Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP For Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Uploaded by
Joan Rose Rendon-Hung78%(18)78% found this document useful (18 votes)
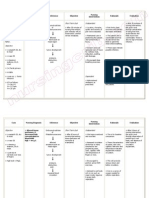
32K views4 pages o Assist with ADLs as
o Assist with turning needed based on
q2hrs. individual condition
and abilities.
o Prevent skin
breakdown and
contractures. Also
reduces risk of
pneumonia from
pooling of secretions.
o Assist with range of o Maintain joint
motion exercises as mobility and prevent
tolerated. contractures. Also
stimulates circulation
and prevents
complications of
immobility.
o Assist with feeding as o Ensure adequate
needed. nutrition and
hydration. May need
supplemental feeding
depending on level of
consciousness and
ability to swallow.
o Provide oral care as o
Original Description:
Original Title
Ncp for Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Read this document in other languages
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
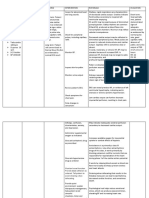
Report this Document o Assist with ADLs as
o Assist with turning needed based on
q2hrs. individual condition
and abilities.
o Prevent skin
breakdown and
contractures. Also
reduces risk of
pneumonia from
pooling of secretions.
o Assist with range of o Maintain joint
motion exercises as mobility and prevent
tolerated. contractures. Also
stimulates circulation
and prevents
complications of
immobility.
o Assist with feeding as o Ensure adequate
needed. nutrition and
hydration. May need
supplemental feeding
depending on level of
consciousness and
ability to swallow.
o Provide oral care as o
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
78%(18)78% found this document useful (18 votes)
32K views4 pagesNCP For Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Uploaded by
Joan Rose Rendon-Hung o Assist with ADLs as
o Assist with turning needed based on
q2hrs. individual condition
and abilities.
o Prevent skin
breakdown and
contractures. Also
reduces risk of
pneumonia from
pooling of secretions.
o Assist with range of o Maintain joint
motion exercises as mobility and prevent
tolerated. contractures. Also
stimulates circulation
and prevents
complications of
immobility.
o Assist with feeding as o Ensure adequate
needed. nutrition and
hydration. May need
supplemental feeding
depending on level of
consciousness and
ability to swallow.
o Provide oral care as o
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
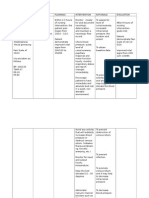
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation
Subjective: Ineffective Short term: Independent: Short term:
tissue After 3-5 hrs of o Determine factors o Influences choice of After 3-5 hrs of
Objective: perfusion nursing related to individual interventions. nursing
- BP: (cerebral) intervention, situation/ cause for Deterioration in intervention,
180/11 related to the client and coma/ decreased neurological signs/ the client and
0 bleeding as the relative cerebral perfusion symptoms or failure the relative
- Dizzine evidenced by will be able to and potential to improve after was able to
ss altered level verbalize increased ICP. initial insult may verbalize
- Inability of understanding reflect decreased understanding
to lift consciousnes of condition, intracranial adaptive of condition,
eyelid s, changes in therapy capacity requiring therapy
- Letharg vital sign and regimens, and patient be regimens, and
ic changes in when to transferred to critical when to
- Vomitin motor contact health care area for contact health
g responses. care provider. monitoring of ICP, care provider.
o Monitor/ document other therapies.
Long term: neurological status Long term:
After 5-6 days frequently and o Assess trends in After 5-6 days
of nursing compare with level of of nursing
intervention baseline. consciousness and intervention
the client will potential for the client was
be able to increased ICP and is able to
demonstrate useful in determining demonstrate
increased location, extent, and increased
perfusion as progression/ perfusion as
individually o Monitor vital signs. resolution of CNS individually
appropriate, Take note of damage. appropriate,
vital signs are Hypertension and vital signs are
on client’s hypotension. o Fluctuations in on clients
normal range, pressure may occur normal range,
alert and because of cerebral alert and
oriented. pressure/ injury in oriented.
o Heart rate and vasomotor area of
rhythm; Auscultate the brain.
for murmurs
o Changes in rate,
especially
bradycardia, can
occur because of the
brain damage.
