Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summary of Reaction Pathways in Organic Chemistry
Uploaded by
Mohd Rais Faiq NicholOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Summary of Reaction Pathways in Organic Chemistry
Uploaded by
Mohd Rais Faiq NicholCopyright:
Available Formats
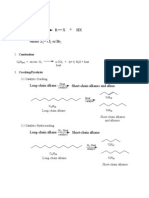
SUMMARY OF REACTION PATHWAYS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
ALKANES POLYALKENES
PRIMARY AMINES
ALKENES DIHALOALKANES
HALOALKANES ALKYL
HYDROGEN EPOXYALKANES DIOLS
SULPHATES
ALCOHOLS
NITRILES
CARBONYLS
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
You need to know the equations, conditions, reagents and type of reaction for all these
reactions.
You need to know the mechanism for some of them.
1. Alkane chloroalkane
reagents: Cl2
conditions: UV light
mechanism: free radical substitution
equation: RH + Cl2 RCl + HCl
2. Alkene polyalkene
Conditions: low T, high p.
Equation:
C C
n C C
Type of reaction: addition polymerisation (free radical)
3. Alkene bromoalkane
Reagent: HX(g)
Conditions: room T
Equation:
C C + H Br C C
Br H
Type of reaction: electrophilic addition
4. Alkene dibromoalkane
Reagent: Br2 in water or in an organic solvent
Conditions: room T
Equation:
C C + Br Br C C
Br Br
Mechanism: electrophilic addition
5. Alkene alkylhydrogensulphate
Reagent: concentrated sulphuric acid
Conditions: cold
Equation:
C C + H OSO3H C C
H OSO3H
Mechanism: electrophilic addition
6. Alkylhydrogensulphate alcohol
Reagent: water
Conditions: warm
Equation:
C C
C C +
+ H2O H OSO3H
H OSO3H
H OH
Type of reaction: hydrolysis
7. Alkene alkane
Reagent: hydrogen
Conditions: 150 oC, Ni catalyst
Equation:
H H C C
C C +
H H
Type of reaction: hydrogenation
8. Alkene alcohol
Reagent: steam
Conditions: 300 oC, 60 atm, H3PO4 catalyst
Equation:
H H
C C + O C C
OH H
Type of reaction: hydration
9. Alkene epoxyalkane
Reagent: oxygen
Conditions: 300 oC, silver catalyst
Equation:
O
C C + 1/2 O O C C
Type of reaction: oxidation
10. Epoxyalkane diol
Reagent: water
Conditions: 60 oC, H2SO4 catalyst
Equation:
O
C C + H H HO C C OH
O
Type of reaction: hydrolysis
11. Haloalkane alcohol
Reagent: NaOH(aq) or KOH(aq)
Conditions: warm under reflux
Equation: R-X + OH- R-OH + X-
Type of reaction: nucleophilic substitution
12. Haloalkane nitrile
Reagent: KCN in aqueous ethanol
Conditions: boil under reflux
Equation: R-X + CN- R-CN + X-
Type of reaction: nucleophilic substitution
13. Haloalkane Amine
Reagent: ammonia in ethanol in a sealed tube
Conditions: heat
Equation: R-X + 2NH3 R-NH2 + NH4X
Type of reaction: nucleophilic substitution
14. Haloalkane alkene
Reagent: KOH in ethanol
Conditions: heat
Equation:
H R R R
C C -
R C C X + X + H2O
R R
R R
Type of reaction: elimination
15. Primary alcohol aldehyde
Reagent: potassium dichromate and dilute sulphuric acid
Conditions: warm, distillation
Equation: RCH2OH + [O] RCHO + H2O
Type of reaction: mild oxidation
16. Secondary alcohol ketone
Reagent: potassium dichromate and dilute sulphuric acid
Conditions: heat, distillation
Equation: R1CH(OH)R2 + [O] R1COR2 + H2O
Type of reaction: oxidation
17. aldehyde carboxylic acid
Reagent: potassium dichromate and dilute sulphuric acid
Conditions: heat, reflux
Equation: R-CHO + [O] R-COOH
Type of reaction: oxidation
18. Alcohols alkenes
Reagent: concentrated sulphuric acid
Conditions: heat
Equation:
C C H C C + H2O
OH
Type of reaction: elimination
19. glucose ethanol
reagent: yeast
conditions: 35 – 55 oC, no air
equation: C6H12O6 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
type of reaction: fermentation
You might also like
- Revision Notes On AlcoholsDocument13 pagesRevision Notes On AlcoholsMuredzwa MuzendaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry I Reaction Sheet v2.1Document11 pagesOrganic Chemistry I Reaction Sheet v2.1Karl WilsonNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ReactionDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry ReactionGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- PMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIFrom EverandPMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Reactions of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7Document53 pagesReactions of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7haha_le12100% (1)
- Mechanism of Aldol Condensation ExplainedDocument30 pagesMechanism of Aldol Condensation ExplainedParameshwari kumar100% (1)
- E1 and E2 ReactionsDocument30 pagesE1 and E2 ReactionsVidhu Pandey100% (1)
