Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Bond
Uploaded by
car_yiiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Bond
Uploaded by
car_yiiCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEMISTRY FORM 4 LESSON 18
Introduction Most of the chemical substances exist naturally as compound. In this chapter, we are going to have a look on how chemical compounds are formed using chemical bond. The 2 chemical bond involved are * Ionic Bond (electrovalent bond) * Covalent bond
5.1 Ionic bond Atoms tend to achieve stability (octet) by donating or receiving electrons When an atom looses or receive electrons, it will form ion. There are 2 types of ions generally, which is cation and anion.
Type of ion Occur when
Positive ion (cation) Electron(s) is donated
Example : sodium, Na ; potassium, K
Negative ion (anion) Electron(s) is received
Example : fluorine, F ; chlorine, Cl
+
Formation of +1 / 1 ion +
e_
e-
+
Sodium ion, Na+ fluoride ion, F-
Eg : magnesium, Mg ; calcium, Ca
E.g. : oxygen, O ; sulphur, S
+
Formation of +2 / 2 ion 2+
2 e2-
2e+
magnesium ion,Mg2+ E.g. : Aluminium, Al ; Boron, B oxide ion, O2E.g. : nitrogen, N ; phosphorous, P
+
Formation of +3 / 3 ion 3+
3 e3-
3e+
aluminium ion,Al3+ nitride ion, N3-
Since an ionic compound is formed when 2 opposite charge ions attract with each other, and they must be electrically neutral. equal [The total positive charges are ...................... to total negative charges. The compounds formed are based on the equal opposite charge ion. + 2+ 3+
X Y2 Z3
AX A2Y A3Z
BX2 BY B3Z2
CX3 C2Y3 CZ
Naming ionic compound cation The naming of ionic compound is based on the rules where shall be nameanion first, followed by .......................... Following table are examples of some ionic compound and its name.
Ionic bond is formed when 2 opposite charged ion are attracted to each other and form a strong electrostatic force between the ions. The type of ions and the molecular formulae formed from 2 different ions are explained in Chapter 3. The rules remain the same. In this chapter, you need to sketch the dot and cross diagram for how the chemical substance is formed. Lets practice some of the dot-and-cross diagram for a few compounds
Sodium and chlorine reacted to form sodium chloride
Na
Cl
Na
Cl
Potassium and oxygen react to form potassium oxide.
2O
Magnesium and fluorine react to form magnesium fluoride
F Mg F
2+
_ F
Mg
Aluminium and nitrogen react to form aluminium nitride
Al
3+
3-
Al
Aluminium and sulphur react to form aluminium sulphide
Al
3+
2S
Al 2
Magnesium react with nitrogen to form magnesium nitride
Mg
2+
3-
Mg 3
N 2
Calcium react with oxygen to form calcium oxide
Ca
2+
2O
Ca
5.2
Covalent bond
When 2 atoms which required electron to achieve stability (especially for group 14, 15, 16 and 17), what they can do is share electrons together in order to achieve octet state. When 2 electrons from each individual atoms share electrons, they will form a bond, named covalent bond. In covalent bond, there are 3 types of bonding that can be formed, depend on the atom and the number of electron required for each individual atom.
1.Single bond Single bond is formed when one electron from 2 atoms shared each other electrons. E.g. : Fluorine gas. F2 (electron arrangement : 2.7)
Chlorine gas, Cl2 (electron arrangement, 2.8.7)
Cl
Cl
2. Double bond Double bond is formed when 2 electrons from 2 atoms shared each other electron to form 2 single bond. e.g. : Oxygen gas, O2 (electron arrangement : 2.6)
3. Triple bond Triple bond is formed when 3 electrons from 2 atoms shared each other electron to form 3 single bond. e.g. :Nitrogen gas, N2 (electron arrangement : 2.5)
Water, H2O H O H
Carbon dioxide, CO2 O
Ammonia, NH3 H H H C H H N H H Methane, CH4
Hydrogen Cyanide, HCN
Ethene, C2H4
H H
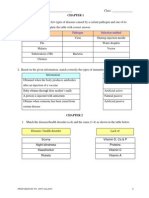
Ionic bond
Covalent bond
Formed between a metal Formed between nonand non metal atoms metal and non metal. Involved electron transfer Involved electron sharing from a metal to non between non metal atoms metal Metal atoms lose Each non-metal atom electrons to form positive contributes an equal ions, whereas non-metal number of electrons for atom gain electrons to sharing form negative Formation of positive and Two atoms share 1, 2, or negative ions enables the 3 pairs of electrons to ions to achieve stable enable each atom to noble gas electron achieve octet arrangements.
