Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is A Technology That Uses The Internet and Central Remote Servers To Maintain Data and
Uploaded by
rohan7801Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is A Technology That Uses The Internet and Central Remote Servers To Maintain Data and
Uploaded by
rohan7801Copyright:
Available Formats
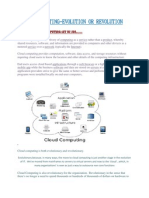
Cloud Computing
Definition
Cloud computing is a technology that uses the internet and central remote servers to maintain data and applications. Cloud computing allows consumers and businesses to use applications without installation and access their personal files at any computer with internet access. This technology allows for much more efficient computing by centralizing storage, memory, processing and bandwidth. Cloud computing is the delivery of computing as a service rather than a product, whereby shared resources, software, and information are provided to computers and other devices as a utility (like the electricity grid) over a network (typically the Internet). Cloud computing provides computation, software applications, data access,data management and storage resources without requiring cloud users to know the location and other details of the computing infrastructure. End users access cloud based applications through a web browser or a light weight desktop or mobile app while the business software and data are stored on servers at a remote location. Cloud application providers strive to give the same or better service and performance than if the software programs were installed locally on end-user computers. A simple example of cloud computing is Yahoo email, Gmail, or Hotmail etc. You dont need a software or a server to use them. All a consumer would need is just an internet connection and you can start sending emails. The server and email management software is all on the cloud ( internet) and is totally managed by the cloud service provider Yahoo , Google etc. The consumer gets to use the software alone and enjoy the benefits. The analogy is , 'If you need milk , would you buy a cow ?' All the users or consumers need is to get the benefits of using the software or hardware of the computer like sending emails etc. Just to get this benefit (milk) why should a consumer buy a (cow) software /hardware ? Cloud computing is broken down into three segments: "application" "storage" and "connectivity." Each segment serves a different purpose and offers different products for businesses and individuals around the world. In June 2011, a study conducted by VersionOne found that 91% of senior IT professionals actually don't know what cloud computing is and two-thirds of senior finance professionals are clear by the concept, highlighting the young nature of the technology. In Sept 2011, an Aberdeen Group study found that disciplined companies achieved on average an 68% increase in their IT expense because cloud computing and only a 10% reduction in data center power costs
Characteristics
Cloud computing exhibits the following key characteristics: Empowerment of end-users of computing resources by putting the provisioning of those resources in their own control, as opposed to the control of a centralized IT service (for example) Agility improves with users' ability to re-provision technological infrastructure resources. Application programming interface (API) accessibility to software that enables machines to interact with cloud software in the same way the user interface facilitates interaction between humans and computers. Cloud computing systems typically use REST-based APIs.
Cost is claimed to be reduced and in a public cloud delivery model capital expenditure is converted to operational expenditure. This is purported to lower barriers to entry, as infrastructure is typically provided by a third-party and does not need to be purchased for one-time or infrequent intensive computing tasks. Pricing on a utility computing basis is fine-grained with usage-based options and fewer IT skills are required for implementation (in-house). Device and location independence enable users to access systems using a web browser regardless of their location or what device they are using (e.g., PC, mobile phone). As infrastructure is off-site (typically provided by a third-party) and accessed via the Internet, users can connect from anywhere. Virtualization technology allows servers and storage devices to be shared and utilization be increased. Applications can be easily migrated from one physical server to another. Multi-tenancy enables sharing of resources and costs across a large pool of users thus allowing for: Centralization of infrastructure in locations with lower costs (such as real estate, electricity, etc.) Peak-load capacity increases (users need not engineer for highest possible load-levels) Utilisation and efficiency improvements for systems that are often only 1020% utilised. Reliability is improved if multiple redundant sites are used, which makes well-designed cloud computing suitable for business continuity and disaster recovery. Scalability and Elasticity via dynamic ("on-demand") provisioning of resources on a fine-grained, self-service basis near real-time, without users having to engineer for peak loads. Performance is monitored, and consistent and loosely coupled architectures are constructed using web services as the system interface. Security could improve due to centralization of data, increased security-focused resources, etc., but concerns can persist about loss of control over certain sensitive data, and the lack of security for stored kernels. Security is often as good as or better than other traditional systems, in part because providers are able to devote resources to solving security issues that many customers cannot afford. However, the complexity of security is greatly increased when data is distributed over a wider area or greater number of devices and in multi-tenant systems that are being shared by unrelated users. In addition, user access to security audit logs may be difficult or impossible. Private cloud installations are in part motivated by users' desire to retain control over the infrastructure and avoid losing control of information security. Maintenance of cloud computing applications is easier, because they do not need to be installed on each user's computer and can be accessed from different places.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing brings with it many benefits to the end user. These include: 1. 2. Access to a huge range of applications without having to download or install anything Reduced Cost It helps keep the cost down for both the users and website owners. Also for the users, they can access it from any computer and still have the file they need. For the owners, they do not need to reproduce the software and ship it out. They just rent the server space. Consumption is billed as a utility with minimal upfront costs. Users can avoid expenditure on hardware and software; only using what they need More Storage They can hold more storage than a personal computer can. It takes away the need for the upgrading computer memory, which also helps keep the cost down for the companies and users alike. Scalability via on-demand resources
3.
4.
5. 6.
7. 8.
Automatically Updated Owners no longer need to hire people to update more than one server, and it also helps the users who do not like to download updates for the software. The server gets the updates and everyone who uses the service gets the updates without updating anything on their end. Computing Flexibility It has more flexibility than other network computing systems and saves time plus money for people who are in a time crunch. Mobility Like most networks it allows users to connect even without their own computers, meaning you can do your work from anywhere in the world as long as you have a internet connection and a computer access. So you can take your work with you on your wedding and vacations. Applications can be accessed from any computer, anywhere in the world. No Downloads The users do not need to download anything, so that saves time and hard drive space for users. They can just log onto the network. Shared Resources A key component of cloud computing is that companies share resources. With cloud computing, this allows them all to have access to the resources via cloud computing. This again saves businesses time and money by placing their resources all in one location that is easy for their workers to look up and access. Companies can share resources in one place
Drawbacks
Cloud Computing has many benefits, however there are also some associated risks with using cloud computing. These include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Users do not physically possess storage of their own data, which leaves the responsibility and control of data storage with the provider Users could become dependent upon the cloud computing provider With data held externally, business continuity and disaster recovery are in the hands of the provider Data migration issues when changing cloud provider What happens if your cloud provider goes out of business?
Cloud Computing Service Models.
Cloud computing providers offer their services according to three fundamental models: Infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS) where IaaS is the most basic and each higher model abstracts from the details of the lower models.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS or HaaS)
In this most basic cloud service model, cloud providers offer computers as physical or more often as virtual machines , raw (block) storage, firewalls, load balancers, and networks. IaaS providers supply these resources on demand from their large pools installed in data centers. Local area networks including IP addresses are part of the offer. For the wide area connectivity, the Internet can be used or - incarrier clouds - dedicated virtual private networks can be configured. To deploy their applications, cloud users then install operating system images on the machines as well as their application software. In this model, it is the cloud user who is responsible for patching and maintaining the operating systems and application software. Cloud providers typically bill IaaS services on a utility computing basis, that is, cost will reflect the amount of resources allocated and consumed. Hardware as a Service (HaaS) SaaS and PaaS are providing appliancess to customers, HaaS does not. It offers the hardware so that your organization can put whatever they want onto it Rather than purchase servers, software, racks, and having to pay for the datacenter space for them, the service provider rents those resources: - Server space - Network equipment - Memory - CPU cycles - Storage space Examples: Amazon EC2, Rackspace Mosso, GoGrid.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
In the PaaS model, cloud providers deliver a computing platform and/or solution stack typically including operating system, programming language execution environment, database, and web server. Application developers can develop and run their software solutions on a cloud platform without the cost and complexity of buying and managing the underlying hardware and software layers. With some PaaS offers, the underlying compute and storage resources scale automatically to match application demand such that the cloud user does not have to allocate resources manually. PaaS APIs normally based on HTML or JavaScript. provides automatic facilities for concurrency management, scalability,failover, and security. supports web development interfaces such as SOAP and REST able to access databases & reuse services within a private network A general model is implemented under which developers build appls designed to run on the providers infrastructure delivered to users in via an Internet browser Downfall A lack of interoperability and portability among providers If you create an appl with one cloud provider & decide to move to another, you may not be able to do so or youll have to pay a high price Examples: Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure, Zoho Creator, NetSuite NetFlex, Akamai EdgePlatform, Salesforce Force.com, Facebook Platform
Software as a Service (SaaS)
In this model, cloud providers install and operate application software in the cloud and cloud users access the software from cloud clients. The cloud users do not manage the cloud infrastructure and platform on which the application is running. This eliminates the need to install and run the application on the cloud user's own computers simplifying maintenance and support. What makes a cloud application different from other applications is its elasticity. This can be achieved by cloning tasks onto multiple virtual machines at run-time to meet the changing work demand. Load balancers distribute the work over the set of virtual machines. This process is transparent to the cloud user who sees only a single access point. To accomodate a large number of cloud users, cloud applications can be multitenant, that is, any machine serves more than one cloud user organization. It is common to refer to special types of cloud based application software with a similar naming convention:desktop as a service, business process as a service, Test Environment as a Service, communication as a service. The pricing model for SaaS applications is typically a monthly or yearly flat fee per user
Characteristics of SaaS: 1. Software applications or services are stored remotely 2. A user can then access these services or software applications via the Internet 3. In most cases, a user does not have to install anything onto their host machine, all they require is a web browser to access these services in some cases, additional plug-in/add-on for certain services are needed 4. Network-based manag & access to available software from central locations rather than at each customers site, enabling customers to access applications remotely via the Internet centralized enhancement and patch updating 5. Appl delivery from a one-to-many model, as opposed to a traditional one-to-one model. single-instance, multitenant architecture
The Cloud Pyramid
Storage as a Service (SaaS):
Also known as disk space on demand The ability to leverage storage that physically exists at a remote site but is logically a local storage resource to any application that requires storage.
Its a means that a third-party provider rents space on their storage to end-users who lack the budget or capital budget to pay for it on their own. Ideal when technical personnel are not available or have inadequate knowledge to implement and maintain that storage infrastructure Given the complexity of current backup, replication, and disaster recovery needs, the service has become popular Hundreds of cloud storage providers on the Web, more seem to be added each day. The biggest advantage is cost savings: Storage rented from provider using a cost-per-gigabyte-stored or perdata-transferred model
Examples of specialized providers 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Google Docs Web email providers like Gmail, Hotmail, and Yahoo! Mail Flickr and Picasa YouTube Hostmonster and GoDaddy store files and data for many client web sites. Facebook and MySpace are social networking sites MediaMax and Strongspace offer storage space for any kind of digital data
Database as a Service (DaaS):
Databases: repositories for information with links within the information that help make the data searchable. Distributed databases, like Amazons SimpleDB, spread information among physically dispersed hardware To the client, the information seems to be located in one place. Idea behind DaaS is to avoid the complexity and cost of running your own database The power is to leverage database technology that would typically cost thousands of dollars in hardware and software licenses. Provides the ability to leverage the services of a remotely hosted database, sharing it with other users and having it logically function as if the database were local.
Benefits: o Ease of use o Power o Integration o Management
Information as a Service:
It refers to the ability to consume any type of remotely hosted information
E.g. stock price information, address validation, credit reporting, through a well-defined interface such as an API ability to mix and match a variety of information from many different sources through a single application or mashup. We can get stock quotes from one information-as-a-service provider,census data from another GeoNames Web API, from geonames.org, o a geographical database containing over 8 million geographical names o provides a broad range of information on each, from its population and form of government to its topology to its road and railway systems and more.
Communication as a Service (CaaS)
CaaS is an outsourced enterprise communications solution Providers of this type of cloud-based solution are responsible for the management of hardware and software Designed on a utility-like pricing model Requires little to no management oversight from customers. Network capacity and feature sets can be changed dynamically, so functionality keeps pace with consumer demand and provider-owned resources are not wasted. Delivers - Voice over IP (VoIP) services, - Instant Messaging (IM), and - Video conferencing capabilities - Advanced features: chat, multimedia conferencing, Microsoft Outlook integration, real-time presence, soft phones (software-based telephones), video calling, unified messaging and mobility etc.
Identity as a Service:
Offers a digital identitya set of bytesto describe the user Based on this information, the application can determine who the user is and what he or she is allowed to do. In-house applications rely on services like Active Directory to provide this information. Clouds, however, have to use their own identity services. If you sign on services to Amazon cloud services, you have to sign on using an Amazondefined identity. Googles App Engine requires a Google account Windows uses Windows Live ID for use with Microsofts cloud applications. OpenID o is an open, decentralized, single sign-on standard that allows users to log in to many services using the same digital identity. o is in the form of a uniform resource locator (URL) and does not rely on a central authority to authenticate a users identity.
o o
Since a specific type of authentication is not required, nonstandard forms of be used, including smart cards, biometric, or passwords. Used by many organizations, including: Google, IBM, Microsoft, Yahoo!
authentication may
Monitoring as a Service (MaaS)
Outsourced provisioning of security, primarily on business platforms that leverage the Internet to conduct business. Security monitoring involves protecting an enterprise or government client from cyber threats Security-as-a-service, is the ability to deliver core security services remotely over the Internet. While the typical security services provided are rudimentary, more sophisticated services such as identity management are becoming available.
Process as a Service
Remote resource that can bind many resources together, e.g. services & data hosted within the same CC resource or remotely to create business processes Business process: meta-application that spans systems, leveraging key services& information combined into a sequence to form a process These processes are easier to change than are applications and thus provide agility to those who leverage these process engines delivered on demand
Integration as a Service
The ability to deliver a complete integration stack from the cloud including interfacing with applications, semantic mediation, flow control, integration design, and so on. includes most of the features and functions found within traditional enterprise application integration technology, but delivered as a service
Governance/Management as a Service (GaaS):
Any on-demand service that provides the ability to manage one or more cloud services. These are typically simple things such topology, resource utilization, virtualization, and uptime management Governance systems are becoming available as well, offering, for instance, the ability to enforce defined policies on data and services.
Testing as a Service (TaaS):
Ability to test local or cloud-delivered systems using testing software and services that are remotely hosted. While a cloud service requires testing unto itself, TaaS systems have the ability to test other cloud applications, Web sites, and internal enterprise systems, and they do not require a hardware or software footprint within the enterprise.
Whats New! Amazon services:
Amazon was one of the first companies to offer cloud services to the public, and they are very sophisticated Most extensive cloud service to date Offers a number of cloud services 1. Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) offers virtual machines and extra CPU cycles foryour organization. 2. Simple Storage Service (S3) allows you to store items up to 5GB in size in Amazons virtual storage service. 3. Simple Queue Service (SQS) allows your machines to talk to each other using this message-passing API. 4. SimpleDB is a web service for running queries on structured data in real time. This service works in close conjunction with S3 and EC2, collectively providing the ability to store, process, and query data sets in the cloud. 5. CloudFront enables to place online content at the edges of the network, meaning that content is delivered from a location close to the user requesting it.
Microsofts solution for CC: Windows Azure
An OS that allows organizations to run Windows apps and store files and data using Microsofts datacenters Azure Services Platform includes services that allow developers to: o establish user identities, o manage workflows, o synchronize data, o perform other functions as they build software programs on Microsofts online computing platform. Key components of Azure Services Platform include o provides service hosting and management and low-level scalable storage, computation, and networking. o SQL Services - provides database services and reporting. o .NET Services - provides service-based implementations of .NET Framework concepts such as workflow. o Live Services - used to share, store, and synchronize documents,photos, and files across PCs, phones, PC applications, and web sites.
SharePoint Services and Dynamics CRM Services - used for businesscontent, collaboration, and solution development in the cloud.
Salesforce
Force.com - on-demand cloud computing platform (PaaS) offers: o Apex, an integrated development environment o Programmable interface, User interface options o Business logic, Workflow and approvals engine o Automatic mobile device deployment o Web services integration, A relational database o Reporting and analytics Visualforce o Framework for creating new interface designs o Enables user interactions that can be built and delivered with no software or hardware infrastructure requirements o uses HTML, AJAX, and Flex, for business applications CRM (customer relationship management) offering consists of the Sales Cloud and the Service Cloud with five core applications: o Sales, o Marketing, o Service, o Collaboration, o Analytics, o Custom applications AppExchange - is a directory of applications built for Salesforce.com by third-party developers. - users can purchase and add to their Salesforce.com environment.
You might also like
- Implementation of Cloud Based Query Solver System For Educational Institutes Featuring OntologyDocument7 pagesImplementation of Cloud Based Query Solver System For Educational Institutes Featuring OntologyIjarcet JournalNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Cloud ComputingDocument21 pagesPresentation On Cloud ComputingPraveen Kumar PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesSeminar Reportshinchan noharaNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesSeminar Reportshinchan noharaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document13 pagesUnit 1Bnod MsraNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesSeminar ReportJp Sahoo0% (1)
- Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesCloud ComputingGHOST 007No ratings yet
- A Study of Cloud Computing MethodologyDocument5 pagesA Study of Cloud Computing MethodologyR Dharshini SreeNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing DraftDocument14 pagesCloud Computing Draftakhil829208No ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument82 pagesCloud ComputingKartheeswari SaravananNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument3 pagesCloud Computingjoel kNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Presentation ByDocument20 pagesCloud Computing: Presentation Bymahesh_mallidiNo ratings yet
- Topic:Cloud Computing Name:Aksa Kalsoom Submitted To:Sir Amir Taj Semester:7 ROLL# 11PWBCS0276 Section:BDocument6 pagesTopic:Cloud Computing Name:Aksa Kalsoom Submitted To:Sir Amir Taj Semester:7 ROLL# 11PWBCS0276 Section:BlailaaabidNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Interview Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesCloud Computing Interview Questions and Answersਰਜਨੀ ਖਜੂਰਿਆNo ratings yet
- A Technical Seminar ReportDocument7 pagesA Technical Seminar ReportAitha SatishNo ratings yet
- Cloud computing allows sharing of computing resources via digital networksDocument13 pagesCloud computing allows sharing of computing resources via digital networksEkta TayalNo ratings yet
- Best College Kharian: Assignment On Cloud Computing Course Title: Computer NetworkDocument7 pagesBest College Kharian: Assignment On Cloud Computing Course Title: Computer Networkateeq mughalNo ratings yet
- My Seminar Report On Cloud ComputingDocument18 pagesMy Seminar Report On Cloud ComputingKevin NettarNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing DocumentationDocument11 pagesCloud Computing DocumentationSailaja MannemNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesCloud ComputingAnjali SoniNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Benefits of Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesAssignment On Benefits of Cloud ComputingMonir HossainNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing ExplainedDocument17 pagesCloud Computing Explainedsaurabh128No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Book (2017-Regulation) PDF-1-89 Unit - I & IIDocument89 pagesCloud Computing Book (2017-Regulation) PDF-1-89 Unit - I & IIVishnu Kumar KumarNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: An Introduction to the Delivery of Computing as a ServiceDocument5 pagesCloud Computing: An Introduction to the Delivery of Computing as a ServiceHarshvardhan SainiNo ratings yet
- Abstract of Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesAbstract of Cloud ComputingJanaki JanuNo ratings yet
- Virtualizing The Private Cloud For Maximum Resource UtilizationDocument5 pagesVirtualizing The Private Cloud For Maximum Resource UtilizationIjarcet JournalNo ratings yet
- AN Assignment ON "Cloud Computing" "Master of Computer Application" Session 2012-2015Document8 pagesAN Assignment ON "Cloud Computing" "Master of Computer Application" Session 2012-2015ravindersehgalNo ratings yet
- IIIT Allahabad: Software Testing & Quality Assurance Cloud ComputingDocument9 pagesIIIT Allahabad: Software Testing & Quality Assurance Cloud ComputingRohit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing 1Document11 pagesCloud Computing 1hardesh_123No ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument3 pagesCloud ComputingNandan KumarNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud Computing?: ComputersDocument8 pagesWhat Is Cloud Computing?: ComputersNaidu SwethaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Cloud Computing TechnologyDocument3 pagesOverview of Cloud Computing Technologyzubair90No ratings yet
- CC DocumentDocument13 pagesCC Documentgopikrishnan1234No ratings yet
- Unit-1: Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument14 pagesUnit-1: Introduction To Cloud ComputingmadhavNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument12 pagesCloud ComputingELSADNo ratings yet
- Paper Presentation-Cloud ComputingDocument14 pagesPaper Presentation-Cloud Computingdeepakfct100% (4)
- FALLSEM2022-23 CSE3035 ETH VL2022230103255 Reference Material I 20-07-2022 IntroductionDocument12 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 CSE3035 ETH VL2022230103255 Reference Material I 20-07-2022 IntroductionAditi SudhirNo ratings yet
- Introduction - What Is ItDocument9 pagesIntroduction - What Is ItLalit KundaliaNo ratings yet
- Part B ETIDocument10 pagesPart B ETISoNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Explained: Access Server Resources Via the InternetDocument5 pagesCloud Computing Explained: Access Server Resources Via the InternetAnurag GoelNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Interview Questions and AnswersDocument30 pagesCloud Computing Interview Questions and Answerssenthilkumar_surulNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Research PaperDocument11 pagesCloud Computing Research PaperPracheta BansalNo ratings yet
- Iot R16 - Unit-5Document23 pagesIot R16 - Unit-5Surendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing - PrashantDocument6 pagesCloud Computing - PrashantSachin MauryaNo ratings yet
- Fog ComputingDocument30 pagesFog Computingabid princeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CCDocument11 pagesIntroduction To CCHAFIZ AMEENUDDINNo ratings yet
- Fog ComputingDocument31 pagesFog ComputingPranjali100% (2)
- Azure FundamentalsDocument38 pagesAzure Fundamentalsumakant bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Everything you need to know about cloud computingDocument14 pagesEverything you need to know about cloud computingamphoen2528100% (3)
- Cloud Computing Evolution and ConceptsDocument6 pagesCloud Computing Evolution and ConceptsaaryavamanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Cloud ComputingGopinath MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing For Beginners: in This Tutorial, You Will LearnDocument11 pagesCloud Computing For Beginners: in This Tutorial, You Will Learnsangeet83No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Age of InternetDocument6 pagesCloud Computing: Age of InternetAlmore Cato IINo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: (A Computing Platform For Next-Generation Internet)Document7 pagesCloud Computing: (A Computing Platform For Next-Generation Internet)Srini VasuluNo ratings yet
- Cloud computing architecture explainedDocument15 pagesCloud computing architecture explainedpankajNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet
- Cloud: Get All The Support And Guidance You Need To Be A Success At Using The CLOUDFrom EverandCloud: Get All The Support And Guidance You Need To Be A Success At Using The CLOUDNo ratings yet
- Cloud computing: Moving IT out of the officeFrom EverandCloud computing: Moving IT out of the officeBCS, The Chartered Institute for ITNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionFrom EverandCloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionNo ratings yet
- AT&T Sign-UpDocument2 pagesAT&T Sign-UpKaren PierceNo ratings yet
- Waters DP 2017 R2 Installation and Configuration Guide 715005543raDocument37 pagesWaters DP 2017 R2 Installation and Configuration Guide 715005543racarlos julio german ariasNo ratings yet
- Peq10 - 13&PDocument602 pagesPeq10 - 13&PAaron Rodas100% (4)
- Huawei Cli Introduction PDFDocument3 pagesHuawei Cli Introduction PDFHussein DhafanNo ratings yet
- SoftJin VerificDocument3 pagesSoftJin VerificmohanbirsinghNo ratings yet
- Inteligen 500: Operator GuideDocument41 pagesInteligen 500: Operator Guide曾浩然100% (1)
- SW2Document6 pagesSW2ziblurNo ratings yet
- Gpucoder UgDocument560 pagesGpucoder UgciaobubuNo ratings yet
- HubSpot Sales Forecasting TemplateDocument14 pagesHubSpot Sales Forecasting TemplateFAUZULNo ratings yet
- Explosive Trace Detection Etd SystemsDocument2 pagesExplosive Trace Detection Etd Systemsaciy437No ratings yet
- Cage Parent SurveyDocument2 pagesCage Parent Surveyapi-248414582No ratings yet
- JWM-9000 Guard Monitoring SystemDocument3 pagesJWM-9000 Guard Monitoring SystemDinesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- ABB Robot Basic TrainingDocument35 pagesABB Robot Basic TrainingTensaigaNo ratings yet
- Instructions For Android 10.0Document13 pagesInstructions For Android 10.0Lombardi ProductionNo ratings yet
- M.Phil Computer Science Biometric System ProjectsDocument3 pagesM.Phil Computer Science Biometric System ProjectskasanproNo ratings yet
- BSBOPS503 Student GuideDocument30 pagesBSBOPS503 Student GuideBui AnNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamentals Application PRELIM ModuleDocument24 pagesComputer Fundamentals Application PRELIM ModuleTrisha Lei T. BatangNo ratings yet
- 0504 SAP Data Migration at KelloggDocument30 pages0504 SAP Data Migration at KelloggclaokerNo ratings yet
- A New Algorithm For Computing Boolean Operations On PolygonsDocument17 pagesA New Algorithm For Computing Boolean Operations On PolygonsIacob AlinNo ratings yet
- Coffey Global MapInfo Introduction 2009Document51 pagesCoffey Global MapInfo Introduction 2009Ahmed GhoneimNo ratings yet
- CD Lab - ProgramDocument16 pagesCD Lab - Programapi-434094364No ratings yet
- MOTOBRIDGE Brochure FinalDocument4 pagesMOTOBRIDGE Brochure Finalpy5rcbNo ratings yet
- DGA SMI CompleteDocument5 pagesDGA SMI CompletesujaraghupsNo ratings yet
- SonicWALL TELE3 SP Administrators GuideDocument210 pagesSonicWALL TELE3 SP Administrators GuideJeejan JosephNo ratings yet
- Unit II PDFDocument7 pagesUnit II PDFManthan JadhavNo ratings yet
- Report On Project ManagementDocument21 pagesReport On Project ManagementSaurabh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Conduct Testing and Documentation: Course: TM I By: Saniata G. BautistaDocument15 pagesConduct Testing and Documentation: Course: TM I By: Saniata G. BautistaSanie Gaspar BautistaNo ratings yet
- 06 SashSensors MKT 0070Document16 pages06 SashSensors MKT 0070VICTOR MANUEL SALAZAR GARCIANo ratings yet
- Computer MCQs NewDocument2 pagesComputer MCQs NewMr ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Periodical Examination 3rd QuarterDocument4 pagesPeriodical Examination 3rd QuarterDanico Balasa CorunoNo ratings yet