Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 4:: Professor William Hefley
Uploaded by
api-315444897Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 4:: Professor William Hefley
Uploaded by
api-315444897Copyright:
Available Formats
1
Assignment 4:
Group Topic: Cloud Computing
Group 9: Dorcas Sipoche, Matthew Lahde, Murtaza Ali
Professor William Hefley
ITSS, 4370, 501, Information Technology Management
Date: 3/4/2016
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Introduction: What is Cloud Computing? .......................................................................................3
Deployment models.4
Cloud Models...5
Projects, Capabilities & Benefits.5
System of Measuring...7
Conclusion 10
References..11
INTRODUCTION
Cloud computing
When the idea of the cloud was first introduced to the general public, people had different
ideas about what it really was and to some the correct definition is yet to be established.
What is the Cloud?
In the book, The Basics of Cloud Computing by Derrick Roundtree, The Cloud is defined
simply as a service or group of services. This is said to be partially the reason why it has been
difficult to have a definite definition for it. The range of definitions is further evidenced by IBM
(International Business Machines) whose website, ibm.com define cloud computing as simply
computing as a service over the internet.
??
Over time the cloud and the services it offers have changed, others very quickly to adapt to
customers needs. These rapid changes have also contributed to changes to its definition over
time by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Despite the changes is definitions, the NIST definition of the cloud is still the standard mostly
referred to when talking about the cloud. This definition has three main components:
i)
ii)
iii)
Five key cloud characteristics
Four cloud deployment models
Three cloud service models
Some earlier definitions of the cloud described it as a web-based application that was more
affordable than other applications and that was also could easily be accessed from anywhere
being web-based. There are five key cloud computing characteristics outlined by the NIST
definition that must be present in order for a service to be considered true cloud service. They are
as follows:
1. On-demand self-service: This means that the consumer can request and receive access to
a service offering, without an administrator or some sort of support.
2. Broad network access: Users should not be required to have a large amount of
bandwidth to use the service. The solutions provided are at a greater advantage if
architected in such a way that doesnt require a client at all. For services that require
client application the provider may have to build platform-specific applications.
3. Resource pooling: This helps save costs and allows flexibility on the provider. Resource
pooling is often achievers using virtualization, which allows providers to increase the
density of their systems.
4. Rapid elasticity: Describes the ability of the cloud environment to easily grow to satisfy
user demand. It is usually accomplished through the use of automation and orchestration
such that, when resource usage hits a certain point, a trigger is setoff and it automatically
begins the process of capacity expansion.
5. Measured service: Cloud computing also has the pay as you go feature, therefore
cloud services must have the ability to measure usage which can be quantified using
various metric such as time used, bandwidth used, and data used.
Deployment Models
Due to vast array of services or products provided by various organizations, the requirements for
the cloud will differ from organization to organization. The organizations have to determine if
the cloud is the more suitable option for them in order to get the benefits. Therefore the cloud
environment can be implemented using different service models in order to accommodate the
requirements of various organizations. There are four different cloud deployment models
outlined by the NIST definition of cloud computing: public, private, community and hybrid.
The public cloud is a set of computing resources provided by third-party organization. The
environments are entirely managed and serviced by an external service provider. Some examples
of the most popular public clouds include Amazon Web Services, Google AppEngine, and
Microsoft Azure.
The private cloud is built and completely managed and maintained within a single organization.
All the infrastructure for the environment will be housed in a datacenter controlled by the same
organization. Organizations use software that enables cloud functionality, such as VMWare,
vCloud Director, or OpenStack.
The community cloud is not used as much as public or private. It shares computing resources
across several organizations, and can be managed by either organizational IT resources or thirdparty providers.
The hybrid cloud is a mix of computing resources provided by both private and public clouds.
This mix is mistaken to be an environment in which some components are public and some
private. However in the hybrid cloud environment multiple separate cloud environments (public
or private) are connected together. The hybrid will most likely become the most common cloud
implementation as the cloud era matures.
Cloud Models
There are several cloud models in existence but according to NISTs definition of the cloud, the
three main models are: Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
Software as a Service (SaaS) is consider by most people as the original cloud service model.