- Chemistry of Natural Products PDFDocument21 pagesChemistry of Natural Products PDFhosseini_9864No ratings yet
- Organometallic Transition Metal Catalysis: A Holistic Approach to Understanding and Predicting their MechanismsFrom EverandOrganometallic Transition Metal Catalysis: A Holistic Approach to Understanding and Predicting their MechanismsNo ratings yet
- SN1 Vs SN2Document1 pageSN1 Vs SN2nurhanieyNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Retrosynthesis: Organic Synthesis using Reaxys and SciFinderFrom EverandHybrid Retrosynthesis: Organic Synthesis using Reaxys and SciFinderNo ratings yet
- Retrosynthetic Analysis PDFDocument6 pagesRetrosynthetic Analysis PDFNoleNo ratings yet
- Moon - Exam 2 - Summer 2011Document10 pagesMoon - Exam 2 - Summer 2011Andres Pena100% (2)
- Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7Document52 pagesStructure and Synthesis of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7haha_le12100% (1)
- Experimental Inorganic/Physical Chemistry: An Investigative, Integrated Approach to Practical Project WorkFrom EverandExperimental Inorganic/Physical Chemistry: An Investigative, Integrated Approach to Practical Project WorkNo ratings yet
- AromaticityDocument24 pagesAromaticitymilindthakare75No ratings yet
- Organometallic Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Eighth International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry, Kyoto, Japan, 12-16 September 1977From EverandOrganometallic Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Eighth International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry, Kyoto, Japan, 12-16 September 1977Y. IshiiNo ratings yet
- Reaction Guide by James Ashenhurst. 1-James AshenhurstDocument76 pagesReaction Guide by James Ashenhurst. 1-James AshenhurstSankar AdhikariNo ratings yet
- SGDGDDDocument33 pagesSGDGDDyopoboy100% (1)
- Huckel's Rule for AromaticityDocument25 pagesHuckel's Rule for AromaticityUmar Farooq100% (1)
- Synthetic ReagentsDocument75 pagesSynthetic ReagentsBapu Thorat100% (1)
- Reactions of HaloalkanesDocument10 pagesReactions of Haloalkanesapi-504683923No ratings yet
- Reductions, oxidations, substitutions and rearrangementsDocument9 pagesReductions, oxidations, substitutions and rearrangementsArka MukhopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Organic 2 PDFDocument864 pagesOrganic 2 PDFaisyahNo ratings yet
- Understanding organic reactions through clear diagrams and notesDocument1 pageUnderstanding organic reactions through clear diagrams and notescadence98No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2Document298 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2arielNo ratings yet
- Hetero-Cyclic CompoundsDocument69 pagesHetero-Cyclic CompoundsNaveed SajidNo ratings yet
- Types of Organic ReactionsDocument31 pagesTypes of Organic ReactionsNurulMAprilia80% (5)
- Vollhardt 6e Lecture PowerPoints - Chapter 11Document58 pagesVollhardt 6e Lecture PowerPoints - Chapter 11superfr3shmNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Organic Chemistry by Eyes of Ajnish Kumar Gupta (AKG)Document24 pagesIntroduction of Organic Chemistry by Eyes of Ajnish Kumar Gupta (AKG)ajju_208180% (5)
- Organic ALL RXN Table 2Document11 pagesOrganic ALL RXN Table 2Angie MTNo ratings yet
- Inductive EffectDocument38 pagesInductive EffectJoe JNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 Wade 8thDocument66 pagesChapter 05 Wade 8thanupamgupta112No ratings yet
- Reactions of AlkanesDocument1 pageReactions of AlkanesnofacejackNo ratings yet
- Aromaticity CompleteDocument104 pagesAromaticity Completewahidalwahdi100% (1)
- Mechanism of Organic Reactions 1Document23 pagesMechanism of Organic Reactions 1Suresh Vedpathak100% (2)
- Intro To Organic ChemDocument91 pagesIntro To Organic ChemMiguel Marquez GelacioNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument28 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and EthersDnyanesh Shinde100% (1)
- Problems On Named ReactionsDocument103 pagesProblems On Named ReactionsBapu ThoratNo ratings yet
- Chem 206: Introduction to Frontier Molecular Orbital TheoryDocument22 pagesChem 206: Introduction to Frontier Molecular Orbital TheoryeraborNo ratings yet
- AromaticsDocument70 pagesAromaticsEceDiril100% (1)
- Resonance and Inductive Effects in Organic ChemistryDocument36 pagesResonance and Inductive Effects in Organic Chemistryeagl33yeNo ratings yet
- Reaction MechanismDocument68 pagesReaction MechanismSiddarth Singh73% (11)
- Asymmetric SynthesisDocument7 pagesAsymmetric SynthesisstrakkeNo ratings yet
