Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Light: Year 9 Science Semester Revision
Uploaded by
api-32133818Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Light: Year 9 Science Semester Revision
Uploaded by
api-32133818Copyright:
Available Formats
Year 9 Science Semester Revision
Light
Remember
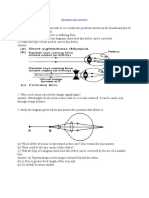
1. 2. What is refraction and what causes it? Complete the light rays in the diagram below as they move from one medium into another. All blocks are glass and surrounded by air.
3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18.
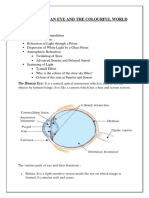
How does the speed of light in glass compare with the speed of light in air? In which direction does light bend, in relation to the normal, if it moves from glass into air? Draw and label the shape of: a convex lens a concave lens. Which type of lens causes light rays to diverge? A friend is looking through a lens and says that she can see everything smaller and upright. What kind of lens is she most likely looking through? Which two parts of the eye work together to form a sharp image on the retina? What is the visible spectrum? According to Isaac Newton, how many colours make up white light? How can you prove that white light is, in fact, a mixture of colours? How many colours are our eyes sensitive to? What is a primary colour? What are the three primary colours in human vision? What is a secondary colour? Explain how each of the three secondary colours is formed.
Think
1. 2. Hot air above a fire or a hot stove makes the objects behind it seem distorted. What does this tell you about the speed of light in hot air? Light travels more slowly through diamond than any other transparent material. How could a jeweller determine if a piece of diamond is real or fake? What happens to the car in the diagram at right if it meets the bitumensand boundary head-on?
3.
4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
11. 12. 13.
Explain, with the aid of a diagram, why the image in a convex lens can be upside down. Why can only convex lenses make real images? What is a virtual image? If an object is nearby, the lens of the eye changes shape to create a sharp image. Does the lens become thicker or thinner? Is the image that the eye produces on the retina real or virtual? Explain your answer. In what substance is light refracted to form a rainbow? Look at the picture of the triangular prism on the right and decide which colour blue or red has been refracted most by the glass. Which colour red or blue has the lower speed in glass? The primary and secondary colours make up only six colours altogether. How are all the other colours made? What is the difference between total internal reflection and the reflection of light by a mirror?
Extension
1. Show what happens to the light ray as it passes through these glass shapes surrounded by air. (Hint: In each case, draw the normal first.) An alien species from the planet Chroma has four types of colour-sensitive cell. a. How many primary colours would there be in this aliens world? b. How many secondary colours would exist on the planet Chroma? If you are underwater in a swimming pool, looking up at the surface, you may notice that a large part of the surface looks like a mirror. Explain why the water surface looks like a mirror rather than being transparent? Why does total internal reflection happen only when light travels from a medium like glass or water to air, but not the other way around
2. 3. 4.
Check and Challenge Questions
1. 2. 3. What causes light to change direction when it travels from air to glass? In your own words, explain how a change of speed can lead to a change in direction of a light ray. Identify the glass objects that are hidden in each box in the diagram below.
4. 5. 6. 7.
8. 9.
10. 11. 12.
13.
When light moves from one medium to another, it bends. However, there is one exception to this rule. What is it? When light travels from glass to air, it changes speed. Does it speed up or slow down? What happens to light that moves from glass to air when its angle of incidence is equal to the critical angle? Complete these sentences about light which strikes a boundary at an angle other than 90: i. When travelling from air to water, light bends _____________the normal. ii. When travelling from glass to air, the light bends ________________ the normal. What happens to light that moves from glass to air when its angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle? Total internal reflection can occur only when light travels a. from a slower medium to a faster medium. b. from a faster medium to a slower medium. c. from air into water. d. between any two media. Which shaped lens causes incoming light to diverge convex or concave? Imagine a convex lens. Where should an object be placed so that its image is enlarged and the right way up? The image of a candle flame is smaller than the actual flame. It is projected onto a screen, but it is upside down. a. What type of lens is used to form the image? b. Is the image real or virtual? How do you know? Seen through a particular lens, everything looks smaller, but remains upright. What kind of lens is it? Explain your answer.
14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20.
How does the focal length of a thick convex lens compare with the focal length of a thinner convex lens? If you are unable to focus on a nearby image, it is usually because your cornea and lens dont bend light enough. Which shaped lens could correct this problem convex or concave? What are the seven colours that Newton identified when he used a prism to split white light into colours? Given that the eye has only three kinds of colour sensitive cells (red, blue and green), how is it possible that we see many different colours in a variety of shades? Why does blue light refract more than red light as it travels through a glass prism? The balloons in the photo at right are all illuminated by white light. Explain why each of the three objects appears, to our eyes, to have a colour other than white. Selective absorption and reflection describes why we see objects in different colours. Red objects reflect red light, but absorb all other colours. Yellow objects absorb some colours but reflect two colours. The two colours of light mix together, and we see a yellow object. The main two colours of light that are reflected from a yellow object are most likely a. blue and green. b. red and blue. c. green and red. d. cyan and magenta. e. white and black.
You might also like
- Chung Cheng High School (Main) Sec 1 Physics Chapter E3Document16 pagesChung Cheng High School (Main) Sec 1 Physics Chapter E3Ken TanNo ratings yet
- Light Is An Amazing Form of Energy. It Travels in Straight Lines Through Transparent Materials or Empty Space at Speeds of Around 300000km/sDocument23 pagesLight Is An Amazing Form of Energy. It Travels in Straight Lines Through Transparent Materials or Empty Space at Speeds of Around 300000km/smichelle_krellNo ratings yet
- Human Eye Adhyasa Deepika 2022-2023Document7 pagesHuman Eye Adhyasa Deepika 2022-2023prakashNo ratings yet
- HumanEye and Colourful World 7Document26 pagesHumanEye and Colourful World 7VinodKumarTummalurNo ratings yet
- 10 Science TP 11 1Document5 pages10 Science TP 11 1Ananaya BansalNo ratings yet
- 06 Human Eye and Colourful World Chapter Wise Important Questions PDFDocument12 pages06 Human Eye and Colourful World Chapter Wise Important Questions PDFTannu KaurNo ratings yet
- Human Eye 1Document6 pagesHuman Eye 1Aadil ShakulNo ratings yet
- 11-1Document5 pages11-1paparaoNo ratings yet
- Q4_LAS 11Document4 pagesQ4_LAS 11JESSA SUMAYANGNo ratings yet
- Light NB WorkDocument4 pagesLight NB Workdakshsri24No ratings yet
- Human Eye and Colourful World QuestionsDocument12 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful World QuestionsSahishna SurapaneniNo ratings yet
- X April Physics LightDocument2 pagesX April Physics Lightprasidh2021No ratings yet
- General Organic and Biological Chemistry Structures of Life 5th Edition Timberlake Test BankDocument36 pagesGeneral Organic and Biological Chemistry Structures of Life 5th Edition Timberlake Test Bankservantmerceryxfced100% (34)
- Human Eye AssignmentDocument6 pagesHuman Eye Assignmentrishabhsharma94163No ratings yet
- Physics 72.1 Peer ReviewDocument12 pagesPhysics 72.1 Peer Reviewviviene24No ratings yet
- CHapter 11 Human Eye and Colorful WorldDocument7 pagesCHapter 11 Human Eye and Colorful WorldMihir SagarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01 11 Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument5 pagesCbse Test Paper-01 11 Human Eye and The Colourful WorldTanmay KatyalNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet Class X The Human Eye and Its Colourful WorldDocument2 pagesPhysics Worksheet Class X The Human Eye and Its Colourful WorldNamratha BalajeeNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Q4 Week 3Document23 pagesPhysical Science Q4 Week 3Julie anne100% (1)
- Physical Science Q4 Week 3 v2Document22 pagesPhysical Science Q4 Week 3 v2Balmon MonbalNo ratings yet
- Physical 3Document19 pagesPhysical 3Kirby SuarezNo ratings yet
- Class X Physics Question Bank - HUMAN EYE and The COLOURFUL WORLDDocument5 pagesClass X Physics Question Bank - HUMAN EYE and The COLOURFUL WORLDNitish UnniNo ratings yet
- Study Material Class 10 Chapter 11 2017Document13 pagesStudy Material Class 10 Chapter 11 2017satishNo ratings yet
- Chap 1.4Document9 pagesChap 1.4smisbahul90No ratings yet
- 7.1 Answers: RememberingDocument21 pages7.1 Answers: RememberingDanny TNo ratings yet
- 0000Document8 pages0000taetaehyungNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Humms Phenomena of LightDocument2 pagesGrade 12 Humms Phenomena of LightJay r DomingoNo ratings yet
- Finding Unicorn's New Home!: 1. Core CompetenceDocument3 pagesFinding Unicorn's New Home!: 1. Core CompetenceRegina Nur LuthfiahNo ratings yet
- MCQ Type QuestionsDocument2 pagesMCQ Type QuestionsAnonymous rn5Te9MwkNo ratings yet
- Light and Optics Complete PDFDocument34 pagesLight and Optics Complete PDFJorge Montero Vallejo0% (2)
- Dispersion Scattering ColourDocument7 pagesDispersion Scattering ColourJohn JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Physics 10th Human Eye and Colourful World - 082934Document5 pagesPhysics 10th Human Eye and Colourful World - 082934defalter090No ratings yet
- 10 Science Imp Ch11 HotsDocument2 pages10 Science Imp Ch11 HotsUday JoshiNo ratings yet
- A Sound Person's Guide To LightingDocument4 pagesA Sound Person's Guide To LightingnidharshanNo ratings yet
- Techniques in MicrosDocument45 pagesTechniques in MicrosdoodoobutteredNo ratings yet
- Light and Color ScienceDocument32 pagesLight and Color Sciencenfs100No ratings yet
- Chapter Notes Human Eye & Colourful WorldDocument11 pagesChapter Notes Human Eye & Colourful Worldroseanneblossom.kimNo ratings yet
- The Human Eye and Colour VisionDocument6 pagesThe Human Eye and Colour VisionChetan BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Physics b type questionDocument17 pagesPhysics b type questionHappy RoyNo ratings yet
- Class VIII LightDocument2 pagesClass VIII Lightbose baraniNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument12 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful Worldapi-246793885100% (1)
- The Human Eye and The Colourful World (Complete)Document9 pagesThe Human Eye and The Colourful World (Complete)Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- RS - X - Physics - July - Notes of Human Eye - 2022-23Document6 pagesRS - X - Physics - July - Notes of Human Eye - 2022-23RishikaNo ratings yet
- Ch.11. The Human Eye and The Colourful World: The Human Eye: It Is A Natural Optical Instrument Which Is Used To See TheDocument17 pagesCh.11. The Human Eye and The Colourful World: The Human Eye: It Is A Natural Optical Instrument Which Is Used To See TheIshi SNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter-11 The Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument9 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter-11 The Human Eye and The Colourful WorldkunalNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Notes 11 Human Eye and Colourful World 1Document9 pages10 Science Notes 11 Human Eye and Colourful World 1piyush prasadNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Notes 11 Human Eye and Colourful World 1Document11 pages10 Science Notes 11 Human Eye and Colourful World 1Koustav BiswasNo ratings yet
- Vision and World of ColoursDocument6 pagesVision and World of ColoursAsish ThampiNo ratings yet
- LIGHT PART II: Reflection, Refraction, Mirrors and Lenses The Big IdeaDocument24 pagesLIGHT PART II: Reflection, Refraction, Mirrors and Lenses The Big IdeanidharshanNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and The Colorfull WorldDocument16 pagesHuman Eye and The Colorfull Worldanushanashi362No ratings yet
- PH 11 OpticsDocument12 pagesPH 11 Opticsneiljain10002No ratings yet
