Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circuit Analysis Tutorial: Find Currents, Voltages, Equivalent Circuits
Uploaded by
asvini001Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Circuit Analysis Tutorial: Find Currents, Voltages, Equivalent Circuits
Uploaded by
asvini001Copyright:
Available Formats
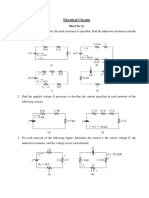
Circuit Analysis Tutorial
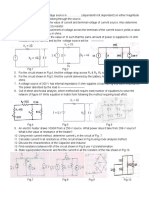
1. Simplify the following circuit. If the output of the voltage source is 4 volt, find the current
drawn from the source.
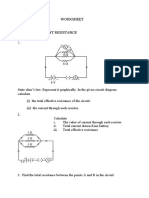
2. Consider the series/parallel resistor circuit shown in the Figure below.
(a !valuate the total resistance of the circuit and hence find the current drawn from the
source.
(b Find the voltages at the nodes ", #, and C (with respect to the reference node shown.
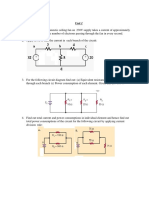
$. %he following circuit is used to measure the internal resistance of a battery, r
b.
%he load
resistance, &
'
, is () . *hen the switch is open, +
out
,-..+ while, when the switch is closed,
+
out
,-.4/+. *hat is r
b
0
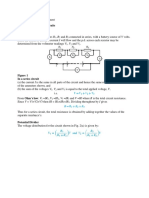
4. Consider the circuit shown in Figure 1 below. Solve the values for
currents I1, I2 and I3.
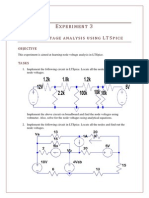
.. Find +oltage +
"#
for the below given circuit.
1. For the below circuit, the voltage source is having internal resistance -)2. %wo loads of
())2 and ()32 are connected across the voltage source in two different cases (case - and
case (. Show that the Supply voltage varies with the load. 4ow do you e5pect this variation
should be if you had an ideal voltage source of the same voltage value0
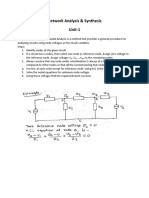
7. 6se 7odal analysis find the value of +
a
and +
b
in the following circuit.
Case - Case (
+oltage source +oltage source
8. 6se loop or mesh current analysis method to analy8e the following circuit. *hat is the net
current passing through +s(0
9. &ecall that, in the lecture, we have analy8ed the following circuit using principle of
superposition. *ould you now use both mesh current and nodal analysis methods to solve I
)
0
10. (a 6se the principle of superposition to determine the power dissipated in the /
resistor in the circuit as shown. (b *hat is the %hevenin e9uivalent circuit that the / 2
resistor sees0 "nd use this e9uivalent circuit to calculate the power dissipation in the / 2
resistor0
11. Find the %hevenin and 7orton e9uivalent circuits for the following circuit at the output
indicated by the two open circles.
-(. (a For the below circuit diagram, find the current through all the resistors. (4int: ;a3e
use of <C' and <+' for the wor3ing out the branch currents.
(b =raw the %hevenin e9uivalent circuit for the above diagram 3eeping /2 resistor as the
load resistor.
