Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eportfoliomirco
Uploaded by
api-248403849Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eportfoliomirco
Uploaded by
api-248403849Copyright:
Available Formats
Megan Ray
ePortfolio
Assignment
Micro 2010-003
Spring 2015
Costs of Production and Profit Maximization
Analysis for the Perfect Competitive Market Structure
Average Average
Total
Total
Total
Average
Marginal Market Price
Total
Variable
Total
Total
Output/h Fixed
Variable
Fixed Cost
Cost
Perfect
Cost (TC)
Cost
Cost
Revenue
r
Cost (TFC) Cost (TVC)
(AFC)
(MC)
Competition
(AVC)
(ATC)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
$10
$10
$10
$10
$10
$10
$10
$10
$10
$10
$10
$10
0
7
10
12
13
15
18
22
27
33
40
48
$10
$17
$20
$22
$23
$25
$28
$32
$37
$43
$50
$58
0
10
5
3
3
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
0
7
5
4
3
3
3
3
3
4
4
4
0
17.00
10.00
7.33
5.75
5.00
4.67
4.57
4.63
4.78
5.00
5.27
~
7
3
2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
$5
$5
$5
$5
$5
$5
$5
$5
$5
$5
$5
$5
$0
$5
$10
$15
$20
$25
$30
$35
$40
$45
$50
$55
Total
Profit
Marginal
Revenue
(MR)
($10)
($12)
($10)
($7)
($3)
$0
$2
$3
$3
$2
$0
($3)
~
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
Maximum Profit
at Profit
Maximizing Output
Marginal Cost=
Marginal Revenue
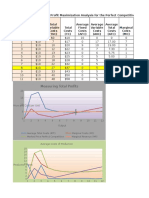
1. In the perfectly competitive market situation above the profit maximizing production level is at 8 units. At this producation level the
marginal cost equals the marginal revenue. This is shown by the marginal cost of $5 for the 8th unit and a marginal revenue of $5 for the
8th unit. Producting at a level of 8 is the profit maximizing level because the cost of production the 8th unit is equal to the return you get
producing it.
2. If the price level of the perfectly competitive market were to decrease to a price level of $4.25 the production level would decrease to 7
which would be the loss minimizing level of production. This is due to a marginal cost $4.57 and the marginal revenue of $4.25. At a level of
7 units the marginal cost of minimized.
3. The firm could continue to operate at a price level of 7 if it was a temporary price decrease and the price would increase after some
point in time. The firm should not continue to operation if the price cut is going to be for the long run because the marginal cost is greater
than the marginal revenue.
Average Cost of Production
18
Total Production Cost
Average Fixed Cost (AFC)
Average Variable Cost (AVC)
Total Fixed Cost (TFC)
Average Total Cost (ATC)
Marginal Cost (MC)
Total Cost (TC)
$70
14
$60
12
$50
Dollar Cost
Production Costs
16
10
8
6
$40
$30
$20
$10
$0
0
1
5
6
Output
10
11
12
Total Cost (TC)
6
7
Output
10
11
12
10
11
Measuring Total Profits
Profit Maximaization
Total Revenue
Average Total Cost (ATC) 0
Marginal Cost (MC) ~
Marginal Revenue (MR) ~
$70
18.00
$60
16.00
$50
Price and Cost per Unit
Revenue and Cost
Total Variable Cost (TVC)
$40
$30
$20
$10
14.00
12.00
10.00
8.00
6.00
4.00
2.00
$0
1
Output
10
11
12
0.00
1
6
7
Output
Monopoly Profit Maximizing Analysis
Total
Output
Units
Price Per
Total
Total Cost
Total
Unit
Revenue
(TC)
Profit (TP)
(Demand)
(TR)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
$8.00
$7.80
$7.60
$7.40
$7.20
$7.00
$6.80
$6.60
$6.40
$6.20
$6.00
$5.80
$5.60
0.00
7.80
15.20
22.20
28.80
35.00
40.80
46.20
51.20
55.80
60.00
63.80
67.20
10.00
14.00
17.50
20.75
23.80
26.70
29.50
32.25
35.10
38.30
42.70
48.70
57.70
-10.00
-6.20
-2.30
1.45
5.00
8.30
11.30
13.95
16.10
17.50
17.30
15.10
9.50
Average
Marginal
Total
Cost
Cost
(MC)
(ATC)
0
~
14.00
4.00
8.75
3.50
6.92
3.25
5.95
3.05
5.34
2.90
4.92
2.80
4.61
2.75
4.39
2.85
4.26
3.20
4.27
4.40
4.43
6.00
4.81
9.00
1. The profit maximizing point for the
monopoly is between 9 and 10 units this is
because at this level the marginal cost of
producting an additional unit is equal to the
marginal revenue making it so they are
producting where the additional dollars spent
are being returned in revenue.