- PYQs Mid Term CH 10 Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument39 pagesPYQs Mid Term CH 10 Human Eye and The Colourful Worldeekshi0003No ratings yet
- Light-Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument23 pagesLight-Human Eye and The Colourful Worldapi-268345960No ratings yet
- Seeing Light: The Science of VisionDocument38 pagesSeeing Light: The Science of VisionKrish ChopraNo ratings yet
- Class X Physics Question Bank:: HUMAN Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument9 pagesClass X Physics Question Bank:: HUMAN Eye and The Colourful WorldSCReddyNo ratings yet
- CH-11 Light PPT-2Document33 pagesCH-11 Light PPT-2SUHANEERIYANo ratings yet
- Fine Art Flower Photography: Creative Techniques and the Art of ObservationFrom EverandFine Art Flower Photography: Creative Techniques and the Art of ObservationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- A Practical Manual of the Collodion Process: Giving in Detail a Method For Producing Positive and Negative Pictures on Glass and PaperFrom EverandA Practical Manual of the Collodion Process: Giving in Detail a Method For Producing Positive and Negative Pictures on Glass and PaperNo ratings yet
- Choosing A Landing SiteDocument9 pagesChoosing A Landing Siteapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Simple ElectroscopeDocument2 pagesSimple Electroscopeapi-32133818No ratings yet
- BloodDocument1 pageBloodapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Identifying ChemicalsDocument2 pagesIdentifying Chemicalsapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Two TheoriesDocument8 pagesTwo Theoriesapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Famous Crimes Assignment 2015Document3 pagesFamous Crimes Assignment 2015api-32133818No ratings yet
- Indentification Revision (1) PagesDocument1 pageIndentification Revision (1) Pagesapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Making A Crystal GardenDocument3 pagesMaking A Crystal Gardenapi-32133818No ratings yet
- 9sci Chapter 8 1Document13 pages9sci Chapter 8 1api-32133818No ratings yet
- Pin Hole Camera DimensionsDocument1 pagePin Hole Camera Dimensionsapi-32133818No ratings yet
- ElectromagnetismDocument10 pagesElectromagnetismapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Design Your Own UniverseDocument1 pageDesign Your Own Universeapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Cause of DeathDocument3 pagesCause of Deathapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Flying Clocks - EntomologyDocument2 pagesFlying Clocks - Entomologyapi-32133818No ratings yet
- The Origins of The UniverseDocument2 pagesThe Origins of The Universeapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Handwriting Analysis Q SheetDocument1 pageHandwriting Analysis Q Sheetapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Iodine FumingDocument2 pagesIodine Fumingapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Prac 1 1Document1 pagePrac 1 1api-32133818No ratings yet
- FingerprintsDocument2 pagesFingerprintsapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Entomology Case WorksheetDocument1 pageEntomology Case Worksheetapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Blood Splatter Case StudyDocument1 pageBlood Splatter Case Studyapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Trace Evidence Case Study Question SheetDocument1 pageTrace Evidence Case Study Question Sheetapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Entomology WorksheetDocument2 pagesEntomology Worksheetapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Bloodstain Pattern Analysis Q SheetDocument3 pagesBloodstain Pattern Analysis Q Sheetapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Dna ResearchDocument2 pagesDna Researchapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Is It BloodDocument2 pagesIs It Bloodapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Paint Chips Question SheetDocument2 pagesPaint Chips Question Sheetapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Foot Length Vs HeightDocument1 pageFoot Length Vs Heightapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Microscopic EvidenceDocument1 pageMicroscopic Evidenceapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Developing Fingerprints in BloodDocument2 pagesDeveloping Fingerprints in Bloodapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2sakinah azizanNo ratings yet