You might also like
- Superposition and Norton Theorems PresentationDocument24 pagesSuperposition and Norton Theorems PresentationMahmudul AlamNo ratings yet
- Simulating Electrical CircuitsDocument8 pagesSimulating Electrical CircuitsNavya ChirutaNo ratings yet
- LEC/BJT DC Analysis Examples SolDocument5 pagesLEC/BJT DC Analysis Examples SolFilipe da SilveiraNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit and Electronics NoteDocument34 pagesElectric Circuit and Electronics NoteEzekiel JamesNo ratings yet
- Assignment CTDocument9 pagesAssignment CTdhinojahimeshNo ratings yet
- Kirchoff's Laws, Thevenin's Theorem, Superposition TheoremDocument3 pagesKirchoff's Laws, Thevenin's Theorem, Superposition TheoremarunajithNo ratings yet
- Chapter One1Document29 pagesChapter One1مسلم محمودNo ratings yet
- Dr. Modar Shbat Division of Engineering Modar - Shbat@smu - CaDocument34 pagesDr. Modar Shbat Division of Engineering Modar - Shbat@smu - CaIGIHOZO HeritierNo ratings yet
- ESO 210 Lecture-4 - 2014Document55 pagesESO 210 Lecture-4 - 2014Amit MondalNo ratings yet
- Elementary Electrical Engineering - MODULE 8 Part 2 - Series Parallel ConditionsDocument14 pagesElementary Electrical Engineering - MODULE 8 Part 2 - Series Parallel ConditionsRubdubRNo ratings yet
- 3-Series DC CircuitsDocument17 pages3-Series DC CircuitsghlafhlyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4.2Document42 pagesChapter 4.2Muhd RzwanNo ratings yet
- 3 Circuit Analysis Using SubcircuitsDocument21 pages3 Circuit Analysis Using SubcircuitsAlejandro Salas VásquezNo ratings yet
- EE 1151 Circuit Theory Question BankDocument19 pagesEE 1151 Circuit Theory Question BankVIVEK AHLAWATNo ratings yet
- Elementary Electrical Engineering - Series Parallel ConditionsDocument14 pagesElementary Electrical Engineering - Series Parallel ConditionsRubdubRNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits - Sheets - 1Document13 pagesElectrical Circuits - Sheets - 1محمد عجوة100% (1)
- Contoh Soal Hukum Pembagi ArusDocument7 pagesContoh Soal Hukum Pembagi ArusTomi MentariNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 For CircuitsDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 For CircuitsAmir EyniNo ratings yet
- Question Bank On Unit IDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank On Unit IanupamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document30 pagesLecture 4uoaliyuNo ratings yet
- Ee602 Circuit AnalysisDocument55 pagesEe602 Circuit AnalysisArryshah DahmiaNo ratings yet
- 1472402133WORKSHEET CombinationDocument7 pages1472402133WORKSHEET CombinationbaaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - Basic ElectronicsDocument19 pagesQuestion Bank - Basic ElectronicsDivyang Patel100% (3)
- Electrical HerrmannDocument14 pagesElectrical HerrmannMauro Ferreira De LimaNo ratings yet
- Lab2 1+2 2-NhânDocument7 pagesLab2 1+2 2-NhânNhan Nguyen van MinhNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit AnalysisDocument12 pagesElectric Circuit AnalysisMATHANKUMAR.SNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 1: TheoryDocument6 pagesExperiment - 1: TheoryKiran Kumar KandregulaNo ratings yet
- DC Network Theorem SuperpositionDocument21 pagesDC Network Theorem SuperpositionSenthil IlangovanNo ratings yet
- DC Circuit AnalysisDocument16 pagesDC Circuit AnalysisganeshNo ratings yet
- Ee6201 CT U1 5 QBDocument10 pagesEe6201 CT U1 5 QBsakilakumaresanNo ratings yet
- Islamic University of Technology (Iut) : Course: Experiment No Name of The ExperimentDocument2 pagesIslamic University of Technology (Iut) : Course: Experiment No Name of The ExperimentshiamNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis TechniquesDocument22 pagesNetwork Analysis TechniquesHarsh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Question Bank-21EEE15ADocument18 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Question Bank-21EEE15AG46Anand P KNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis: by Mrs - Eranki Laita Mrs Jyoti MaheshwariDocument47 pagesNetwork Analysis: by Mrs - Eranki Laita Mrs Jyoti Maheshwarilalitaeranki100% (1)
- Circuit Analysis Technique Mesh (Loop) Current Method (Maxwell's Method)Document8 pagesCircuit Analysis Technique Mesh (Loop) Current Method (Maxwell's Method)Rahma HanifaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Electrical Circuits Objective QuestionsDocument8 pagesBasics of Electrical Circuits Objective QuestionsSweetlineSoniaNo ratings yet
- Circuit SystemsDocument28 pagesCircuit SystemsRashmi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Verify Thevenin's TheoremDocument10 pagesVerify Thevenin's TheoremJay SathvaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28-Direct Current CircuitsDocument47 pagesChapter 28-Direct Current CircuitsGled HysiNo ratings yet
- Circuit and Network 1Document63 pagesCircuit and Network 1Simion OngoriNo ratings yet
- ME324 Lecture3Document12 pagesME324 Lecture3Jam Maica TuboNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code: 22115: B.E./B.Tech - Degree Examinations, April/May 2011 Regulations 2008Document5 pagesQuestion Paper Code: 22115: B.E./B.Tech - Degree Examinations, April/May 2011 Regulations 2008Vinodh GanesanNo ratings yet
- EE Uptu Old QuesDocument1 pageEE Uptu Old Quesm_mustaqeemNo ratings yet
- Co2 PDFDocument43 pagesCo2 PDFSrikanth chowdary SereddyNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Electronics GuideDocument3 pagesElectricity and Electronics GuiderezaNo ratings yet
- Dövrələr NəzəriyyəsiDocument10 pagesDövrələr NəzəriyyəsiNərgiz QasımovaNo ratings yet
- Calculating Circuit Values and EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCalculating Circuit Values and EquivalentsAbhishek Kumar SinhaNo ratings yet
- BENG 3013 - Chapter 1 - DeltaDocument39 pagesBENG 3013 - Chapter 1 - DeltaWan MamatkNo ratings yet
- Unsolved Problem SheetDocument20 pagesUnsolved Problem SheetDeveshNo ratings yet
- Verification of Circuit TheoremsDocument27 pagesVerification of Circuit TheoremsCarlton Lobo0% (1)
- Circuits with Independent and Dependent SourcesDocument30 pagesCircuits with Independent and Dependent Sourcessamuel fiifi yeboahNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document2 pagesLab 3Kishan PujaraNo ratings yet
- Project of Electric Circuit Analysis (Eca) : TopicDocument22 pagesProject of Electric Circuit Analysis (Eca) : TopicMuhammad Hamza AminNo ratings yet
- Project of Electric Circuit Analysis (Eca) : TopicDocument17 pagesProject of Electric Circuit Analysis (Eca) : TopicMuhammad Hamza AminNo ratings yet
- ECE 204 Experiment 1 ExercisesDocument4 pagesECE 204 Experiment 1 ExercisesMamadou DemNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4: PH1102 /CY1302/SM2-16B - Fields & OscillationsDocument4 pagesTutorial 4: PH1102 /CY1302/SM2-16B - Fields & OscillationsstarlcNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios AnalogicaDocument22 pagesEjercicios AnalogicaManel GarciaNo ratings yet
- PSCAD Power System Lab ManualDocument23 pagesPSCAD Power System Lab ManualShiva Kumar100% (2)
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Skin On HandDocument11 pagesSkin On Handasvini001No ratings yet
- Lit Review of 5 Minds of A Manager.Document5 pagesLit Review of 5 Minds of A Manager.asvini001No ratings yet
- BG31005 Tutorial PartI SolutionDocument27 pagesBG31005 Tutorial PartI Solutionasvini001No ratings yet
- ProEngineer HelpDocument158 pagesProEngineer Helpasvini001No ratings yet
- ProEngineer HelpDocument158 pagesProEngineer Helpasvini001No ratings yet
- BU8101 Week3Document57 pagesBU8101 Week3asvini001No ratings yet
- Electrical Safety PDFDocument40 pagesElectrical Safety PDFasvini001No ratings yet
- Lect 1 - Int RatesDocument37 pagesLect 1 - Int Ratesasvini001No ratings yet
- Homework 1Document2 pagesHomework 1asvini001No ratings yet
- BG3104 Set 1 2014-15Document108 pagesBG3104 Set 1 2014-15asvini001No ratings yet
- The Engineer in SocietyDocument40 pagesThe Engineer in Societyasvini001No ratings yet
- Basic Circuit AnalysisDocument81 pagesBasic Circuit Analysisasvini001No ratings yet
- The Engineer in SocietyDocument40 pagesThe Engineer in Societyasvini001No ratings yet
- Bg100310111 - Chemistry For Engineering EPDocument12 pagesBg100310111 - Chemistry For Engineering EPasvini001No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 SolutionDocument9 pagesTutorial 1 Solutionasvini001No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2asvini001No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 SolutionDocument9 pagesTutorial 1 Solutionasvini001No ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument12 pagesThermodynamicsasvini001No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1asvini001No ratings yet