Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conv Civil I
Uploaded by
sonu_saurabhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Conv Civil I
Uploaded by
sonu_saurabhCopyright:
Available Formats
SI .. No ..
18401
I A-FTF-J-DFA I
t.~r;r"t.fl!: ~t:. qi~Q"T, •• - -.~ •• ~,
En ei n ~~ r 1 n jl Sc r vice Exam ina t ion. :-
.,
CIVIL ENGINEERING
Paper I (Conventional)
I Time Allowed .- Three Hours I I Maxi;lUm Marks .- 200 I
INSTRUCTIQ-NS
Candidates should attempt any FIVE questions.
The number of marks carried by each subdivision of a question is indicated at the end of the subdivision.
The total number of marks for each- question will be 40.
Wherever a question is attempted, all its subdivisions are to be attempted, ·
Notations used are standard and will have their . us ual meanings,
ASSUI11e suitable data, if found necessary, and indicate them clearly. Newton may be converted to kgf using the relation 1 kilonewton _
. (1 kN) = 100 kg{, if found necessary.
"
Answers must be written in ENGLISH.
- A-FTF-J-DFA
2
(Contd.)
·1. (a). (1) Draw a sketch showing the typical creep strain-time curve under uniaxial..
compression for concrete. 4
(ii) Draw a neat sketch of macrostructure of
exogenous tree. 3 .
(iii) Draw neat sketches showing various
types of shakes. 3
•
(b)
(i) Why is seasoning of timber required?
List out the methods of ·seasoning. 4
(ii) Write briefly on the composition and
properties of refractory bricks. 6
(c) Briefly describe the admixtures generally used in concrete and the properties they impart to the concrete. 10
(d) (i). Give a detailed account of the cylinder
splitting test of concrete. . 8
(ii) What are the limitations of the above test in evaluating the real tensile strength of c~cre~. 2
...
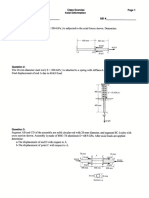
2. (a)
T
1m
A stepped vertical steel bar ABeD is fixed
,
at the top end A. Each segment of the bar
AB, Be and CD is 1 m long and has crosssections 20 mm x 20 rom, 10 mm x 10 nun and 20 mm x 20 mm respectively. A 5 kN load is applied directly at D and 6 kN loads are applied on, the levers attached to the stepped bar at Band C as shown in the above figure. Find the vertical displacement of D and the change in
volume of the bar. '
E = 2 x 105 MPa and Poisson's ratio J..l = 0·25. Connections between the levers and bar at Band C, are hinged. 15
·A-FfF-J-DFA
3
(Contd.)
A'-FTF'-J-DFA
4
(Contd.)
..
(b) A cantilever beam with circular cross-section of radius 100 mrrr is subjected to a uniformly distributed load over the enti!e span. It 1S given
. that the deflected shape of the beam has a maximum curvature of 1·018592 x 1(r6 mm"! and a maximum shear force of 1 kN. Find the intensity of loading on the beam and its span.
o E = 2 x 105 MPa. 10
.
(~) A solid circular shaft of diameter 50 mrn is
subjected to pure bending of 3·5 kN-m. Find the maximum twisting moment that can be applied on this shaft such that the rnatcrial of the shaft does not yield. Use Tresca's theory (maximum shear stress theory) of failure. The
-yield stress of the material in urriaxial tension is 400 N/mm2. 15
3. (;1) A uniformly distributed load of 2000 kg/rn, 6 m long crosses over a girder simply supported at ends over a span of 10m from left to right. Calculate maximum bending moment in the girder at a point 4·5 m from left hand end using influence lines. . 20
5
(Contd.)
•
(b)
600 kgf/m
+ 700 kgf _......,::~ccx::::x:~~ 2m
L
..
1
2m
-t-
A portal frame ABCDEF with inclined legs has hinges at B~ D and E .as shown in the above figure. Joint at C is mono1ithic. Supports at A and F are fixed. Calculate all components of reactions. 20
ponents of the reactions atA and B.
