Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Study of Consumer Buying Behavior Regarding The Different Brands of Mobile Handsets
Uploaded by
Prashant SinghOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Study of Consumer Buying Behavior Regarding The Different Brands of Mobile Handsets
Uploaded by
Prashant SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
Study of Consumer Buying Behavior
regarding the different Brands of
Mobile Handsets
(Research Project Report)
Submitted to:-
University of Pune
In Partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of the Degree
of
Master in Marketing Management (2009-11)
Under the supervision of:-
Submitted by:-
Mr. Ajit Borde Prashant
Singh
Mr. Ullhas Pramanik MMM 2nd
Sem,
Roll
No. 93302
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 1
Institute of Business Management &
Research,
Chinchwad, PUNE
Acknowledgement
In the successful completion of this project inspiration and guidance of
many people was involved. A mere form of acknowledgement would be
demeaning the status of this whole effort which has had the blessings and
supervision of the eminent person around me.
First of all I would like to thank Mr. Ajit Borde & Mr. Ullhas
Pramanik who was there to guide me at every step during the course of
this project. They gave me tips for the improvement in project whenever
required. Apart from this I feel indebted to all faculty members of IBMR,
especially who have helped, developed the right kind of attitude and
scholastic excellence in me. Last but not the least; I am very much
thankful to my parents, friends and all those persons who made this
research project possible, for their consistent guidance and constructive
criticism.
Prashant
Singh
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 2
MMM (II
sem.)
Roll No:
93302
Table of Contents
Chapter Particulars Page no.
No.
1 Introduction 4-13
2 Research Methodology 14-17
3 Data Analysis and Interpretation 15-30
4 Results and Findings 31-32
5 Conclusion and Summary 33
Appendix 34-38
Bibliography 39
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 3
List of tables
S.No. Particulars Page
No.
Table 1.1 Showing market share of major global players of 7
mobile phones in 2009
Table 3.1 Showing number of respondents owing a mobile 18
phone
Table 3.2 Showing different brands of mobiles phones used 19
by the respondents
Table 3.3 Showing respondents using same brand as they 20
had earlier
Table 3.4 Showing reasons for using mobile phone by the 21
respondents
Table 3.5 Showing the factors considered by respondent 22
while purchasing a mobile hand set
Table 3.6 Showing the sources which influenced the buying 23
decision of the respondents
Table 3.7 Showing different purposes for which mobile is 24
used by the respondents
Table 3.8 Showing ranking of various features of mobile 25
handsets by the respondents according to their
Table 3.9 Showing range of preferences
price that respondents like to 26
spend on mobile hand set
Table Showing features preferred in a particular brand 27
3.10 of mobile phone
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 4
Table Showing agreement level of the respondents on 27
3.11 various factors influencing purchase decision
Table Showing satisfaction level of the respondents 29
3.12
Table Showing additional features required by the 30
3.13 respondents in their mobile handsets
List of Figures
S.No. Particulars Page
No.
Figure India’s mobile subscriber base 10
1.1
market share in percentage of the mobile phone 11
Figure number of respondents
players inowing
India a mobile phone 18
3.1
Figure different brands of mobiles phones used by the 19
3.2 respondents
Figure respondents using same brand as they had 20
3.3 earlier
Figure reasons for using mobile phone by the 21
3.4 respondents
Figure factors considered by respondent while 22
3.5 purchasing a mobile hand set
Figure sources which influenced the buying decision of 23
3.6 the respondents
Figure different purposes for which mobile is used by 24
3.7 the respondents
Figure ranking of various features of mobile handsets 25
3.8 by the respondents according to their
Figure range of price thatpreferences
respondents like to spend on 26
3.9 mobile hand set
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 5
Figure3.1 features preferred in a particular brand of 27
0 mobile phone
Figure3.1 agreement level of the respondents on various 27
1 factors influencing purchase decision
Figure3.1 Satisfaction level of respondents 29
2
Figure3.1 additional features required by the respondents 30
3 in their mobile handsets
Chapter 1
1.1 INTRODUCTION
Information technology is "the study, design, development,
implementation, support or management of computer-based information
systems, particularly software applications and computer hardware."
Encompassing the computer and information systems industries,
information technology is the capability to electronically input, process,
store, output, transmit, and receive data and information, including text,
graphics, sound, and video, as well as the ability to control machines of all
kinds electronically.
Information technology is comprised of computers, networks, satellite
communications, robotics, videotext, cable television, electronic mail ("e-
mail"), electronic games, and automated office equipment. The
information industry consists of all computer, communications, and
electronics-related organizations, including hardware, software, and
services. Completion of tasks using information technology results in rapid
processing and information mobility, as well as improved reliability and
integrity of processed information. It is a convenient term for including
both telephony and computer technology in the same word. It is the
technology that is driving what has often been called "the information
revolution". Nowadays it has become popular to broaden the term to
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 6
explictly include the field of electronic communication so that people tend
to use the abbreviation ICT (Information and Communication Technology).
"Electronic and information technology" is a term used in the 1998
amendments to Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act. The term is used
to define the scope of products covered under Section 508. Section 508
requires that electronic and information technology that is developed,
procured, maintained, or used by the federal government be accessible.
Electronic and information technology includes computer hardware and
software, operating systems, web-based information and applications,
telephones and other telecommunications products, video equipment
and multimedia products, information kiosks, and office products such as
photocopiers and fax machines.
1.2 History
Information technology dates back to 5000BC, when people started using
alphabets as a medium of communication. However, its actual emergence
started with the first ever use of the computer. The real modern
mechanical computer was conceived in 1822 by Charles Babbage. Then
came the electromechanical age in 1840s with the discovery of different
ways to harness electricity and the information was converted into electric
impulses. This led to the beginning of telecommunication and telegraphy
in late 1800s. As the loading coil and vacuum tube made possible the
early telephone network, the wireless revolution began only after low
cost microprocessors and digital switching became available.
Since then, four generations of computers have evolved. Each generation
represented a step that was characterized by hardware of decreased size
and increased capabilities. The first generation used vacuum tubes, the
second transistors, and the third integrated circuits. The fourth (and
current) generation uses more complex systems such as Very-large-scale
integration or System-on-a-chip.