2. The monopolist will price the product where
it will maximize total profits at a minimum the
cost. This will allow the monopolist to make an
economic profit.
3. A monopoly is considered an inefficient use
of resource because they will produce less
then the market demand at a great price
which does not utitilze as many available
resources as would be used in a perfectly
competitive market. The monopoly is also
considered inefficient because they do not
alway operate at the mininum cost or
Marginal
Revenue
(MR)
~
7.80
7.40
7.00
6.60
6.20
5.80
5.40
5.00
4.60
4.20
3.80
3.40
$15.00
Revenue-Cost Comparison
Demand Price
$10.00
MC=MR
Average
Total Cost
$5.00
$0.00
1
10 11 12
OUTPUT
Price Per Unit (Demand) $8.00
Average Total Cost (ATC) 0
Marginal Cost (MC) ~
Marginal Revenue (MR) ~
Total Costs/Total Revenue
PRICE, MARGINAL REVENUE, AND COST
Monopoly Profit Determination
80.00
70.00
60.00
50.00
40.00
30.00
20.00
10.00
0.00
1
10
Output
Total Revenue (TR)
Total Cost (TC)
11
12
13
You might also like
- 655 Week 9 Notes PDFDocument75 pages655 Week 9 Notes PDFsanaha786No ratings yet
- Long Run and Short Run (Final)Document39 pagesLong Run and Short Run (Final)subanerjee18No ratings yet
- Economics For Managers GTU MBA Sem 1 Chapter 13Document41 pagesEconomics For Managers GTU MBA Sem 1 Chapter 13Rushabh VoraNo ratings yet
- Add Equipment Edit Equipment Remove All EquipmentDocument16 pagesAdd Equipment Edit Equipment Remove All EquipmentTots HolaresNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit Office-QuezonDocument71 pagesInternal Audit Office-QuezonNanaram Nhoj100% (1)
- FOREXDocument8 pagesFOREXIvy NisorradaNo ratings yet
- Variable Costs:: Exercise 5-13: B/E Analysis and CVP GraphingDocument21 pagesVariable Costs:: Exercise 5-13: B/E Analysis and CVP GraphingAshish BhallaNo ratings yet
- Cost of ProductionDocument61 pagesCost of ProductionPankit KediaNo ratings yet
- Micro 2010 2Document1 pageMicro 2010 2api-240401313No ratings yet
- Micro Eportfolio Part 1Document1 pageMicro Eportfolio Part 1api-277697234No ratings yet
- Econ 2010 EportDocument5 pagesEcon 2010 Eportapi-260023878No ratings yet
- Sacoya Pedersen-CompetitionDocument1 pageSacoya Pedersen-Competitionapi-253546752No ratings yet
- Micro Eportfolio Fall 13 Assign PC and Monop 2 Version 2 XLSBDocument10 pagesMicro Eportfolio Fall 13 Assign PC and Monop 2 Version 2 XLSBapi-338557409No ratings yet
- Ecn 2010 e PortfolioDocument8 pagesEcn 2010 e Portfolioapi-248689489No ratings yet
- Microecon Perfect CompetionDocument4 pagesMicroecon Perfect Competionapi-252908662No ratings yet
- Econ - E-PortfolioDocument12 pagesEcon - E-Portfolioapi-302595625No ratings yet
- ZachDocument17 pagesZachapi-242784130No ratings yet
- Micro Eportfolio Spring 2014 NjensenDocument14 pagesMicro Eportfolio Spring 2014 Njensenapi-253721071No ratings yet
- Rolando Final ProjectDocument15 pagesRolando Final Projectapi-242856546No ratings yet
- Micro Eportfolio Fall 13 Assign PC and Monop 2Document1 pageMicro Eportfolio Fall 13 Assign PC and Monop 2api-252975243No ratings yet
- Econ Eportfolio Part 1Document5 pagesEcon Eportfolio Part 1api-252980817No ratings yet
- Econ Eportfolio Part 2Document3 pagesEcon Eportfolio Part 2api-252980817No ratings yet
- Monopoly Profit Maximizing AnalysisDocument2 pagesMonopoly Profit Maximizing Analysisapi-253078310No ratings yet
- Eportfolio Micro EconomicsDocument10 pagesEportfolio Micro Economicsapi-352017375No ratings yet
- Eportfolio MicroeconomicsDocument16 pagesEportfolio Microeconomicsapi-241510748No ratings yet
- Micro Eportfolio Part 2Document5 pagesMicro Eportfolio Part 2api-240741436No ratings yet
- Bretts Econ ExcelDocument18 pagesBretts Econ Excelapi-259787781No ratings yet
- Class 1Document46 pagesClass 1Parina AhluwaliaNo ratings yet
- Econ 2010 Eport 2Document4 pagesEcon 2010 Eport 2api-260023878No ratings yet
- Sacoya Pedersen-MonoployDocument1 pageSacoya Pedersen-Monoployapi-253546752No ratings yet
- Market TypesDocument32 pagesMarket TypesJintu Moni BarmanNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Notes On - Cost Curves DerivationDocument24 pagesTopic 4 Notes On - Cost Curves DerivationsilasmafungaNo ratings yet
- Production SR 2Document6 pagesProduction SR 2YarlagaddaSandeepNo ratings yet
- Theory of Cost and ProfitDocument20 pagesTheory of Cost and ProfitCrystal De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Economics: The Nature of Cost in Long Run and Short RunDocument30 pagesEconomics: The Nature of Cost in Long Run and Short RunRavi Kumar BajajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Costs of Production - AllDocument29 pagesChapter 4 - Costs of Production - AllNetsanet MeleseNo ratings yet
- 1 Lecture 6 - Short-Run Costs and Output DecisionsDocument14 pages1 Lecture 6 - Short-Run Costs and Output DecisionsyasirNo ratings yet
- Costanalysis 100202064231 Phpapp02Document39 pagesCostanalysis 100202064231 Phpapp02tarunadurejaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Costs of Production-1Document42 pagesChapter 4 - Costs of Production-1idolhevevNo ratings yet
- Aladdin Games Monte Carlo Simulation T1Document204 pagesAladdin Games Monte Carlo Simulation T1KousheekNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - Cost and ProductionDocument25 pagesUnit 7 - Cost and ProductionRax-Nguajandja KapuireNo ratings yet
- Practise Assignment 1Document2 pagesPractise Assignment 1vivek shuklaNo ratings yet
- CAPCOST ProjectDocument16 pagesCAPCOST ProjectJonathanNo ratings yet
- Cost and Revenue An in Depth StudyDocument36 pagesCost and Revenue An in Depth StudyJatin Anand0% (1)
- Manecon ReviewerDocument165 pagesManecon ReviewerAron AbastillasNo ratings yet
- Group 6 - Marginal AnalysisDocument26 pagesGroup 6 - Marginal AnalysisGilang SaktiNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy Quiz 3Document5 pagesWind Energy Quiz 3Ivan RozoNo ratings yet
- The Costs of Production: Ayesha Afzal Assistant Professor Lahore School of EconomicsDocument19 pagesThe Costs of Production: Ayesha Afzal Assistant Professor Lahore School of EconomicsAsad KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Revenue and Cost and Break EvenDocument13 pagesUnit 7 Revenue and Cost and Break Evenafreen khanNo ratings yet
- Cost AnalysisDocument33 pagesCost AnalysisPatnana ArunaNo ratings yet
- Cost Analysis IDocument16 pagesCost Analysis IRajkumar BharathNo ratings yet
- CF Assignment FauxDocument48 pagesCF Assignment Fauxmaazali12No ratings yet
- EconDocument16 pagesEconvivek3790No ratings yet
- Economics Powerpoint For FinalsDocument94 pagesEconomics Powerpoint For FinalsJowel BaldemorNo ratings yet
- CPC Ec 01Document34 pagesCPC Ec 01Arslan RammayNo ratings yet
- CFO POE12 PPT 08Document41 pagesCFO POE12 PPT 08Batuhan GyulerNo ratings yet
- Financial-Management Adil AliDocument15 pagesFinancial-Management Adil AliAdil AliNo ratings yet
- Economics Notes Unit 3Document12 pagesEconomics Notes Unit 3Prothom UzzamanNo ratings yet
- Costs & Output DecisionsDocument18 pagesCosts & Output DecisionsIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Cashflow ExampleDocument1 pageCashflow Examplemanikandan039715No ratings yet
- MECLA1Document9 pagesMECLA1zaza wordNo ratings yet
- Oil Well, Refinery Machinery & Equipment Wholesale Revenues World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryFrom EverandOil Well, Refinery Machinery & Equipment Wholesale Revenues World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryNo ratings yet
- Sound Recording Studio Revenues World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryFrom EverandSound Recording Studio Revenues World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 3 - Adjusting - Accounts - NUS ACC1002 2020 SpringDocument48 pagesLecture - 3 - Adjusting - Accounts - NUS ACC1002 2020 SpringZenyuiNo ratings yet
