Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SAP New GL Migration Phases
Uploaded by
Tani ShabOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SAP New GL Migration Phases
Uploaded by
Tani ShabCopyright:
Available Formats
SAP New GL Migration Phases
Migration is divided into six phases. 1. Setup Phase You perform few manual confirmations in this phase such as data volume and if one total table is enough or if more than one total table are required due to large data volume. Migration plan is created in this step and company codes are included in migration plan. You can create more than one migration plans. Each company code can only be assigned to one migration plan. It might be appropriate to assign the company codes with different fiscal years variant to different migration plan as migration date is fixed for migration plan. You can also introduce new concepts such as segment or document splitting in this phase. Validation can be created to ensure data quality during migration and reduce errors after migration. You can configure validations as warnings only during Phase1 and errors in Phase2. This way you get chance to resolve issues during Phase1 without interrupting work. 2. Checkup Phase In this phase, multiple check programs are run to check consistency of the system. For example, profit center master data is checked for segment assignment, if the segments are active. There are additional manual confirmation steps to ensure system is ready for migration. 3. Preparation Phase In this phase, you check various things such as ledger comparison to ensure we are ready for Migration Phase. 4. Migration Phase In this phase, data is copied from Classic GL to New GL. You should first back up the data in this phase in case things go wrong. You then build worklists of documents to be migrated for Phase0 and Phase1. Balance carry forward and open items are copied in Phase0 and data is copied to New GL table FAGLFLEXT. Additional details such as segment or splitting information will need to be updated in additional steps, if appropriate. In Phase1, documents are posted in both Classic GL and New GL. You can use this phase to identify and resolve issues. 5. Validation Phase In this phase you validate and test final times with the quality data you now have in the system. This Phase is the last opportunity to reset and cancel the migration. 6. Activation Phase In this phase, you finally activate New GL and deactivate various classic GL functions that are no longer required such as Classic GL PCA, Reconciliation Ledger, Special ledgers etc. The migration has now completed.
SAP New GL Migration Cockpit
Migration Cockpit is a tool to simplify migration to New GL. SAP delivers the tool when you buy service based migration. Migration Cockpit contains a process tree with activities in logical sequence specific to scenarios. Activities can generally be divided into Manual Confirmation, Transactions and Check Programs. Manual confirmation requires user to confirm if certain steps have been performed. Transaction activity requires user to perform certain transactions such as postings. Check program checks system for consistency. For example, if Segment has been introduced, check program checks for the existence of segment master data. You can store start and end dates of activities. Cockpit also stores status of activities and system logs
SAP New G/L
With MYSAP ERP releases (ECC 5.0 onwards) SAP introduced New GL functionality. Most of the User interfaces and transactions remain same, however internal architecture and available functionality has changed significantly. Need for the Changes SAP mentions need to satisfy various accounting principles quickly, faster period end close, supporting management and segment reporting and reconcile data in real time as some of the reasons for New and enhanced functionality. All of these are valid reasons. When SAP introduced G/L functionality in R/3, there was a clear demarcation between Financial Accounting (FI) and Controlling (CO) modules and it was stressed that FI is to be used only for external reporting and CO to be used for internal reporting. Business users always had tough time over this difference because accounting department has always seen these two functions as one. Also, accounting landscape has changed over the period of time and standard SAP functionality was not able to meet the requirements. SAP clients came up with all kind of innovative solutions including modifying standard system. As, it is always a bad idea to anger people with money (Finance department), New G/L attempts to satisfy financial users by giving them a single unified tool for all the reporting needs.
Architectural changes Ledger Concept - Earlier Business had to deal with different ledgers in different modules. Classic G/L Ledger for legal reporting, Reconciliation ledger to reconcile CO with FI, COGS ledger for Cost of Sales accounting, Special Purpose Ledgers to meet special reporting requirements. Users had to run thru all these different modules to extract reports. FI and CO also had to be manually reconciled. Now, all these ledgers are combined in G/L by introducing parallel ledger concepts. Leading Ledger is assigned to all Company Codes and Non Leading ledgers can be assigned to individual company codes to meet specific requirements. Leading Ledger is the similar to Classic G/L ledgers. There can be only one leading ledgers. All the data from other modules such as Controlling and sub-ledgers such as AA, AP, AR flows to leading ledgers. Segment - Segment can be used to create financial statement at level other than Company Code. Once segments are activated, Profit center master data will have a new field for Segment assignment. Document Splitting -Document splitting concept was introduced to find missing account assignments like Profit Center and Segment for balance sheet items. That way financial statement can be prepared at profit center and Segment level. Scenarios -Scenarios defines fields which are updated in Ledger during the posting such as Cost center scenario, profit center scenario. Key Tables BKPF, BSIK, BSIS, BSID, BSAK, BSAS, BSAD Used in New G/L the same way as before BSEG Items affecting Leading ledger BSEG_ADD Items affecting Non leading ledger FAGLFLEXA Actual split line items FAGLFLEXP Planned split line items FAGLFLEXT Total for split line items GLT0, GLPCA, GLPCP, GLPCT No longer used Migration to New GL accounting Migration should be planned very carefully. SAP has introduced a 3 Phase approach for migration.