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 7
Mobile rigs were the beginning of mobile phones for use in vehicles such
as taxicab radios, two way radios in police cruisers, and the like. A large
community of mobile radio users, known as the mobileers, popularized the
technology that would eventually give way to the mobile phone. The
concept of using hexagonal cells for mobile phone base stations was
invented in 1947 by Bell Labs engineers at AT&T and was further
developed by Bell Labs during the 1960s.
One of the first truly successful public commercial mobile phone networks
was the ARP network in Finland, launched in 1971.The first hand held
mobile phone to become commercially available was the Motorola
DynaTAC 8000X, which received approval in 1983. Until the late 1980s,
most mobile phones were too large to be carried in a jacket pocket, so
they were usually permanently installed in vehicles as car phones. With
the advance of miniaturization and smaller digital components, mobile
phones got smaller and lighter.
1.3 Current scenario
Mobile phones have gained a lot of popularity and are the considered to
be great multimedia tools. Mobile phones are being used for
entertainment purposes due the introduction of new features everyday.
They have become more than just call making and receiving devices.
Mobile phone handsets now have more business-friendly applications that
can enhance anybody’s business. With emerging technology, mobile
phones have become more than communication devices; they are the
tools to stay ahead of competitors and peers in the present times. Soon
mobile phones will evolve from communication tools to integrated
communication devices, media terminals, credit cards, and remote
controls.
1.4 Global mobile handset market
The phenomenal rise of the mobile phone has seen its image change from
a yuppie status symbol to a daily essential. Along the way, it has created
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 8
thousands of jobs, changed the way we do business, and made an awful
lot of money for investors. Today Key Handset technologies include GSM,
CDMA, and 1xEV-DO, WiFi VoIP, TDMA, 3G, 4G and Blue Tooth. Worldwide
mobile phone sales cruise to 990.8 million units in 2006, up a hefty 21.3%
from 2005’s 816.6 million units. The estimated growth figures are—6.4%
in 2007, 4.8% in 2008 and 2.6% in 2009. Notwithstanding the gradual
decline in the growth figures, the annual handset sales are predicted to
reach more than US $ 3 Billion by 2009.The total number of mobile phone
subscribers in the world was estimated at 2.14 billion in 2005.
Around 80% of world's population have mobile phone coverage as of
2006. This figure is expected to increase to 90% by the year 2010. With
the periodic introduction of new features and multimedia tools in the
mobile handsets due to technological advances, more and more people in
the Asian continent fancy buying them. There are many diversities and
complexities in the Asian mobile handset market due to types of
customers, government regulations, regional/geographical wireless
infrastructure, and the purchasing power. Basically, the Asian market
looks at the mobile handsets as status symbols. The market is seen best
for the low-end phones, but there is a huge rise in the demand for flashier
and costlier phones. India, China, Korea, and Malaysia are fast evolving as
the biggest markets for mobile handsets and in coming years they will
mainly carry on the global handset sales.
1.5 Major Global Players
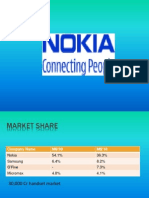
Table 1.1: showing market share of major global players of mobile
phones in 2009
Company 2009 Market Share
(%)
Nokia 38
Samsung 20
LG 10
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 9
Sony Ericcson 5
Motorola 5
ZTE 4.5
Kyocera 4
Others 13.5
Total 100.0
Nokia Corporation is currently the world's largest manufacturer of
mobile telephones. It produces mobile phones for every major market and
protocol, including GSM, CDMA, and W-CDMA (UMTS).The corporation also
produces telecommunications network equipment for applications such as
mobile and fixed-line voice telephony, ISDN, broadband access, voice over
IP, and wireless LAN.
Nokia's Mobile Phones division provides the general public with mobile
voice and data products across a wide range of mobile devices. The
division aims to target primarily high-volume category sales of mobile
phones and devices, with consumers being the most important customer
segment. Nokia believes that design, brand, ease of use and price are
mainstream mobile phones' most important considerations to customers.
Nokia's product portfolio includes camera phones with features such as
megapixel cameras which appeal to the mass market.
Motorola is an American multinational communications company based
in Schaumburg, Illinois, a Chicago suburb.Most of Motorola's products
have been radio-related, starting with a battery eliminator for radios,
through the first walkie-talkie in the world, defense electronics, cellular
infrastructure equipment, and mobile phone manufacturing. Motorola has
recently been regaining market share in the cellular-phone business from
Nokia, Samsung, and others due to stylish new cellular phone designs.
Samsung Electronics is one of the world's largest IT companies by
revenue. The company also claims to be have the highest brand value
among consumer electronics companies. Headquartered in Seoul, South
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 10
Korea, it is part of the Korean Samsung Group, operating in approximately
over 100 countries.It is the number 1 mobile phone manufacturer in Asia.
Sony Ericsson is a joint venture established in 2001 by the Japanese
consumer electronics company Sony Corporation and the Swedish
telecommunications company Ericsson to make mobile phones. Both
companies have stopped making their own mobile phones. The reason for
this merger is to combine Sony's consumer electronics expertise with
Ericsson's technological leadership in the communications sector. The
company's global management is based in Hammersmith, London. It also
has research & development teams in Sweden, Japan, China, Canada, the
Netherlands, the United States,India and the United Kingdom.
LG Electronics is one of the world's leading electronics companies. It is
part of the Korean LG Group, operating in approximately 80 countries. Its
mobil phones division provides CDMA, GSM, 3G Handsets.
ZTE (Zhong Xing Telecommunication Equipment Company
Limited) is a publicly-owned, Chinese corporation that designs and
manufactures telecommunications equipment and systems. Based in
Shenzhen, and established in 1985 ZTE offers a wide variety of
telecommunication products that provide services, including value-added
services such as video on demand and streaming media to its customers,
which are primarily telecommunications service providers, mobile network
operators, etc
Kyocera Communications Inc.(KCI) is a manufacturer of mobile
telephones for CDMA networks and is a wholly owned subsidiary of
Kyocera Corporation that was formed in February 2000 when Kyocera
acquired QUALCOMM's San Diego, California-based terrestrial handset
division. It produces mobile phones, cellular routers, and Mobile PC Cards
for markets in North America, South America, Australia, and New Zealand.