Although it us similar to the old application service provider (ASP) model, there are some key
differences. In the old ASP model, the applications hosted were usually client/server applications
where some type of special infrastructure and client were needed to access the applications. SaaS
or cloud-based applications run on distant computers in the cloud that are owned and operated
by others and that conned to users computers via the internet and, usually a web browser.
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a service offering whereby customers are given a platform to
use for their computing needs without the cost and complexity of buying and managing the
underlying hardware, software, provisioning and hosting.
Infrastructure (IaaS) provides core services such as computing power, storage, networking and
operating systems, which organization can use on a pay as you go basis.
Additional Service Models include, Database as a Service, Desktop as a Service and Storage as
Service.
Projects, Capabilities & Benefits
Switching to cloud computing is a very demanding task; however, it is something that offers
many benefits. It requires transferring all processes and computing to the cloud. Similar to
pumping water to your house, cloud computing resources are available when you need them and
are charged as you use them. This allows companies to expand their usage in times of high needs
and save money when they are not using them as much. Cloud computing allows companies to
get rid of hardware obsolescence, updating applications, and hiring IT extremely expensive IT
professionals. Cloud computing offers three very important benefits: Pay per use, Elasticity, and
self-service provisioning. Pay per use allows companies to use computing resources and only pay
for what they use. This allows customers to save money on computing power and reduce the
costs on hardware and update costs. Elasticity is another benefit of cloud computing. Elasticity
allows companies to scale up when computing need increases and scale back down when
computing power decreases. Self-service provisioning is an important benefit in which end users
can spin up computing resources for almost any type of workload on demand. These three
benefits save the company money, time and resources by switching there computing to the cloud.
Although Cloud computing offers a lot of benefits to a company it also comes with some risks.
The risk of switching over to cloud computing is that it relies heavily on internet connection. If
the company server or connection goes down unless the company has a hybrid system or some
type of back up the company will not be able to perform high level computing through the cloud.
This risk forces the company to be extremely dependent on internet connection. Another risk that
the company runs by using cloud computing is security. This is an area in which the company
can lose valuable data and secrets. With everything on the cloud and the company storing all of
its computer processing on the cloud there will always be security concerns whether it is
corporate sabotage or not.
The cost of cloud computing would be relatively low with regards to how much cloud computing
costs in comparison to having your own database, hardware, and software. However switching to
cloud computing can be costly because it requires retraining staff on how to use the cloud. It
requires a redesign of infrastructure. It may also lead to the obscurity of the current hardware and
software solutions the company was previously using, which isnt technically a cost but it is a
loss. Regardless of the cost of cloud computing in the grand picture it is actually a benefit of
switching to cloud computing in that it makes IT cheaper and saves the organization money,
resources, and labor.
Based on types of projects in the Grochow article, this project is a form of Technology
Migration. Shifting from in house hardware and software to Cloud Computing would be
considered Technology Migration. It is considered Technology migration because it is switching
Old capabilities to new capabilities. It is causing the benefits of capability, reliability, and
performance improvements. It is asking for an acceptance of new technology. Lastly the cost
associated with it are phased cost model and migration costs. The process of switching to cloud
computing has all of the characteristics of a technological migration project.
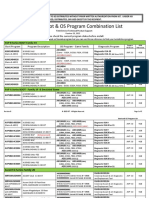
In order to measure the success of this project, we would implement the use of the infrastructure
Health check rating system from the Grochow article. This system looks at the usability,
reliability, technological obsolescence, and cost to maintain. It evaluates all of these categories
and aggregates them into a health check rating that tells you how often you will need to fix the
system, upgrade the system, or replace the system. This system allows us to quantify the level of
success that our project will achieve by evaluating levels of the project that affect its success the
most.
