocument40 pagesTransport in ManßéršerK4040 KyùNo ratings yet
- Act 12Document3 pagesAct 12Rose CostaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System (Seeley)Document110 pagesCardiovascular System (Seeley)Reniella HidalgoNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument6 pagesHeartAhmed OmaarNo ratings yet
- W.G. Igcse Transport in HumansDocument20 pagesW.G. Igcse Transport in Humansbloodshooter1996No ratings yet
- 6 2 The Transport SystemDocument18 pages6 2 The Transport Systemapi-235355872No ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument53 pagesThe Circulatory SystemVera June RañesesNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument23 pagesThe Cardiovascular Systemrobhel740% (2)
- Cardiovascular System Chapter SummaryDocument4 pagesCardiovascular System Chapter Summarycuksam27No ratings yet
- TUMS - GE. ReadingScience. UnitFiveDocument39 pagesTUMS - GE. ReadingScience. UnitFivemohammadNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System P2Document17 pagesThe Circulatory System P2Kristal CampbellNo ratings yet
- Transport in Man 2Document54 pagesTransport in Man 2ßéršerK4040 KyùNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals-Topic 9Document14 pagesTransport in Animals-Topic 9sukiiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System BSN 1Document16 pagesCardiovascular System BSN 1Arianne Jen GenotivaNo ratings yet
- 8th CIRCULATORY SYSTEMDocument6 pages8th CIRCULATORY SYSTEMammarahn0No ratings yet
- The 12 fields of Chinese medicineDocument5 pagesThe 12 fields of Chinese medicineMiguel Nunez100% (1)
- Transport in AnimalsDocument19 pagesTransport in Animalsmohamed komiNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System and Heart Biology Summarisation.Document5 pagesCirculatory System and Heart Biology Summarisation.Jumana ElkhateebNo ratings yet
- Y10 Heart & CirculationDocument11 pagesY10 Heart & CirculationTri MariyantiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument40 pagesCardiovascular SystemDouglas Jacques100% (1)
- Chapter VIII CardiovascularDocument7 pagesChapter VIII CardiovascularTitoMacoyTVNo ratings yet
- IM-AnSci-111-Module-4Document24 pagesIM-AnSci-111-Module-4Riza Mae Duran RangasNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument31 pagesThe Circulatory SystemAyesha DuaNo ratings yet
- CardiovascularDocument6 pagesCardiovascularMabes100% (1)
- Bio Transport in HumansDocument24 pagesBio Transport in HumansNicoleNo ratings yet
- CPT CH 3 10-11-04 PDFDocument24 pagesCPT CH 3 10-11-04 PDFghindaruNo ratings yet
- امتحان تشريحDocument3 pagesامتحان تشريحAhmed Mohammed AttallahNo ratings yet
- SGS CVS (Lec 10-12) - 2022 StudentDocument7 pagesSGS CVS (Lec 10-12) - 2022 StudentNUR RADHIAH MOHD SAZLINo ratings yet
- Pre - Lab # 4 - Circulatory System: Label The Diagrams of Anterior, Posterior and Coronal View of The HeartDocument23 pagesPre - Lab # 4 - Circulatory System: Label The Diagrams of Anterior, Posterior and Coronal View of The Heartmpetrov_2No ratings yet
- Blood and Circulation: Done by Dania, Najla and VarshaDocument39 pagesBlood and Circulation: Done by Dania, Najla and VarshaD HNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs: Blood Pressure: Video 2.1: Introduction To The Blood VesselsDocument8 pagesVital Signs: Blood Pressure: Video 2.1: Introduction To The Blood VesselsNelu CastravetNo ratings yet
- The circulatory system in 30 secondsDocument11 pagesThe circulatory system in 30 secondsRentika SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document71 pagesLesson 3Angel joyce ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Name: - Class: - Date: - Note-MakingDocument2 pagesName: - Class: - Date: - Note-MakingSakina HaiderNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System ExplainedDocument15 pagesCardiovascular System ExplainedArif WahyuNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Notes IgcseDocument19 pagesCirculatory System Notes IgcseWork WiseNo ratings yet
- Notes Grade: 9 Subject: Biology Chapter No: 9 Chapter Name: Transport in Animals ObjectivesDocument36 pagesNotes Grade: 9 Subject: Biology Chapter No: 9 Chapter Name: Transport in Animals Objectivespraneeth satishNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Transport in HumansDocument11 pages5.2 Transport in Humans박찬우No ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument6 pagesBio NotesJessica KunderNo ratings yet
- CardiovascularDocument7 pagesCardiovascularapi-294104473No ratings yet
- Anp2001 Test 1 Questions 2014Document7 pagesAnp2001 Test 1 Questions 2014Jerilee SoCute WattsNo ratings yet
- Cardio 1Document4 pagesCardio 1Liam Jacque LapuzNo ratings yet
- Review and Comprehension (Blood Vessel)Document4 pagesReview and Comprehension (Blood Vessel)9pjh6pzxmsNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Study GuideDocument11 pagesCardiovascular System Study GuideS. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument33 pagesTransport in AnimalssamskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Training OverviewDocument50 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Training OverviewAlisa BrownNo ratings yet
- 03 The Cardiorespiratory SystemDocument24 pages03 The Cardiorespiratory SystemDuane N Lin WertNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The HeartDocument3 pagesStructure and Function of The Heartuserdev987No ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument43 pagesTransport in AnimalsEdwins MaranduNo ratings yet