1.6 Mobile Handset Market in India
The cell phones industry has shown a remarkable growth in the last
decade. In 1989 the number of its subscribers was zero in India. India’s
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 11
love affair with cell phones started in the mid-1990s, as the mobile
revolution took hold and India had just 10 million mobile and landline
connections. Delhi was the first state to launch cell phones in India.
Growth then soared in the last four years due to regulatory change and
falling costs of calls and handsets. India’s wireless market is a test bed for
alternative infrastructure, handsets, billing systems, business models and
marketing strategies that will likely prove applicable to other developing
countries.
On a numerical basis, India is the biggest growth market adding about 6 million
cell phones every month. CAGR for mobile phones is 86% in India. It is one of the
fastest growing mobile markets in the world; in April 2006 mobile subscriber
base crossed 100 million mark. This has been accomplished by rethinking
handsets, network infrastructure, enhanced services and content. More than two-
third of mobile subscriptions are with GSM operators and rest with CDMA. India
has one of the lowest mobile phone tariffs in the world resulting in low Average
Revenue per User (ARPU) of 9.04 USD per year (CDMA 5.74 USD and GSM 8.89
USD).
Indian land area covered by mobile networks is approx 30%. CAGR of Mobile
Market Value for 2004- 2009 is 36.9%.With 156.31 million cell phones;
teledensity in the country is still low at 17.45%. Fewer than eight in every 100
Indians use mobiles, compared with China's 30 per cent. In India, about 13
percent of people have cell phones which has increased from 8% in 2005 and is
expected to reach 40 percent within a few years. A lack of investment in the
infrastructure needed to support landline services means there are only 50
million fixed-line users in the country, leaving the stage set for mobile operators.
India is expected to have the third largest mobile user base, behind China and
the US, by the year end and will become the second largest market of mobile
handsets by 2010. Indian cellular market would account for 11% of the overall
Asia Pacific and Japan market by 2009 and is expected to reach 500 million
subscribers by end of 2010 with CAGR of 33.7% for 2004- 2010.
Fig. 1.1 India’s mobile subscriber base
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 12
1.7 Major players in India
The major players in the handsets segment in India include Nokia,
Motorola, Sony Ericsson, Samsung, LG, Philips, Panasonic, Bird, Sagem
and BenQ. Nokia has retained the top slot in Indian market with 70 %
share, while US giant Motorola has 15 % share and Sony Ericsson has
gained around 8% share this year. Samsung has 5% share and LG has
1.8% share.
Fig. 1.2 market share in percentage of the mobile phone players
in India
market share %
5 1.8 0.02
8
15
70
nokia motorola sony ericsson samsung LG others
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 13
1.8 Consumer Buying Behavior
Everybody in the world is the consumer. Each of us buys and sells or
consumes goods and services in the life. Consumer behavior is very
complex and is determined to a large extent by social and psychological
factors. Consumer behavior can be defined as those acts of individuals
directly involved in obtaining, using and disposing of economic goods and
services.
The relevance and importance of understanding consumer behavior is
rooted in the modern marketing. The needs of not even two consumers
are the same. Therefore, they buy only those products and services, which
satisfy their wants and desires. To survive in the market, a firm has to be
constantly innovating and understand the latest consumer needs and
tastes it will be extremely useful in exploiting marketing opportunities and
in meeting the challenges that the Indian market offers. A study of
consumer behavior is significant for regulating consumption of goods and
thereby maintaining economic stability. Within the broad framework of
marketing, the area that entices the most researchers is the study why a
consumer behaves in a particular way. The complexity of the behavior,
however, varies with the nature of the product and the need, which it is
required to satisfy. The study of consumer behavior is the study of how
individuals make decisions to spend their available resources on
consumption of related items.
Consumer behavior is an applied discipline. Its application exists at two
different levels of analysis. One is at the micro level perspective and other
at the macro level perspective. Micro level seeks application of the
knowledge faced by the individual, firm or an organization. The macro
perspective applied knowledge of consumer includes the aggregate level
of problem faced by large groups or by society as a whole.
Consumer behavior provides a sound basis for identifying and
understanding consumer needs. It is the act of the individuals directly
involved in obtaining and using economic goods and services.
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 14
The study of consumer behavior is an essential component of marketing.
The adoption of marketing concept by the marketers provides the impetus
for the study of consumer behavior.
In case of New Product Introduction in the market, there is a risk of
product failure. To increase the chances of success of new products,
better information of the consumer behavior is required. Their desires,
tastes and preferences are to be taken care of. So from all these aspects
the study of consumer behavior is important.
1.9 About the Project
The importance of cell phones goes way beyond the ability to make or
receive phone calls. Today's technically advanced cell phones can perform
as many or even more tasks than a home computer. They are capable of
internet access, sending and receiving photos and files, storing data, to
name just a few of the available options. So a question arises as to why
different people choose different brands and what are the features they
look for while purchasing a mobile handset.
Hence a study was undertaken in IBMR College among the mobile phone
user students. It provides a scope to understand the consumers buying
behavior (especially students) towards the mobile handsets. The
increasing importance of cell phones has made them almost a necessity
for most people. Mobile penetration is on rise. It has even exceeded
landline connections. Since various brands of mobile phones are in the
market for quite a long time, their performance provides sufficient data
for study. The results of the study would give the mobile manufacturing
companies an insight about the preferences of the consumers and also
their expectations from the mobile phones. This would help the companies
to understand the potential of the market and target the right consumers.
1.10 Objectives of the study are:
1. To examine the factors those influence the customer choice while
purchasing a mobile hand set.
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 15
2. To know which features in a particular brand are preferred by the
mobile phone users.
3. To find out what additional features are demanded by consumers.
4. To study the satisfaction level of mobile phone users.
Chapter 2
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter describes the research methodology adopted to achieve the
objectives of the study. It includes the scope of the study, research
design, collection of data, analysis of data and limitations of the study.
2.1 Scope of the study
The scope of the study is to get the first hand knowledge about the
buying behavior of consumers towards different brands of mobile
handsets in IBMR students. The scope is restricted to study the factors
affecting the preference of consumers while choosing a mobile handset in
IBMR college students. This is done to avoid perceptual bias and for
providing objectivity to the study.