Key dates are Migration date End of Phase 0 and Start of Phase 1 (Last date of current Fiscal year) Activation Date End of Phase 1 and Start of Phase 2 Phases are Phase 0 Analyse system, crate blueprint, and prepare for phase1. You can split the document in this phase. Phase 1 You customize changes for New GL in this phase, Validate document splitting and perform actual migration at end of phase 1. Phase 2 Start using New GL.
Considerations during SAP New G/L Migration Project
When you switch from Classic GL to New GL, here are functionalities that can be covered under standard SAP Fixed price Service based migration scenarios. Merging Various FI Ledgers This is basic functionality that is always accomplished after new GL migration. Classic Ledger, Cost of Sales Ledger, and Consolidation ledger are merged into leading ledger in New GL. For each account, it can be specified which ledger will be used as source for new GL leading ledger. Migrating Special Ledger or Profit Center Special ledgers can be migrated to New GL ledgers. Profit center tables GLPCT/GLPCA can be migrated to New GL tables FAGLFLEXT/FAGLFLEXA. Profit center and Partner profit center will be updated in New GL tables. Segment field can also be updated if required. Document Splitting If document splitting is used on profit center, business area or Segment, migration scenario can include information related to splitting. Parallel Valuation Parallel ledger is new concept in New GL. You can consider moving from Parallel accounts solution to Parallel Ledger solution and include this in migration.
Additional Functionality if SAP New GL
SAP has introduced additional functionality with New G/L. Here is the short summary. Parallel Ledger Parallel accounts concept was used to prepare financial statements based on different legal requirements. This functionality still exits. However, the functionality is difficult to use if non shared GL accounts are high. Parallel ledgers have been introduced to provide another option for parallel reporting. Total table GLT0 has been replaced with FAGLFLEXT with many more fields such as Cost Element, Cost Centre, Profit Centre, Functional area and Segment. Customer specific or Industry specific fields can also be configured. Segment Reporting Segment reporting replaces business area reporting or Profit centre reporting for producing financial statements at levels below company code such as market segments or products. Profit centre master data contains a new field for Segment assignment. Document Splitting Document splitting enable preparation of balance sheet with zero balance at Profit centre or Segment level. Real time integration between FI and CO In classic GL, postings from FI to CO were posted in real time. However, postings from CO to FI were not always real time. KALC was needed to run to reconcile CO to FI. Integration is real time in New GL. User Interface User interface has been slightly changed to include new fields such as Ledger in reports.
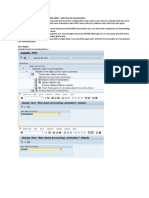
SAP New GL Configuring Document Splitting
Document splitting is key concept in SAP New GL. To configure Document splitting, you need to understand following key concepts.
Item Category Item Category is the key characteristic of GL accounts. For many accounts this can be automatically determined such as Customer, Vendor or assets. For other accounts, it needs to assigned to GL accounts in configuration.
Business Transaction SAP delivers Business transactions that identifies posting. This is used to limit item categories the business transaction can be posted to. Business Transaction Variant Variant is subset of Business Transaction. This can be used to further limit item categories for a business transaction.
Document types Document type has the same function as was in Classic GL. However, in new GL, Document type has more significance. Document types are assigned to Business Transaction and Transaction variant.
Document splitting Characteristic Here you can choose to split document on Business area, Profit center or segment. You can also indicate if the characteristic should be mandatory in documents and if zero balance is required.
Splitting method Spitting method defines the way in which spitting is carried out in transaction. Based on Spitting method, business transaction and transaction variant, you can specify what item categories are split and based on what item categories.
Inheritance You can specify in splitting rule if item category should inherit document splitting characteristic (such as profit center) from item category, if not specified during posting. How all this work? Based on document type, business transaction and transaction variant are derived during posting. Splitting method, along with business transaction and transaction variant, then determines the splitting rules ie what item categories are edited based on base item categories as defined in config of splitting rule.
