Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Audit Con Solid Taed Notes
Uploaded by
hussainf04Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Audit Con Solid Taed Notes
Uploaded by
hussainf04Copyright:
Available Formats
Credit approval: valuation and allocation Shipping? Check sales invoices Sales returns? Receiving Order online?
No need for a sales ordering department If the auditor is concerned with completeness, he or she would test the client's controls that are designed to determine that all sales that occur are recorded. These controls could include the entity accounting for all prenumbered shipping documents, which provide the basis for recording sales, to determine that none have been omitted. An integrated test facility is a method of testing programmed controls by creating a small subsystem within the regular EDP system. Dummy files and records are appended to existing client files and fictitious test transactions, specifically coded to correspond with the dummy files and records, are introduced into a system together with actual transactions. Control procedures over the payroll function include the reconciliation of job time tickets to employee clock card hours. Purchasing agent has authority to purchase, not authority to initiate purchases. If the auditors determine that the client's internal control is effective at preventing or detecting misstatements, they will assess the control risk low. They can then accept a higher level of detection risk, and the substantive testing can be decreased. The supporting documentation should be canceled by the check signer (usually the treasurer) and not the accounts payable department. Once a general understanding of internal control has been obtained, the auditor only needs to test specific controls if it is efficient to do so. If the general internal control system appears to be well designed, testing specific controls to verify their efficiency can lead to a reduction in the assessed level of control risk. Hopefully, the amount of substantive testing can then be reduced because the desired level of detection risk does not need to be so low. This decrease in substantive testing can lead, possibly, to an overall reduction in the time and cost of performing the audit. Conversely, if the internal control appears to be weak, no benefit is gained by testing those controls further. It is not likely that those weaknesses can be overcome. Risk is the basic fundamental concept that underlies the audit process. It is the acceptance by auditors that there is some level of uncertainty in performing the audit function. In identifying fraud risks, the auditors consider various fraud risk factors that may be indicative of fraud. The factors are organized around three fundamental conditions necessary for the commission of fraud and have been shown to be present in circumstances where frauds have occurred. The CPA must keep gathering evidence until the perceived audit risk is reduced to an appropriately low level (4 percent in this case). Mathematically, audit risk is the product of three components: inherent risk, control risk, and the auditor's detection risk. Inherent risk has already been assessed as 80 percent and control risk as 20 percent. At this point, .80 times .20 gives .16 (or 16 percent risk). The auditors quandary is to determine the amount of substantive testing that still needs to be performed to reduce detection risk enough to drop overall audit risk from this 16 percent to 4 percent (or .04). Or, stated differently, .80 x .20 x DR = .04. Only 25 percent or .25 will reduce the .16 down to .04. When detection risk drops to 25 percent, then .80 x .20 x .25 will equal the desired level of audit risk of 4 percent.
Materiality: use BS accounts Competent, sufficient evidence? Audit program Illegal acts effect f/s directly: Illegal acts that have a material but indirect effect on the financial statements are those acts that are removed from transactions and events reflected in the financial statements. The auditor should be aware that they have occurred, although an audit provides no assurance that they will be detected. Kiting: When money is moved from one account to another but the deposit and the withdrawal are recorded in different time periods to inflate the amount of cash being reported, the term kiting is used to identify that fraud. The operational audit is usually performed by internal auditors in order to evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness of some parts of an organization in achieving specific goals. Quality control comprises the methods used to ensure that the firm meets its professional responsibilities to clients and others. There are five elements of quality control: (1) independence, integrity and objectivity; (2) personnel management; (3) acceptance and continuation of clients and engagements; (4) engagement performance; and (5) monitoring. None of these qualities pertain to advertising or marketing the business. If you are a partner where an audit for a public company is performed you are automatically a covered member (perform clerical duties does not a covered member) While Bravo is involved in a suit related to its audit client, independence is not impaired in this situation unless Bravo initiates a cross claim against client management or the audit client also initiates a lawsuit against the auditor Statements that use the word "should" are considered "presumptively mandatory." As stated in another answer choice, presumptively mandatory standards do impose a requirement on the auditor, but the auditor may depart in rare cases from such standards if justification for the departure is documented.
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Regulation NotesDocument3 pagesRegulation Noteshussainf04No ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Secured Party Rights to Purchase CollateralDocument4 pagesSecured Party Rights to Purchase Collateralhussainf04No ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Regulation Note2Document8 pagesRegulation Note2hussainf04No ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Regulation NotesDocument3 pagesRegulation Noteshussainf04No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- 08 Hands On Activity 222 ARG DelacruzDocument6 pages08 Hands On Activity 222 ARG DelacruzFrancis CaminaNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- 1.0 HsemsDocument47 pages1.0 HsemsQizz92100% (4)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- 5S (Methodology) : 5S Is The Name of A Workplace Organization Method That Uses A List ofDocument4 pages5S (Methodology) : 5S Is The Name of A Workplace Organization Method That Uses A List ofaneet aroraNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Targeted SelectionDocument16 pagesTargeted SelectionSpeter Dan100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- ErpmDocument19 pagesErpmakshay kushNo ratings yet
- Value Management in Nigerian ConstructionDocument95 pagesValue Management in Nigerian ConstructionIgwe Isuanaoma100% (2)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Adekta Marbun Gizi 1 A Jurnal 2Document7 pagesAdekta Marbun Gizi 1 A Jurnal 2Levi AnggrainiNo ratings yet
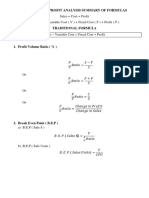
- CVP Formulas SummaryDocument2 pagesCVP Formulas SummaryNitish VermaNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- CB & OR SOP Final July 3-2018 PDFDocument38 pagesCB & OR SOP Final July 3-2018 PDFbirhane gebreegziabiherNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- 11.2. Annexure (11.2) RACI MatrixDocument2 pages11.2. Annexure (11.2) RACI Matrixmanishcsap3704No ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- We Look Into The Future Keeping The Present in MindDocument48 pagesWe Look Into The Future Keeping The Present in MindSiddhesh SawantNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
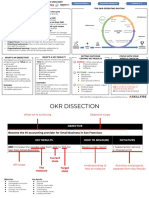
- Okr Cheat Sheet: Objective (Ideally 1) Key Results (Ideally 3-5) Initiatives ( 1)Document2 pagesOkr Cheat Sheet: Objective (Ideally 1) Key Results (Ideally 3-5) Initiatives ( 1)Tùng Hoàng50% (2)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- 2-95 pgs-OK ISO 9000-2000 LEAD AUDITOR COURSEDocument96 pages2-95 pgs-OK ISO 9000-2000 LEAD AUDITOR COURSEDaun KelorNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Transportation Manager or International Manager or Logistics SupDocument3 pagesTransportation Manager or International Manager or Logistics Supapi-78592002No ratings yet
- Capable of Being Foretold: Found in The Ordinary Course of EventsDocument2 pagesCapable of Being Foretold: Found in The Ordinary Course of EventsIskandarAminudinNo ratings yet
- Embracing: Low-Code DevelopmentDocument8 pagesEmbracing: Low-Code DevelopmentMridul HakeemNo ratings yet
- Strategic Decision Making ProcessDocument34 pagesStrategic Decision Making ProcessArpita PatelNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 DR ShantalDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 DR ShantalBishoy EmileNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13, Taped Quiz: Table 13-9Document2 pagesChapter 13, Taped Quiz: Table 13-9Jay REyNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- PMP ITTO Process Chart PMBOK Guide 6th Edition-1aDocument14 pagesPMP ITTO Process Chart PMBOK Guide 6th Edition-1aSyed SadiqNo ratings yet
- Nice Example of Dissertation in Management-SMEDocument60 pagesNice Example of Dissertation in Management-SMEAlex88% (24)
- Essentials of Contemporary Management: Final Exam Project Prof. Dr. Rania El-Reedy Reham Samir Alaa Sobhy Rana SamirDocument16 pagesEssentials of Contemporary Management: Final Exam Project Prof. Dr. Rania El-Reedy Reham Samir Alaa Sobhy Rana SamirMohamed Raheem100% (1)
- Harpic Case Study AnalysisDocument13 pagesHarpic Case Study AnalysisSujit80% (5)
- TVLDocument8 pagesTVLtss100% (4)
- Final Thesis 123 - For MergeDocument127 pagesFinal Thesis 123 - For MergeJoevan PonceNo ratings yet
- Operational Risk Management: Himanshu Puri Assistant Professor (Finance) Iilm CmsDocument6 pagesOperational Risk Management: Himanshu Puri Assistant Professor (Finance) Iilm CmsSatvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Questions Scope PDFDocument10 pagesQuestions Scope PDFabdou madjidNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Graham Management - Leadership Competency Frameworks 2021Document70 pagesGraham Management - Leadership Competency Frameworks 2021Angie ChuNo ratings yet
- BSBPMG522 1 SummaryDocument5 pagesBSBPMG522 1 SummarySergio OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Navy Blue and Black Professional Resume PDFDocument15 pagesNavy Blue and Black Professional Resume PDFNandish NNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)