2.2 Research Design
The research design constitutes the blueprint for the collection,
measurement and analysis of data. It is the strategy for a study and the
plan by which the strategy is to be carried out.
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 16
The research design of the project is descriptive as it describes data and
characteristics associated with the population using mobile phones.
Descriptive research is used to obtain information concerning the current
status of the phenomena to describe "what exists" with respect to
variables in a given situation.
2.3 Data Collection
2.3.1 Primary Data
Primary data is that data which is collected for the first time. It is
original in nature in the shape of raw material. For the purpose of
collection of primary data, a well structured questionnaire was framed
which was filled by the respondents. The questionnaire comprises of close
ended as well as open ended questions. In close ended questions
dichotomous, ranking, checklist questions and multiple choice questions
are used.
2.3.2 Secondary Data
Secondary data is the data which is already collected by
someone. They are secondary in nature and are in shape of finished
product. Secondary data was collected so as to have accurate results.
Required data was collected from various books, magazines, journals and
internet.
2.4 Sampling Design
Sampling refers to selecting some of the elements in a population by
which one can draw conclusions about the entire population.
2.4.1 Universe
Universe is the infinite number of elements which the researcher is
targeting in his study. Since the study is restricted to IBMR students only
the universe for the study consists of all the mobile phone owners in IBMR.
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 17
2.4.2 Population
Population is finite number of elements which the researcher is going to
target in particular area. All the mobile phone user students in IBMR
college form the population for the study.
2.4.3 Sampling Unit
Sampling Unit is the single unit of the population. A single individual who
owns a mobile phone form the sampling unit of the study.
2.4.4 Extent
Extent refers to the geographical area where there is a scope of
population. The extent of the study is IBMR, Pune.
2.4.5 Sampling Technique
The selection of the respondents was done on the basis of convenience
technique based on the non probability method of sampling.
2.4.6 Sample size
Sample size is the size of sample drawn from the population which is the
true representative of the research.
The number of respondents included in the study was 50 for convenience
in evaluating and analyzing the data and because of time constraint.
2.5 Data Analysis and Interpretation
For the purpose of analyzing, raw data was summarized in a
master table and from this table the results have been carried out. The
questions having multiple/ alternative choices were analyzed by taking
percentages. In the case of questions on likert scale, the mean scores
were calculated.
In case of ranking questions the total score has been added and
final ranking is given by calculating mean. In case of checklist questions
the average of total no. of responses was calculated. In case of
explanatory questions, the general suggestions were summarized.
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 18
Limitations of the study
Sincere efforts have been made to collect authentic and reliable
information from respondents, however the report is subject to following
limitations:
i. Some respondents were reluctant to give the information, so their
responses may be biased.
ii. Time could be a major limitation as it may have affected the
inferences drawn in the study. Only 50 respondents have been
contacted due to time constraint.
iii. Sample may not be the true representative of the universe.
iv. Study was conducted in IBMR, Pune only. So the results of the study
may not be applicable in other areas.
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 19
Chapter 3
ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
This chapter analyse the behavior and preferences of the consumers for
various brands of mobile hand set based on various factors which
influence their buying decision.
This chapter therefore deals with analysis and discussions of the project.
Results of the study
Table3.1: Showing number of respondents owing a mobile phone
No. Of Respondents %
Yes 50 100
No 0 0
Total 50 100
Fig.3.1
Table3.2: Showing different brands of mobiles phones used by the
respondents
Brands No. of respondents %
Nokia 31 62
Sony Ericsson 3 6
Motorola 6 12
Samsung 4 8
LG 2 4
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 20
Others 4 8
Total 50 100
Fig.3.2
Interpretation:
From the above table and figure, we can conclude that out of 50
respondents 62% have Nokia hand set,6% have Sony Ericsson , 12% use
Motorola ,8% have Samsung, 4% have LG. Apart from these brands 8% of
respondents have other brands like Spice, Micromax, Panasonic etc. It’s
evident from the figures that Nokia is most preferred brand of the
students in IBMR College.
Table3.3: Showing respondents using same brand as they had earlier
RESPONSES NO. OF RESPONDENTS PERCENTAGE
Yes 32 64
No 18 36
Total 50 100
Table3.3
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 21
70
60
50
percentage
40
30
20
10
0
yes no
re s pons e s
Interpretation:
From the above, it is interpreted that 64% of the respondents had same
brand of mobile hand set earlier while 36% had different brands. Some
switched over due to new features available in other brands and others
due to inefficiency in earlier brand. But above figures conclude that most
of the respondents are brand loyal.
Table3.4: Showing reasons for using mobile phone by the respondents
Reasons No. of Respondents %
Communication 19 38
Status 18 36
Don’t have landline 3 6
Others 10 20
Total 50 100
Fig.3.4
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 22
Interpretation:
Above table and figure depict that 38% of respondents use mobile for
communication, 36% use it as a status symbol, 6% use mobile because
they don’t have landline connections and 20% of respondents have other
reasons like necessity, games, music etc.
Table 3.5: Showing the factors considered by respondent while
purchasing a mobile handset
Factors No. of responses Average
Price 23 0.19
Appearance 24 0.20
Brand 24 0.20
Features 32 0.26
Easy to carry/Weight 18 0.15
Total 121 1
Fig.3.5
0.15 0.19 Price
Appearance
Brand
0.26 0.2 Features
0.2 Easy to carry/W eight
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 23
Interpretation:
From above it can be concluded that features in a mobile hand set is the
most important factor which is considered by the respondents while
purchasing the mobile phone. Brand and Appearance are the other very
important factor influencing the purchase decision. Price is also an
important factor. Easy to carry is the least important factor that is
considered in the purchase decision. It’s clear that students at IBMR give
maximum importance to features, appearance and brand of a mobile
phone.
Table3.6: Showing the sources which influenced the buying decision of
the respondents
Sources No. of respondents %
Friend 18 36
Family member 9 18
Advertisement 15 30
Dealer 8 16
Total 50 100
Fig.3.6
Interpretation:
From the above table it is concluded that out of 50 respondents, 36% and
18% respondents purchased the mobile hand set under the influence of
their friends and family member, 30% respondents under the influence of
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 24
various advertisements, 16% respondents bought the car on the
suggestion of dealer.
Table3.7: Showing different purposes for which mobile is used by the
respondents
Diff. Purposes No. of Respondents Average
Receiving/making calls 50 0.34
SMS/MMS 35 0.23
Games 13 0.08
E-mail/Internet 12 0.04
Music 25 0.17
Camera 20 0.14
Total 155 1
Fig.3.7
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 25
0.4
0.34
0.35
0.3
0.25 0.23
average
0.2 0.17
0.14
0.15
0.1 0.08
0.04
0.05
0
l ls
t
ne
S
ca
a
es
ic
M
er
er
us
am
/M
ng
am
nt
M
S
ki
l/I
G
C
M
a
ai
m
-m
g/
E
in
iv
ec
R
Interpretation:
From the above figures it can be concluded that in spite of using mobile
phone for calls and SMS which are its basic purposes, Students of IBMR
are using them increasingly for Music and Camera. Using Internet on
mobile phones is still not common.
Table 3.8: Showing ranking of various features of mobile handsets by
Features Mean scores Rank
Bluetooth 3.29 5th
MP3 Player 3.16 2th
Camera 3.23 3rd
Data Storage Capacity 3.13 1st
GPRS 4.87 6th
Personal Info. 4nd
Management 3.32
the respondents according to their preferences
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 26
Fig.3.8
Interpretation:
Since 1 is given to the most preferred feature and 6 to the least preferred
feature in a mobile hand set, therefore from the table, we can conclude
that data storage capacity is the most preferred feature in a mobile hand
set. 2nd and 3rd ranks are given to MP3 player and camera in the mobile
phone respectively. After them the features of personal information
management and Bluetooth are given preference. GPRS is the least
preferred feature in the mobile phones. Therefore it’s clear from above
that students of IBMR give more preference to the feature of data storage
and MP3 player.
Table 3.9: Showing range of price that respondents like to spend on
mobile hand set
Range No. of respondents %
Below 5000 16 32
5000-10000 20 40
10000-15000 11 22
Above 15000 3 6
Total 50 100
Fig. 3.9
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 27
Interpretation:
Camera Bluetooth Music Memory
Player
No. of respondents
Nokia 34 31 15 37
Motorola 9 13 8 5
Sony 7 5 27 8
Ericsson
Samsung 0 0 0 0
Total 50 50 50 50
From above it is interpreted that 39% of respondents prefer to spend
between the ranges of Rs. 5000-10000, 22% between Rs. 10000-15000,
7% above Rs. 15000and 32% below Rs. 5000. It concludes that mobile
phone users here are price sensitive. Mobile phones are no longer a status
symbol instead they have become a necessity.
Table 3.10: showing features preferred in a particular brand of mobile
phone
Fig. 3.10
Interpretation:
From above table and figure it is concluded that students of IBMR prefer
Camera, Bluetooth and Memory features of Nokia and music player of
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 28
Sony Ericsson. Features of Motorola and Samsung are also liked by some
respondents but features of LG are not at all preferred by them.
Table 3.11: Showing agreement level of the respondents on various
factors influencing purchase decision
Strongl Disagr Neutr Agree Strong Mean
y ee al ly Score
Disagre Agree
Factors e -2 1
2
-1 0
Repairable -2(2) -1(1) 0(6) 1(21) 2(20) 56/50=1.12
Availability of -2(2) -1(3) 0(10) 1(20) 2(15) 44/50=0.88
spare parts
Proximity to -2(1) -1(2) 0(21) 1(19) 2(7) 31/50=0.62
service provider
Promotional -2(1) -1(7) 0(16) 1(18) 2(8) 24/50=0.48
activities
Fig. 3.11
Interpretation:
From the above table we can conclude that respondents strongly agree
with the repairable factor of a mobile phone, the mean score being 1.12.
Respondents are also to a large extent agreeing with the factor of
availability of spare parts and proximity of service provider but as far as
promotional activities are concerned they are neutral towards this factor.
Table 3.12: Showing satisfaction level of the respondents
No. of Respondents %
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 29
Yes 46 92
No 4 8
Total 50 100
Fig. 3.12
Interpretation:
From the above table, we can conclude that out of 50 respondents, 92%
respondents are satisfied with the performance of their mobile hand set
whereas 8% are not completely satisfied. The main problem faced by
them is the battery life of their hand sets. In general, students of IBMR
are satisfied with their brand of mobile phone.
Table 3.13: Showing additional features required by the respondents in
their mobile handsets
Features No. of responses Average
Wi-Fi 19 0.26
TV 17 0.23
Video Conferencing 18 0.25
Windows 19 0.26
Total 73 1
Fig. 3.13
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 30
Interpretation:
From above table and figure it is concluded that features of Wi-Fi and
Windows are more in demand. TV and Video Conferencing too are
considered almost equally important.
Chapter 4
FINDINGS OF THE STUDY
1. Nokia is the most popular and widely used brand by students of IBMR.
2. Brands like Motorola and Sony Ericsson are also gaining ground with
regard to popularity but not like Nokia.
3. 64% of the respondents used same brand earlier. It shows that most of
the mobile users of IBMR are brand loyal.
4. But on the other side 36% of response depicts the fact that people
constantly switch from one brand to another on the dearth of new
features and advance technology.
5. Mobile phone is no more a status symbol now for the students of IBMR.
It has increasingly become a necessity to reduce communication gap
and to maintain mobility.
6. It is clear from the above that students of IBMR give due importance
to factors like features, appearance and brand of mobile phones while
making purchase decision.
7. Price comes after the satisfaction of above factors and easy to carry
facility is least considered during purchase decision.
8. It’s clear that people in students of IBMR purchase a particular brand
of mobile handsets on the basis of the positive report about their
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 31
performance received from their friends and family members who
already own that brand.
9. Advertisements also play an important role in influencing the buying
decision.
10.Besides receiving and makings calls and SMS students of IBMR are
also using mobile for listening music and camera.
11.Use of mobile for games has significantly reduced. And still people are
not accustomed with the use of internet on their mobile phones.
12.As far features of mobile phones are concerned it’s clear from above
that students of IBMR give more preference to the features of data
storage, MP3 and Camera. GPRS is the least preferred feature in the
mobile phones.