Infrastructure
system
Meets
need
(usability)
Outage
Frequency
(reliability)
Up to Date
Architecture (tech
Obsolescence)
Cost to
maintai
n
Health
Check
Rating
Service
management
system
Enterprise
storage
Web server
Wireless
network
Database
Identity and
access
management
Wired network
Printing
management
system
Emergency
response system
3.5
2.5
2.5
2.5
3.375
1.5
1.5
2.5
2
3
2
1
2.5
2
2
1.5
5
3
4
3
4
5
2
3.125
3.75
3.5
5
5
5
4
5
3.5
3.5
4
4.625
4.75
System of Measurement
One metric that can be used to measure a project of cloud computing is that of rapid provisioning.
Rapid provisioning deals with the scaling of resources in relation to business activity. Under a
cloud system less time is spent on development stages and the system is deployed quickly allowing
for business value to start accruing more quickly. Businesses experiencing high growth can gain
more IT resources quickly to support this growth. With an increase in rapid provisioning due to
cloud computing, organizations can also quickly redirect resources. If a business notices one area
of the business growing rapidly they can quickly utilize IT resources to support this new growth
area. Or if the business notices a decrease in demand in another aspect, the organization can quickly
reduce the IT resources to that area in order to save money.
Businesses that want their projects to start making money as soon as possible will value the
metric speed of cost reduction. Speed of cost reduction is measuring how fast after adopting an
IT system the costs start to decrease. A business ideally wants to minimize costs and maximize
benefits. A cloud computing system provides many benefits to increase the speed costs are
reduced. First it allows for the easy use of pre-built functions which takes out all the stages of
development and only leaves two stages, installation and deployment. In Cloud Computing the
buyer can move from a CAPEX to an OPEX model through purchasing the use of the service
rather than having to own and manage the assets of that service,(The Open Group). The main
cost savings come from this lack of ownership and management, all the business pays for is the
service. A cloud computing system also allows for faster change to new capabilities. As business
needs change quick adopting of new technologies can give a business an edge or let the business
enter a new market.
Normally when an IT project is handed off to another company, some of the features a business
may want are not realized. With cloud computing though, the business gets exactly what it wants
without having to develop its own system. This benefit of cloud computing can be measured
through the metric of optimization of ownership use. When the business chooses a cloud service
they decide what they need not just for the present but also what they predict they will need in
the future. Patches and upgrades or new technology are in theory invisible to the end user of the
service as they are included as part of the automatic asset management features, (The Open
Group). Because patches and new technology are taken over by the cloud provider the
organization doesnt have to work on its end to keep the system running in the future. Too many
organizations fail to optimize their ownership of an IT product because they dont support those
products into the future. Optimization of ownership use works not only to reduce the gap
between design-time and run-time but to deliver on performance of features not just for the
present but also for the future.
Adopting a cloud computing system has an impact on many of the critical capabilities of the ITCMF. Capability Asset Management is one critical capability affected by cloud computing. After
adoption the organization should be able to utilize more IT resources and manage their
capabilities to an improved degree and with greater speed. Green IT is another capability
positively affected by the adoption of a cloud computing system. Instead of running a giant
server room in an organization you can use however many you need in an off-site facility that
was likely designed with energy saving in mind. Information Security Management would be
affected as well because new security standards would have to be adopted. New security
standards would be necessary because important company data would be moved into the cloud.
The cloud company and organization would have to reach a mutually beneficial agreement about
what should be known about the data. Adoption of cloud computing allows an organization to
skip the service design part of the ITIL lifecycle. It also allows the organization to focus its
resources more on the service improvement and the service operations parts of the lifecycle.
Figure 1
10
Figure 2
Conclusion
Cloud computing is rapidly changing how computing has been done from private to commercial
use. For different organizations there are various factors that would drive their decision to
change or adopt to cloud computing. These may include Cost of Services, Information or
Security, Accessibility, Mobility etc. Depending on how an organization adopts the cloud model
(as a private, community, public, or hybrid resource) and depending on how the cloud based
services (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) are delivered , cloud computing brings different opportunities for
change to consumers and subscribers. The need for computational power, data storage,
information security, and bandwidth continues to drive demand for more highly capable systems,
and cloud computing manes such large-scale implementation more possible than is typically the
case with other models.
11
References:
Roundtree, D., & Castrillo, I. (2013). The Basics of Cloud Computing.