Properties
Ionic compound
Covalent compound Gigantic molecule Simple molecular
Melting point and boiling point Physical state at room temperature Volatility Electrical conductivity In water Solubility In organic solvent
High Solid Low Good Soluble Insoluble
High Solid Low Poor Insoluble Soluble
Low Solid, liquid or gas High Poor Insoluble Soluble
You might also like
- System PuzzleDocument7 pagesSystem Puzzlecar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Borang Markah KK 2015Document4 pagesBorang Markah KK 2015car_yiiNo ratings yet
- Reflection in a line and axis Cartesian plane worksheetDocument2 pagesReflection in a line and axis Cartesian plane worksheetcar_yiiNo ratings yet
- PLC ExerciseDocument1 pagePLC Exercisecar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Pat Sains 2015Document3 pagesJawapan Pat Sains 2015car_yiiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Latih Tubi Math1Document2 pagesChapter 1 Latih Tubi Math1car_yiiNo ratings yet
- Write Down Reflection Before Leave The Laboratory.: Exist CardDocument1 pageWrite Down Reflection Before Leave The Laboratory.: Exist Cardcar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Reflection in a line and axis Cartesian plane worksheetDocument2 pagesReflection in a line and axis Cartesian plane worksheetcar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Program Dasar 60:40 Sains Ting 1 Pameran, Pertandingan, Model, Lawatan KuizDocument1 pageProgram Dasar 60:40 Sains Ting 1 Pameran, Pertandingan, Model, Lawatan Kuizcar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Tree MapDocument2 pagesTree Mapcar_yiiNo ratings yet
- PLC ExerciseDocument1 pagePLC Exercisecar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Minggu9 Good FridayDocument2 pagesMinggu9 Good Fridaycar_yiiNo ratings yet
- 11 JuneDocument5 pages11 Junecar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Class 2 Revision Time StatisticsDocument1 pageClass 2 Revision Time Statisticscar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Heat and Light ReactionsDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Heat and Light Reactionscar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Exam: Pra SPM Subject: Kimia (Paper 2) Tarikh Peperiksaan: 8/10/2014Document2 pagesExam: Pra SPM Subject: Kimia (Paper 2) Tarikh Peperiksaan: 8/10/2014carina_yii9690No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Directed NumbersDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Directed Numbersnaza9775100% (3)
- Rancangan Amali Tahunan 2o15Document5 pagesRancangan Amali Tahunan 2o15car_yiiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Part 1Document21 pagesChapter 5 Part 1car_yiiNo ratings yet
- Type of System in HumanDocument1 pageType of System in Humancar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Space Word Search: Human Body Word ScrambleDocument2 pagesSpace Word Search: Human Body Word Scramblecar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Ex Other MicDocument4 pagesEx Other Miccar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Students Matching F 5Document10 pagesStudents Matching F 5faezahsapixNo ratings yet
- Human Body Word ScrambleDocument2 pagesHuman Body Word Scramblecar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Topical Test 4Document2 pagesTopical Test 4car_yiiNo ratings yet
- Filter SaltDocument1 pageFilter Saltcar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Form 4 SC SummaryDocument2 pagesForm 4 SC Summarycar_yiiNo ratings yet
- ProprioceptorsDocument4 pagesProprioceptorscar_yiiNo ratings yet
- VariationDocument3 pagesVariationcar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Investigate How Surface Area Affects The Rate of CoolingDocument1 pageInvestigate How Surface Area Affects The Rate of Coolingcar_yiiNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- CHEM1100 - Module 1 - SEM2 - 2019 - Combined Student Notes 1pp - 2.pd PDFDocument297 pagesCHEM1100 - Module 1 - SEM2 - 2019 - Combined Student Notes 1pp - 2.pd PDFNicholas BahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document4 pagesChapter 5Nelviana NahNo ratings yet
- Química AmbientalDocument179 pagesQuímica Ambientaldavid5pineda-2No ratings yet
- Laboratory Methods of Inorganic Chemistry - Biltz & Biltz (1928)Document287 pagesLaboratory Methods of Inorganic Chemistry - Biltz & Biltz (1928)whiyeNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry - Acids and BaseDocument14 pagesGeneral Chemistry - Acids and BasePaul JacalanNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compound NotesDocument30 pagesCarbon and Its Compound Noteskrishna industries100% (1)
- Science 9 Quarter 2Document12 pagesScience 9 Quarter 2Catherine Yorong PedranoNo ratings yet
- Modern Chemistry Chapter 6Document56 pagesModern Chemistry Chapter 6LaurenNo ratings yet
- The Lewis Electron Dot StructureDocument10 pagesThe Lewis Electron Dot StructureMaribel Membrado GreciaNo ratings yet
- CHEM 2 Chemistry in Your World 2nd Edition Hogg Solutions Manual 1Document10 pagesCHEM 2 Chemistry in Your World 2nd Edition Hogg Solutions Manual 1beatriceNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Science 9Document4 pagesModule 2 Science 9Reyzel de RayaNo ratings yet
- Test Planner For Two Year Medical Phase-02 - AY 2021-2022Document10 pagesTest Planner For Two Year Medical Phase-02 - AY 2021-2022Rishi UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- TBR OChem1 Opt PDFDocument324 pagesTBR OChem1 Opt PDFKuantin Tarantino100% (1)
- Periodic Table Super Sheet 2021Document17 pagesPeriodic Table Super Sheet 2021raahat soniNo ratings yet
- Introductory Chemistry 4Th Edition Tro Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument39 pagesIntroductory Chemistry 4Th Edition Tro Test Bank Full Chapter PDFmasonfisheribasedgcyx100% (9)
- (CM2213&2223) Organic Chemistry Principles in Context - Green PDFDocument722 pages(CM2213&2223) Organic Chemistry Principles in Context - Green PDFSreedevi Krishnakumar100% (1)
- Class 11 Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument139 pagesClass 11 Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structureprateek yadavNo ratings yet
- Q2 M2 Octet-Rule-And-Lewis-StructureDocument18 pagesQ2 M2 Octet-Rule-And-Lewis-StructureElysha Mae RamirezNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Paper 1 2 3 SBP Trial SPM 2009Document21 pagesMarking Scheme Paper 1 2 3 SBP Trial SPM 2009Mohd Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- LAS Sci9 q2 Week6 V2Document12 pagesLAS Sci9 q2 Week6 V2Jim TanNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument23 pagesChemical Bondingaljan torrecerNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY-30-07 - 13th Objective (In)Document6 pagesCHEMISTRY-30-07 - 13th Objective (In)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Structure 2.2Document30 pagesStructure 2.2Mohamed Ahmed FarahNo ratings yet
- 4.3 (153 Marks) : MarkschemeDocument62 pages4.3 (153 Marks) : MarkschemeSemwezi EnockNo ratings yet
- Ujian Topikal Jadual Berkala UnsurDocument6 pagesUjian Topikal Jadual Berkala UnsurNurul Hana BalqisNo ratings yet
- H2 Chem Notes 9729 PDFDocument78 pagesH2 Chem Notes 9729 PDFBobNo ratings yet
- Periodic-Table-Groups B v6 Anm s1Document31 pagesPeriodic-Table-Groups B v6 Anm s1Sophi VijayNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith, ch1Document40 pagesOrganic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith, ch1sungyeon heoNo ratings yet
- Electronic Theory of Valency &bondingDocument12 pagesElectronic Theory of Valency &bondingshivakafle039No ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry I-VIDocument134 pagesInorganic Chemistry I-VIMurad AlDamen100% (3)