Dysrhythmias and
murmurs may reflect
cardiac disease,
o Respirations, noting which may have
patterns and rhythm. precipitated CVA.
Periods of apnea
after o Irregularities can
hyperventilation, suggest location of
Chyne-Stokes cerebral insult/
respiration. increasing ICP and
need further
intervention,
o Provide information including possible
regarding the client’s respiratory support.
condition.
o To increase the
o Maintain bed rest; client’s relatives,
provide quiet knowledge about the
environment; restrict condition.
visitors/ activities as
indicated. Provide o Continual
rest periods between stimulation/ activity
care activities, limit can increase ICP.
duration of Absolute rest and
procedures. quiet may be needed
to prevent
o Prevent straining at rebleeding in the
stool, holding breath. case hemorrhage.
o Valsalva maneuver
o Assess for nuchal increases ICP and
rigidity, twitching, potentiates risk for
increased rebleeding.
restlessness,
irritability, onset of o Indicative of
seizure activity. meningeal irritation,
especially in
o Interview client’s hemorrhagic
relatives regarding disorders.
their perception of
situation.
o To assist client’s
o Discuss to relatives relatives in
for meeting the understanding the
client’s self care client’s condition.
needs.
o Varying levels of
assistance may be
required/ need to be
Collaborative: planned for bases on
o Administer individual situation.
supplemental oxygen
as indicated.
o Reduces hypoxemia,
which can cause
cerebral vasodilation
Dependent: and increase
o Administer pressure/ edema
antihypertensive as formation.
ordered.
o Preexisting/ chronic
hypertension
requires cautious
treatment because
aggressive
o Administer stool management
softeners as ordered. increases the risk of
extension of tissue
damage.
o Prevent straining
during bowel
movement and
corresponding
increase of ICP.
You might also like
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7Document2 pagesIneffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7dana100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan For Subarachnoid HemorrhagicDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Subarachnoid HemorrhagicAshram Smart0% (1)
- Nanda NCP BasedDocument14 pagesNanda NCP Baseddeliejoyce100% (1)
- NCP #1 Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument4 pagesNCP #1 Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionsteffiNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesIneffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionHanya Bint Potawan88% (25)
- Nursing Care Plan Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan Hemorrhagic StrokeJeffrey Dela Cruz50% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan For Acute Head InjuryDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Acute Head InjuryAngie Mandeoya67% (3)
- NCP Acute Pain Related To Tissue Ischemia As Manifested by Changes in Level of Consciousness PDFDocument3 pagesNCP Acute Pain Related To Tissue Ischemia As Manifested by Changes in Level of Consciousness PDFOGNTVNo ratings yet
- Aneurysm NCPDocument4 pagesAneurysm NCPAnneUXD100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans - Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plans - Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionKate Cruz75% (8)
- NCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionAngelo ︻╦̵̵͇̿̿̿̿╤── Bulacan50% (6)
- NCP - Tissue Perfusion (Cerebral)Document2 pagesNCP - Tissue Perfusion (Cerebral)moodlayers50% (6)
- NCP - Head InjuryDocument3 pagesNCP - Head Injurykaheliyala94% (33)
- Nursing Care Plan SeizureDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Seizuretimie_reyes100% (1)
- 14 Cerebrovascular Accident Nursing Care PlansDocument5 pages14 Cerebrovascular Accident Nursing Care PlansNickesha Mckenzie75% (4)
- "Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient'sDocument4 pages"Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient'sAllisson BeckersNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation No Subjective Cues ObjectiveDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation No Subjective Cues ObjectiveMaverick LimNo ratings yet
- NCP AneurysmDocument4 pagesNCP AneurysmJanielle Christine Monsalud100% (1)
- NCP-Esophageal Varices Pleural EffusionDocument6 pagesNCP-Esophageal Varices Pleural Effusiontinatin98933% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan: Epidural Hematoma Post CraniotomyDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan: Epidural Hematoma Post CraniotomyTepperoni78% (23)
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument8 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityKM78% (9)
- NCP For Altered ConciousnessDocument2 pagesNCP For Altered Conciousnesshaniehaehae100% (1)
- NCP Altered Mental StatusDocument2 pagesNCP Altered Mental StatusACVP1188% (16)
- NCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion STROKEDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion STROKEMa. Elaine Carla TatingNo ratings yet
- CVA Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageCVA Activity IntoleranceNursesLabs.com75% (4)
- NCP For StrokeDocument4 pagesNCP For StrokeJASON OGALESCONo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument9 pagesNursing Care PlanJam AbantaoNo ratings yet
- NCP TbiDocument4 pagesNCP TbiWyen CabatbatNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPJet Ray-Ann GaringanNo ratings yet
- Hyperkalemia: Ateneo de Naga University College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageHyperkalemia: Ateneo de Naga University College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanRenie Serrano100% (1)
- NCP For Mi PainDocument2 pagesNCP For Mi PainKahMallariNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageIneffective Tissue PerfusionEm Castillo50% (2)
- Nursing Diagnoses For PT With Altered Level of ConsciousnessDocument5 pagesNursing Diagnoses For PT With Altered Level of Consciousnessmikaela_pascua95% (40)
- Stroke Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageStroke Nursing Care PlanTracy PearlNo ratings yet
- Cva NCPDocument2 pagesCva NCPAkima Mulok0% (1)
- NCP - Risk Impaired Skin RT Altered Circulation (Spinal Injury)Document2 pagesNCP - Risk Impaired Skin RT Altered Circulation (Spinal Injury)yanny0350% (2)
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion NCPDocument5 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion NCPJasmin Calata50% (2)
- NCP - Decreased Intracranial Adaptive Capacity R/T Space - Occupying Lesion.Document1 pageNCP - Decreased Intracranial Adaptive Capacity R/T Space - Occupying Lesion.Carl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (6)
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYDocument4 pagesNCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYMa. Elaine Carla Tating100% (2)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- Craniotomy Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesCraniotomy Nursing Care PlanNikko Dela Cruz94% (17)
- NCP Cva Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageNCP Cva Ineffective Tissue Perfusionexcel21121No ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesCerebrovascular Accident Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis67% (12)
- Nursing Care Plan Acute Pain (Fronto-Temporal Mass)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan Acute Pain (Fronto-Temporal Mass)deric100% (1)
- NCP RHDDocument7 pagesNCP RHDHenry Roque Tagalag80% (5)
- Afib NCPDocument3 pagesAfib NCPGen RodriguezNo ratings yet
- NCP For Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument3 pagesNCP For Acute Coronary Syndromesarahtot75% (4)
- NCP AnginaDocument3 pagesNCP AnginaShie LA100% (1)
- NCP-Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument9 pagesNCP-Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument3 pagesDisturbed Thought ProcessAira AlaroNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation of Hemorrhagic Stroke Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument69 pagesCase Presentation of Hemorrhagic Stroke Subarachnoid HemorrhageShin FerranculloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceYum C88% (26)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Short Term: Independent: Short TermDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Short Term: Independent: Short TermMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Format X1Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan Format X1Ramiel ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For HypertensionKathleen Dimacali100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Artery Blockage May BeDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Artery Blockage May BeDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Jade R. Dinolan BSN-4: Diagnosi SDocument5 pagesJade R. Dinolan BSN-4: Diagnosi SJhade Relleta100% (1)
