Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Important Term: Gradient Function : Chapter 3: Integration
Uploaded by
mohamad_bidariOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Important Term: Gradient Function : Chapter 3: Integration
Uploaded by
mohamad_bidariCopyright:
Available Formats
Add Maths Form 5 1
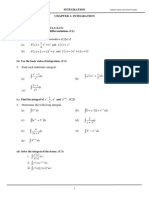
Chapter 3: Integration
Symbol for integration:
dy
Reverse process of differentiation: If
dx
f ' ( x) , then f ' ( x) dx y c .
dy
Important term: gradient function =
dx
.
Integration in the form of (ax b) n
dx
or substitution method.
(I) Indefinite Integrals
Examples:
dy
1. Given that y f (x) and
dx
h(x) , find 3h( x) dx .
dy
2. Given that
dx
6(3 x 1) , where y 9 x 2 6 x , find 6(3x 1) dx .
dy
3. Given that
dx
6(3 x 1) , where y 9 x 2 6 x , find (3 x 1) dx .
4. Given y 3(2 x 5) 4 .
dy
(a) Find .
dx
(b) Hence, find (2 x 5) 3
dx .
5. Determine each of the following indefinite integrals.
“Float like a butterfly, sting like a bee.” – Muhammad Ali
Add Maths Form 5 2
3 x8
(a) dx
(f) dx
4 2
(b) dx
5 x
(g) dx
7
(c) 7 x dx
14
(d) 40 x dx4
(h)
x5
dx
3 6
(e) x dx 1
5 (i) dx
4x6
2
(j) dx
x
“Float like a butterfly, sting like a bee.” – Muhammad Ali
Add Maths Form 5 3
“Float like a butterfly, sting like a bee.” – Muhammad Ali
Add Maths Form 5 4
Integrate each of the following algebraic expressions with respect to x.
“Float like a butterfly, sting like a bee.” – Muhammad Ali
Add Maths Form 5 5
(k) 7x 2 4x 6 2
(o) 4
1 3x 3
(l) 9x
x
3
(p)
x
2
5 4x 3
(m) 5
4 (1 2 x ) 2
2 (q)
(n) 8x 1 2
x4
“Float like a butterfly, sting like a bee.” – Muhammad Ali
Add Maths Form 5 6
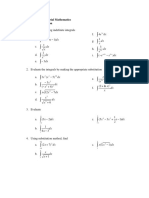
6. Determine the following indefinite integrals.
“Float like a butterfly, sting like a bee.” – Muhammad Ali
Add Maths Form 5 7
x 2 x 2 18
(a) 2
(3 x 9) dx
(c) dx
4x 4 x x3
(b)
dx 2
12 x x 3x 2
(d) dx
x2
“Float like a butterfly, sting like a bee.” – Muhammad Ali
Sri Bintang Tuition Centre 8
20
7. Find: (a) (4 x 1) 4
dx (b) 3(1 2 x) 3
dx (c)
( 4 x 5) 5
dx
dy
8. Given that 4 x 2 x 5 and y 1 when x 1 , express y in terms of x.
dx
dy 1 1
9. Given that 2 x 2 and y 0 when x , express y in terms of x.
dx 2x 2
d2y dy
10. Given 9 x 4 and that 3 when x = 1 and y = 2. Express y in terms of x.
dx 2 dx
3
11. A curve has a gradient function of x . If the curve passes through the point 1,1 , find the
x2
equation of the curve.
17 1
12. If the gradient of a curve at a point 1, is , find the equation of the curve.
16 (3 4 x) 5
dy
13. The gradient function of a curve is given by 3 x ( x k ) , where k is a constant. The gradient of the
dx
curve at a point ( 2, 3) is 12. Find
(a) the value of k,
(b) the equation of the curve.
“Float like a butterfly, sting like a bee.” – Muhammad Ali
You might also like
- 1 Lista de Cálculo II 1) Calcule As Integrais: A) K) 2 4 5 (C) M) D) N) E) O) F) P) G) Q) H) R)Document3 pages1 Lista de Cálculo II 1) Calcule As Integrais: A) K) 2 4 5 (C) M) D) N) E) O) F) P) G) Q) H) R)Lucas IgnácioNo ratings yet
- Lista de IntegraisDocument3 pagesLista de IntegraisLucas IgnácioNo ratings yet
- Integration 1Document2 pagesIntegration 1knoxmathsNo ratings yet
- SM 025 - Integration SoalanDocument9 pagesSM 025 - Integration SoalansharuNo ratings yet
- Practica 6Document10 pagesPractica 6LUNANo ratings yet
- Integration Techniques and ApplicationsDocument9 pagesIntegration Techniques and ApplicationssharuNo ratings yet
- INPS Indefinite Integration Study MaterialDocument41 pagesINPS Indefinite Integration Study MaterialSps BloggerNo ratings yet
- 11 Indefinite Integration (I) : C X DX XDocument32 pages11 Indefinite Integration (I) : C X DX XWong TonyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9 (Baru06)Document6 pagesTutorial 9 (Baru06)nabilahNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-12-21 at 7.42.59 PMDocument4 pagesScreenshot 2022-12-21 at 7.42.59 PMTsz yuo NnaNo ratings yet
- assignment3Document3 pagesassignment3HimanshuTV OfficialNo ratings yet
- Basic Integration Problems #1Document4 pagesBasic Integration Problems #1John Marlo GorobaoNo ratings yet
- Basic Integration TutorialDocument4 pagesBasic Integration TutorialElayaraja AruchunanNo ratings yet
- Basic Integration Problems Author Holland Central School District-CompressedDocument4 pagesBasic Integration Problems Author Holland Central School District-CompressedraduNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 IntegrationDocument16 pagesCHAPTER 1 IntegrationSaidatul FarhaniNo ratings yet
- Integration 19-3-2023 L1Document7 pagesIntegration 19-3-2023 L1ella2003transNo ratings yet
- Derivative of Root and Transcendental FunctionsaDocument7 pagesDerivative of Root and Transcendental FunctionsaRalph Piolo BuanNo ratings yet
- DERIVATIVE OF ROOT AND TRANSCENDENTAL FUNCTIONSaDocument7 pagesDERIVATIVE OF ROOT AND TRANSCENDENTAL FUNCTIONSaRalph Piolo BuanNo ratings yet
- CalculusDocument52 pagesCalculushumphrey tarimoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Integral Calculus NewDocument106 pagesChapter 6 Integral Calculus NewSIMBA The Lion KingNo ratings yet
- Taller MN2-11Document2 pagesTaller MN2-11AIR TECHNOLOGY COMPRESORNo ratings yet
- Taller MN2-11Document2 pagesTaller MN2-11AIR TECHNOLOGY COMPRESORNo ratings yet
- Introduction To IntegrationDocument2 pagesIntroduction To IntegrationPaul ThompsonNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Notes (Day 3) InkedDocument2 pages3.1 Notes (Day 3) Inked吳恩No ratings yet
- Integration Important QuestionsDocument20 pagesIntegration Important QuestionsBol BakHoleS100% (1)
- Calculating Integrals of Polynomial FunctionsDocument4 pagesCalculating Integrals of Polynomial FunctionsCharalampidis DimitrisNo ratings yet
- Tut 8Document3 pagesTut 8Batrisya LeeNo ratings yet
- 13 BBMP1103 T9Document18 pages13 BBMP1103 T9elizabeth lizNo ratings yet
- Element of Culculus in Economics-1Document52 pagesElement of Culculus in Economics-1chingtonyNo ratings yet
- Solving first-order differential equationsDocument2 pagesSolving first-order differential equationsFabian GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Integration ChapterDocument17 pagesIntegration ChapterISMADI SURINNo ratings yet
- Exercise Topic 4 - Integration PDFDocument6 pagesExercise Topic 4 - Integration PDFNur Natasya NajwaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Mathematics WorksheetDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 12 Mathematics WorksheetVaibhav Bajpai100% (1)
- Lista 1Document4 pagesLista 1mariaNo ratings yet
- (18246) Sheet 08 Definite Integration BDocument107 pages(18246) Sheet 08 Definite Integration BJay AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Sheets-Spring 2015-2016Document38 pagesSheets-Spring 2015-2016amralquraishi411No ratings yet
- Modul 13 IntegrationDocument16 pagesModul 13 Integrationhasnitajb0% (1)
- Integration Formulas and TechniquesDocument8 pagesIntegration Formulas and Techniquesfatin HumairaNo ratings yet
- 2 IntegrationDocument21 pages2 Integrationviena patriciaNo ratings yet
- 12MAI - Notes 1.2Document7 pages12MAI - Notes 1.2JessicaNo ratings yet
- Derivatives: Concept of DerivativeDocument4 pagesDerivatives: Concept of Derivativesunny rathodNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Excercise 2Document3 pagesFinal Exam Excercise 2Esther LiongNo ratings yet
- Integral: Integration or Anti-Differentiation Is The Inverse Operation of Differentiation Where TheDocument13 pagesIntegral: Integration or Anti-Differentiation Is The Inverse Operation of Differentiation Where Themintchoco98No ratings yet
