Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electromagnetic Waves
Uploaded by
Jana JanardhanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electromagnetic Waves
Uploaded by
Jana JanardhanCopyright:
Available Formats
Electromagnetic waves
Dipole moment Charge q oscillating as y(t) produces the same electric field as q/2 moving as y(t) and q/2 moving as y(t) The latter is an oscillating dipole
d y ( t ) = qy( t ) = d 0cos( t )
q d0= 0 0 y 0
Electric field in terms of dipole moment
q E( t ) = a( t r / c ) sin 0 0 0 r c 0 E( t ) = d y ( t r / c ) sin 0 0 0 r c
Current
& I (t ) = q (t ) & = lI (t ) & & d
y
I (t ) = Isin(t )
Electric field in terms of current
lI E (t ) = cos[ (t r / c)]sin 0 0 0 r c
Energy Density
0 0 0 0 U = 0 + E B 0 00 0 0 0 0 U = 0 + 0 E E 0 0 0 c U = 0 E
0
0 c = 0 0
0
Average Energy
E ( x, t ) = E cos(t kx)
E
0
= E /0
0 0 U = 0 E 0
Energy Flux vector
0 0 0 0 r q y0 sin S = U c= 2 r 22 0 0 c 0 r
Radiation pattern
http://ocw.mit.edu/ans7870/8/8.02T/f04/visualizations/light/01-DipoleRadiation/01-Dipole_320.html
Electric Dipole Oscillator
SPK/SB
Dipole radiation
SPK/SB
SPK/SB
TV Antenna
Car Antenna
Electromagnetic spectrum
The Radio Milky Way
NRAO Green Bank
Cosmic microwave background fluctuation
Cosmic Background Explorar
Ultraviolet Galaxy
NASA/JPL-Caltech/SSC
(1,2,0)
x
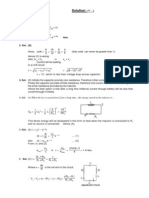
A dipole of length 1 m is oscillating along y axis (see figure). The frequency of oscillating current, driving the dipole is 3x106 radian/sec .The amplitude of the current is 2A. Find the magnitude and the direction of field at (1,2,0)
x z
Magnitude of the electric field
Il sin E= 0 0 0 c r
Il r sin E= 0 0 0 0 c r
Accelerating charge gives rise to radiation Sinusoidal motion of charge gives rise to electromagnetic radiation gives rise to plane electromagnetic wave at a large distance. The direction of electric field, magnetic field and propagation are mutually perpendicular to each other. Electric and magnetic field are in phase.
1. FEYNMAN LECTURES ON PHYSICS VOL I Author : RICHARD P FEYNMAN, IIT KGP Central Library Class no. 530.4 2. OPTICS Author: EUGENE HECHT IIT KGP Central Library Class no. 535/Hec/O Images from Astra's Stellar Cartography Demo
You might also like
- (Continued) : The Laws of Electromagnetism Maxwell's Equations Displacement CurrentDocument21 pages(Continued) : The Laws of Electromagnetism Maxwell's Equations Displacement CurrentJai ChangNo ratings yet
- Lecture6 Ch3 PhotonsDocument17 pagesLecture6 Ch3 PhotonsKenny H G Jiménez100% (1)
- ElectrodynamicsDocument68 pagesElectrodynamicsFer MoncadaNo ratings yet
- HFE0611 BennettDocument4 pagesHFE0611 Bennettarunkr1No ratings yet
- CH 8Document47 pagesCH 8Antoine Dumont NeiraNo ratings yet
- Radio and Light Radiations From A Moving Charged Particle Are Different 2016Document12 pagesRadio and Light Radiations From A Moving Charged Particle Are Different 20161357531No ratings yet
- Introduction to Solid State Physics LectureDocument28 pagesIntroduction to Solid State Physics Lecturem4_prashanthNo ratings yet
- Topper Sample Paper 3 Class XII-Physics Solutions: Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 70Document14 pagesTopper Sample Paper 3 Class XII-Physics Solutions: Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 70coolspanky_227053No ratings yet
- EM Waves and Quantum Mechanics LectureDocument19 pagesEM Waves and Quantum Mechanics LectureJayeshAtreyaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic field effect in atomic ionizationDocument5 pagesMagnetic field effect in atomic ionizationz.umul9031No ratings yet