SAP New GL Scenarios
Scenarios are assigned to ledgers and determine which fields are updated when postings are received from different modules. Standard SAP comes with 6 scenarios. You cant create customer specific scenarios. You can, however, use custom fields if required while assigning scenario to GL. All six scenarios can be assigned to a ledger; however this will impact the performance. More totals records will be created in Total table and writing/retrieving data will be slower. Data Entry vs General Ledger view In New G/L each document will have 2 views for display. Data Entry view is same as Classic G/L display. General Ledger view is enhanced view and displays fields updated because of assigned scenarios. You can also choose ledger here to see document in each ledger. Scenarios and fields updated Business Area Scenario Sender Business Area and Receiver Business area
Profit Center Update Scenario Profit Center and Partner Profit Center Segmentation Scenario Segment, Partner Segment, and Profit Center Preparation for Consolidation Scenario Consolidation Transaction Type and Trading Partner Cost of Sales Accounting Scenario Sender Functional Area and Receiver Functional Area Cost Center Update Scenario Sender Cost Center and Receiver Cost Center
You might also like
- SAP New GL AccountingDocument120 pagesSAP New GL AccountingJyotiraditya BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Migrate Classic GL to NewGLDocument8 pagesMigrate Classic GL to NewGLtifossi6665No ratings yet
- Asset Acc in s4Document7 pagesAsset Acc in s4moorthy100% (1)
- 10 Best Practices For Implementing New GLDocument51 pages10 Best Practices For Implementing New GLraghu100% (3)
- S4 Hana Asset AccountingDocument12 pagesS4 Hana Asset AccountingAkash100% (2)
- Parallel Accounting in New General LedgerDocument7 pagesParallel Accounting in New General Ledgerfylee74100% (1)
- New LedgerDocument42 pagesNew LedgerMADHURA RAULNo ratings yet
- New GLDocument30 pagesNew GLkalkikaliNo ratings yet
- S - 4 HANA - New Asset Accounting - Considering Key Aspects - SAP BlogsDocument15 pagesS - 4 HANA - New Asset Accounting - Considering Key Aspects - SAP BlogsgirijadeviNo ratings yet
- Finance Migration To SAP S4HANADocument18 pagesFinance Migration To SAP S4HANAAmit PaulNo ratings yet
- Configuration Example: SAP Electronic Bank Statement (SAP - EBS)From EverandConfiguration Example: SAP Electronic Bank Statement (SAP - EBS)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Mysap Fi Fieldbook: Fi Fieldbuch Auf Der Systeme Anwendungen Und Produkte in Der DatenverarbeitungFrom EverandMysap Fi Fieldbook: Fi Fieldbuch Auf Der Systeme Anwendungen Und Produkte in Der DatenverarbeitungRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Narayan Jyotiraditya Bala Banik Configuration Steps: Main Customizing ActivitiesDocument20 pagesNarayan Jyotiraditya Bala Banik Configuration Steps: Main Customizing ActivitiesJyotiraditya BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- SAP S4 Asset Accounting ConfigurationDocument42 pagesSAP S4 Asset Accounting ConfigurationLaurent Payan50% (2)
- SAP Group Reporting and ConsolidationDocument21 pagesSAP Group Reporting and ConsolidationA V Srikanth100% (4)
- How To Use The Extension Ledger Functionality in SAP SDocument17 pagesHow To Use The Extension Ledger Functionality in SAP SKrishnendu Mukherjee100% (4)
- Cross-Company - Inter-Company Transactions - SAP BlogsDocument26 pagesCross-Company - Inter-Company Transactions - SAP Blogspuditime100% (1)
- New Asset Accounting in SAP S4/HANA Finance ConfigurationDocument7 pagesNew Asset Accounting in SAP S4/HANA Finance Configurationlovely lovelyNo ratings yet
- PARALLEL LEDGERS IN ASSET ACCOUNTINGDocument35 pagesPARALLEL LEDGERS IN ASSET ACCOUNTINGSharad TiwariNo ratings yet
- Sap Fi - Co Interview QuestionsDocument30 pagesSap Fi - Co Interview QuestionsTirupatirao Bashyam100% (1)
