Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human Body Systems Vocabulary
Uploaded by
api-1963570910 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
244 views4 pagesOriginal Title
human body systems vocabulary
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
244 views4 pagesHuman Body Systems Vocabulary
Uploaded by
api-196357091Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Human Body Systems Vocabulary
Cells & Genetics
characteristics quality of an organism
DNA material in life forms that transfers genetic characteristics
inherited characteristics from parents
likeness similarity
organism individual living system
traits distinguishing characteristics
cell the basic unit of life
multicellular composed of several or many cells
unicellular (single cell) composed of one cell
permeable able to pass through
tissue similar cells with a specific function
direct evidence evidence you collect yourself
indirect evidence
evidence that you do not collect yourself, but rely on evidence collected by
others
fitness the state of being healthy
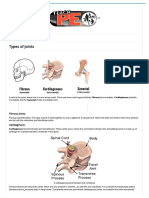
Skeletal System
ball/socket joint joint that allows twisting and turning movements; example: hip joint
bones forms the substance of a skeleton, support the body
cartilage flexible connective tissue
cranium skull
femur longest, largest, and strongest bone in the human body; located in the leg
fracture to break or crack
framework supports, i.e. human skeleton
gliding joint joint that allows to flat bones to slide over each other; example: foot, wrist
hinge joint
joint that allows movement in a certain spot, like the opening and closing of a
door; example: elbow, knee, ankle
humerus long bone in arm extending from the shoulder to the elbow
immovable not able to be moved
joints place where two parts are joined or united to allow motion
mandible jaw bone
patella flat moveable bone in the front of the knee, also known as the knee bone
pelvis funnel-shaped, part of skeleton supporting lower limbs
phalanges bones that make up the fingers or feet
radius bone of forearm on the thumb side
ribs bones that support and protect organs such as the lungs
autonomic
nervous system
system of nerves that controls involuntary functions
axon part of neuron that takes information away from a cell body
brain controls mental and physical actions, located in the cranium (skull)
brain stem part of brain near spinal cord; controls reflexes, breathing, and heartbeat
cerebellum large portion of the brain, controls voluntary motions
scapula shoulder blade
skeleton framework that supports the body
skull head bone
spine backbone
sternum breastbone
tarsals bones in the feet
tibia shinbone
torso upper part of the body
ulna forearm bone, located on the side opposite the thumb
vertebrae bones in the spine
Muscular System
bicep muscle at the front of the upper arm
cardiac muscle type of muscle in the heart
contract to draw together
endurance ability or strength to continue or last without becoming tired
exertion activity of using your muscles in various ways to keep fit
extend to increase in length
flex to bend
involuntary muscle controlled without thinking about it (pumping heart)
ligaments tissues that connect bones, hold organs in place
muscles tissues that cause motion in the body when contracted
musculoskeletal muscular and skeletal systems
resistance
Exercise that involves working your muscles against free weights or your body's
own weight (walking, running, pushups)
skeletal muscle muscle connected at either end with a bone
smooth muscle found in the walls of internal organs, blood vessels, hair follicles
tendons connects muscle to bone
tricep muscle located at the back of the upper arm
voluntary muscle whose action is controlled by the person (example: lifting an arm)