- Final - Year End Tax Planning Toolkit - 2016 - 17Document141 pagesFinal - Year End Tax Planning Toolkit - 2016 - 17yiang.tranNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Hospitality Fifth Edition John R. Walker: Chapter 3: The Hotel BusinessDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Hospitality Fifth Edition John R. Walker: Chapter 3: The Hotel BusinessScotch PelosoNo ratings yet
- Acc 380 Discussion TwoDocument5 pagesAcc 380 Discussion TwoHabte DebeleNo ratings yet
- What Are The Sources of Revenue For The Local Government UnitDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Sources of Revenue For The Local Government UnitKris UngsonNo ratings yet
- Pension ProposalDocument14 pagesPension ProposalprastacharNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Chapter 9Document66 pagesFinancial Accounting Chapter 9Jihen SmariNo ratings yet
- MG 3027 TAXATION - Week 10 Income From Self-Employment-Computation of IncomeDocument34 pagesMG 3027 TAXATION - Week 10 Income From Self-Employment-Computation of IncomeSyed SafdarNo ratings yet
- Gpro From HTfedDocument19 pagesGpro From HTfedMunteanu Bogdan BlackHelmets100% (1)
- CH 19Document50 pagesCH 19anwar.maulanaNo ratings yet
- Dissertation - Shariah-Compliant Stocks Screening and Purification-FMG - July 2015Document46 pagesDissertation - Shariah-Compliant Stocks Screening and Purification-FMG - July 2015Hayiath QureshiNo ratings yet
- 4.77 B.com Accounting and Finance Semester I and II Syllabus With Course StructureDocument70 pages4.77 B.com Accounting and Finance Semester I and II Syllabus With Course StructureVaril Pereira100% (1)
- FIn 201 AnswersDocument5 pagesFIn 201 AnswersShahinNo ratings yet
- 2022 ICTSI Balance Sheet Income Statement - pg.53Document1 page2022 ICTSI Balance Sheet Income Statement - pg.53loveartxoxo.commissionNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Submitted By:: Dr. Bobby B.Pandey Aniket Sao Lecturer Roshan Kumar Vijay Bharat Ravi Lal UraonDocument15 pagesSubmitted To: Submitted By:: Dr. Bobby B.Pandey Aniket Sao Lecturer Roshan Kumar Vijay Bharat Ravi Lal Uraonales_dasNo ratings yet
- Unit-2: Banking and Insurance Services: Collection of Cheques, Bills and DraftsDocument45 pagesUnit-2: Banking and Insurance Services: Collection of Cheques, Bills and DraftsRaghu BMNo ratings yet
- Committee Member StatementsDocument10 pagesCommittee Member StatementsJohn AllisonNo ratings yet
- Cover Sheet PDF Serv LetDocument1 pageCover Sheet PDF Serv LetKarthik ChellamuthuNo ratings yet
- Introduction SsiDocument44 pagesIntroduction SsiSheetal IyerNo ratings yet
- Final Term Project: Report On MCB PakistanDocument6 pagesFinal Term Project: Report On MCB PakistanBHATTINo ratings yet
- The Impact of Financial Management System On Human Resource Utilization (A Case in Gondar Municipality)Document67 pagesThe Impact of Financial Management System On Human Resource Utilization (A Case in Gondar Municipality)meseret sisayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Standard Costing PDFDocument107 pagesChapter 5 Standard Costing PDFjigyasaNo ratings yet
- Motilal Oswal Finance Services IPO Note Aug 07 EDELDocument17 pagesMotilal Oswal Finance Services IPO Note Aug 07 EDELKunal Maheshwari100% (1)
- Jose Maria College College of Business Education: Name: - Date: - Instructor: John Paul S. Tan, Cpa, MDM, CatpDocument8 pagesJose Maria College College of Business Education: Name: - Date: - Instructor: John Paul S. Tan, Cpa, MDM, CatpAngelica CastilloNo ratings yet
- Accounting Textbook Solutions - 55Document19 pagesAccounting Textbook Solutions - 55acc-expertNo ratings yet
- Grammar QuizesDocument20 pagesGrammar QuizesEswary MohanNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet & Profit LossDocument7 pagesBalance Sheet & Profit LossJenny Davidson50% (2)