Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cardiac Monitor: Arterial Lines
Uploaded by
Jason AvellanoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cardiac Monitor: Arterial Lines
Uploaded by
Jason AvellanoCopyright:
Available Formats
CARDIAC MONITOR
PULSE OXIMETER.
SWAN GANS
ARTERIAL LINES
CENTRAL VENOUS TUBE.
NASOGASTRIC TUBE
CHEST TUBE
ENDOTRACHEL TUBE
URINARY CATHETER
TRACTHEOSTOMY TUBE
VENTILATO
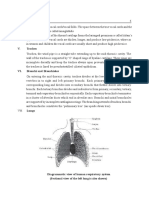
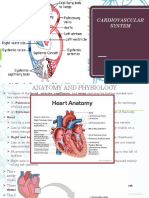
CARDIAC MONITOR a device for the continuous observation of cardiac function. It may include electrocardiograph and oscilloscope readings, recording devices, and a visual and/or audible record of heart function and rhythm. An alarm system may be set to identify abnormal rhythms or heart rates. PULSE OXIMETER is to measure the oxygen saturation level of a person. It is used to determine how many oxygen molecules are attached to the hemoglobin molecules found in the blood. A maximum of four oxygen molecules can attach themselves to one hemoglobin molecule. The normal percentage of a person would be around 90 SWAN GANS catheter is the passing of a thin tube (catheter) into the right side of the heart and the arteries leading to the lungs to monitor the heart's function and blood flow, usually in persons who are very ill. Swan-Ganz catheter a soft, flow-directed catheter with a balloon at the tip for measuring pulmonary arterial pressures.ARTERIAL LINES in catheter inserted into an artery. It is most commonly used in intensive care medicine and anesthesia to monitor the blood pressure real-time (rather than by intermittent measurement), and to obtain samples for arterial blood gas measurements. It is not generally used to administer medication. central venous tube A catheter (tube) that is passed through a vein to end up in the thoracic (chest) portion of the vena cava (the large vein returning blood to the heart) or in the right atrium of the heart. A chest tube is a hollow tube placed between the lung and the chest wall (pleural space). The chest tube provides a way to drain air, blood or other fluids that may have accumulated in the pleural space. The pleural space normally has a small amount of fluid within ENDOTracheal tube is a catheter that is inserted into the trachea in order for the primary purpose of establishing and maintaining a patent airway and to ensure the adequate exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. URINARY C retained by means of a balloon at the tip that is inflated with sterile water. The balloons typically come in two different sizes: 5 cm3 and 30 cm3. They are commonly made in silicone. TRACHESTOMY TUBE To relieve breathing difficulties or upper airway obstruction. To improve respiratory function by reducing length of the airway in special lung conditions.If you inherited abnormality of larynx or trachea.If you have inability to swallow or cough with an impaired vocal function. rubber or natural rubber. VENTILATOR In its simplest form, a modern positive pressure ventilator consists of a compressible air reservoir or turbine, air and oxygen supplies, a set of valves and tubes, and a disposable or reusable "patient circuit". The air reservoir is pneumatically compressed several times a minute to deliver roomair, or in most cases, an air/oxygen mixture to the patient. If a turbine is used, the turbine pushes air through the ventilator, with a flow valve adjusting pressure to meet patient-specific parameters. When overpressure is released, the patient will exhale passively due to the lungs' elasticity, the exhaled air being released usually through a one-way valve within the patient circuit called the patient manifold. The oxygen content of the inspired gas can be set from 21 percent (ambient air) to 100 percent (pure oxygen). Pressure and flow characteristics can be set mechanically or electronically.