- Calculate Mass of Air, Pressure at Pool Bottom, Breathing UnderwaterDocument2 pagesCalculate Mass of Air, Pressure at Pool Bottom, Breathing UnderwaterHaffiz AtingNo ratings yet
- Afrl ML WP TR 2001 4159Document1,154 pagesAfrl ML WP TR 2001 4159Rodrigo MarinNo ratings yet
- Resume MedisDocument6 pagesResume MedisRina ekaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Process 2Document8 pagesPresentation On Process 2Sourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- Wessington Catalogue June 2015Document46 pagesWessington Catalogue June 2015ritesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Cu-Psha A Matlab Software For PshaDocument26 pagesCu-Psha A Matlab Software For PshaPartha Sarathi ParhiNo ratings yet
- Carbon Fibre ReportDocument14 pagesCarbon Fibre ReportyoyotoyoNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Chapter 3 SolutionsDocument5 pagesReinforced Concrete Chapter 3 SolutionsFofer Fofe100% (1)
- Brochure Ftir Cary 630 5990-8570en Us AgilentDocument12 pagesBrochure Ftir Cary 630 5990-8570en Us AgilentMarcela RobayoNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Thermal Calculation by Rey FiedacanDocument5 pagesHeat Exchanger Thermal Calculation by Rey FiedacanRajdeepsinhNo ratings yet
- CV3012 EC3 Column Axial Bending Moment Xx1Document115 pagesCV3012 EC3 Column Axial Bending Moment Xx1Steven KuaNo ratings yet
- Welding TMCP SteelsDocument7 pagesWelding TMCP SteelsElias Kapa100% (1)
- Checklist Pekerjaan Spun PileDocument1 pageChecklist Pekerjaan Spun PileBudhi Kurniawan100% (1)
- TakengonDocument11 pagesTakengonTeguh PriadiNo ratings yet
- Simple Mass Spring SystemDocument11 pagesSimple Mass Spring SystemArindam MondalNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project File 2Document12 pagesInvestigatory Project File 2hepele8650No ratings yet
- 10 Problem For The Topic 9 & 10 Hicao GroupDocument4 pages10 Problem For The Topic 9 & 10 Hicao GroupArvin ArmojallasNo ratings yet
- Metodo ASTM D402Document5 pagesMetodo ASTM D402Roberto ChamorroNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 FUNDAMENTALS OF ARC INTERRUPTIONS (Switchgear and Protection)Document21 pagesUnit 5 FUNDAMENTALS OF ARC INTERRUPTIONS (Switchgear and Protection)sujithNo ratings yet
- Application Applicationnotes: What Are Contact Angles?Document2 pagesApplication Applicationnotes: What Are Contact Angles?Anthony GalayNo ratings yet
- Vincent PDFDocument4 pagesVincent PDFSarinKorthawornwongNo ratings yet
- Astm D3350 - 06 PDFDocument7 pagesAstm D3350 - 06 PDFRaul Humberto Mora VillamizarNo ratings yet
- Pipingchevronoffshore 2Document56 pagesPipingchevronoffshore 2Velpandian ManiNo ratings yet
- IMI CCI Product VSGIC DesuperheaterDocument4 pagesIMI CCI Product VSGIC DesuperheaterangeloNo ratings yet
- M 236 ContentDocument103 pagesM 236 ContentgeetanandnNo ratings yet
- IFEM Ch13Document32 pagesIFEM Ch13Siri RaviNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit in High-Voltage Ceramic Station Post InsulatorsDocument7 pagesShort Circuit in High-Voltage Ceramic Station Post InsulatorsJiraya15No ratings yet
- Physics Year 10 Assessment TestDocument16 pagesPhysics Year 10 Assessment TestJoyceNo ratings yet
- Determining The Work of The Thermodynamic System in Polytropic Processes PV ConstDocument2 pagesDetermining The Work of The Thermodynamic System in Polytropic Processes PV ConstTHÀNH NGUYỄN PHÚNo ratings yet