Retrieved March 01, 2016, from
http://proquest.safaribooksonline.com/9780124059320
(n.d.). Retrieved March 02, 2016, from
http://www.smartdatacollective.com/junedghanchi/362621/mobile-cloudcomputing-and-its-critical-role-data-management
What is Cloud Computing? (n.d.). Retrieved March 02, 2016, from
http://www.ibm.com/cloud-computing/what-is-cloud-computing.html
Gorelik, E. (2013). Cloud Computing Models. 1-82. Retrieved March 03,
2016, from http://web.mit.edu/smadnick/www/wp/2013-01.pdf
Peeva, Boyana. "Website Monitoring & Server Monitoring Blog." Website
Monitoring Server Monitoring Blog. Tech, 04 July 2013. Web. 02 Mar.
2016.
"Cloud Computing for Business : What Is Cloud?" Cloud Computing for
Business : What Is Cloud? The Open Group, 2013. Web. 02 Mar. 2016.
Rouse, Margaret. "What Is Cloud Computing? - Definition from
WhatIs.com."SearchCloudComputing. WhatIS.com, 01 Feb. 2015. Web. 02
Mar. 2016.
"Building Return on Investment from the Cloud." The Open Group. The
Open Group.org, Apr. 2010. Web. 02 Mar. 2016.
12
You might also like
- Introduction To Azure FundamentalsDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Azure FundamentalsReeghesh JuleemunNo ratings yet
- BA160 Concepts of Information Systems, Project On Microsoft Azure by Henok Seifu & Natnael NegussieDocument8 pagesBA160 Concepts of Information Systems, Project On Microsoft Azure by Henok Seifu & Natnael NegussieHenok SeifuNo ratings yet
- Igt - Boot Os List Rev B 10-28-2015Document5 pagesIgt - Boot Os List Rev B 10-28-2015Hector VillarrealNo ratings yet
- A&F Method OfInspectionDocument26 pagesA&F Method OfInspectionzoomerfins22100% (1)
- Tally QuestionsDocument73 pagesTally QuestionsVishal Shah100% (1)
- CEH v12 Lesson 12 - Introduction To Cloud CompDocument23 pagesCEH v12 Lesson 12 - Introduction To Cloud CompAbhay JainNo ratings yet
- AWS ClassDocument15 pagesAWS ClassAshishNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ibm CloudDocument91 pagesIntroduction To Ibm CloudlijamannuNo ratings yet
- INTUNE Interview QuestionsDocument68 pagesINTUNE Interview QuestionsHemanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Interview Questions and AnswersDocument30 pagesCloud Computing Interview Questions and Answerssenthilkumar_surulNo ratings yet
- Cast Resin Busduct PDFDocument48 pagesCast Resin Busduct PDFanand2k1100% (1)
- A Study of Cloud Computing MethodologyDocument5 pagesA Study of Cloud Computing MethodologyR Dharshini SreeNo ratings yet
- Data Collection ProcedureDocument58 pagesData Collection ProcedureNorjenn BarquezNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing JUNE 2022Document12 pagesCloud Computing JUNE 2022Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Tutorial For BeginnersDocument38 pagesCloud Computing Tutorial For BeginnersPraveen Madupu100% (1)
- Draft Horse Primer Guide To Care Use of Work Horses and Mules 1977Document396 pagesDraft Horse Primer Guide To Care Use of Work Horses and Mules 1977Radu IliescuNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide to Unlocking the Full Potential of Cloud Services: Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide to Unlocking the Full Potential of Cloud Services: Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesWhat Is Cloud ComputingDillip Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- "Business Models in Cloud Computing": Assignment-1Document22 pages"Business Models in Cloud Computing": Assignment-1Ajay KakkarNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesCloud ComputingsweetgirlieNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: An Overview: Charandeep Singh Bedi, Rajan SachdevaDocument10 pagesCloud Computing: An Overview: Charandeep Singh Bedi, Rajan SachdevaCharndeep BediNo ratings yet
- Garments & Tailoring Business: Submitted byDocument6 pagesGarments & Tailoring Business: Submitted bykartik DebnathNo ratings yet
- Arya College of Engineering and Research Centre: Industrial TrainingDocument28 pagesArya College of Engineering and Research Centre: Industrial Trainingriya ahujaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing1Document32 pagesCloud Computing1NiharikaNo ratings yet
- Enterprise-level benefits achieved from Cloud ComputingDocument7 pagesEnterprise-level benefits achieved from Cloud ComputingMis MaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 notes (1)Document24 pagesChapter 1 notes (1)Anekket DharaneNo ratings yet
- Cloud 1Document12 pagesCloud 1Hanzala KhanNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Assignment Questions 1st April 2021Document5 pagesCloud Computing Assignment Questions 1st April 2021Kiran Sk100% (1)
- Term Paper On Cloud ComputingDocument14 pagesTerm Paper On Cloud ComputingShifath Shams50% (2)
- Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesCloud Computingshariful islamNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Cloud ComputingDocument12 pagesUnit 1 - Cloud ComputingMohamed SugailNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 New Trends in MISDocument31 pagesLecture 4 New Trends in MISmaryallaine02No ratings yet
- Reading 2Document23 pagesReading 2FisalAmarShahNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Overview: Key Concepts and ApplicationsDocument6 pagesCloud Computing Overview: Key Concepts and ApplicationsArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document24 pagesUnit 5diwansingh29081999No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Pros and ConsDocument7 pagesCloud Computing Pros and ConsKarla Isael AscNo ratings yet
- Mi AssignmentDocument11 pagesMi AssignmentVarun MavaniNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing For Beginners: in This Tutorial, You Will LearnDocument11 pagesCloud Computing For Beginners: in This Tutorial, You Will Learnsangeet83No ratings yet
- bca 3rd year cloud computing notesDocument9 pagesbca 3rd year cloud computing notesrishabhtoyouNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Cloud Computing Overview RKSDocument22 pagesUnit 5 Cloud Computing Overview RKSmr yashNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Lab Manual 1Document25 pagesCloud Computing Lab Manual 1OMSAINATH MPONLINE100% (1)
- Cloud Computing - Lecture MaterialDocument14 pagesCloud Computing - Lecture Materialchirayush chakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Hybrid, Private and Public Clouds: Pravin Ganore CommentsDocument12 pagesCloud Computing: Hybrid, Private and Public Clouds: Pravin Ganore CommentsNaveen SihareNo ratings yet
- Network Essentials Group 10 Assignment-1 PDFDocument16 pagesNetwork Essentials Group 10 Assignment-1 PDFelvisNo ratings yet
- Cloud CompuingDocument5 pagesCloud CompuingMuppalla PravallikaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Primer Ebook PDFDocument19 pagesCloud Computing Primer Ebook PDFgubdaNo ratings yet
- OCI-1 Cloud OverviewDocument7 pagesOCI-1 Cloud OverviewEli PalmieriNo ratings yet
- Emerging Technology for Engineering - Cloud Computing Benefits and ServicesDocument17 pagesEmerging Technology for Engineering - Cloud Computing Benefits and ServicesManya JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing NIST Model: Essential CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesCloud Computing NIST Model: Essential CharacteristicsDrishti GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 (Introduction To Cloud)Document15 pagesUnit-1 (Introduction To Cloud)Binay YadavNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Relies On Restricting Sharing of Resources To Achieve Coherence and Economies of ScaleDocument13 pagesCloud Computing Relies On Restricting Sharing of Resources To Achieve Coherence and Economies of Scaleharshitasarraf13No ratings yet
- A View of Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesA View of Cloud ComputingmasharabNo ratings yet
- Cloud ServiceDocument4 pagesCloud ServiceDuyên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Student Manual # 06 Cloud Computing 101Document18 pagesStudent Manual # 06 Cloud Computing 101Manish AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics: Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesBusiness Analytics: Cloud ComputingShadab MirzaNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument20 pagesCloud ComputingانجنیرخرمNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesWhat Is Cloud Computingnaresh sahuNo ratings yet