You might also like
- Monitoring Equipment in the ICUDocument5 pagesMonitoring Equipment in the ICUMon ManguilinNo ratings yet
- EQUIPMENTS in ICCUDocument5 pagesEQUIPMENTS in ICCUrhyanne100% (1)
- The Respiratory SystemDocument13 pagesThe Respiratory SystemEduardson PHNo ratings yet
- Icu Equipments BY: Presented Bhupender Kumar MehtoDocument35 pagesIcu Equipments BY: Presented Bhupender Kumar Mehtobhupendermehto012No ratings yet
- EP Lec 4 - Medical-Surgical Equipment in Acute Care SettingsDocument27 pagesEP Lec 4 - Medical-Surgical Equipment in Acute Care SettingsMichels Garments S.H Nawaz HosieryNo ratings yet
- Nasal Cavity. The Nasal Cavity, Also Known As TheDocument11 pagesNasal Cavity. The Nasal Cavity, Also Known As TheWilly Chandra HermawanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Gemalyn BulawanDocument122 pagesRespiratory System: Gemalyn BulawanSofia Deneise AnasariasNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Machine1Document9 pagesAnesthesia Machine1shoibyNo ratings yet
- Chest Tube Care Basics: Drainage, Positioning and MonitoringDocument5 pagesChest Tube Care Basics: Drainage, Positioning and MonitoringRaina Ginella DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Chest Tube Therapy Care GuideDocument14 pagesChest Tube Therapy Care GuideJake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- Concept On Oxygenation: Gas TransportDocument135 pagesConcept On Oxygenation: Gas TransportNikko MelencionNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemsDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemsTrishna ShahNo ratings yet
- Monitor and All Related LifeDocument8 pagesMonitor and All Related LifeJeraldine GumpalNo ratings yet
- Swan Ganz Catheterization GuideDocument24 pagesSwan Ganz Catheterization GuideArchana Maharjan100% (1)
- Machanical Ventilator Nursing Care PalnDocument13 pagesMachanical Ventilator Nursing Care PalnAnnie Priscilla100% (1)
- Medical PhysicsDocument24 pagesMedical PhysicsgeethaNo ratings yet
- Heart Lung MachineDocument27 pagesHeart Lung MachineAnonymous 4WYu0OKJpENo ratings yet
- ICU EquipmentDocument12 pagesICU EquipmentAbeer NooreldeenNo ratings yet
- Chest Trauma Diagnosis and ManagementDocument19 pagesChest Trauma Diagnosis and ManagementRhetsckid CbNo ratings yet
- Resumen Article IcDocument14 pagesResumen Article Icapi-689165620No ratings yet
- Emergency UltrasoundDocument32 pagesEmergency UltrasoundChoga ArlandoNo ratings yet
- Assisting in Thoracostomy Tube InsertionDocument54 pagesAssisting in Thoracostomy Tube Insertioncoosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- 11 VentDocument69 pages11 VentOMER GOSHNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation Part 1Document86 pagesOxygenation Part 1Shaira Mae Fangon De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilatior: CCC C CCCCCCCCCC PDocument4 pagesMechanical Ventilatior: CCC C CCCCCCCCCC PWendz Palma-TudaNo ratings yet
- Biofluid Assignment 3Document6 pagesBiofluid Assignment 3Dina AssefaNo ratings yet
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- Swan GanzDocument35 pagesSwan Ganzdrivaner1No ratings yet
- Biology for Engineers - Module 3Document14 pagesBiology for Engineers - Module 3cutieNo ratings yet
- WEEK 7 - PERFUSION TECHNOLOGY v2Document44 pagesWEEK 7 - PERFUSION TECHNOLOGY v2Marc Jeff GabasaNo ratings yet
- CH 25 Respiratory AssessmentDocument14 pagesCH 25 Respiratory Assessmentهدوء النسمةNo ratings yet
- Ventilator The Basic CourseDocument117 pagesVentilator The Basic CourseTputrinya FaniddaNo ratings yet
- Care of Chest Tube Drainage & Nursing Manangement SHDocument82 pagesCare of Chest Tube Drainage & Nursing Manangement SHJoanna RemollinoNo ratings yet