- Optics Express Vol. 16, Issue 5, Pp. 3178-3190 (2008)Document13 pagesOptics Express Vol. 16, Issue 5, Pp. 3178-3190 (2008)abrownbk.ruNo ratings yet
- Physics HandbookDocument10 pagesPhysics HandbookNational Physical Laboratory100% (1)
- Solution:: DT DQ e RC C V BDocument5 pagesSolution:: DT DQ e RC C V BAritra LahiriNo ratings yet
- Lecture4 PDFDocument7 pagesLecture4 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics Part IDocument62 pagesWave Optics Part IAt TanwiNo ratings yet
- Del Giudice, Emilio Preparata, Giuliano Vitiello, Giuseppe - Water As A Free Electric Dipole Laser PDFDocument4 pagesDel Giudice, Emilio Preparata, Giuliano Vitiello, Giuseppe - Water As A Free Electric Dipole Laser PDFЮрий ЮрийNo ratings yet
- Part 8: Sources of Electromagnetic Radiation: PHYS370 - Advanced ElectromagnetismDocument37 pagesPart 8: Sources of Electromagnetic Radiation: PHYS370 - Advanced Electromagnetismkumar_9583No ratings yet
- Nonsequential double ionization Keldysh-type analysisDocument6 pagesNonsequential double ionization Keldysh-type analysisz.umul9031No ratings yet
- EMI and ACDocument14 pagesEMI and ACbharathNo ratings yet
- Measuring RLC Parameters & Resonant Frequencies Using OscilloscopeDocument9 pagesMeasuring RLC Parameters & Resonant Frequencies Using OscilloscopeTuan NguyenNo ratings yet
- AP621-Lect01-Basic Electron OpticsDocument92 pagesAP621-Lect01-Basic Electron OpticsHassanNo ratings yet
- Manolis KoliopoulosDocument58 pagesManolis KoliopoulosSushil MundelNo ratings yet
- The Advent of Quantum PhysicsDocument152 pagesThe Advent of Quantum PhysicsMary Grace Magpayo LanwangNo ratings yet
- Electrical Properties of Metals TyDocument5 pagesElectrical Properties of Metals TyNeelam KapoorNo ratings yet
- p461 PDFDocument20 pagesp461 PDFHemant SinghNo ratings yet
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2014 Practice Problem Set 11 Solutions Problem 1: Electromagnetic Waves and The Poynting VectorDocument23 pagesMassachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2014 Practice Problem Set 11 Solutions Problem 1: Electromagnetic Waves and The Poynting VectorAditiNo ratings yet
- Radiation Damping: R.P. WalkerDocument20 pagesRadiation Damping: R.P. WalkerKhurram KirmaniNo ratings yet
- Maxwell's Equations and the Transverse Nature of Light WavesDocument24 pagesMaxwell's Equations and the Transverse Nature of Light WavesFarizalNo ratings yet
- University Physics: Waves and Electricity: Dr.-Ing. Erwin SitompulDocument37 pagesUniversity Physics: Waves and Electricity: Dr.-Ing. Erwin SitompulAliNo ratings yet
- Examples of Uniform EM Plane WavesDocument26 pagesExamples of Uniform EM Plane WavesMehmar AsadNo ratings yet
- Aieee-2012 Physics SolutionsDocument5 pagesAieee-2012 Physics SolutionsAman Bhutta100% (1)
- Low-Voltage TheoryDocument10 pagesLow-Voltage Theorymichelle_lilNo ratings yet
- AIPMT - 2011:: CP Tower, IPIA, Road No.1, Kota (Raj.), PH: 0744-3040000Document22 pagesAIPMT - 2011:: CP Tower, IPIA, Road No.1, Kota (Raj.), PH: 0744-3040000TheMedNerdNo ratings yet
- Basic network elements and their propertiesDocument7 pagesBasic network elements and their propertiesarpit sharmaNo ratings yet
- EmonopolDocument3 pagesEmonopolFlavio FontanaNo ratings yet
