Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organizational Structure
Uploaded by
Siva Prasad KantipudiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organizational Structure
Uploaded by
Siva Prasad KantipudiCopyright:
Available Formats
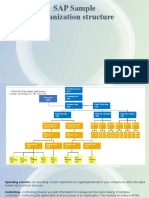
1-Organizational Structure
The definitions of organization units is a fundamental step in any project.
Company or client: A company is an organizational unit in accounting which represents a business organization according to the requirements of commercial law in a particular country and it has one local currency in which its transaction figures are recorded. It has 3 active clients Development client Testing client Production client Company Code: Company code which is a legally independent entity is created according to tax law commercial law and other financial accounting criteria. Its is an organizational unit used in accounting Plant: The plant is an operating area or branch within a company from which the goods are delivered to the customer. It is also known as Delivering Plant from SD view point. Each plant is assigned to a unique company code. A plant has the following attributes: A plant has an address. A plant has a language. A plant belongs to a country. A plant has its own material master data. Sales Organization: Its the highest level of organizational unit in SD, responsible for the sale of certain products or services. The responsibility of a sales organization may include legal liability for products and customer claims. A Sales Organization is assigned to exactly one company code. A Sales Organization is assigned to one or more Plants. Each Sales Organization has its own Master data for example its own customer and material master data as well as condition records. Distribution Channel: The Channel through which the goods reach the customers. We can use different distribution channels in S&D to provide the market with the best possible service. Distribution Channels provide a general structure for distributing goods. wholesale trade, sales to industrial customers or direct sales from a plant are typical examples of distribution channels.
Customers can be served through one or more distribution channels within a sales organization. Within a distribution channel, you can define your own master data for customers or materials as well as your own conditions and pricing. You can determine sales offices for a distribution channel. Division: A Broad range Of Products the Company is manufacturing is referred to as divisions. Material is always assigned to one division only. For each combination of sales organization and division there is a reference division for master data and sales document types. This allows the data in the reference division to be used in the original division too Sales Area: A particular combination of sales organization, distribution channel and division is known as a SALES AREA. You can assign any number of distribution channels and divisions to a sales organization Sales Office: A physical location (for example, a branch office) that has responsibility for the sale of certain products or services within a given geographical area. Sales offices are assigned to sales areas A sales office can be divided into several vendor groups. A selection field for the delivery and billing due list. Sales Group: A group of sales people who are responsible for processing sales of certain products or services. A sales group is responsible for all items in a sales document. You can assign a sales group to one or more sales offices. Storage Location: The physical location, under the plant level at which the material is stored. There may be one or more storage locations within a plant. Stocks are managed only on a quantity basis and not on a value basis at storage location level. Physical inventories are carried out at storage location level. It is possible to store material data specific to a storage location. Shipping Point: The physical location from which the items are shipped to the customer. For example a warehouse or collection of loading ramps etc. The shipping point is the top level in the organization for shipping. The shipping points in the system can be predefined, based on different combinations of : Plants, shipping conditions, loading group.
Loading point: The exact physical location where the loading of a deliver item takes place. For example, the number of a specific loading bay. A loading point is a subdivision of a shipping point. The loading point can be entered manually in the delivery header.
Assignments
Assign Company code to company: One company can have many company codes but one company has to be assigned to one company. This relation is called one to many. Assign Plant to Company Code: One or more plants can be assigned to one company code. It is recommended to create a company code for each country in which a plant is situated. Assign Sales Organization to Company code: One or more sales organizations can be assigned to a company code. This establishes a link between the SD and FI systems. Assign Distribution Channel to Sales Organization: One or more distribution channels can be allocated to a sales organizations. Assign Division to Sales Organization: As many divisions as desired can be allocated to a sales organization. Any one division can belong to several sales organizations. Set up Sales Area: In this step, the sales areas are set up. A sales area can be set up for any combination of sales organization, distribution channel and divisions. Assign Sales Office to Sales Area: One or many sales offices can be assigned to the sales area. Any one sales office can belong to several sales areas at the same time. Assign Sales Group to Sales Office: As many sales groups as desired can be assigned to the sales offices. Any one sales group can belong to several sales offices. Assign Sales Area to Credit Control Area: One or more sales areas can be assigned to a credit control area. This assignment is done to activate the credit management system for a particular sales area. Assign Sales Org- Dist. Channel Plant:
One or more plants can be assigned to a combination of sales organization and distribution channel. A plant can be assigned more than once. This assignment explains the SDMM integration.
Assign Shipping Point to Plant: As many shipping points as desired can be assigned to the plants. Any one shipping point can belong to several plants. Consistency Check ( For S&D Settings): Consistency check is performed to check whether all definitions are complete after defining the organizational units and allocated them to one another. For example whether the addresses were maintained for all sales organizations. whether the allocation to a company code was made. a sales area created. To check the entire Structure go to EC02
Common Master Data
You can define that customer master records, which have been created for each sales organization for a distribution channel (or division), are also valid in other distribution channels (or divisions). This makes it easier to create and change master records. PREREQUISITES: In Customizing for Master Data (Sales and Distribution) : Define Common Distribution Channels Define Common Divisions
2-Initialization and Master Data
Master records containing all data necessary for processing business transactions are known as Master Data. Entering more master data reduces business transaction processing time, as the system proposes the relevant master data in the business transaction. Financial Accounting and Logistics use Master data.
Customer Master Data Material Master Data Customer/material Info Sales Document
Texts Conditions Control Tables
The system automatically proposes data about customers, materials, prices, texts etc. when you create a sales document. Maintaining Master Records is crucial for remained system performance.
Types of Master Data: Customer Master Data Material Master Data Customer Material Information Record Output Master Data Condition Master Data Business Partners Business Partner Types Customers: With whom the company has entered into a legal contact. (who buys from us) Vendors: Who execute a service or delivery for the company. (from whom we buy) Personnel: Employees of the company. (our employees) Four Basic Partner Functions (mandatory) SP Sold-to party (German AG) SH Ship-to party (German WE) BP Bill-to party (German RE) PY Payer (German RG) Partner Functions are assigned to Partner Type. The partner type could be a customer, contact person or a vendor. It is mandatory to maintain the following partner functions for a partner type (customer): Sold-to Party (SP) - Places the order. Ship-to Party (SH) - Receives goods or service. Bill-to Party (BP) - Receives the invoice. Payer (PY) - Responsible for Payment. Customer Master - SH Ship to Address Goods receiving hours Tax Customer Master - BP Billing Address Customer Master - PY Terms of payment Credit limit check
Customer Master - SP Pricing Incoterms Shipping conditions
Customer Account Group: OBD2(T CODE) An account group controls the number range and properties of different fields (mandatory, optional, display, etc) in the customer master
Partner determination: Define account group Define number ranges Assign account group to number ranges Partner functions i)partner determination procedure ii)partner function in procedure iii)partner determination procedure assigmnent iv)account group function assignment
Field Control through Account Group
You might also like
- Organizational Structure & Master DataDocument35 pagesOrganizational Structure & Master Datazs_sapNo ratings yet
- SAP Org StructureDocument7 pagesSAP Org StructureBhanu ChanderNo ratings yet
- SAP Order To Cash Business ProcessDocument75 pagesSAP Order To Cash Business Processrk_solomon100% (2)
- Welcome To Level 2 Training: by LGS TeamDocument31 pagesWelcome To Level 2 Training: by LGS Teamkrishna_1238No ratings yet
- Fullfilment Process NewestDocument24 pagesFullfilment Process NewestDanias KarlmayerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Enterprise StructureDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Enterprise Structuremorya19No ratings yet
- Creation of Cost Center in SAP MM - TekslateDocument18 pagesCreation of Cost Center in SAP MM - Tekslatekpkdhar 36No ratings yet
- SD Process FlowDocument54 pagesSD Process Flowshravanz252100% (1)
- SD OverviewDocument85 pagesSD OverviewSamatha GantaNo ratings yet
- 03 - System-Wide ConceptsDocument43 pages03 - System-Wide ConceptsBoyyNo ratings yet
- Sales and Distribution OverviewDocument29 pagesSales and Distribution OverviewNitesh NigamNo ratings yet
- SD Model 1ansDocument10 pagesSD Model 1anssharathmscNo ratings yet
- 03 - System-Wide ConceptsDocument42 pages03 - System-Wide ConceptsNova Krisdayanti TafonaoNo ratings yet
- What Is OrgDocument11 pagesWhat Is OrgpramodNo ratings yet
- Introduction SAP R/3 - MM: Dr. Djamal Ziani King Saud UniversityDocument67 pagesIntroduction SAP R/3 - MM: Dr. Djamal Ziani King Saud UniversitySachin RachanaikarNo ratings yet
- Introduction SAP R/3 - MM: Dr. Djamal Ziani King Saud UniversityDocument67 pagesIntroduction SAP R/3 - MM: Dr. Djamal Ziani King Saud UniversityBaalu KathirveluNo ratings yet
- Sales Order ProcessDocument42 pagesSales Order ProcessManny AR100% (2)
- SD Flow Document 1 - Enterprise StructureDocument16 pagesSD Flow Document 1 - Enterprise Structurepranshu_sapNo ratings yet
- SD PresentationDocument43 pagesSD Presentationesameer7837No ratings yet
- TSCM-60 Sales Process OverviewDocument51 pagesTSCM-60 Sales Process Overviewsg75% (8)
- SAP Sales and Distribution OverviewDocument13 pagesSAP Sales and Distribution OverviewtupacshakrNo ratings yet
- INFS 5024 - Enterprise Systems Sales & Distribution ModuleDocument33 pagesINFS 5024 - Enterprise Systems Sales & Distribution ModulePhuoc HuynhNo ratings yet
- Introduction SAP R/3 - MM: Dr. Djamal Ziani King Saud UniversityDocument65 pagesIntroduction SAP R/3 - MM: Dr. Djamal Ziani King Saud UniversitymusicshivaNo ratings yet
- SAP SD Implementation Notes for Sales Organizations and Distribution ChannelsDocument1 pageSAP SD Implementation Notes for Sales Organizations and Distribution ChannelsOm PrakashNo ratings yet
- SAP SD Frequently Asked Questions - ERP Operations - SCN WikiDocument6 pagesSAP SD Frequently Asked Questions - ERP Operations - SCN WikiNeeraj JainNo ratings yet
- Solution Organisational Structure Final-IntexDocument39 pagesSolution Organisational Structure Final-IntexAnonymous rA8yuYJHwNo ratings yet
- O2C Cycle PresentationDocument82 pagesO2C Cycle PresentationRNo ratings yet
- SAP SD Interview QuestionsDocument11 pagesSAP SD Interview QuestionsrameshNo ratings yet
- Why Order Management Is Necessary ?Document31 pagesWhy Order Management Is Necessary ?SUMITFORBIZNo ratings yet
- General Ledger: Instructor: MANISH CHAUHANDocument53 pagesGeneral Ledger: Instructor: MANISH CHAUHANRanbeer CoolNo ratings yet
- SAP SD Overview SlideDocument25 pagesSAP SD Overview SlideSaroshNo ratings yet
- SAP Sales and Distribution Frequently Asked Combined QuestionDocument164 pagesSAP Sales and Distribution Frequently Asked Combined QuestionNitish Ranjan80% (5)
- 02-Enterprise Structures in Sales and DistributionDocument60 pages02-Enterprise Structures in Sales and DistributionSoraNo ratings yet
- SAP SD DefinitionsDocument11 pagesSAP SD DefinitionsSridharan RajagopalanNo ratings yet
- Basics of Sap SD ModuleDocument18 pagesBasics of Sap SD ModuleAnkit ChauhanNo ratings yet
- SAP SD - OverviewDocument32 pagesSAP SD - OverviewMarieTee100% (1)
- SAP Services and Organizational UnitsDocument9 pagesSAP Services and Organizational UnitssharathmscNo ratings yet
- CH 7 - Operational Issues Marketing OMDocument49 pagesCH 7 - Operational Issues Marketing OMKey OnNo ratings yet
- Sap SD Q&aDocument8 pagesSap SD Q&adhirajNo ratings yet
- SAP SD Corporate Structure QuestionDocument43 pagesSAP SD Corporate Structure Questionpradipta1984No ratings yet
- 1.SD - Sales & DistributionDocument140 pages1.SD - Sales & DistributionPuji MargariyantoNo ratings yet
- SAP SD Notes (Until Material Determination)Document8 pagesSAP SD Notes (Until Material Determination)Angelique TenerosNo ratings yet
- SAP Sales and Distribution Module (SD)Document56 pagesSAP Sales and Distribution Module (SD)Vicky Abraham100% (1)
- Sap Review Questions and Answers2Document37 pagesSap Review Questions and Answers2Jayaram prasadNo ratings yet
- SD Master Data OverviewDocument11 pagesSD Master Data Overviewchandra_kumarbrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.sap SDDocument29 pagesChapter 1.sap SDNabanita DasNo ratings yet
- Org STR ModDocument18 pagesOrg STR ModmkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- Sap SD Certification Preparation Self NotesDocument24 pagesSap SD Certification Preparation Self NotesBhuchitra BorgohainNo ratings yet
- SAP ProcurementDocument6 pagesSAP ProcurementyusufzainasirNo ratings yet
- TECHNICAL STUDY: PRODUCT, LOCATION, SCHEDULEDocument79 pagesTECHNICAL STUDY: PRODUCT, LOCATION, SCHEDULEJelyne PachecoNo ratings yet
- SAP Enterprise Structure Concept and Configuration Guide: A Case StudyFrom EverandSAP Enterprise Structure Concept and Configuration Guide: A Case StudyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Purchasing, Inventory, and Cash Disbursements: Common Frauds and Internal ControlsFrom EverandPurchasing, Inventory, and Cash Disbursements: Common Frauds and Internal ControlsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Comprehensive Case Study In TOGAF® 10: Case Studies in Software Architecture & Design, #1From EverandComprehensive Case Study In TOGAF® 10: Case Studies in Software Architecture & Design, #1No ratings yet
- Visit For More Documents: Tables in SapDocument18 pagesVisit For More Documents: Tables in SapSiva Prasad KantipudiNo ratings yet
- SAP Commands TcodesDocument4 pagesSAP Commands TcodesSiva Prasad KantipudiNo ratings yet
- Visit For More Documents: Tables in SapDocument18 pagesVisit For More Documents: Tables in SapSiva Prasad KantipudiNo ratings yet
- Pricing in SAP SD - Create New Condition Types and ProcedureDocument1 pagePricing in SAP SD - Create New Condition Types and ProcedureSiva Prasad KantipudiNo ratings yet
- ContractsDocument15 pagesContractsluhar2No ratings yet
- Rancang Bangun Sistem Informasi Penjualan Toko Kelontong Winda SlemanDocument16 pagesRancang Bangun Sistem Informasi Penjualan Toko Kelontong Winda Slemanpetty riantiNo ratings yet
- Unlock Networking Possibilities With CloudDocument16 pagesUnlock Networking Possibilities With CloudthedreafNo ratings yet
- Click To Edit Master Title Style Crawl, Walk, RunDocument43 pagesClick To Edit Master Title Style Crawl, Walk, RunFlavio XongasNo ratings yet
- Marrow E4 FMT 2Document151 pagesMarrow E4 FMT 2Cherry KolaNo ratings yet
- Conectividad para Sistemas Industriales Jun 2018Document49 pagesConectividad para Sistemas Industriales Jun 2018Cristian TorresNo ratings yet
- Your Order Has Been ApprovedDocument5 pagesYour Order Has Been ApprovedSUBA NANTINI A/P M.SUBRAMANIAMNo ratings yet
- Ipv4 Address Classes PDFDocument2 pagesIpv4 Address Classes PDFAmol IngleNo ratings yet
- Banlga Text To Bangla Sign Language Parvez For ConferenceDocument6 pagesBanlga Text To Bangla Sign Language Parvez For ConferenceDr. Muhammad Aminur RahamanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Chapter 1 Understanding Computers 12th Edition Overview of Understanding Computers PDFDocument84 pagesDokumen - Tips - Chapter 1 Understanding Computers 12th Edition Overview of Understanding Computers PDFMuhammad ArslanNo ratings yet
- CVJuan David Ramírezdelos RíosDocument1 pageCVJuan David Ramírezdelos Ríositzel083No ratings yet
- Simplified Cantera User Guide - Python Edition 2015Document6 pagesSimplified Cantera User Guide - Python Edition 2015Jonb_86100% (1)
- Date Sheet (MST-I)Document12 pagesDate Sheet (MST-I)Tauqeer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Langdo Led Lighting Co.,LimitedDocument24 pagesLangdo Led Lighting Co.,LimitedRudi CressaNo ratings yet
- ICT158 Workshop 7Document2 pagesICT158 Workshop 7Jaya MathiNo ratings yet
- Low Cost PCO Billing Meter PDFDocument1 pageLow Cost PCO Billing Meter PDFJuber ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Power Point Chapter - 15Document6 pagesPower Point Chapter - 15Shahwaiz Bin Imran BajwaNo ratings yet
- Fabrice CVDocument2 pagesFabrice CVAnonymous 2v7rI0HjNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbine Generator SoftwareDocument3 pagesWind Turbine Generator SoftwareamitNo ratings yet
- Malappuram Sahodaya Aptitude Test EXAMINATION 2016-17: General InstructionsDocument7 pagesMalappuram Sahodaya Aptitude Test EXAMINATION 2016-17: General InstructionsRamziya JabirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PPT CondensedDocument5 pagesChapter 1 PPT CondensedRaymond GuillartesNo ratings yet
- MOAC Virtual Lab ExercisesDocument3 pagesMOAC Virtual Lab ExercisesJyoti PatelNo ratings yet
- PDADocument38 pagesPDASaima NazNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - IMEDDocument37 pagesUnit 1 - IMEDAlishka RawatNo ratings yet
- Cut Over Activities - Plant Maintenance - SAP Easy Access - SAP BlogsDocument7 pagesCut Over Activities - Plant Maintenance - SAP Easy Access - SAP BlogsOmprakashNo ratings yet
- 2010 PAARL Standards For Academic LibrariesDocument6 pages2010 PAARL Standards For Academic LibrariesChristian Robert NalicaNo ratings yet
- DFFDocument6 pagesDFFShailesh WagholeNo ratings yet
- Battle of The Giants - Comparing Kimball and InmonDocument15 pagesBattle of The Giants - Comparing Kimball and InmonFelipe Oliveira GutierrezNo ratings yet
- PC Programming Manual: KX-TDA30/KX-TDA100 KX-TDA200/KX-TDA600Document842 pagesPC Programming Manual: KX-TDA30/KX-TDA100 KX-TDA200/KX-TDA600anon_588155774No ratings yet
- Pervasive Healthcare Computing: EMR/EHR, Wireless and Health MonitoringDocument3 pagesPervasive Healthcare Computing: EMR/EHR, Wireless and Health MonitoringPajak RedikonNo ratings yet
- Accounting 12 Course OutlineDocument3 pagesAccounting 12 Course OutlineKenrose LaguyoNo ratings yet