- Surgical Tubes GuideDocument57 pagesSurgical Tubes GuideAli ahmedNo ratings yet
- Fundamentalof Ventilation & PacemakerDocument22 pagesFundamentalof Ventilation & PacemakerLucila Lugo100% (1)
- Module 3 Biology NotesDocument12 pagesModule 3 Biology NotesKnock KnockNo ratings yet
- Haemodynamic mo-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesHaemodynamic mo-WPS Officermconvidhya sri2015No ratings yet
- Normal Changes With Aging in The Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesNormal Changes With Aging in The Cardiovascular SystemSheenarieNo ratings yet
- Circuitary and Cannulation TechniquesDocument125 pagesCircuitary and Cannulation Techniquesshivalingam20No ratings yet
- V. Trachea: Zoology-IIDocument22 pagesV. Trachea: Zoology-IIVenkatesh JoguNo ratings yet
- Areas de WestDocument12 pagesAreas de WestYamely VargasNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary CirculationDocument4 pagesPulmonary CirculationDr Md Abedur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Automation in Heart Lung MachineDocument23 pagesAutomation in Heart Lung MachineKushal PatelNo ratings yet
- Care of Patients Undergoing Valvular Heart SurgerryDocument62 pagesCare of Patients Undergoing Valvular Heart SurgerryanusarannyaNo ratings yet
- Complex Functional Single VentricleDocument35 pagesComplex Functional Single Ventriclethecount28991No ratings yet
- Chapter V - Respiratory System: Procedures Arterial Blood Gas AnalysisDocument2 pagesChapter V - Respiratory System: Procedures Arterial Blood Gas AnalysisIndranil SinhaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology GuideDocument36 pagesCardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology GuideShield Mae BalanlayNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument3 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory SystemsJeffrey Costan100% (1)
- How Ventilators Work to Assist Lung FunctionDocument2 pagesHow Ventilators Work to Assist Lung Functionrohit860No ratings yet
- VENTILATERSDocument12 pagesVENTILATERSDeekshith KumarNo ratings yet
- Revascularizacion Miocardio 3Document16 pagesRevascularizacion Miocardio 3api-688140642No ratings yet
- Respiratory AssessmentDocument25 pagesRespiratory AssessmentLIBIN PALLUPPETTAYIL JOSE100% (2)
- Medical TerminologiesDocument14 pagesMedical TerminologiesShannine Del Rosario BeridaNo ratings yet
- Key Notes Adapted From Smeltzer Medical Surgical Nursing 11 EditionDocument5 pagesKey Notes Adapted From Smeltzer Medical Surgical Nursing 11 EditionKarla LopezNo ratings yet
- HemothoraxDocument3 pagesHemothoraxkrz05No ratings yet
- Respiratory System & ParametersDocument35 pagesRespiratory System & Parametersrobert robNo ratings yet
- Chest Tubes: By: Morgan Kraut, Bonnie Glover and Allison HildebrandDocument19 pagesChest Tubes: By: Morgan Kraut, Bonnie Glover and Allison Hildebranddebbie921100% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology of HeartDocument69 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of HeartRitu Arun Kaushik100% (1)
- What Is CPB CircuitDocument4 pagesWhat Is CPB CircuitkhanNo ratings yet
- Cat Herr IzationDocument4 pagesCat Herr IzationJason AvellanoNo ratings yet
- FurosimideDocument4 pagesFurosimideJason AvellanoNo ratings yet
- Research DesignDocument2 pagesResearch DesignJason AvellanoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJason AvellanoNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Thought ProcessesDocument2 pagesDisturbed Thought ProcessesJason Avellano100% (3)
- Discharge PlanDocument1 pageDischarge PlanRazell Diaz50% (2)
- Discharge PlanDocument1 pageDischarge PlanRazell Diaz50% (2)
- Macroeconomics II: Search and Matching: Luiz BrotherhoodDocument18 pagesMacroeconomics II: Search and Matching: Luiz BrotherhoodMartin GutovskieNo ratings yet