13.Students of IBMR prefer to spend between Rs. 5000 and Rs. 10000 on
a mobile phone. It again depicts that mobile phones are no longer a
status symbol now and has become necessity.
14. Students of IBMR agree that factors like reparability and availability of
spare parts are important to consider while making buying decision for
a brand of mobile phone. But as far as promotional activities are
concerned they are neutral towards this factor.
15.Most of the population is satisfied with their existing brands. The main
problem faced otherwise is related to the battery life of a mobile hand
set.
16.Students of IBMR require additional features of Wi-Fi, Windows, TV and
Video Conferencing in their mobile phones. It depicts that people here
are techno savvy and want to use innovative features.
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 32
Chapter 5
CONCLUSION AND SUMMARY
The Mobile phone represents the convergence instrument of the future. It
have become a necessity for many people throughout the world. The
ability to keep in touch with family, business associates, and storing data
are only a few of the reasons for the increasing importance of mobile
phones. Cell phone manufacturers have produced a wide range of cell
phones, which sell for prices that range from very inexpensive to
thousands of rupees.
The above findings and results reflected the preferences, expectations
and satisfaction level of mobile phones users in IBMR Collage, Pune. The
study would help the companies in understanding the factors that
influence the purchase decision of the consumers and their expectations
from the mobile handsets. The results of the study indicate that mobile
phones are no longer the status symbol for the students of IBMR. Brand
and features in a handset are preferred over their prices. People here are
techno savvy and require new innovative features in mobile phones every
new day.
Since the study was restricted to the IBMR Collage only so the there is
need to study more in other places of city to get the clear view of the
findings.
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 33
APPENDIX
QUESTIONNAIRE
Personal Details:
Name: _________________
Age: _________________Gender: _________________
Address: __________________________________
__________________________________
Contact No. ____________________
‘’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’
’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’’
Q1) Do you have a mobile phone?
YES NO
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 34
Q2) a) Which brand of mobile hand set do you have? (Please Tick)
i. Nokia _______
ii. Sony Ericsson _______
iii. Motorola _______
iv. Samsung _______
v. Any other (please specify) _______
b) Which model ____________
If it is your first mobile phone then skip Q3
Q3a) Did you have the same brand earlier?
YES NO
b) If NO then which brand you had earlier (please specify)
______________
c) Why have you switched from earlier brand to latest one?
i. Advanced technology _______
ii. New features _______
iii. Inefficiency in earlier mobile _______
iv. Any other( please specify) _______
Q4) Why have you bought the mobile? (Tick one option)
i. Communication purpose ________
ii. Status ________
iii. Don’t have landline phone ________
iv. Any other (please specify) ________
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 35
Q5) Which of the following factors you considered while choosing the
mobile hand set?
(can tick more than one option)
i. Price ________
ii. Appearance ________
iii. Brand ________
iv. Features ________
v. Easy to carry/Weight ________
Q6) Who influenced you to buy this brand? (Tick one option)
i. Friend _______
ii. Family member _______
iii. Advertisement _______
iv. Dealer _______
v. Any other (please specify) _______
Q7) For which different purposes do you use your mobile?
(can tick more than one option)
i. Receiving / making calls ________
ii. SMS/ MMS ________
iii. Games ________
iv. E-Mail/ Internet ________
v. Music ________
vi. Camera ________
Q8) Rank the following features of your hand set according to your
preference (rank 1 to most preferred and rank 6 to least preferred)
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 36
i. Bluetooth _________
ii. MP3 Player/ Video Player _______
iii.Camera _________
iv. Data Storage Capacity _________
v. GPRS _________
vi. Personal information management _________
(Notes, to-do list,contacts,etc.)
Q9) Tick the range of price you would like to spend on a mobile handset?
Nokia Motorola Sony Samsung
Ericsson
Camera
Bluetooth
Music Player
Memory
i. Below 5000 ________
ii. 5000- 15000 ________
iii. 15000- 25000 ________
iv. Above 25000 ________
Q10) Tick the following features you like in particular brand:
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 37
Q 11) Do you agree that following factors must be considered while
choosing a brand of mobile hand set?
Strongl Disagre Neutral Agree Strongl
y e y Agree
Disagre
e
Repairable
Availability of spare
parts
Proximity to service
provider
Promotional activities
Q 13) a) Are you satisfied with your existing mobile hand set?
YES NO
b) If no, then what are the problems faced by you?
_______________________________________________________________
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 38
_______________________________________________________________
Q 14) what additional features do you want in your mobile handset?