20
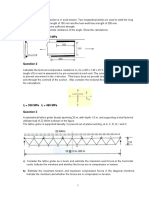
4. '(a)
tv /unit length
~A __ '_" ~B~
f / 2 J
~ ~ ~
11'------ L 'f L 1
A stepped beam ABC, simply supported at A
.: and fixed at C as shown in the above figure carries a uniformly distributed load of intensity '(f)' peer unit' Jength over Be. Determine the vertical reaction at A using moment are~ or energy method. 20
(b)
AU the members of steel truss shown, in the above figure are pin-jointed and have same area
of cross-section. ,;
Calculate the vertical and horizontal corn-
A-FIF-J-DFA
6
(Contd.)
•
A-FIF-J-DFA
7
(Contd.)
5.· (a) An unequal angle section 200 mm x 150 mm x 15 mm is to be used in a truss as a strut of ~eng~h 4·5 rn.I The cross-sectional properties of . the section are as follows:
Area of cross-section = 5025 mm2
I = 2 X 107 mm": I -= 9·7 x 106 mm":
xx ,'YY' . ,
I = -8·3 x 106 ffim4 xy
. using the table of permissible compressive stresses given below, determine the safe load on the member.
Slenderness 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180
Ratio
Permissible .
compres- 80 72 64 57 51 45 41 37 33
sive stress
MPa 20
(b) A mild steel T section has the following crosssectional dimensions ': .
Total depth = 200 mm
Width of flange = 120 mm
Thickness of flange = 20 mm
Thickness of web = 20 mm .
_ If the yield stress, a = 250 MPa determine the plastic moment ~apacity of the section. Also calculate the shape factor for the section. 20
A reinforced concrete beam of rectangular cross-section (6001nm x 300 mrn) is shown in the above figure. Assume M20 grade concrete and Fe 415 grade steel. Permissible compressive stress of concrete in bending ache =7-0 MPa fOT M20 concrete.
Compute the maximum stresses in concrete and steel when a moment of 50 kNm is applied to the cross-section. 25
6 .. (a)
A-FIF'-J-DFA'
'""'-I 11(1----" b = 300 ----1 .. ~1
8
AJJ dimensions are in mm
NA
44»25
(Contd.)
..
(b)
p, q per uni t length
p
~'~~--------~IJ~I----------~~I '
A simply supported high strength concrete beam of rectangular cross-section (b x D) .. shown in the above figure, supports uniformly distributed dead and live loads of intensities
'p and q per unit length respectively. The beam is prestressed by a straight tendon carrying a prestressing force P at an eccentricity e. Show clearly and neatly the stress distributions, through the beam' depth, due to eccentric prestressing, dead and live loads at a crosssection where maximum stresses occur. 15
"
7. (a)
(i) Briefly explain the different types of
bulldozers according to their uses. 6
(ii) Explain the Derrick crane with a neat'
sketch. 4
A-FIF-J-DFA
9·
(Contd.)
'(b) (i) Enlist and explain Time estimates In
· PERT. 6
(ii) Explain Resources Allocation.
4
(c) A construction work consists ofactivities with J'ERT durations in days as given below :
Activity - p Q R S T U W Y Z
Predecessor - p~ T' Q - s - s s u.w
'0 3 4 4 3 8 1 2 4 6
.
tm 6 8 5 3 14 4 5 7 15
.
tp 9 9 9 3 17 7 14 13 30 Determine :
(j) The probability of completing the job in 32 days and
(ii) The completion time with 50% probability .
.
Z . Probability %
-1·5 0·07
-1 .. 3 0·10 .
-}·o 0·16 10
A-F I'F-J-DFA
10
•
Normal - Crash
,
Activity I
Duration Cost Duration Cost
Days Rs. Days. Rs.
~
-
1-2 5 4000 4 ,5000
1-3 7 8000 . 3· 10000
2-3 6 6000 2 8400 "
(d) Calculate optimum cost .and optimum duration for jobs of network given in the table below;
Indirect cost = Rs. 1000/- per day. Sketch pro: ject time-cost diagram. 10
•
..
A ... f'TF-I-DFA
11
..
----.--.-----~------------------
You might also like
- IES Civil Engineering Conventional Paper 2014Document27 pagesIES Civil Engineering Conventional Paper 2014mantuiitNo ratings yet
- IES Civil Engineeering Conventional 2015Document27 pagesIES Civil Engineeering Conventional 2015Vishal BabuNo ratings yet
- L-2/T-1/CE Date: 31/01/2012: Section - ADocument17 pagesL-2/T-1/CE Date: 31/01/2012: Section - AMahmudul Hasan PathikNo ratings yet
- Me218 Fa15 W3 HoDocument10 pagesMe218 Fa15 W3 HonhiuNo ratings yet
- Mu 3 Sem Mech PapersDocument26 pagesMu 3 Sem Mech PapersJyoten PanditpautraNo ratings yet
- QQ 10623 Ques PaperDocument6 pagesQQ 10623 Ques PaperJsvijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Ib Tutorial 4 (12 13) Sem 2Document5 pagesIb Tutorial 4 (12 13) Sem 2omarnasriNo ratings yet
- NR 10105 Engineering MechanicsDocument13 pagesNR 10105 Engineering MechanicsVijay PrakashNo ratings yet
- Detailed Calculation For Box Girder DesignDocument109 pagesDetailed Calculation For Box Girder Designleodegarioporral100% (8)
- 2014-2015 (L-2, T-1) - CeDocument18 pages2014-2015 (L-2, T-1) - CeRizwan saleheenNo ratings yet
- Strut and tie modeling, yield line analysis, and plastic analysis of concrete and steel structuresDocument9 pagesStrut and tie modeling, yield line analysis, and plastic analysis of concrete and steel structuresmalumius100% (2)
- Biaxial Bending Analysis of Reinforced Brick ColumnsDocument12 pagesBiaxial Bending Analysis of Reinforced Brick Columnsdonban1992No ratings yet
- JNTU BTech Civil Engineering Advanced Structural Analysis Exam QuestionsDocument19 pagesJNTU BTech Civil Engineering Advanced Structural Analysis Exam QuestionsMohammed AbidNo ratings yet
- NAME-2010-2011(L-2,T-1)Document16 pagesNAME-2010-2011(L-2,T-1)partho RoyNo ratings yet
- Mace 60035Document7 pagesMace 60035eng_ayman_H_MNo ratings yet
- Sheet No.2 (Simple Stress)Document3 pagesSheet No.2 (Simple Stress)elhalawanyh46No ratings yet
- Modeloprovadoutorado 2020Document12 pagesModeloprovadoutorado 2020Thaís RamosNo ratings yet
- Design of RCC StructureDocument14 pagesDesign of RCC Structuremark bingNo ratings yet
- Solid MechanicDocument7 pagesSolid MechaniczinilNo ratings yet
- Ce2201 QB2Document15 pagesCe2201 QB2Balaji KumarNo ratings yet
- Forces in members of a trussed structureDocument8 pagesForces in members of a trussed structureSrikrishna JanaNo ratings yet
- Rotal No. of Questions-121 (Rotal No. of ' (?D J"JDocument7 pagesRotal No. of Questions-121 (Rotal No. of ' (?D J"JAshenafi Gebremeskel MezgeboNo ratings yet
- Compression MembersDocument11 pagesCompression Membersayush kumarNo ratings yet
- 11.a.ii - ME03031 QA 1Document22 pages11.a.ii - ME03031 QA 1Bakkiya Raj100% (1)
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: InstructionsBhavesh PipaliyaNo ratings yet
- TE 1997 and 2003 Course Oct 2009Document492 pagesTE 1997 and 2003 Course Oct 2009Ajay Solate0% (1)
- International Institute of Management & Technical Studies: Structural Analysis - IIDocument5 pagesInternational Institute of Management & Technical Studies: Structural Analysis - IImohammed qasimNo ratings yet
- Lista 3Document7 pagesLista 3Rodolfo Souza MartinsNo ratings yet
- Engineering Exam Practice Questions: Steel Design, Structural Analysis & DesignDocument4 pagesEngineering Exam Practice Questions: Steel Design, Structural Analysis & DesignPalesa TshetlanyaneNo ratings yet
- IT-09-2nd SemDocument11 pagesIT-09-2nd SemHimanshu VimalNo ratings yet
- Examination: Testing of Metallic Materials / SS 2011Document6 pagesExamination: Testing of Metallic Materials / SS 2011BijoyBanikNo ratings yet
- 9A01302 Strength of Materials - IDocument8 pages9A01302 Strength of Materials - IsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- L-2/T - 2/CE: Date: 15/0112017Document17 pagesL-2/T - 2/CE: Date: 15/0112017ﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Sample Question PaperDocument4 pagesMechanical Engineering Sample Question PaperManiVijayNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids PDFDocument8 pagesMechanics of Solids PDFprashanthreddy26No ratings yet
- IES Conventional Electrical Engineering 2012Document28 pagesIES Conventional Electrical Engineering 2012Srujan BobbyNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Autumn 2012Document7 pagesMachine Design Autumn 2012stansilawNo ratings yet
- Chap5 7Document136 pagesChap5 7estafahad63% (8)
- Mechanics of Solids (CIE 1051)Document4 pagesMechanics of Solids (CIE 1051)aryansorout1612No ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Question BankDocument59 pagesEngineering Mechanics Question BankvelavansuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 07 AE670Document3 pagesAssignment 07 AE670Audrey BrooksNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Machinery r10 May-2016Document20 pagesDynamics of Machinery r10 May-2016Srimanthula SrikanthNo ratings yet
- CE199 2L 1Q1819 DC 1st TakeDocument10 pagesCE199 2L 1Q1819 DC 1st TakeJohn Michael Ramos100% (1)
- Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument4 pagesDepartment of Mechanical EngineeringAshok DaraNo ratings yet
- Mock Quiz Solution Key PDFDocument20 pagesMock Quiz Solution Key PDFLong Live TauNo ratings yet
- CVEN3302 - Final Examination 2009Document5 pagesCVEN3302 - Final Examination 2009fflegendsNo ratings yet
- 9A21504 Aerospace Vehicle Structures IIDocument8 pages9A21504 Aerospace Vehicle Structures IIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Worked Example (Not in Notes) : Reinforced Concrete Beam: Z F A Z F M BD F A F D Z F B F A X E F D XDocument5 pagesWorked Example (Not in Notes) : Reinforced Concrete Beam: Z F A Z F M BD F A F D Z F B F A X E F D XJakir Hussain SyedNo ratings yet
- r13 Mos Old Q PapersDocument21 pagesr13 Mos Old Q PapersSrinu ReddyNo ratings yet
- Jun 2016Document2 pagesJun 2016RadhaAnanthalekshmiNo ratings yet
- L-2/T-2/WRE Date: 06/07/2013Document18 pagesL-2/T-2/WRE Date: 06/07/2013MuradNo ratings yet
- Tutorials 2016Document54 pagesTutorials 2016Mankush Jain100% (1)
- 4 ME Som Model Examination 2013Document3 pages4 ME Som Model Examination 2013BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: InstructionsBhavesh PipaliyaNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionFrom EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionNo ratings yet
- Parts Catalog: Dgda DGDBDocument85 pagesParts Catalog: Dgda DGDBsonu_saurabh100% (1)
- Thrust BearingDocument8 pagesThrust Bearingsonu_saurabh100% (1)
- Diesel EnginesDocument1 pageDiesel Enginessonu_saurabhNo ratings yet
- Casting ProcessDocument30 pagesCasting ProcessParas ThakurNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Waterjet CuttingDocument24 pagesPresentation On Waterjet Cuttingsonu_saurabhNo ratings yet
- AIEEE 2011 Information BrochureDocument32 pagesAIEEE 2011 Information BrochureAnkur PriyamNo ratings yet
- Abhi Kuch Dino SeDocument2 pagesAbhi Kuch Dino Sesonu_saurabhNo ratings yet