- FI-SD IntegrationDocument47 pagesFI-SD IntegrationVaibhav batraNo ratings yet
- New GL Configuration in Sap Ecc6Document29 pagesNew GL Configuration in Sap Ecc6Tani ShabNo ratings yet
- Parallel LedgerDocument35 pagesParallel LedgerhshasapNo ratings yet
- Introducing New Asset Accounting in S - 4 HANADocument13 pagesIntroducing New Asset Accounting in S - 4 HANAUsmanKhalidNo ratings yet
- S4 HANA FinanceDocument6 pagesS4 HANA FinanceDivya DhawanNo ratings yet
- New Assets Accounting SAP SDocument47 pagesNew Assets Accounting SAP SdhirajNo ratings yet
- SAP S/4 HANA Finance - Po We Re D by SA P HA NADocument58 pagesSAP S/4 HANA Finance - Po We Re D by SA P HA NANaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- In House Cash MGTDocument25 pagesIn House Cash MGTmikirichaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Guide To Parallel AccountingDocument56 pagesComprehensive Guide To Parallel AccountingManish Dharnidharka100% (2)
- TRM Template Desc en deDocument4 pagesTRM Template Desc en deSam KuNo ratings yet
- SAP FM Open and Close Periods/Fiscal YearDocument1 pageSAP FM Open and Close Periods/Fiscal Yearhoney_2132No ratings yet
- SAP FICO Interview Questions AnswersDocument46 pagesSAP FICO Interview Questions AnswerspavankalluriNo ratings yet
- Important Sap Fico QuestionsDocument33 pagesImportant Sap Fico Questionsswetha devarakondaNo ratings yet
- New GL Doc SplittingDocument56 pagesNew GL Doc SplittingSam Kol100% (2)
- MR11 ExpertDocument5 pagesMR11 ExpertUday RedekarNo ratings yet
- SAP Dunning Configuration Very ImportDocument26 pagesSAP Dunning Configuration Very Importvittoriojay123No ratings yet
- Sap Fico Real Time Issues Solutions PDFDocument2 pagesSap Fico Real Time Issues Solutions PDFumeshkjagtap100% (1)
- SAP Fi QuestionnaireDocument18 pagesSAP Fi Questionnairejitinmangla970No ratings yet
- IFRS Fixed Asset ConfigurationDocument65 pagesIFRS Fixed Asset Configurationkumarr84100% (6)
- AC305 - Asset AccountingDocument646 pagesAC305 - Asset AccountingRoberto Ramires Filho50% (8)
- SAP Year End Closing ProcessDocument10 pagesSAP Year End Closing ProcesssurendraNo ratings yet
- Sap New GL Configuration - Document - SMDocument23 pagesSap New GL Configuration - Document - SMArindam BhuinNo ratings yet
- Best Practices in SAP FI-Asset AccountingDocument32 pagesBest Practices in SAP FI-Asset AccountingSyed Zain Ul Abdin100% (2)
- S4HANA Simple Finance Course ContentDocument6 pagesS4HANA Simple Finance Course ContentsrinivasNo ratings yet
- Asset Accounting IssueDocument17 pagesAsset Accounting IssueAtulWalvekarNo ratings yet
- S4HANA Asset Sample PDFDocument166 pagesS4HANA Asset Sample PDFIván Andrés Marchant NúñezNo ratings yet
- SAP Month End Closing ProcessDocument30 pagesSAP Month End Closing ProcesssurendraNo ratings yet
- Configuration of SAP Asset Accounting Capital LeaseDocument1 pageConfiguration of SAP Asset Accounting Capital Leaseneverever143100% (3)
- SAP FI Month End and Year End Activities GuideDocument3 pagesSAP FI Month End and Year End Activities Guideramanareddy_anathapurNo ratings yet
- Sap IhcDocument46 pagesSap Ihcssrihari75% (4)
- SAP Foreign Currency Revaluation: FAS 52 and GAAP RequirementsFrom EverandSAP Foreign Currency Revaluation: FAS 52 and GAAP RequirementsNo ratings yet
- SAP S/4HANA Central Finance and Group Reporting: Integrate SAP S/4HANA ERP Systems into Your Financial Data and Workflows for More AgilityFrom EverandSAP S/4HANA Central Finance and Group Reporting: Integrate SAP S/4HANA ERP Systems into Your Financial Data and Workflows for More AgilityNo ratings yet
- Configuring SAP ERP Financials and ControllingFrom EverandConfiguring SAP ERP Financials and ControllingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- PersonalEditionInstallation6 XDocument15 pagesPersonalEditionInstallation6 XarulmozhivarmanNo ratings yet
- 11th English ExamDocument4 pages11th English ExamsandchhonkarNo ratings yet
- UCSP Exam Covers Key ConceptsDocument2 pagesUCSP Exam Covers Key Conceptspearlyn guelaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 3 Notes - Water ResourcesDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 3 Notes - Water Resourcesrishabh gaunekarNo ratings yet
- Cross Culture Management & Negotiation IBC201 Essay TestDocument2 pagesCross Culture Management & Negotiation IBC201 Essay TestVu Thi Thanh Tam (K16HL)No ratings yet
- Corporate Provisional Voter ListDocument28 pagesCorporate Provisional Voter ListtrueoflifeNo ratings yet
- Straight and Crooked ThinkingDocument208 pagesStraight and Crooked Thinkingmekhanic0% (1)
- What's New?: Changes To The English Style Guide and Country CompendiumDocument40 pagesWhat's New?: Changes To The English Style Guide and Country CompendiumŠahida Džihanović-AljićNo ratings yet
- Your Guide To Starting A Small EnterpriseDocument248 pagesYour Guide To Starting A Small Enterprisekleomarlo94% (18)
- United States Court of Appeals, Tenth CircuitDocument5 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals, Tenth CircuitScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Phone, PTCs, Pots, and Delay LinesDocument1 pagePhone, PTCs, Pots, and Delay LinesamjadalisyedNo ratings yet
- Logitech Case Analysis: Solving Problems of Transportation Cost and Political RiskDocument7 pagesLogitech Case Analysis: Solving Problems of Transportation Cost and Political RiskdinishaNo ratings yet
- Man and Cannabis in Africa: A Study of Diffusion - Journal of African Economic History (1976)Document20 pagesMan and Cannabis in Africa: A Study of Diffusion - Journal of African Economic History (1976)AbuAbdur-RazzaqAl-MisriNo ratings yet
- Aerial Hijacking and The International LawDocument14 pagesAerial Hijacking and The International LawAnonymous vUVxDQNo ratings yet
- People v. Campomanes PDFDocument10 pagesPeople v. Campomanes PDFJaneNo ratings yet
- This Content Downloaded From 181.65.56.6 On Mon, 12 Oct 2020 21:09:21 UTCDocument23 pagesThis Content Downloaded From 181.65.56.6 On Mon, 12 Oct 2020 21:09:21 UTCDennys VirhuezNo ratings yet
- Different Western Classical Plays and Opera (Report)Document26 pagesDifferent Western Classical Plays and Opera (Report)Chaorrymarie TeañoNo ratings yet
- Simic 2015 BR 2 PDFDocument23 pagesSimic 2015 BR 2 PDFkarimesmailNo ratings yet
- Queen of Kings: Kleopatra VII and the Donations of AlexandriaDocument30 pagesQueen of Kings: Kleopatra VII and the Donations of AlexandriaDanson Githinji ENo ratings yet
- MS 1806 Inventory ModelDocument5 pagesMS 1806 Inventory ModelMariane MananganNo ratings yet
- Arvind Goyal Final ProjectDocument78 pagesArvind Goyal Final ProjectSingh GurpreetNo ratings yet
- Module 6 ObliCon Form Reformation and Interpretation of ContractsDocument6 pagesModule 6 ObliCon Form Reformation and Interpretation of ContractsAngelica BesinioNo ratings yet
- New Earth Mining Iron Ore Project AnalysisDocument2 pagesNew Earth Mining Iron Ore Project AnalysisRandhir Shah100% (1)
- Skills 360 - Negotiations 2: Making The Deal: Discussion QuestionsDocument6 pagesSkills 360 - Negotiations 2: Making The Deal: Discussion QuestionsTrần ThơmNo ratings yet
- Guide to Sentence Inversion in EnglishDocument2 pagesGuide to Sentence Inversion in EnglishMarina MilosevicNo ratings yet
- Gender and Human SexualityDocument23 pagesGender and Human SexualityTricia CavanesNo ratings yet
- IMMI Refusal Notification With Decision Record-4Document6 pagesIMMI Refusal Notification With Decision Record-4SHREYAS JOSHINo ratings yet
- Airline Operation - Alpha Hawks AirportDocument9 pagesAirline Operation - Alpha Hawks Airportrose ann liolioNo ratings yet
- 3 AL Banin 2021-2022Document20 pages3 AL Banin 2021-2022Haris HaqNo ratings yet
- Lawyer Disciplinary CaseDocument8 pagesLawyer Disciplinary CaseRose De JesusNo ratings yet