- 25f8e d64fDocument6 pages25f8e d64fapi-233604231No ratings yet
- 2019 Torch and Consumables Catalog: For Mechanized Plasma SystemsDocument64 pages2019 Torch and Consumables Catalog: For Mechanized Plasma SystemsRaj DomadiyaNo ratings yet
- DigiMasterIII Car Model ListDocument72 pagesDigiMasterIII Car Model ListRAGB1989No ratings yet
- EAPP w2Document13 pagesEAPP w2Elijah AquinoNo ratings yet
- El DoradoDocument12 pagesEl Doradoandrewwilliampalileo@yahoocomNo ratings yet
- 43-101 Technical Report Quimsacocha, February 2009Document187 pages43-101 Technical Report Quimsacocha, February 2009Marco Vinicio SotoNo ratings yet
- Basicline BL 21t9stDocument28 pagesBasicline BL 21t9stgabriel6276No ratings yet
- Business Plan of Easy Meal ServiceDocument41 pagesBusiness Plan of Easy Meal ServiceCeddie UnggayNo ratings yet
- Rizal's Allegorical Play 'El Consejo de Los DiosesDocument9 pagesRizal's Allegorical Play 'El Consejo de Los DiosesAlexiahree ChaiNo ratings yet
- DPT ProcedureDocument3 pagesDPT ProcedureAmit HasanNo ratings yet
- Traxonecue Catalogue 2011 Revise 2 Low Res Eng (4!5!2011)Document62 pagesTraxonecue Catalogue 2011 Revise 2 Low Res Eng (4!5!2011)Wilson ChimNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometric Determination of Triclosan Based On Diazotization Reaction: Response Surface Optimization Using Box - Behnken DesignDocument1 pageSpectrophotometric Determination of Triclosan Based On Diazotization Reaction: Response Surface Optimization Using Box - Behnken DesignFitra NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Matlab For SolidworksDocument18 pagesMatlab For SolidworksAle' AmoudiNo ratings yet
- Biology Standard XII Human Reproduction WorksheetDocument10 pagesBiology Standard XII Human Reproduction WorksheetPriya SinghNo ratings yet
- Solving Rational Equations and InequalitiesDocument5 pagesSolving Rational Equations and InequalitiesJaycint - Rud PontingNo ratings yet
- 2021 Vallourec Universal Registration DocumentDocument368 pages2021 Vallourec Universal Registration DocumentRolando Jara YoungNo ratings yet
- Mastercam 8.1 Beta 4: New Verification Engine in Beta 4! Sub-Programs Post ChangesDocument48 pagesMastercam 8.1 Beta 4: New Verification Engine in Beta 4! Sub-Programs Post ChangesSaul Saldana LoyaNo ratings yet
- Prometheus BoundDocument10 pagesPrometheus BoundPhillip HosfeldtNo ratings yet
- Vedic Astrology OverviewDocument1 pageVedic Astrology Overviewhuman999100% (8)
- Telemark PulloverDocument2 pagesTelemark Pulloverkidknits100% (1)
- Unit-2 Final KshitijDocument108 pagesUnit-2 Final KshitijShubham JainNo ratings yet
- Koh Pich Construction Company Cambodia-China Polytechnic University Daily Activities ReportDocument7 pagesKoh Pich Construction Company Cambodia-China Polytechnic University Daily Activities ReportNhoek RenNo ratings yet
- BR A Consumables Catalog ElecDocument31 pagesBR A Consumables Catalog Elecdweil1552No ratings yet
- Engineering Aspects of Food Emulsification and HomogenizationDocument325 pagesEngineering Aspects of Food Emulsification and Homogenizationfurkanturker61No ratings yet
- 2023-05-11 St. Mary's County TimesDocument40 pages2023-05-11 St. Mary's County TimesSouthern Maryland OnlineNo ratings yet
- 5-in-1 Document Provides Lessons on Trees and Environmental ConservationDocument45 pages5-in-1 Document Provides Lessons on Trees and Environmental ConservationPriya DharshiniNo ratings yet
- Stats Set-1Document4 pagesStats Set-1Harsha KSNo ratings yet
- Surface Roughness Measurement - MitutoyoDocument2 pagesSurface Roughness Measurement - MitutoyoSelvaraj BalasundramNo ratings yet
- 2206 - Stamina Monograph - 0 PDFDocument3 pages2206 - Stamina Monograph - 0 PDFMhuez Iz Brave'sNo ratings yet