Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(Nutrition) Dental Caries
Uploaded by
Zara Sebastianne GarciaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(Nutrition) Dental Caries
Uploaded by
Zara Sebastianne GarciaCopyright:
Available Formats
DENTAL CARIES Is an infectious microbioloigic disease of the teeth that results in localized dissolution and destruction of the calcified
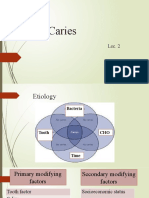
d tissues. Dev't of Dental Caries Depends on four interrelated factors: Host Bacteria Diet Time Dental plaque - a gelatinous mass of bacteria adhering to the tooth surface. Sugar + Bacteria (in plaque) = Acid Acid + Healthy tooth = Decay Two Principal Groups of Bacteria Implicate Dental Caries 1. Mutans streptococci - S. Mutans and S. Sobrinus; initiates formation of caries 2. Lactobacilli *MS and Lactobacilii - acidogenic and aciduric bacteria *MS are strongly associated with the onset of caries *Lactobacilli are assoc with active progression of cavitated lesions The Caries Balance 1. Pathological Factors - acidogenic bacteria; reduced salivary flow; frequency of fermentable carb ingestion; demineralization 2. Protective factor - Saliva flow and component; proteins, calcium, phosphate, flouride, immunoglobulin; antibacterials in saliva and extrinsicflouride, chlorhexidine iodine; remineralization If the pathological factors outweigh the protective factors, then carries progresses.
These can lead to erosion: -bacteria -acid environment -low salivary flow -poor "quality of saliva -low flouride exposure Demineralization: -critical pH 5.5 -presence of bacteria -External acid source -Internal acid source Recovery by remineralization and Decreases bacterial level Dec frequency of sucrose intake Reminarilization -increasing pH levels -sufficient Ca and phosphate present How does flouride prevent tooth decay? Flouride combats the formation of tooth decay: a. Flouride promotes the remineralization of a tooth. b. Flouride can make a tooth more resistant to the formation of tooth decay.
You might also like
- Management of Deep Carious LesionsFrom EverandManagement of Deep Carious LesionsFalk SchwendickeNo ratings yet
- Etiology of Dental CariesDocument35 pagesEtiology of Dental Cariesayshil mary sajiNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Dental CariesDocument6 pagesPrevention of Dental CariesRadhwan Hameed AsadNo ratings yet
- Carious Activity and Role of Related Bio-Environmental Interaction Review ArticleDocument4 pagesCarious Activity and Role of Related Bio-Environmental Interaction Review ArticleKhaled AdelNo ratings yet
- Microbiology of Dental Caries: Tomasz M. Karpiński, Anna K. SzkaradkiewiczDocument4 pagesMicrobiology of Dental Caries: Tomasz M. Karpiński, Anna K. SzkaradkiewiczFlorin AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Preven Lec 2Document7 pagesPreven Lec 2ريام الموسويNo ratings yet
- Etiology and Etiological TheoriesDocument14 pagesEtiology and Etiological TheoriesAmit GaurNo ratings yet
- Caries DentalDocument9 pagesCaries DentalMaría Victoria Ordóñez VerdesotoNo ratings yet
- Dental caries prevention and managementDocument9 pagesDental caries prevention and managementGaby Araya AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Dental Caries: Defination Etiology MicrobiologyDocument18 pagesDental Caries: Defination Etiology MicrobiologyRbk FairladyNo ratings yet
- Dental Caries Etiology and MicrobiologyDocument18 pagesDental Caries Etiology and MicrobiologytapovijaymNo ratings yet
- Dental CariesDocument78 pagesDental CariesSham DiyahNo ratings yet
- Cariology FellowshipDocument70 pagesCariology Fellowshipraghh roooNo ratings yet
- Current Concepts On Pathogenesis of Dental CariesDocument4 pagesCurrent Concepts On Pathogenesis of Dental CariesKelly YeowNo ratings yet
- CariesDocument99 pagesCariesKaran Arora100% (1)
- Dental Caries DevelopmentDocument8 pagesDental Caries Developmentريام الموسويNo ratings yet
- Etiology of Periodontal Diseases: Dental Plaque (Microorganisms)Document9 pagesEtiology of Periodontal Diseases: Dental Plaque (Microorganisms)محمد محمود القحيفNo ratings yet
- 61.shamita SivarajooDocument19 pages61.shamita Sivarajoobdsaimstb17No ratings yet
- HSPartners TinanoffDocument29 pagesHSPartners TinanoffbayuNo ratings yet
- 8.diet, Nutrition, and Sugar SubstitutesDocument29 pages8.diet, Nutrition, and Sugar Substituteskhush sidhuNo ratings yet
- Prevetion of Dental CariesDocument76 pagesPrevetion of Dental CariesmithunjithNo ratings yet
- Dental Caries Is A Term That Refers To Both The Disease and The Resulting LesionDocument2 pagesDental Caries Is A Term That Refers To Both The Disease and The Resulting Lesiontoha hakimNo ratings yet
- Progress of Antimicrobial Discovery AgainstDocument44 pagesProgress of Antimicrobial Discovery AgainstSITI AZKIA WAHIDAH RAHMAH ZEINNo ratings yet
- Group ADocument34 pagesGroup AMahmodol HasanNo ratings yet
- Cause of Dental Caries: BacteriaDocument1 pageCause of Dental Caries: Bacteriatirsaaa1No ratings yet
- Preventive DentsDocument12 pagesPreventive DentsMyra N SupriadiNo ratings yet
- Dental Plaque and Caries by Agbafor Chidera Autosaved)Document14 pagesDental Plaque and Caries by Agbafor Chidera Autosaved)Agbafor DeraNo ratings yet
- Section 1 Introduction: Evolution of Caries Treatment Approaches and Comorbidity With Systemic Health ProblemsDocument10 pagesSection 1 Introduction: Evolution of Caries Treatment Approaches and Comorbidity With Systemic Health ProblemsAnggita Dwi PutriNo ratings yet
- Unit 27-30 Dental Plaque, Caries, Periodontal Disease and Other Dental InfectionsDocument47 pagesUnit 27-30 Dental Plaque, Caries, Periodontal Disease and Other Dental InfectionsHBJBHNo ratings yet
- Etiology of Dental CariesDocument35 pagesEtiology of Dental CariesRaghu Ram100% (2)
- Caries 2Document37 pagesCaries 2samar yousif mohamedNo ratings yet
- Operative Assignment: Dental CariesDocument10 pagesOperative Assignment: Dental CariesAlaa MagdyNo ratings yet
- Lec2/ Epidemiology of Dental CariesDocument7 pagesLec2/ Epidemiology of Dental Cariesمحمد العراقيNo ratings yet
- Lec2/ Epidemiology of Dental CariesDocument7 pagesLec2/ Epidemiology of Dental Cariesمحمد العراقيNo ratings yet
- Aetiology of Periodontal Disease NUBDocument14 pagesAetiology of Periodontal Disease NUBpvsmj5kdk4No ratings yet
- Dental Plaque and Dental CariesDocument17 pagesDental Plaque and Dental CariesAbdullah EmadNo ratings yet
- 2 - Dental Caries-Pathology1Document13 pages2 - Dental Caries-Pathology1حمزة تلاحمةNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentelishaNo ratings yet
- Dental Caries SeminarDocument119 pagesDental Caries SeminarManva Monish88% (8)
- Lec 11 Dental CariesDocument8 pagesLec 11 Dental Cariesاحمد حسن جاسم كاظمNo ratings yet
- Tooth DecayDocument28 pagesTooth DecayRyan Carlo CondeNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Dental Caries: Name:Huda Khan ROLL #: 753Document33 pagesPrevention of Dental Caries: Name:Huda Khan ROLL #: 753Hudh HudNo ratings yet
- Dental PlaqueDocument19 pagesDental PlaqueKhalid MortajaNo ratings yet
- Plaque Id GelDocument13 pagesPlaque Id Gelsmiledesigner_13No ratings yet
- Dental CariesDocument36 pagesDental Cariesnight-stalker1996No ratings yet
- Nutrients: Streptococcus Mutans, Caries and Simulation ModelsDocument9 pagesNutrients: Streptococcus Mutans, Caries and Simulation ModelsChandra RonikaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19 Rampant CariesDocument12 pagesLecture 19 Rampant CariesKhaled Al-haddadNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of Dental CariesDocument11 pagesEpidemiology of Dental CariesAsad Khan5556No ratings yet
- Dental CariesDocument209 pagesDental Cariesdrhiteshk75% (4)
- Referat EnglezaDocument6 pagesReferat EnglezaCorinaNo ratings yet
- Dental PlaqueDocument10 pagesDental PlaqueAnonymous 4FVm26mbcONo ratings yet
- Dental Caries: by DR: Hanan Eid GamalDocument107 pagesDental Caries: by DR: Hanan Eid Gamalruchika100% (1)
- More Milk, Stronger Teeth? (Part I)Document4 pagesMore Milk, Stronger Teeth? (Part I)Nicole StoicaNo ratings yet
- Community Lec5Document23 pagesCommunity Lec5woow0217No ratings yet
- A:Essential RequirementsDocument8 pagesA:Essential Requirementssaged loaiNo ratings yet
- Dental Public Health MSA BDocument83 pagesDental Public Health MSA BMustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- Oral Microorganisms: Bella Fernanda, DRGDocument26 pagesOral Microorganisms: Bella Fernanda, DRGandre gidion laseNo ratings yet
- Defining, Classifying, and Placing Incipient Caries Lesions in PerspectiveDocument23 pagesDefining, Classifying, and Placing Incipient Caries Lesions in Perspectiveenrique rosasNo ratings yet
- Overview On Concepts of Dental Caries Hemabs, Saloni Goenka, Poorva VermaDocument9 pagesOverview On Concepts of Dental Caries Hemabs, Saloni Goenka, Poorva VermaAmee PatelNo ratings yet
- (RestoDent) Pathophysiology of CariesDocument30 pages(RestoDent) Pathophysiology of CariesZara Sebastianne Garcia100% (1)
- RAC-IW Oral Hygiene LectureDocument25 pagesRAC-IW Oral Hygiene LectureZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- SS ProsthoDocument11 pagesSS ProsthoZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- IMPACTIONDocument9 pagesIMPACTIONZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- Student Org WaiverDocument1 pageStudent Org WaiverZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- (RestoDent) Dentin-Pulp ComplexDocument28 pages(RestoDent) Dentin-Pulp ComplexZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- (RestoDent) Caries Accdg To SurfacesDocument41 pages(RestoDent) Caries Accdg To SurfacesZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- (RestoDent) Pathophysiology of CariesDocument30 pages(RestoDent) Pathophysiology of CariesZara Sebastianne Garcia100% (1)
- (RestoDent) EnamelDocument42 pages(RestoDent) EnamelZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- (Gen Ana) PharynxDocument51 pages(Gen Ana) PharynxZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- (RestoDent) Components of Cavity PrepDocument47 pages(RestoDent) Components of Cavity PrepZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- (RestoDent) CariesDocument17 pages(RestoDent) CariesZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- (RestoDent) Caries Accdg To SurfacesDocument41 pages(RestoDent) Caries Accdg To SurfacesZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- (GenPath) Cellular InjuryDocument73 pages(GenPath) Cellular InjuryZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- (RestoDent) EnamelDocument42 pages(RestoDent) EnamelZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- (RestoDent) Dentin-Pulp ComplexDocument28 pages(RestoDent) Dentin-Pulp ComplexZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- (Gen Ana) Craniovertebral JointsDocument57 pages(Gen Ana) Craniovertebral JointsZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- Cranial Fossae: Zara Denisse Garcia Ella Carmela Chavez Mae Nen Vedeja Mardred MarceloDocument40 pagesCranial Fossae: Zara Denisse Garcia Ella Carmela Chavez Mae Nen Vedeja Mardred MarceloZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- MicroDocument3 pagesMicroZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- Membrane Potential (Gen Physio)Document29 pagesMembrane Potential (Gen Physio)Zara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- (Nutrition) FatsDocument3 pages(Nutrition) FatsZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- (Nutrition) MineralsDocument3 pages(Nutrition) MineralsZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- Microbial DiversityDocument36 pagesMicrobial DiversityAndrea IndadañoNo ratings yet
- Membrane and Action Potential (Gen Physio)Document24 pagesMembrane and Action Potential (Gen Physio)Zara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- (Nutrition) ProteinsDocument3 pages(Nutrition) ProteinsZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- (Micro Bio) Microbial NutritionDocument61 pages(Micro Bio) Microbial NutritionZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- Nervous TissueDocument71 pagesNervous TissueZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The BackDocument43 pagesMuscles of The BackZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- Duodenum, Pancreas, and Hepatic Portal VeinDocument22 pagesDuodenum, Pancreas, and Hepatic Portal VeinZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- Recovering from Emotionally Immature Parents: Practical Tools to Establish Boundaries and Reclaim Your Emotional AutonomyFrom EverandRecovering from Emotionally Immature Parents: Practical Tools to Establish Boundaries and Reclaim Your Emotional AutonomyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (201)
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossFrom EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)