atrophy to waste away or decrease in size
Nervous System
cerebrum largest part of the brain, controls voluntary movements and mental actions
dendrites part of a neuron that brings information to a cell body
nerves bundle of fibers that send impulses from the brain to other parts of the body
neurons specialized, impulse-conducting cells (composed of cell body, axon, dendrites)
peripheral
nervous system
lies outside brain and spinal cord, includes nerves to arms, legs, and sense organs
relay to transmit a signal
signals messages sent from brain to nerves
spinal cord cord of nerve tissue extending through the spinal column
spinal nerve nerves that start in the spinal cord
stimuli
something that causes an action (example-stimulus: hot stove, response: moving
hand away from hot stove)
synapse place where nerve messages are sent and received
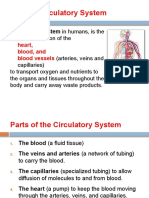
Circulatory and Cardiovascular Systems
blood a fluid that circulates throughout the body to sustain life
cholesterol found in animal tissues, too much can lead to heart disease
red blood cells
blood cells constantly traveling through your body delivering oxygen and
removing waste
white blood cells blood cells that help protect the body by fighting off infections and diseases
platelets smallest blood cells to help form clots if you have an injury
plasma liquid part of the blood; contains blood's proteins, suspends blood cells
aerobic exercise exercise that increases the need for oxygen
anaerobic
exercise
exercise that builds muscles through tension
aorta
part of the heart, circulates blood from the heart to all of the body (except the
lungs)
arteries blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart
atrium
two upper chambers on each side of the heart, receives blood from veins and
forces blood into ventricles
blood vessels any of the vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries) through which the blood circulates
capillaries
small blood vessels between the ending of the arteries and the beginning of the
veins
cardiac relating to the heart
circulation flowing (such as the flow of blood throughout the body)
heart
organ (consisting of four chambers) that circulates blood, divided into four
chambers (valves)
heart rate number of heartbeats in one minute
pulmonary artery transports blood from the heart to the lungs
pulse regular throbbing of arteries caused by heart contractions
veins blood vessels that carry blood toward the heart
ventricles located in the heart, left and right, pumps blood to the entire body
BREAK
Respiratory System
air sac air-filled spaces in the body
alveoli very small air sacs; where air breathed in goes
bronchial tubes
two tubes at the end of the trachea, brings in air from trachea and helps clean
lungs; one tube goes to right lung, one to left
diaphragm
sheet-like muscle separating the chest from the abdominal cavity; creates suction
to draw in air and expand lungs
exhale to breathe out
inhale to breathe in
larynx voice box
lungs two respiratory organs
nasal passages
(nasal cavity)
helps with inhaling and exhaling of air through the nose
pharynx throat; collects incoming air from the nose and passes air to the trachea
respiration inhaling and exhaling air, breathing
ribs bones that protect and support the chest
sinuses
hollow spaces in the bones of the head, helps regulate temperature of air
breathed in
trachea windpipe; passage from pharynx to lungs
Digestive and Excretory Systems
anus where solid waste exits through the body
appendix located near the small and large intestine, purpose unknown
bile duct stores bile (yellow, green liquid from the liver)
digestion processing food in the body
epiglottis
located in the back of the mouth; prevents food and drink from entering the
larynx
esophagus muscular passage connecting the mouth and the stomach, rhythmic motion