- Name Reactions: Detailed Reaction MechanismsDocument4 pagesName Reactions: Detailed Reaction MechanismsvanbanbinhdinhNo ratings yet
- Sn1 MechanismDocument24 pagesSn1 MechanismDian MustikasariNo ratings yet
- Name Reaction 3569Document38 pagesName Reaction 3569Ashish AmbekarNo ratings yet
- Alcohols-Phenols and EthersDocument16 pagesAlcohols-Phenols and EthersTr Mazhar PunjabiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Chapter 15: Aromaticity of BenzeneDocument65 pagesOrganic Chemistry Chapter 15: Aromaticity of BenzeneShreya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Reactions and Interconversions of Organic Functional GroupsDocument3 pagesReactions and Interconversions of Organic Functional Groupsmichelsonyip100% (1)
- Alkynes: An Introduction To Organic SynthesisDocument9 pagesAlkynes: An Introduction To Organic Synthesisggwp21No ratings yet
- Vapour Liquid Equilibrium Data CollectionDocument53 pagesVapour Liquid Equilibrium Data Collectionvazzoleralex6884No ratings yet
- Nucleophilic Addition To The Carbonyl GroupDocument16 pagesNucleophilic Addition To The Carbonyl GroupYuni PurnamasariNo ratings yet
- Functional GroupsDocument1 pageFunctional GroupsjimcarryfromindiaNo ratings yet
- Senarai Produk SawitDocument16 pagesSenarai Produk SawitYuliana PohanNo ratings yet
- Fukuyama Group - Group Meeting Problems 2001/08/22: N N N HDocument2,429 pagesFukuyama Group - Group Meeting Problems 2001/08/22: N N N HGia PhướcNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde Ketone PPT 2Document21 pagesAldehyde Ketone PPT 2muskan dahiyaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - 24577953Document4 pagesClass 12 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - 24577953Aryan KhandkaNo ratings yet
- Metalated Hetero Cycles and Their Applications in Synthetic Organic ChemistryDocument56 pagesMetalated Hetero Cycles and Their Applications in Synthetic Organic Chemistrygokay05No ratings yet
- Organic Compounds Containing NitrogenDocument9 pagesOrganic Compounds Containing NitrogenAUM S. PATELNo ratings yet
- Discussion Lab 6 chm207Document2 pagesDiscussion Lab 6 chm2072023300959No ratings yet
- Surface Tension of Various Liquids PDFDocument43 pagesSurface Tension of Various Liquids PDFneha sahuNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 10 PDFDocument13 pages12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 10 PDFSahil Kalra100% (1)
- Problems and Solutions in Organic Chemistry: PressDocument21 pagesProblems and Solutions in Organic Chemistry: PressSandipan Saha100% (1)
- CEM 3005W Aromatic and Heteroaromatic Notes 2013Document26 pagesCEM 3005W Aromatic and Heteroaromatic Notes 2013Zama MakhathiniNo ratings yet
- General Organic Chemistry: Entry of Vvips - Nomenclature of Organic Compounds With Mono Functional GroupDocument12 pagesGeneral Organic Chemistry: Entry of Vvips - Nomenclature of Organic Compounds With Mono Functional GroupYaswanth PedapudiNo ratings yet
- The Industrial Applications of AlkenesDocument15 pagesThe Industrial Applications of Alkenesiman kashifNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles: Please ReadDocument12 pagesChapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles: Please ReadNeil GaymanNo ratings yet
- Short Notes Class 12 Chemistry 2023Document37 pagesShort Notes Class 12 Chemistry 2023Susmita BhowmikNo ratings yet
- Che MenuDocument509 pagesChe MenuSrimathiNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Aldehydes and KetonesDocument11 pagesModule 4 Aldehydes and Ketonesaliya margo gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Module 2Document25 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Module 2ChaithraMalluNo ratings yet
- 01 Chapter 17 Alcohols and PhenolsDocument51 pages01 Chapter 17 Alcohols and PhenolsMinh Hoàng LươngNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Grade 10Document88 pagesOrganic Chemistry Grade 10Sai Pranav100% (2)
- Aromatic Compounds IUPAC Naming and StructuresDocument4 pagesAromatic Compounds IUPAC Naming and StructuresNurain azmanNo ratings yet
- 6 Aldehydes and Ketones-ReactionsDocument33 pages6 Aldehydes and Ketones-ReactionsPrashant NalindeNo ratings yet
- CElegans NetworkDocument893 pagesCElegans NetworkMelissa HaganNo ratings yet
- Monosaccharides LectureDocument24 pagesMonosaccharides LectureSaeed AkhterNo ratings yet
- DPPONIUPACSUPERSIXER4Document5 pagesDPPONIUPACSUPERSIXER4Kartik YadavNo ratings yet
- 1972 (Vol 8)Document1,557 pages1972 (Vol 8)Amir AbazaNo ratings yet