- The Cardiac CycleDocument27 pagesThe Cardiac Cycletapan_parikh_2No ratings yet
- Comprobación de Lectura 3Document7 pagesComprobación de Lectura 3leomartinez2907No ratings yet
- B2U3 CirculationNotesDocument15 pagesB2U3 CirculationNotesVanusha Azzriel100% (1)
- Heart Page - (1677340777450)Document1 pageHeart Page - (1677340777450)ainalashari69No ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Transport In HumansFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Transport In HumansNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 3t Workbook Biology Answers 202122 11 14Document4 pages3t Workbook Biology Answers 202122 11 14api-222703744No ratings yet
- 3t Workbook Biology Answers 202021 Senses PDFDocument3 pages3t Workbook Biology Answers 202021 Senses PDFapi-222703744No ratings yet
- 3t Workbook Biology Answers 202021 16 PDFDocument5 pages3t Workbook Biology Answers 202021 16 PDFapi-222703744No ratings yet
- 2t Workbook 2019 2627Document1 page2t Workbook 2019 2627api-222703744No ratings yet
- 1t WB Answers 2019 U3 Ws 3 PDFDocument2 pages1t WB Answers 2019 U3 Ws 3 PDFapi-222703744No ratings yet
- Cambridge Checkpoints AnswersDocument3 pagesCambridge Checkpoints Answersapi-22270374454% (13)
- Workbook Biology 3t 201415 SP Answers 1 Ecology 1123Document2 pagesWorkbook Biology 3t 201415 SP Answers 1 Ecology 1123api-222703744No ratings yet
- Ojwbookt 2014pDocument31 pagesOjwbookt 2014papi-222703744No ratings yet
- WB Answers 2t U3Document3 pagesWB Answers 2t U3api-222703744No ratings yet
- Ky'air Thomas AutopsyReport Original 2023-03-08Document6 pagesKy'air Thomas AutopsyReport Original 2023-03-08Matt ThomasNo ratings yet
- Monitoring of Critically Ill PatientDocument11 pagesMonitoring of Critically Ill PatientAnusikta PandaNo ratings yet
- Feeding techniques for babies with cleft lip or palateDocument14 pagesFeeding techniques for babies with cleft lip or palateTrishaNo ratings yet
- Quiz Results: NURS 502 Med / Surg Cardiovascular System Correct Answers: 7Document7 pagesQuiz Results: NURS 502 Med / Surg Cardiovascular System Correct Answers: 7Moshi LoveNo ratings yet
- NBME 26 QuestionDocument54 pagesNBME 26 Questionsabrina kawkabNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology SlidesDocument372 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Slidesnursereview100% (184)
- Biology SS2 1ST Term E-NotesDocument53 pagesBiology SS2 1ST Term E-NotesINIOLUWA AKEJU100% (5)
- Nilai Normal Lab Osce Dan SocaDocument8 pagesNilai Normal Lab Osce Dan SocaLeilybadryaNo ratings yet
- Tetrapods + AmniotesDocument40 pagesTetrapods + Amnioteskfagg0tNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure LectureDocument102 pagesCongestive Heart Failure Lectureluke100% (1)
- Comparative Rates of Conduction System FiringDocument3 pagesComparative Rates of Conduction System FiringSulochana ChanNo ratings yet
- All Previous Krok ExamsDocument224 pagesAll Previous Krok ExamsOnur KoyuncuNo ratings yet
- Venous Return - MagderDocument11 pagesVenous Return - MagderagyaprempehNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument29 pagesBiologyDejan UrbanekNo ratings yet
- Abduraham Rayyan-Module-Cardiovascular-SystemDocument17 pagesAbduraham Rayyan-Module-Cardiovascular-SystemRAYYAN ENIL ABDURAHAMNo ratings yet
- PMLS 2 ReviewerDocument8 pagesPMLS 2 ReviewerNepoy Beltran Entendez100% (3)
- Diz AutopsyDocument5 pagesDiz AutopsyJennifer SaylorNo ratings yet
- Left and Right Heart Cath Procedure OverviewDocument43 pagesLeft and Right Heart Cath Procedure OverviewIr Soebagoes100% (2)
- Early Complications of MIDocument11 pagesEarly Complications of MIjen262004No ratings yet
- Questions Tricks and Tips For The Echocardiography BoardsDocument489 pagesQuestions Tricks and Tips For The Echocardiography BoardsArtur TarsaNo ratings yet
- General Heart Diagram, Handout Heart Diagram, Vessels HandoutDocument4 pagesGeneral Heart Diagram, Handout Heart Diagram, Vessels HandoutJNo ratings yet
- CV Examples PDFDocument5 pagesCV Examples PDFAsp Corp SlaveNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For High Acuity Nursing 7th Edition WagnerDocument25 pagesSolution Manual For High Acuity Nursing 7th Edition WagnerJamesThomasngec100% (31)
- Siemens Acuson Sc2000 Interventional FlyerDocument6 pagesSiemens Acuson Sc2000 Interventional Flyerbashir019No ratings yet
- The Anatomy of The Coronary SinusDocument7 pagesThe Anatomy of The Coronary Sinusmihalcea alinNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument48 pagesCardiomalisalukmanNo ratings yet
- Fetal Echocardiography Views and Anatomy (40Document63 pagesFetal Echocardiography Views and Anatomy (40Muhammad Abeesh100% (1)
- Patient Profile and History of Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument32 pagesPatient Profile and History of Acute Coronary SyndromenidhiNo ratings yet
- The Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Valve SteDocument6 pagesThe Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Valve SteNiarti Ulan SariNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Biology Circulation and Transportation Part 1Document8 pagesClass 10 Biology Circulation and Transportation Part 1HEMALAH SNo ratings yet