large intestine where stool (solid waste) accumulates
liver
filters blood coming from the digestive tract, releases bile, helps take toxins
(poisons) from chemicals in the body
mouth where digestion begins
pancreas about 6" long, located behind the stomach, secretes insulin
rectum straight section of the intestine, ending in the anus, stores solid waste
saliva watery fluid for tasting and swallowing food, chewing, keeping mouth moist
salivary glands secretes (releases) saliva
small intestine helps in the passage of food that comes from the stomach
stomach organ in the digestive system that stores and digests food
tongue organ in the mouth; functions include eating, tasting, speaking
You might also like
- Problem 2 ReflectionDocument3 pagesProblem 2 ReflectionMegan MakelaNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems Study GuideDocument1 pageHuman Body Systems Study Guideapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Nutritional PlanDocument20 pagesNutritional Planapi-259457599No ratings yet
- Nutrition MacronutrientsDocument22 pagesNutrition Macronutrientsnoddy60No ratings yet
- Threshold and RecruitmentDocument16 pagesThreshold and RecruitmentShamaine Anne SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Improve Your Energy Balance by Adding Dairy and ExerciseDocument8 pagesImprove Your Energy Balance by Adding Dairy and ExercisealafiaNo ratings yet
- Label The Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesLabel The Circulatory SystemMaciel Barraza0% (1)
- Heart Rate LabDocument3 pagesHeart Rate LabMary Chaser0% (1)
- The Longevity ProjectDocument1 pageThe Longevity ProjectThe Press-Enterprise / pressenterprise.com0% (1)
- Surgical Exposures in Orthopaedics: The Anatomic ApproachDocument29 pagesSurgical Exposures in Orthopaedics: The Anatomic ApproachidaramaNo ratings yet
- GM Food Debate: Benefits vs RisksDocument2 pagesGM Food Debate: Benefits vs Risksscribd100% (1)
- Colony MorphologyDocument9 pagesColony MorphologyKirk AdderleyNo ratings yet
- Baby Doctor's Guide To Anatomy and Physiology: Science for Kids Series - Children's Anatomy & Physiology BooksFrom EverandBaby Doctor's Guide To Anatomy and Physiology: Science for Kids Series - Children's Anatomy & Physiology BooksNo ratings yet
- Ferodo Car Racing CatalogueDocument662 pagesFerodo Car Racing CatalogueBenny BigwantoNo ratings yet
- Understanding MeiosisDocument38 pagesUnderstanding MeiosisAl-Arqam OmarNo ratings yet
- 3.6 - The Respiratory SystemDocument4 pages3.6 - The Respiratory SystemDjej100% (1)
- Chapter 3. Muscular, Skeletal, and Nervous SystemDocument53 pagesChapter 3. Muscular, Skeletal, and Nervous SystemFatiha AmiraNo ratings yet
- Lec-21,22,23 - Circulatory SystemDocument28 pagesLec-21,22,23 - Circulatory SystemAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- Sports Nutrition in The Martial Arts - Learn All You Need To Know About Keeping A Diet Fit For Your NeedsDocument8 pagesSports Nutrition in The Martial Arts - Learn All You Need To Know About Keeping A Diet Fit For Your NeedsRobert Boris Vaca ReyesNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument18 pagesThe Circulatory SystemTina PedersenNo ratings yet
- Cell Division - Mitosis and The Cell CycleDocument43 pagesCell Division - Mitosis and The Cell CycleJomar CarabotNo ratings yet
- Take Control of Your Health & Escape The Sickness IndustryDocument355 pagesTake Control of Your Health & Escape The Sickness IndustryCarol MacraeNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument31 pages1 - Introduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyMinh Thiên VõNo ratings yet
- Mambo Medicine Ball Exercise ChartDocument1 pageMambo Medicine Ball Exercise Chartgzapata31No ratings yet