- 1 Synchronization and Frequency Estimation Errors: 1.1 Doppler EffectsDocument15 pages1 Synchronization and Frequency Estimation Errors: 1.1 Doppler EffectsRajib MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Damping: Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544Document3 pagesMagnetic Damping: Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544mshameliNo ratings yet
- Part-A: Q.1 To Q.7 Has Four Choices (A), (B), (C), (D) Out of Which ONLY ONE Is Correct. (Q. No.1 To Q.No.4 3 Marks)Document20 pagesPart-A: Q.1 To Q.7 Has Four Choices (A), (B), (C), (D) Out of Which ONLY ONE Is Correct. (Q. No.1 To Q.No.4 3 Marks)Prashant KathuriaNo ratings yet
- Exam III PHY 2049 Summer C July 16, 2008Document7 pagesExam III PHY 2049 Summer C July 16, 2008Ytzel NëssieNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet: Electricity and MagnetismDocument3 pagesFormula Sheet: Electricity and MagnetismThivagar RajasekaranNo ratings yet
- Laser Induced Electron Acceleration in An Electromagnetic Standing Wave Wiggler With External Magnetic Tapering ParametersDocument4 pagesLaser Induced Electron Acceleration in An Electromagnetic Standing Wave Wiggler With External Magnetic Tapering ParametersijsretNo ratings yet
- T R K E T Z y X T R K B T Z y X: and B Constant On Planar "Phase Front" Wave Propagates Along K, Magnitude 2Document10 pagesT R K E T Z y X T R K B T Z y X: and B Constant On Planar "Phase Front" Wave Propagates Along K, Magnitude 2Imran ImranNo ratings yet
- 210 AC 2013 StuentsDocument28 pages210 AC 2013 StuentsKieran CullenNo ratings yet
- Interaction of Light and Matter: 8.1 Electromagnetic Waves at An InterfaceDocument34 pagesInteraction of Light and Matter: 8.1 Electromagnetic Waves at An InterfaceWilson Aponte HuamantincoNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems-Ch23-Electric Forces New Fall 2015-2014Document21 pagesSolved Problems-Ch23-Electric Forces New Fall 2015-2014believer149No ratings yet
- Chapt 3 FrenchDocument61 pagesChapt 3 FrenchSaurabh BorseNo ratings yet
- Wave Propagation PackageDocument18 pagesWave Propagation PackagealfredomatiasrojoNo ratings yet
- Em Waves JeeDocument14 pagesEm Waves JeeTobiramaNo ratings yet
- Analog Mod NotesDocument50 pagesAnalog Mod NotesSmriti Rai M.Tech. Dept. of Electronics Engg. IIT (BHU)No ratings yet
- Formulas Optica Ondulatoria (By Carrascal)Document9 pagesFormulas Optica Ondulatoria (By Carrascal)Iñaki0% (1)
- Study On The Vibration Mechanism of The Relay Coil in A Three-Coil WPT SystemDocument10 pagesStudy On The Vibration Mechanism of The Relay Coil in A Three-Coil WPT SystemZhiqiang XuNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Problems in PhysicsDocument9 pagesTheoretical Problems in PhysicsbananasausageNo ratings yet
- Drude Model Overview and AssumptionsDocument16 pagesDrude Model Overview and AssumptionsHongyang Alexander0% (1)
- Chapter 40 Electromagnetic WavesDocument2 pagesChapter 40 Electromagnetic Wavesabbh07No ratings yet
- Phys 1004 - Cheat - Sheet. Electromagnetism and WavesDocument2 pagesPhys 1004 - Cheat - Sheet. Electromagnetism and WavesNadya B.No ratings yet
- Basic ConceptsDocument11 pagesBasic ConceptsEka Nakano RahmadhaniNo ratings yet
- SEO-Optimized Title for Physics Problems on Cylinder Suspended by Spring, Magnetic Field Induced EMF, and MoreDocument11 pagesSEO-Optimized Title for Physics Problems on Cylinder Suspended by Spring, Magnetic Field Induced EMF, and Moresanchit199617100% (1)
- ch32 PDFDocument14 pagesch32 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet