Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adhd
Uploaded by
api-267113076Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adhd
Uploaded by
api-267113076Copyright:
Available Formats
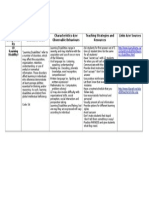
Name of
Exceptional
ity
Definition & Alberta
Education Code
FASD
- is a pattern of birth defects,
learning and behavioural
problems affecting
individuals whose mothers
consumed alcohol during
pregnancy.
Fetal Alcohol
Spectrum
Disorder
- A student/child with a severe
physical, medical or
neurological disability,
including autism, is one who:
a) has a medical diagnosis of
a physical disability, specific
neurological disorder or
medical condition which
creates a significant impact
on the students/ECS childs
ability to function in the
school environment (note:
some physical or medical
disabilities have little or no
impact upon the
students/ECS childs ability
to function in the school
environment); and b)
requires extensive adult
assistance and modifications
to the learning environment
in order to benefit from
schooling.
Coding: 44
Incident Rate In 2012/13
Characteristics &/or
Observable Behaviours
- Three key features: small eye slit 1.
openings, flattened vertical columns
in the upper lip (philtrum) and a thin
upper lip.
- FASD causes a variety of
symptoms, including extreme
impulsivity, poor judgment, poor
memory, difficulty learning basic
skills, organizational difficulties,
language and speech delays, and
gross and fine motor delays.
- May include physical birth defects
and health problems including
2.
developmental delays, learning
disabilities, memory problems, as
well as difficulties in communicating
feelings and understanding
consequences.
- Difficulty with behaviour
regulation, which often includes
mood swings. Individuals may
quickly go from excited and happy
to morose or angry. Many have
neurological systems that become
easily overwhelmed by stimulation.
3.
- May show irritability, volatile
anger, shut downs or other
withdrawal behaviours. Other
emotional difficulties include
Teaching Strategies and
Resources
Reduce visual and auditory
Distractions - This can be as easy as
using calm colors on the walls and
bulletin boards to decrease
distraction. Arrange desk to minimize
distraction, consider placing the FASD
student at the front of class to retain
attention. Any materials that are not
being used should be stored
appropriately in boxes and cupboards,
not on any countertops. Have
available earplugs or headphones to
abolish any noise or stress that may
overwhelm students with FASD.
Teaching Routines- By developing
routines with your student this can
aid in minimizing distraction. Allow
your class to bring water bottles into
the class so they dont need to be
constantly leaving the classroom for a
drink. If your student has a aid make
sure that this aid or staff is working
consistently with the student to
ensure that the routines are being
accomplished. Have extra supplies
easily accessible for your students.
Functional Assessment- Students
with an FASD may score within normal
limits on a formal assessment, but
could have difficulty applying and
using their knowledge in the
classroom. So it is important to
Links &/or Sources
Alberta Education Teaching
Students with FASD
http://education.alberta.ca/
media/377037/fasd.pdf
FASD Medical/Disability
Information for School
Teachers
http://www.learnalberta.ca/
content/inmdict/html/fasd.
html
A Team Approach to
Supporting Students with
FASD
http://education.alberta.ca/
media/932737/redefining_
final.pdf
Special Education Coding
Criteria
http://education.alberta.ca/
media/825847/spedcoding
criteria.pdf
FASD Alberta Information
Website
http://fasd.alberta.ca/getto-know-fasd.aspx
BC Education: Teaching
Students with FASD
Resource
http://www.bced.gov.bc.ca/
specialed/fas/
there were 962 ECS students,
and 8,399 in grade 1 to 12.
obsessive repetitions of certain
actions, or perseveration of
particular actions or ideas.
conduct a functional assessment
when evaluating a student with FASD.
In Figure 1, you will find questions
that will help you gain a better
understanding of what types of
supports your student will need for
success in the classroom and within
the school.
4. Communication- It becomes
extremely difficult to gain a student
with FASDs attention before
progressing with their learning. That
being said you have a wide variety of
communication strategies you can
use such as establish cue words,
rhythmic clapping, call and response,
silent countdown from five, 1,2,3
scale for noise. The examples above
allow for you to establish structure
and reminders to diminish the
possibility of the student losing focus.
Things to consider when giving
instruction try using demonstrations
and checklists to guide our student to
the intended learning outcomes.
When instructing be conscious of the
rate in which you talk, be brief in your
descriptions and avoid lengthy
periods of lecturing. Making sure that
anything that is implemented for the
students benefit of learning it is
necessary for all students to follow
the routines that are in place.
University of South Dakota
FASD Educational
Strategies http://www.usd.edu/medica
l-school/center-fordisabilities/upload/fasdedu
cationalstrategies.pdf
FASD Positive Behaviour
Resourcehttp://www.pbsc.info/educa
tion/
You might also like
- Differentiation ToolboxDocument9 pagesDifferentiation Toolboxapi-247367783No ratings yet
- Exceptionalities ToolboxDocument13 pagesExceptionalities Toolboxapi-266758188No ratings yet
- Toolbox FinalDocument13 pagesToolbox Finalapi-268585214No ratings yet
- ToolboxDocument22 pagesToolboxapi-268472487No ratings yet
- Exceptionality Name Definition & Alberta Ed. CodeDocument20 pagesExceptionality Name Definition & Alberta Ed. Codeapi-316248639No ratings yet
- Ragan K PP FinalDocument18 pagesRagan K PP Finalapi-297921940No ratings yet
- Curriculam and Material ModificationDocument2 pagesCurriculam and Material ModificationAli AhamadNo ratings yet
- Physical Needs, Conditions and Support for Learning DisabilitiesDocument4 pagesPhysical Needs, Conditions and Support for Learning DisabilitiesSoniya GhisingNo ratings yet
- Inclusive EeDocument85 pagesInclusive EeCherrylou Umbao Ano-osNo ratings yet
- SPED 213 Final ExamDocument3 pagesSPED 213 Final ExamAngelito CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Menu Acc (Standard 2)Document5 pagesMenu Acc (Standard 2)api-284398686No ratings yet
- Disabilities Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesDisabilities Lesson Planapi-606324138No ratings yet
- REVIEW MODULE ANSWERDocument10 pagesREVIEW MODULE ANSWERMaria Leonora FuerteNo ratings yet
- Good MorningDocument53 pagesGood MorningENSIGN ORCUSENo ratings yet
- Disabilities HandbookDocument14 pagesDisabilities Handbookapi-318145494No ratings yet
- CEP840 Fact SheetDocument3 pagesCEP840 Fact Sheetannaculik2671No ratings yet
- Surell John Lery ED 33 Assignment 1 Foundation For Special Inclusive EducationDocument6 pagesSurell John Lery ED 33 Assignment 1 Foundation For Special Inclusive EducationJohn Lery SurellNo ratings yet
- Activity: Facilitating Learner-Centered Teaching ED 105Document4 pagesActivity: Facilitating Learner-Centered Teaching ED 105Lenlyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- EDUC 225 Recognizing Children With Special NeedsDocument47 pagesEDUC 225 Recognizing Children With Special NeedsApolonia MolinaNo ratings yet
- October 12, Tueday NotesDocument10 pagesOctober 12, Tueday NotesIsaiah TongcuaNo ratings yet
- Toolbox 1Document12 pagesToolbox 1api-266693431No ratings yet
- Classroom Management of Children With Specific DisabilityDocument11 pagesClassroom Management of Children With Specific DisabilityIsrahIzabelPairaAdarnaNo ratings yet
- Educ 211Document41 pagesEduc 211ismael celociaNo ratings yet
- LEARNERS WHO ARE GIFTED AND TALENTED OR HAVE DIFFICULTY HEARINGDocument62 pagesLEARNERS WHO ARE GIFTED AND TALENTED OR HAVE DIFFICULTY HEARINGismael celociaNo ratings yet
- Sammy ExceptionalityDocument8 pagesSammy ExceptionalityShacara MillingtonNo ratings yet
- Exam Prep - Eth306w 2015-2018Document24 pagesExam Prep - Eth306w 2015-2018Is'haaq Sayed100% (3)
- POWERPOINTChapter 6Document30 pagesPOWERPOINTChapter 6Lou Jane YescaNo ratings yet
- Education3602 ToolboxDocument15 pagesEducation3602 Toolboxapi-275750758No ratings yet
- Module 7 Assignment - Lesson Part - 2Document28 pagesModule 7 Assignment - Lesson Part - 2api-185226751No ratings yet
- The Listening Child: What Can Go Wrong: What All Parents and Teachers Need to Know About the Struggle to Survive in Today’S Noisy ClassroomsFrom EverandThe Listening Child: What Can Go Wrong: What All Parents and Teachers Need to Know About the Struggle to Survive in Today’S Noisy ClassroomsNo ratings yet
- Navigating Reading: A Guide for Teaching Children with DyslexiaFrom EverandNavigating Reading: A Guide for Teaching Children with DyslexiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 CompilationDocument36 pagesChapter 6 CompilationJunrel J Lasib DabiNo ratings yet