(Can tick more than one option)
i. Wi-Fi ________
ii. TV ________
iii. Video Conferencing ________
iv. Windows ________
BIBLIOGRAPHY
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mobile_phones
http://communities-dominate.blogs.com/brands/2010/02/phone-market-
shares-for-year-of-2009-and-last-quarter-2009.html
http://www.wirelessdesignasia.com/article-
8488globalmobilehandsetshipmentgrew17yoy-Asia.html
http://www.forbes.com/feeds/businesswire/2009/04/24/businesswire12373
5951.html
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 39
“T3-tomororw technology today”, Vol.1, Issue 2, Jan. 2007
http://digital-lifestyles.info/2007/03/05/worldwide-mobile-phone-sales-
grow-21-in-2006/
http://www.gartner.com/it/page.jsp?id=501734
http://www.rncos.com/Report/COM02.htm
http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/News/News-By-
Industry/Telecom/Mobile-handset-sales-pick-up-after-
drought/rssarticleshow/4180130.cms-
http://www.dailyindia.com/show/121503.php/India-to-be-second-largest-
mobile-market-by-2010:-Nokia
http://www.zinnov.com/presentation/Mobile_VAS.pdf
Institute Of Business Management and Research, Pune 40
You might also like
- Project On Customer Satisfaction With Reference To Samsung Galaxy MobileDocument38 pagesProject On Customer Satisfaction With Reference To Samsung Galaxy MobileAmit JainNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Study of Consumer Behaviour and Attitude Towards The Cellular Services With Refrence To AircelDocument108 pagesProject Report On Study of Consumer Behaviour and Attitude Towards The Cellular Services With Refrence To AircelSANDEEP SINGH100% (8)
- Customer Preference Towards Branded and Assembled ComputersDocument85 pagesCustomer Preference Towards Branded and Assembled ComputersOM Kumar100% (2)
- Integrated Marketing Plan of Pulse CandyDocument13 pagesIntegrated Marketing Plan of Pulse CandyPraneit KhotNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Branding on Consumer Buying BehaviorDocument8 pagesThe Impact of Branding on Consumer Buying BehaviorSusilPandaNo ratings yet
- Attitude of People Towards Green ProductsDocument52 pagesAttitude of People Towards Green ProductsMessiNo ratings yet
- Customer Perception HundaiDocument82 pagesCustomer Perception HundaiSai Kumar ChidipothuNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Buying Behaviour of Consumers Towards Indegenious ProductsDocument61 pagesProject Report On Buying Behaviour of Consumers Towards Indegenious ProductsPravin Tripathi94% (120)
- Consumer Perception Towards SamsungDocument5 pagesConsumer Perception Towards SamsungMohsin Ahmed0% (1)
- The Brand Preference of Mobile PhonesDocument46 pagesThe Brand Preference of Mobile PhonesSharia Imteyaz100% (1)
- Merged DocumentDocument93 pagesMerged DocumentsurekhaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Consumer Buying Behavior Products of Hul and P GDocument78 pagesComparative Study of Consumer Buying Behavior Products of Hul and P GShreya chaudharyNo ratings yet
- A Study On Service Quality of HDFC Bank: Mahak Manzoor Roll No: 44Document54 pagesA Study On Service Quality of HDFC Bank: Mahak Manzoor Roll No: 44ANUPAM KAPTINo ratings yet
- PDF Full Project MukulDocument80 pagesPDF Full Project MukulMukul Somgade50% (2)
- A Study On Customer Satisfaction Towards HCL Telecom Products in LucknowDocument33 pagesA Study On Customer Satisfaction Towards HCL Telecom Products in LucknowChandan SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Attitude On Buying Laptops Rev1Document47 pagesConsumer Attitude On Buying Laptops Rev1prasath_subramanian100% (1)
- Changes in Consumer Behaviour of IndiaDocument19 pagesChanges in Consumer Behaviour of Indiasusheel kumar shukla62% (13)
- Mobile Industry ProjectDocument45 pagesMobile Industry ProjectJorawar DeolNo ratings yet
- Reasearch On Consumer Behavior (Nitin Talekar) Final Project MBADocument15 pagesReasearch On Consumer Behavior (Nitin Talekar) Final Project MBANitin TalekarNo ratings yet
- Berkley Alumni Brand Awareness ResearchDocument77 pagesBerkley Alumni Brand Awareness ResearchsudhirparasNo ratings yet
- Buying Behaviour of Mobile PhonesDocument35 pagesBuying Behaviour of Mobile PhonesHms Sameer100% (1)
- BOROSIL GlasswareDocument86 pagesBOROSIL GlasswareushadgsNo ratings yet
- Samsung ProjectDocument8 pagesSamsung ProjectsarthakNo ratings yet
- Brand PreferenceDocument13 pagesBrand PreferenceSHRADDHA shetyeNo ratings yet
- Study On Consumer Buying Behaviour & Satisfaction Level For Hero Honda Motorcycle by Owesh DabawalaDocument70 pagesStudy On Consumer Buying Behaviour & Satisfaction Level For Hero Honda Motorcycle by Owesh Dabawalaishwar2230% (1)
- Project Report CONSUMER PURCHASING BEHAVIOR AND BRAND PROMOTIONDocument65 pagesProject Report CONSUMER PURCHASING BEHAVIOR AND BRAND PROMOTIONSatish P.Goyal86% (7)
- Micromax Advertising & Sales Promotion ManagementDocument18 pagesMicromax Advertising & Sales Promotion ManagementNitish0001100% (1)
- Hindustan TimesDocument67 pagesHindustan TimesBeing Nadeem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Consumer Attitude and Perception Towards Green ProductsDocument7 pagesConsumer Attitude and Perception Towards Green ProductsAvinash kumarNo ratings yet
- Aashika BBA Main ProjectDocument58 pagesAashika BBA Main ProjectRaj naveenNo ratings yet
- Marketing ProjectDocument68 pagesMarketing Projectdivya0% (1)
- Apple Vs Samsung ProjectDocument67 pagesApple Vs Samsung ProjectToshal Pedamkar100% (1)
- Abhilash Bajpai ReportDocument46 pagesAbhilash Bajpai ReportStudy BuddyNo ratings yet
- Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty in Norwegian Online ShoppingDocument123 pagesCustomer Satisfaction and Loyalty in Norwegian Online ShoppingRitoban Mukhopadhyay100% (1)
- LG Company ProfileDocument55 pagesLG Company ProfileKing Nitin Agnihotri100% (2)
- Effect of Branding on Consumer PurchasesDocument4 pagesEffect of Branding on Consumer PurchasespatelpratikNo ratings yet
- Vodafone and AirtelDocument59 pagesVodafone and Airtelkuldeep0773% (15)
- Final Submission (Impact of BTL Activation On Consumer Buyong Behavior and Brand Postioning) (Mohemmed Ammad)Document54 pagesFinal Submission (Impact of BTL Activation On Consumer Buyong Behavior and Brand Postioning) (Mohemmed Ammad)Muhammad AmmadNo ratings yet
- Consumer perception of private brands in organised retailDocument97 pagesConsumer perception of private brands in organised retailVani SharmaNo ratings yet