- Integration by Partial Fractions 2021Document1 pageIntegration by Partial Fractions 2021Ameer KhanNo ratings yet
- Math 120 Common Final ExamDocument6 pagesMath 120 Common Final Exam雪郎かざきNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Formulas PDFDocument7 pagesDifferentiation Formulas PDFStevenzel Eala EstellaNo ratings yet
- 4.unit 4 IntegrationDocument31 pages4.unit 4 Integrationieman najmiNo ratings yet
- Higher Maths: Revision NotesDocument26 pagesHigher Maths: Revision NotesAsep sunaryaNo ratings yet
- Busmath Session 11Document7 pagesBusmath Session 11testNo ratings yet
- FIB Maths Chapter 6Document9 pagesFIB Maths Chapter 6VerrelyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - IntegrationDocument51 pagesChapter 4 - IntegrationWan Fakrool Wan FadzilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1Angelo Paolo CamotaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Integration Part 1 - EditedDocument35 pagesCHAPTER 4 Integration Part 1 - Editedsyahrilazuan8No ratings yet
- Unit 3 (Topics 3.1-3.6) Review - 2019Document8 pagesUnit 3 (Topics 3.1-3.6) Review - 2019Andrew ZhengNo ratings yet
- 2122 - SM025 - Note - CH1 IntegrationDocument15 pages2122 - SM025 - Note - CH1 IntegrationPAKK10622P Nurul Izzah binti MohammadNo ratings yet
- JRS TUTORIALS Integration Problem SheetDocument6 pagesJRS TUTORIALS Integration Problem SheetDeo kumarNo ratings yet
- Benchmark 5Document3 pagesBenchmark 5Dan BautistaNo ratings yet
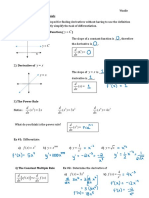
- Chapter Three Derivatives: EX-1 - Find The Derivative of The Function: Sol.Document9 pagesChapter Three Derivatives: EX-1 - Find The Derivative of The Function: Sol.abasNo ratings yet
- Tables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- W15 Exercise 4.3Document2 pagesW15 Exercise 4.3mohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- I J OA OB OC OR OS OT: AR BTDocument3 pagesI J OA OB OC OR OS OT: AR BTmohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- 4.2: Addition & Subtraction of Vectors: OD X yDocument3 pages4.2: Addition & Subtraction of Vectors: OD X ymohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- W10 Chapter 4MatricesExerciseW10Document5 pagesW10 Chapter 4MatricesExerciseW10mohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- Revision Exercise Feb 24Document4 pagesRevision Exercise Feb 24mohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- Y X P y X Q X R X y R Q P R Q P: ExamplesDocument3 pagesY X P y X Q X R X y R Q P R Q P: Examplesmohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- Linear Law P1Document2 pagesLinear Law P1mohamad_bidari0% (1)
- W7Chapter 10 II Plan & ElevationDocument42 pagesW7Chapter 10 II Plan & Elevationmohamad_bidari100% (1)
- Chapter 1: Functions NameDocument2 pagesChapter 1: Functions Namemohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- (cikgubid/AMF5/W10/Mon, March 4 2013/KYRHG) : AnswersDocument3 pages(cikgubid/AMF5/W10/Mon, March 4 2013/KYRHG) : Answersmohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- W7Chapter 10 II Plan & ElevationDocument42 pagesW7Chapter 10 II Plan & Elevationmohamad_bidari100% (1)
- Completing The SquareDocument5 pagesCompleting The Squaremohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- Revision Addmaths SPM histogram quadratic functions areas volumesDocument2 pagesRevision Addmaths SPM histogram quadratic functions areas volumesmohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- Maths Revision Exercise SolutionsDocument12 pagesMaths Revision Exercise Solutionsmohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Quadratic Equations: Examples IDocument3 pagesChapter 2: Quadratic Equations: Examples Imohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- CHP 2 Linear Law (AddMaths Form 5)Document12 pagesCHP 2 Linear Law (AddMaths Form 5)mohamad_bidari0% (2)
- Quadratic Equations Chapter Form 4 AddMathsDocument1 pageQuadratic Equations Chapter Form 4 AddMathsmohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- X X G X X F X X F: Chapter 1: FunctionsDocument2 pagesX X G X X F X X F: Chapter 1: Functionsmohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- Linear Law Chapter 2 ExamplesDocument3 pagesLinear Law Chapter 2 Examplesmohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- Maths Form 5 Chapter 1 Number Bases Revision ExerciseDocument4 pagesMaths Form 5 Chapter 1 Number Bases Revision Exercisemohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Number Bases: (Cikgubid/Mathsf5/W1/Thu/Kyrhg)Document5 pagesChapter 1: Number Bases: (Cikgubid/Mathsf5/W1/Thu/Kyrhg)mohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- Section A - Answer All QuestionsDocument4 pagesSection A - Answer All Questionsmohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3IntegrationW8TueDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 3IntegrationW8Tuemohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- Physics Test - Grade 8Document6 pagesPhysics Test - Grade 8smartamjadNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Positive & Negative Angles in Degrees & Radians: Chapter 5 Triginometric Functions - Add Maths Form 5Document1 page5.1 Positive & Negative Angles in Degrees & Radians: Chapter 5 Triginometric Functions - Add Maths Form 5mohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- Revision W9TueDocument3 pagesRevision W9Tuemohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3IntegrationW8MonDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 3IntegrationW8Monmohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic MonDocument2 pagesArithmetic Monmohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- Section A - Answer All QuestionsDocument4 pagesSection A - Answer All Questionsmohamad_bidariNo ratings yet
- CXC Msths Basic Questions and AnswerDocument20 pagesCXC Msths Basic Questions and AnswerRen Ren Hewitt100% (1)
- Modeling of The Dynamics of Rotors of An Energy Gas Turbine Installation Using An Analytical Method For Analyzing Active Magnetic Bearing CircuitsDocument6 pagesModeling of The Dynamics of Rotors of An Energy Gas Turbine Installation Using An Analytical Method For Analyzing Active Magnetic Bearing Circuitsshamiul himelNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Physics CurriculumDocument1 pageInstrumentation Physics CurriculumKen RubioNo ratings yet
- 1.5 - Solution Sets of Linear SystemsDocument4 pages1.5 - Solution Sets of Linear SystemsMuhammad YasirNo ratings yet
- s4p2 PDFDocument12 pagess4p2 PDFAnh Do VoNo ratings yet
- Steel Beam Design Flowchart EUROCODEDocument7 pagesSteel Beam Design Flowchart EUROCODELong Live TauNo ratings yet
- Tiny ES6 Notebook Curated JavaScript ExamplesDocument100 pagesTiny ES6 Notebook Curated JavaScript ExamplesJesus Leon Cordero100% (1)
- Quantitative 1H NMR SpectrosDocument22 pagesQuantitative 1H NMR Spectrossantosh0912830% (1)
- Ed Thorp - A Mathematician On Wall Street - Statistical ArbitrageDocument33 pagesEd Thorp - A Mathematician On Wall Street - Statistical Arbitragenick ragoneNo ratings yet
- Python Lab Cycle - ITDocument4 pagesPython Lab Cycle - ITeswar jrNo ratings yet
- CALCULOSDocument227 pagesCALCULOSLuisHuamanQuilicheNo ratings yet
- Batteries enDocument1 pageBatteries enRogelio MolinaNo ratings yet
- Coherent Transition Radiation From A Helically Microbunched Electron BeamDocument6 pagesCoherent Transition Radiation From A Helically Microbunched Electron BeamParticle Beam Physics LabNo ratings yet
- Common Monomial FactorDocument31 pagesCommon Monomial FactorErika Lloren Luyun-Galia100% (1)
- XG BoostDocument5 pagesXG Boostola moviesNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics - Module #3Document7 pagesGeneral Mathematics - Module #3Archie Artemis NoblezaNo ratings yet
- EMT175 184finishedDocument30 pagesEMT175 184finishedcharles izquierdoNo ratings yet
- Regression Modelling and Least-Squares: GSA Short Course: Session 1 RegressionDocument6 pagesRegression Modelling and Least-Squares: GSA Short Course: Session 1 Regressioncarles1972mmNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Wheat Flour Production Process Planning in PT Y With Linear Programming MethodDocument5 pagesOptimization of Wheat Flour Production Process Planning in PT Y With Linear Programming MethodInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 3rd Periodic Test - Grade 9Document4 pages3rd Periodic Test - Grade 9sweetheart barrion43% (7)
- Rcs454: Python Language Programming LAB: Write A Python Program ToDocument39 pagesRcs454: Python Language Programming LAB: Write A Python Program ToShikha AryaNo ratings yet
- Format LecDocument71 pagesFormat LecACES JEEL CENDA�ANo ratings yet
- Application To CongruencesDocument16 pagesApplication To CongruencesJUNALYN MANATADNo ratings yet
- Lean-7waste, Takt Time, Crew SizeDocument80 pagesLean-7waste, Takt Time, Crew Sizeapi-3770121100% (2)
- Problems 3Document2 pagesProblems 3Trần Xuân AnhNo ratings yet
- Write The Ratio, Decimal and Percent Equivalent of Each Picture. Write Your Answer On A Sheet of PaperDocument14 pagesWrite The Ratio, Decimal and Percent Equivalent of Each Picture. Write Your Answer On A Sheet of PaperMarlon Ursua BagalayosNo ratings yet
- UR Script ManualDocument102 pagesUR Script ManualAlexandru BourNo ratings yet
- Effective Pandas SampleocrDocument13 pagesEffective Pandas SampleocrrandallNo ratings yet
- Alarp-Comah 2003Document18 pagesAlarp-Comah 2003kenoly123No ratings yet
- Resume Cit PDFDocument1 pageResume Cit PDFJUNE CARLO ENCABONo ratings yet