- Book Inclusive Macapinlac Jaimee Rose Bsed 3Document16 pagesBook Inclusive Macapinlac Jaimee Rose Bsed 3Jaimee Rose MacapinlacNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6: Basic Concepts about Higher Incidence Disabilities and Learning StrategiesDocument70 pagesLesson 6: Basic Concepts about Higher Incidence Disabilities and Learning StrategiesKeith Richjade YbutNo ratings yet
- Physical Cerebral PalsyDocument42 pagesPhysical Cerebral PalsyRenésmee SpeaksNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Learning DisabilitiesDocument29 pagesPresentation On Learning Disabilitiestricia0910100% (4)
- What Is Visual Impairment NotesDocument4 pagesWhat Is Visual Impairment NotesLizzy TaitNo ratings yet
- Learning Disabilities: By: Fiona Bridges, Shante Walker, John Hunter, Amanda SpencerDocument13 pagesLearning Disabilities: By: Fiona Bridges, Shante Walker, John Hunter, Amanda Spencerapi-480715417No ratings yet
- Learning GapDocument7 pagesLearning GapLary BagsNo ratings yet
- AdhdDocument11 pagesAdhdMarlon Parohinog100% (1)
- RPMS Teacher Reflection FormDocument8 pagesRPMS Teacher Reflection FormJff Reyes100% (11)
- Toolbox NotesDocument17 pagesToolbox Notesapi-280150165No ratings yet
- Advice 4 Mentor Working With DyslexiaDocument13 pagesAdvice 4 Mentor Working With DyslexiaFlora FloraNo ratings yet
- Urdaneta City University College of Arts & Languages Urdaneta CityDocument10 pagesUrdaneta City University College of Arts & Languages Urdaneta CityRonyl BravoNo ratings yet
- Module 6 FiseDocument20 pagesModule 6 FiseBryan Jay Cordero RayosNo ratings yet
- Teaching Strategies For Special Students: Dr. Abowaba Johnson Idowu Kings (PHD, Edd)Document9 pagesTeaching Strategies For Special Students: Dr. Abowaba Johnson Idowu Kings (PHD, Edd)fariez79No ratings yet
- Facilitative Teaching Strategies For Hearing Impaired PupilsDocument10 pagesFacilitative Teaching Strategies For Hearing Impaired PupilsHaironisaMalaoMacagaanNo ratings yet
- Edcu 450 Learnerprofile RenadonaldsonDocument6 pagesEdcu 450 Learnerprofile Renadonaldsonapi-249591813No ratings yet
- Students With Learning DisabilitiesDocument5 pagesStudents With Learning DisabilitiesGARAS, JOYLYN JANE M.No ratings yet
- Classroom Interventions For Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity DisorderDocument10 pagesClassroom Interventions For Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity DisorderanhiramdhaniNo ratings yet
- Accommodations MenuDocument16 pagesAccommodations Menuapi-313166146No ratings yet
- E FolioDocument14 pagesE Folioapi-314249648No ratings yet
- WRITTEN REPORT AND CASE STUDYDocument12 pagesWRITTEN REPORT AND CASE STUDYAprylmariejoy TorresNo ratings yet
- Exceptionality Review 2Document6 pagesExceptionality Review 2api-374528178No ratings yet
- CPE103-EXAM For FINALS-1Document4 pagesCPE103-EXAM For FINALS-1Rain Raven Barlizo LabanzaNo ratings yet
- Specific Learning Disabilities: Federal DefinitionDocument4 pagesSpecific Learning Disabilities: Federal Definitionapi-285181434No ratings yet
- FTC 106 LDDocument5 pagesFTC 106 LDLiezel Mae Delacruz AndresNo ratings yet
- Teaching students with special needsDocument19 pagesTeaching students with special needsSathyan Ilangovan100% (1)
- Teacher Induction Module on Special Education StrategiesDocument7 pagesTeacher Induction Module on Special Education StrategiesIRIS JEAN BRIAGASNo ratings yet
- AdhdDocument3 pagesAdhdapi-267113076No ratings yet
- AdhdDocument2 pagesAdhdapi-267113076No ratings yet
- AdhdDocument1 pageAdhdapi-267113076No ratings yet
- AdhdDocument2 pagesAdhdapi-267113076No ratings yet
- AdhdDocument1 pageAdhdapi-267113076No ratings yet
- AdhdDocument1 pageAdhdapi-267113076No ratings yet
- AdhdDocument1 pageAdhdapi-267113076No ratings yet
- AdhdDocument1 pageAdhdapi-267113076No ratings yet
- AdhdDocument1 pageAdhdapi-267113076No ratings yet
- AdhdDocument3 pagesAdhdapi-267113076No ratings yet
- AdhdDocument2 pagesAdhdapi-267113076No ratings yet
- AdhdDocument1 pageAdhdapi-267113076No ratings yet
- AdhdDocument2 pagesAdhdapi-267113076No ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Essay 1Document4 pagesUnit 5 - Essay 1api-316291068No ratings yet
- ACTION RESEARCH Effects of Bullying in The Academic Performance of The LearnersDocument25 pagesACTION RESEARCH Effects of Bullying in The Academic Performance of The LearnersMa An71% (7)
- Inner Repatterning - A Radically Different Eft Approach: by Tania Prince, Eft MasterDocument2 pagesInner Repatterning - A Radically Different Eft Approach: by Tania Prince, Eft MasterAurora Alina Bujor-FlueranNo ratings yet
- FEKH46, Seminar 5Document3 pagesFEKH46, Seminar 5Axel RosenqvistNo ratings yet
- Long Term Effects of Child Abuse Draft 2 2Document11 pagesLong Term Effects of Child Abuse Draft 2 2api-548856677No ratings yet
- Abdellah 21 Nursing ProblemsDocument7 pagesAbdellah 21 Nursing ProblemsKrizle AdazaNo ratings yet
- Managing Emotional EmployeesDocument2 pagesManaging Emotional EmployeesRitik RanaNo ratings yet
- Airs LM Perdev q1 Module-7Document19 pagesAirs LM Perdev q1 Module-7Lynette Licsi100% (1)
- 200 Soft Skills Interview QuestionsDocument9 pages200 Soft Skills Interview QuestionsFlyner PortugalNo ratings yet
- Home Visit Report1Document2 pagesHome Visit Report1api-241286186No ratings yet
- Narayana VidyalayamDocument6 pagesNarayana VidyalayamTajindar Singh KalsiNo ratings yet
- Strategic Lenses Analyze Organizational StrategyDocument7 pagesStrategic Lenses Analyze Organizational StrategyPriyal RoyNo ratings yet
- BORINGOT, Aliah Marie - MAON, Marry Elordy - RIVERA, Mara Ysabel PERPETUA, Anne Dominique - SANCHEZ, Aubrey MhilesDocument32 pagesBORINGOT, Aliah Marie - MAON, Marry Elordy - RIVERA, Mara Ysabel PERPETUA, Anne Dominique - SANCHEZ, Aubrey MhilesAebee Velasco AlcarazNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Cuatrona MicahDocument3 pagesConcept Map Cuatrona Micahrhumel santiagoNo ratings yet
- Human Growth Learning and Development PowerpointDocument366 pagesHuman Growth Learning and Development PowerpointKlaribelle Villaceran100% (10)
- PT 1Document2 pagesPT 1Pedimor Dolor CabansagNo ratings yet
- Smoking, Smoking CessationDocument5 pagesSmoking, Smoking CessationNikhilNo ratings yet
- Dissociative DisorderDocument21 pagesDissociative DisorderAryan Judith DoloresNo ratings yet
- The Twelve Steps of BondingDocument2 pagesThe Twelve Steps of Bondingadstark01No ratings yet
- Goal Setting A Possible Theoretical Framework For Exami 2016 Current OpinioDocument4 pagesGoal Setting A Possible Theoretical Framework For Exami 2016 Current OpiniosesiliaNo ratings yet
- Mapehhealth Q2 Summative-TestDocument2 pagesMapehhealth Q2 Summative-TestDennmark Duran IgutNo ratings yet
- Key Professional DispositionsDocument3 pagesKey Professional DispositionsEmily SneedNo ratings yet
- Paper 2Document60 pagesPaper 2Navitha DNo ratings yet
- Guidance and Counseling PsychologyDocument34 pagesGuidance and Counseling PsychologyShubha JeniferNo ratings yet
- Ibl Guide PDFDocument137 pagesIbl Guide PDFFazlurohman azinarNo ratings yet
- Dr. Maina Waiganjo 1Document11 pagesDr. Maina Waiganjo 1James GikingoNo ratings yet
- Brand Personality of IPL TeamsDocument2 pagesBrand Personality of IPL TeamsAshish KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument2 pagesReview of Related LiteratureDerreck John OmboyNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Media and Crime PDFDocument34 pagesThe Relationship Between Media and Crime PDFFida AbdulsalamNo ratings yet
- HumanismDocument2 pagesHumanismJay100% (1)