- Emerging Trends in RetailDocument32 pagesEmerging Trends in RetailAmit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- A Study On Consumer Buying Behaviour Towards Home Appliances in Salem City PDFDocument18 pagesA Study On Consumer Buying Behaviour Towards Home Appliances in Salem City PDFJessRaj DenisNo ratings yet
- A Study of Consumer Preference and Precept Ion Towards Internet Service Provider in PunjabDocument26 pagesA Study of Consumer Preference and Precept Ion Towards Internet Service Provider in PunjabChandan Kumar Singh100% (4)
- Research Project On Consumer Behaviour Towards Electronic Durables (LOTUS)Document45 pagesResearch Project On Consumer Behaviour Towards Electronic Durables (LOTUS)vasu616293% (41)
- A Study On Women Consumer Attitude of Purchasing CosmeticsDocument7 pagesA Study On Women Consumer Attitude of Purchasing CosmeticsNive Palani100% (1)
- Project Report On TV AdvertisementsDocument45 pagesProject Report On TV Advertisementssarojbalaboora75% (4)
- Summer Internship Project Report OnDocument63 pagesSummer Internship Project Report OnjyotiagohilNo ratings yet
- Sample Project Report - Mobile Subscriber SurveyDocument63 pagesSample Project Report - Mobile Subscriber Surveypradip9933No ratings yet
- Telecommunication SectorDocument79 pagesTelecommunication SectorAPURWA MANENo ratings yet
- Consumer BehAviourDocument37 pagesConsumer BehAviouranon_757894592No ratings yet
- Impact of Reliance Jio On Indian Telecom IndustryDocument55 pagesImpact of Reliance Jio On Indian Telecom IndustryFarhan JagirdarNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior Towards Smartphone UsageDocument6 pagesConsumer Behavior Towards Smartphone UsageAJAYNo ratings yet
- Study of Consumer Buying Behaviour STD 992Document17 pagesStudy of Consumer Buying Behaviour STD 992TejasNo ratings yet
- Bharathi_Airtel12Document39 pagesBharathi_Airtel12chirag suresh chiruNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged 2Document48 pagesIlovepdf Merged 2Zainab MahewishNo ratings yet
- Mobile Usage Survey Finds Demographic DifferencesDocument37 pagesMobile Usage Survey Finds Demographic DifferencesJITENDRA LAMSALNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing Brand Preference of Consumers in Indian Mobile Telecommunications ServicesDocument9 pagesFactors Influencing Brand Preference of Consumers in Indian Mobile Telecommunications Servicesrakesh rakiNo ratings yet
- Mohit Final MBA ReportDocument66 pagesMohit Final MBA ReportAnkit gillNo ratings yet
- Mini Project On Reliance JIODocument30 pagesMini Project On Reliance JIO06manishreddyNo ratings yet
- Survey Findings Towards Mobile Services Usage and M-Commerce AdoptionDocument9 pagesSurvey Findings Towards Mobile Services Usage and M-Commerce AdoptionAjay AntilNo ratings yet
- The Changing Indian Telecommunication IndustryDocument11 pagesThe Changing Indian Telecommunication Industryashish9dubey-16No ratings yet
- Study of Consumer Attitude Toward Mobile PhonesDocument25 pagesStudy of Consumer Attitude Toward Mobile PhonesMd. Mesbah Uddin63% (8)
- Joint Venture ReportDocument15 pagesJoint Venture ReportRavi MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Social Media CRM For Brand Loyalty. (Dissertation Thesis)Document92 pagesSocial Media CRM For Brand Loyalty. (Dissertation Thesis)Manzil Madhwani80% (5)
- Nokia Master ThesisDocument7 pagesNokia Master Thesisaflowlupyfcyye100% (2)
- Schematic Sony St26i PDFDocument3 pagesSchematic Sony St26i PDFNiceMen SafaniNo ratings yet
- 9.mobile Phone Software FaultsDocument96 pages9.mobile Phone Software FaultsJean Paul Muvara Kabiligi33% (3)
- International Marketing - First LessonDocument13 pagesInternational Marketing - First LessonKia PalomarNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Brand Preference of Mobile Phone Among College Students1Document61 pagesProject Report On Brand Preference of Mobile Phone Among College Students1Faraz Haq100% (1)
- Marketing Strategy of A Global Brand - Samsung MobileDocument23 pagesMarketing Strategy of A Global Brand - Samsung Mobileratul_oneNo ratings yet
- How To Use NCK - Xperia Test Point UnlockDocument26 pagesHow To Use NCK - Xperia Test Point UnlockSaul CardozaNo ratings yet
- Sony Ericsson C702Document3 pagesSony Ericsson C702Hutanu GabrielNo ratings yet
- Report Writing Term 1 2021-2022-Unit 4Document18 pagesReport Writing Term 1 2021-2022-Unit 4linhNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Reclamos Publicitarios by ARTWORK ESTUDIOSDocument675 pagesCatalogo Reclamos Publicitarios by ARTWORK ESTUDIOSARTWORK ESTUDIOSNo ratings yet
- Samsung's Marketing Mix in IndiaDocument18 pagesSamsung's Marketing Mix in IndiaAritra BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Nokias Supply Chain ManagementDocument12 pagesNokias Supply Chain ManagementFadli RahmanNo ratings yet
- S. No Sales Invopanel Date Order No. Sub Order Customer NameDocument75 pagesS. No Sales Invopanel Date Order No. Sub Order Customer NameDeepesh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- W595 SchematicsDocument29 pagesW595 SchematicsMuhamad RidhwanNo ratings yet
- Liberacion Ziezamovil 2010Document5 pagesLiberacion Ziezamovil 2010santiagpyepezNo ratings yet
- AmalgamationDocument7 pagesAmalgamationSamia ShahidNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Marketing Management: University of Baluchistan MBA Second SemesterDocument30 pagesAssignment of Marketing Management: University of Baluchistan MBA Second SemesterN.S.100% (1)
- Modes of Global Market EntryDocument25 pagesModes of Global Market EntryMathew VargheseNo ratings yet
- Mobile Handset Industry AnalysisDocument52 pagesMobile Handset Industry AnalysisPayel ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Technology Exports and Joint VentureDocument49 pagesTechnology Exports and Joint VentureSrishti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pipelines, Platforms Group CDocument42 pagesPipelines, Platforms Group CAhmed NaguibNo ratings yet
- Technology Acquisition and AbsorptionDocument35 pagesTechnology Acquisition and AbsorptionkunalNo ratings yet
- Nokia Pricing StrategiesDocument19 pagesNokia Pricing Strategiesvickystupi100% (4)
- Nissan BT Adapter CompabilitylistDocument4 pagesNissan BT Adapter Compabilitylistforismei5644No ratings yet
- Sony As MneDocument29 pagesSony As MneBilal RasoolNo ratings yet
- Mobile Phone Price List in India - October 2011Document7 pagesMobile Phone Price List in India - October 2011bathindiNo ratings yet
- Flare Oct Nov 09Document102 pagesFlare Oct Nov 09rizwan4everyoneNo ratings yet