- NCP Knowledge DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP Knowledge DeficitRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- NCP (Stroke)Document9 pagesNCP (Stroke)Claire M. AuditorNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument9 pagesNursing Care PlanaaaNo ratings yet
- PBL - Day 1 MSKDocument4 pagesPBL - Day 1 MSKAAGKhatriNo ratings yet
- MudrasDocument2 pagesMudrasPopa MirceaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument7 pagesNursing Diagnosis Impaired Gas ExchangeZycon Rodney Ae'zecquel Gachallan50% (2)
- Philippine CPG-2013-uti in Adults-Part1 PDFDocument82 pagesPhilippine CPG-2013-uti in Adults-Part1 PDFVirginia AbalosNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment Lower Back PainDocument3 pagesHealth Assessment Lower Back PainArnold TemporosaNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi VenaDocument5 pagesPatofisiologi VenaNisa AriyantiiNo ratings yet
- Understand The Process and Experience of Dementia: Unit DEM 301Document23 pagesUnderstand The Process and Experience of Dementia: Unit DEM 301Mary0% (1)
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument7 pagesChronic Suppurative Otitis MediaMeis MalirmaseleNo ratings yet
- - أسئلة الهيئه السعوديه للأطباء PDFDocument413 pages- أسئلة الهيئه السعوديه للأطباء PDFwael rizkNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction Wit Pic2Document2 pagesIntestinal Obstruction Wit Pic2matrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- Obesity Exercise PrescriptionDocument34 pagesObesity Exercise Prescriptionkhushbu88% (8)
- Mẫu giấy KSK song ngữDocument3 pagesMẫu giấy KSK song ngữNguyen LawlietNo ratings yet
- Vaccination EPI and Non EPIDocument19 pagesVaccination EPI and Non EPIRakhshanda khanNo ratings yet
- Neck LumpsDocument27 pagesNeck LumpsArifudin Cipto HusodoNo ratings yet
- Drug study-THIRD TWO MEDICAL WARDDocument2 pagesDrug study-THIRD TWO MEDICAL WARDErryl Justine AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Proposal RawDocument12 pagesProposal RawSedem StanisloveNo ratings yet
- HIFUDocument1 pageHIFUKaye RabadonNo ratings yet
- Stroke Hemoragic: Sebagai Salah Satu Tugas Mata Kuliah TIK Akademi Keperawatan (Akper) SawerigadingDocument10 pagesStroke Hemoragic: Sebagai Salah Satu Tugas Mata Kuliah TIK Akademi Keperawatan (Akper) SawerigadingMade Serly KrisdayantiNo ratings yet
- WHO Report On Neglected Tropical DiseasesDocument184 pagesWHO Report On Neglected Tropical DiseasesN Aright ForestNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading Survey OphtalmologyDocument17 pagesJournal Reading Survey OphtalmologynadyajondriNo ratings yet
- Pamj 27 48Document7 pagesPamj 27 48JihanNo ratings yet
- Why Is Alcohol An Instigator of ViolenceDocument4 pagesWhy Is Alcohol An Instigator of Violencearniel somilNo ratings yet
- Diabetes PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesDiabetes PathophysiologyRyan MulanoNo ratings yet
- Book Eczema PsoriazisDocument457 pagesBook Eczema Psoriazisdaniel bNo ratings yet
- To: All Employees From: The School Principal Subject: Covid-19 Guidelines in Maintaining Safe School Operations DATE: MAY 26, 2020Document1 pageTo: All Employees From: The School Principal Subject: Covid-19 Guidelines in Maintaining Safe School Operations DATE: MAY 26, 2020Irene DulayNo ratings yet
- Muhaidat PREVALENCE OF ORAL ULCERATION AMONG JORDANIAN PEOPLEDocument8 pagesMuhaidat PREVALENCE OF ORAL ULCERATION AMONG JORDANIAN PEOPLEPutri FifiNo ratings yet
- Microbiology - BacteriologyDocument24 pagesMicrobiology - Bacteriologytdci.franceskorineganzaNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Colonic Diverticular Disease: Role of Surgery: Controversies in GastroenterologyDocument5 pagesTreatment of Colonic Diverticular Disease: Role of Surgery: Controversies in GastroenterologyGianfranco MuntoniNo ratings yet
- Prof HR - Kasus Anemia EprexDocument30 pagesProf HR - Kasus Anemia EprexSuardy CiayadiNo ratings yet
- Stroke & Neurological Disease Conference: Ninth AnnualDocument2 pagesStroke & Neurological Disease Conference: Ninth Annualyos_peace86No ratings yet