- LO5.1: Analyse The 3 Different Energy Systems & Explain Their Contribution To Different Sports & ActivitiesDocument6 pagesLO5.1: Analyse The 3 Different Energy Systems & Explain Their Contribution To Different Sports & Activitiesnbeer93No ratings yet
- Rat DissectionDocument62 pagesRat DissectionBenNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Lab WorksheetDocument7 pagesEndocrine System Lab WorksheetedwardNo ratings yet
- General Human Physiology and BiochemistryDocument9 pagesGeneral Human Physiology and BiochemistryleeminhoangrybirdNo ratings yet
- Measure Joint Flexibility with a GoniometerDocument3 pagesMeasure Joint Flexibility with a GoniometerwazzupwaleedNo ratings yet
- Body Systems Practice TestDocument5 pagesBody Systems Practice TestTINAIDANo ratings yet
- Basic Energy SystemDocument10 pagesBasic Energy SystemMozil Fadzil KamarudinNo ratings yet
- 22 Ecdysteroids in FernsDocument15 pages22 Ecdysteroids in FernsLuis PedreroNo ratings yet
- Nutrition4 PDFDocument47 pagesNutrition4 PDFAshwinNo ratings yet
- The Cell Structure, Functions of The CellDocument76 pagesThe Cell Structure, Functions of The CellCharles SsekawuNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument11 pagesImmune SystemMar'atus SilmiahNo ratings yet
- My Training Program (Romela) 2Document8 pagesMy Training Program (Romela) 2Charlene RiveraNo ratings yet
- InBody E Book PDFDocument48 pagesInBody E Book PDFu2197977No ratings yet
- Anatomy Part 1 - The Upper LimbDocument27 pagesAnatomy Part 1 - The Upper LimbSolange AcostaNo ratings yet
- Target Heart RateDocument2 pagesTarget Heart Ratetanu1127100% (1)
- You Are What You EatDocument9 pagesYou Are What You EatRemedios BandongNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.1Document2 pagesLesson 3.1Evangelia GkNo ratings yet
- Metabolism and AtpDocument20 pagesMetabolism and AtpAbdul Rafay ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Workbook 2015Document8 pagesEndocrine System Workbook 2015api-298277560100% (1)
- Shifting Paradigms: Matt Wallden, MSC Ost Med, Do, ND, Associate EditorDocument10 pagesShifting Paradigms: Matt Wallden, MSC Ost Med, Do, ND, Associate EditorStephen HonesNo ratings yet
- The Metabolic Adaptation Manual: Problems, Solutions, and Life After Weight LossDocument88 pagesThe Metabolic Adaptation Manual: Problems, Solutions, and Life After Weight Lossmehrdad_44No ratings yet
- AnatomyAndPhysiology LRDocument1,358 pagesAnatomyAndPhysiology LRDavidNo ratings yet
- 07 - Training The Aerobic and Anaerobic Energy SystemsDocument34 pages07 - Training The Aerobic and Anaerobic Energy SystemsIyappan SubramaniNo ratings yet
- Trivia UpdatedDocument11 pagesTrivia Updatedapi-242113272No ratings yet
- Skip The Lies, Go Straight To The Health.Document28 pagesSkip The Lies, Go Straight To The Health.Madalina AlecsandrescuNo ratings yet
- Types of Joints - The Skeleton & Bones - Anatomy & Physiology PDFDocument3 pagesTypes of Joints - The Skeleton & Bones - Anatomy & Physiology PDFPankaj VermaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemLabDocument7 pagesLymphatic SystemLabMax DelvalleNo ratings yet
- Training For Performance (Part-B)Document32 pagesTraining For Performance (Part-B)Rabia RaufNo ratings yet
- Exercise PhysDocument21 pagesExercise Physbaikins92No ratings yet
- Sodium Potassium Pump and Action PotentialDocument4 pagesSodium Potassium Pump and Action PotentialPiyush BhallaNo ratings yet
- Understanding LDL and HDL Cholesterol LevelsDocument16 pagesUnderstanding LDL and HDL Cholesterol LevelsaakashtrivediNo ratings yet
- Paper Work of High Cholesterol: English AssignmentDocument10 pagesPaper Work of High Cholesterol: English AssignmentVyeren VestalNo ratings yet
- BioenergeticsDocument58 pagesBioenergeticscooolnhannaNo ratings yet
- mTOR - WikipediaDocument17 pagesmTOR - WikipediaNicholas FeatherstonNo ratings yet
- Safe Upper Levels For Vitamins and Minerals (FSA)Document360 pagesSafe Upper Levels For Vitamins and Minerals (FSA)jcpchin2No ratings yet
- Molecular and Cellular Aspects of Muscle Function: Proceedings of the 28th International Congress of Physiological Sciences Budapest 1980, (including the proceedings of the satellite symposium on Membrane Control of Skeletal Muscle Function)From EverandMolecular and Cellular Aspects of Muscle Function: Proceedings of the 28th International Congress of Physiological Sciences Budapest 1980, (including the proceedings of the satellite symposium on Membrane Control of Skeletal Muscle Function)E. VargaNo ratings yet
- Asana Based Exercises Low Back PainDocument14 pagesAsana Based Exercises Low Back PainAutumn Carter100% (1)
- Opening Ceremony Thursday July 19th 2018Document1 pageOpening Ceremony Thursday July 19th 2018api-231946379No ratings yet
- American Revolution VocabularyDocument2 pagesAmerican Revolution Vocabularyapi-231946379No ratings yet
- 2018 Dii SyllabusDocument12 pages2018 Dii Syllabusapi-231946379No ratings yet
- Closing Ceremony Sunday July 22nd 2018Document1 pageClosing Ceremony Sunday July 22nd 2018api-231946379No ratings yet
- The Coordinate SystemDocument1 pageThe Coordinate Systemapi-231946379No ratings yet
- Cells Study GuideDocument1 pageCells Study Guideapi-323449449No ratings yet
- Hambright Track 4b Quarter 3 Specials Schedule 2014Document1 pageHambright Track 4b Quarter 3 Specials Schedule 2014api-231946379No ratings yet
- Opening Program For Dii - 8-10-16 1Document2 pagesOpening Program For Dii - 8-10-16 1api-231946379No ratings yet
- Closing Program For Dii - 8-10-16 1Document2 pagesClosing Program For Dii - 8-10-16 1api-231946379No ratings yet
- Unicellularorganisms MicroscopicviewDocument1 pageUnicellularorganisms Microscopicviewapi-231946379No ratings yet
- The 13 Colonies OverviewDocument25 pagesThe 13 Colonies Overviewapi-231946379No ratings yet
- Figurative Language CheatDocument1 pageFigurative Language Cheatapi-231946379No ratings yet
- Tolivers Secret and The American Revolution ProjectDocument4 pagesTolivers Secret and The American Revolution Projectapi-231946379No ratings yet
- Unicellular-Multicellular Organisms NotesDocument2 pagesUnicellular-Multicellular Organisms Notesapi-231946379No ratings yet
- Plant and Animal CellsDocument1 pagePlant and Animal Cellsapi-231946379No ratings yet
- Halloweencoordinategraphingorderedpairsmysterypictures DraggedDocument2 pagesHalloweencoordinategraphingorderedpairsmysterypictures Draggedapi-231946379No ratings yet
- Native Americans Who Discovered AmericaDocument5 pagesNative Americans Who Discovered Americaapi-323449449No ratings yet
- CL 2Document6 pagesCL 2api-231946379No ratings yet
- 770 Vikings and European Explorers The VikingsDocument5 pages770 Vikings and European Explorers The Vikingsapi-231946379No ratings yet
- 1 2 pg14 20Document7 pages1 2 pg14 20api-231946379No ratings yet
- Figurative Language CheatDocument1 pageFigurative Language Cheatapi-231946379No ratings yet
- Positive Effects of The Columbian Exchange Negative Effects of The Columbian ExchangeDocument4 pagesPositive Effects of The Columbian Exchange Negative Effects of The Columbian Exchangeapi-231946379No ratings yet
- Inventory of TraitsDocument13 pagesInventory of Traitsapi-323141584No ratings yet
- Navajo Rug Geometry ProjectDocument1 pageNavajo Rug Geometry Projectapi-231946379No ratings yet
- Headers FamiliesDocument1 pageHeaders Familiesapi-231946379No ratings yet
- Box Top Moving Mustangs ChartDocument1 pageBox Top Moving Mustangs Chartapi-231946379No ratings yet
- Show - Don T Tell!Document44 pagesShow - Don T Tell!api-231946379No ratings yet
- Multiplying and Dividing Whole NumbersDocument2 pagesMultiplying and Dividing Whole Numbersapi-231946379No ratings yet
- Hambright Open House Power Point 2014Document18 pagesHambright Open House Power Point 2014api-231946379No ratings yet
- Zoology Multiple Choice Question (GuruKpo)Document33 pagesZoology Multiple Choice Question (GuruKpo)GuruKPO100% (2)
- Course PlannerDocument2 pagesCourse PlannerThilankaNo ratings yet
- Anemiile Aplastice Copii1Document28 pagesAnemiile Aplastice Copii1Daniela LupanNo ratings yet
- PLOTKINDocument6 pagesPLOTKINElPaisUyNo ratings yet
- Cholesterol TotalDocument9 pagesCholesterol TotalichaaznNo ratings yet
- Chapter No. 1 & 2 Introduction & Structure of BacteriaDocument25 pagesChapter No. 1 & 2 Introduction & Structure of BacteriauzairNo ratings yet
- HAP1 Review: Dr. Garry NiedermayerDocument37 pagesHAP1 Review: Dr. Garry Niedermayersweta paudelNo ratings yet
- SSLP DNA Polymorphisms for Genetic Mapping & FingerprintingDocument8 pagesSSLP DNA Polymorphisms for Genetic Mapping & Fingerprintingmozhi74826207No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle StagesDocument6 pagesCell Cycle StagesCathy MoronioNo ratings yet
- HES 087 Microbiology and Parasitology (Instructional Design S.Y. 2020-2021)Document18 pagesHES 087 Microbiology and Parasitology (Instructional Design S.Y. 2020-2021)Ellery L TrumataNo ratings yet
- CADDDocument15 pagesCADDvigneshwebNo ratings yet
- Book Review: FOOD WARS: THE GLOBAL BATTLE FOR MOUTHS, MINDS AND MARKETS BY TIM LANG AND MICHAEL HEASMAN. PUBLISHED IN 2004 BY EARTHSCAN, LONDON. ISBN 1 - 85383-702-4 (PAPERBACK), 365 PAGESDocument3 pagesBook Review: FOOD WARS: THE GLOBAL BATTLE FOR MOUTHS, MINDS AND MARKETS BY TIM LANG AND MICHAEL HEASMAN. PUBLISHED IN 2004 BY EARTHSCAN, LONDON. ISBN 1 - 85383-702-4 (PAPERBACK), 365 PAGESRandyNo ratings yet
- Studier, 2007, Protein Prod by Auto-Induction in High-Density Shaking CulturesDocument20 pagesStudier, 2007, Protein Prod by Auto-Induction in High-Density Shaking CulturesLaura-Mihaela ChisNo ratings yet
- Retinoblastoma - EyeWikiDocument11 pagesRetinoblastoma - EyeWikimay171989No ratings yet
- Takahashi 1991Document7 pagesTakahashi 1991Tibor SzénásiNo ratings yet
- Class 11 FREE Content (Premium)Document4 pagesClass 11 FREE Content (Premium)soumyasingh17307No ratings yet
- Plant and AnimalDocument32 pagesPlant and AnimalReynold GajusanNo ratings yet
- FOUNDATION OF CONTROL QUESTIONS OF EXAM 2020-2021 General MedicineDocument7 pagesFOUNDATION OF CONTROL QUESTIONS OF EXAM 2020-2021 General MedicineSoz P. KawaniNo ratings yet
- 10 Keys Grounding PDFDocument20 pages10 Keys Grounding PDFDanielaMunioz100% (3)
- Mycota Introduction: Fungi Kingdom OverviewDocument8 pagesMycota Introduction: Fungi Kingdom OverviewPrazwal RegmiNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument19 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsjhabNo ratings yet
- Cpi12 CrashcourseDocument6 pagesCpi12 CrashcourseHaaNo ratings yet
- Science 10-Pretest Third QuarterDocument4 pagesScience 10-Pretest Third QuarterCristian PortugalNo ratings yet
- Ch-8, Cell Class - 8, Science Textbook QuestionsDocument5 pagesCh-8, Cell Class - 8, Science Textbook Questionsbucks GamingNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants: Chapter - 09Document15 pagesTransport in Plants: Chapter - 09Raichal P BijuNo ratings yet
- The developmental project (Unit 1Document3 pagesThe developmental project (Unit 1SKNo ratings yet
- Impact of Plant Breeding On The Genetic Diversity of Cultivated Strawberry As Revealed by Expressed Sequence Tag-Derived Simple Sequence Repeat MarkersDocument12 pagesImpact of Plant Breeding On The Genetic Diversity of Cultivated Strawberry As Revealed by Expressed Sequence Tag-Derived Simple Sequence Repeat MarkersJuan Diego DuqueNo ratings yet
- Bact Growth CurveDocument12 pagesBact Growth Curvehitesh100% (1)