- Part 1 - Describe Cloud ConceptsDocument12 pagesPart 1 - Describe Cloud ConceptsCarlo SeixasNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing An IntroductionDocument39 pagesCloud Computing An Introductionsrishtityagi2020No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Assignment 3Document6 pagesCloud Computing Assignment 3Dipesh KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Cloud U1Document27 pagesCloud U1Sudhanshu PandeyNo ratings yet
- Unit-1: Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument14 pagesUnit-1: Introduction To Cloud ComputingmadhavNo ratings yet
- CC Unit 1Document18 pagesCC Unit 1samruddhi ghodakeNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Cloud Computing Benefits and Models in 40 CharactersDocument12 pagesEnterprise Cloud Computing Benefits and Models in 40 CharactersNitesh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Point of ViewDocument18 pagesCloud Computing Point of ViewTamas MandalNo ratings yet
- Cloud ServiceDocument4 pagesCloud Servicethe.elysian.shop2022No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionFrom EverandCloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionNo ratings yet
- Shrey's PHP - PracticalDocument46 pagesShrey's PHP - PracticalNahi PataNo ratings yet
- GA 7 Parts ManualDocument565 pagesGA 7 Parts ManualDave SchallNo ratings yet
- Autocad 2016Document59 pagesAutocad 2016Kaye OleaNo ratings yet
- NURKSE's Balanced GrowthDocument7 pagesNURKSE's Balanced GrowthArnab MutsuddyNo ratings yet
- Deploy A REST API Using Serverless, Express and Node - JsDocument13 pagesDeploy A REST API Using Serverless, Express and Node - JszaninnNo ratings yet
- Marantz CD4000 PDFDocument28 pagesMarantz CD4000 PDFboroda2410No ratings yet
- Essential earthquake preparedness stepsDocument6 pagesEssential earthquake preparedness stepsRalphNacisNo ratings yet
- Duratone eDocument1 pageDuratone eandreinalicNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Personal Protective Equipment in Pesticide App 2018Document4 pagesThe Importance of Personal Protective Equipment in Pesticide App 2018Anees MalikNo ratings yet
- 19286711Document8 pages19286711suruth242100% (1)
- Computers in Human Behavior: Full Length ArticleDocument9 pagesComputers in Human Behavior: Full Length Articlenabilla rusdiNo ratings yet
- Business Study Quarterly Paper by Vijay SirDocument3 pagesBusiness Study Quarterly Paper by Vijay Sirmonish vikramNo ratings yet
- Apple Led Cinema Display 24inchDocument84 pagesApple Led Cinema Display 24inchSantos MichelNo ratings yet
- Efectele Crizei Economice Asupra Politicilor Pietei Muncii Din RomaniaDocument24 pagesEfectele Crizei Economice Asupra Politicilor Pietei Muncii Din Romaniacristian_incaltarauNo ratings yet
- Payroll Activity SummaryDocument1 pagePayroll Activity SummaryChoo Li ZiNo ratings yet
- Management principles and quantitative techniquesDocument7 pagesManagement principles and quantitative techniquesLakshmi Devi LakshmiNo ratings yet
- IPR GUIDE COVERS PATENTS, TRADEMARKS AND MOREDocument22 pagesIPR GUIDE COVERS PATENTS, TRADEMARKS AND MOREShaheen TajNo ratings yet
- Different Aids For TeachingDocument19 pagesDifferent Aids For TeachingPrecious CabarseNo ratings yet
- Project 863 EvidenceDocument5 pagesProject 863 EvidenceMilan TolhuisenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial: Energy Profiles ManagerDocument6 pagesTutorial: Energy Profiles ManagerDavid Yungan GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Subtract Two 4-Digit Numbers - More Than One Exchange 2019Document2 pagesLesson 3 - Subtract Two 4-Digit Numbers - More Than One Exchange 2019mNo ratings yet
- Loctite 270™: Technical Data SheetDocument4 pagesLoctite 270™: Technical Data SheetM Jobayer AzadNo ratings yet
- Chpter 06 QuizDocument3 pagesChpter 06 QuizGall AnonimNo ratings yet