Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Logistics - Report
Uploaded by
van_1234Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Logistics - Report
Uploaded by
van_1234Copyright:
Available Formats
1|Page
Logistics & Supply Chain Management of DHL
A Detailed Study
2|Page
OBJECTIVE OF THE STUDY The objectives of the project are: PRIMARY OBJECTIVES : To know the effectiveness of logistics management of DHL and to bench mark the organization with respect to the industry. To have a thorough understanding of how logistics system works in DHL
SECONDARY OBJECTIVES: To know about Logistics Industries To understand the value of each organization To know whether the customers are satisfied with the existing range of service pattern.
SCOPE OF STUDY In order to understand the concepts of logistics in terms of practical usage and to glimpse into the how a real company or organization uses logistics as a formidable tool to gain customer satisfaction, reduce overall cost and increase efficiency we selected DHL the worlds leading courier Service Company. The study is done only on how DHL use their logistics system effectively.
3|Page
INDEX
Serial no. 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 2 2.1 2.2
Particulars Introduction to DHL History of DHL Logistics network of DHL DHL India Corporate Profile Product and Services of DHL Integrated Logistics System Inventory Flow Information Flow Coordination Flow Operating Flow Supply Chain Management DHL International Supply Chain - Reverse Logistics - Services Logistics - Inbound to Manufacturing - Medical device Distribution - Distribution to store Management - Engineering response Extended Supply Chain Services Implementation Services Performance Management Outsourcing Projects Innovation of Supply Chain development Solution for Customize end to end logistic worldwide Transportation Transportation functionality Principles Transportation Infrastructure Optimization of logistics with DHL road and rail solutions Air and ocean freight solutions Inventory management & warehousing Warehouse Infrastructure Network - Multi User Centers - Strategic Part Centers (SPC) - Express Logistics Centers (ELC)
Page no. 6 6 7 8 9 10 11 11
3 3.1
14 16
3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 4 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 5 5.1
19 20 21 21 21 23 25 25 26 27 29 30 32 32
4|Page
5.2
5.3 5.4 5.5 6 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 7 8 9
Warehouse Management Solution - Warehouse Management Systems - Strategic Inventory Management - Direct Express Inventory Management - Repair Return Inventory Management - Cross Docking Inventory Optimization Special Warehouse solution Outsourcing Projects Value-added services Co-Packaging Product Assembly Other Value added Service External Performance Measurement Customer Perception Measurement Recommendation Conclusion Bibliography
33
34 35 36 37 37 38 38 39 39 40 41 42
5|Page
1. INTRODUCTION
DHL is the global leader in logistics - with more highly experienced professionals at more locations in more countries than any other provider. Their goal is to build strong, long-term partnerships with customers by providing world class services, across all our operations. In India, they have formed a new joint venture - DHL Lemuir Logistics, which consolidates their position as the leader in International Freight Forwarding, Supply Chain Management, Project Transport and Customs Brokerage. They are the first choice for companies looking for end to end logistics solutions and high quality servicing capabilities. After joining forces with Excel in 2005, they are now also the sector's leading innovator - providing the extraordinary range of cutting-edge solutions. Their customers include over 75% of the worlds largest quoted non-financial enterprises. These organizations trust DHL with their brands and reputations not simply because they are the worldwide market leader, but because they strive to deliver globally consistent services of the highest quality.
1.1 HISTORY AND BACKGROUND OF DHL
DHL are the first letters of the last names of the three company founders, Adrian Dalsey, Larry Hillblom and Robert Lynn. In 1969, just months after the world had marveled at Neil Armstrong's first steps on the moon, the three partners took another small step that would have a profound impact on the way the world does business. The founders began to personally ship papers by airplane from San Francisco to Honolulu, beginning customs clearance of the ship's cargo before the actual arrival of the ship and dramatically reducing waiting time in the harbour. Customers stood to save a fortune. With this concept, a new industry was born: international air express, the rapid delivery of documents and shipments by airplane. The DHL Network continued to grow at an incredible pace. The company expanded westward from Hawaii into the Far East and Pacific Rim, then the Middle East, Africa and Europe. By 1988, DHL was already present in 170 countries and had 16,000 employees. At the beginning of 2002, Deutsche Post World Net became the major shareholder in DHL. By the end of 2002, DHL was 100% owned by Deutsche Post World Net. In 2003,
6|Page
Deutsche Post World Net consolidated all of its express and logistics activities into one single brand, DHL 1.2 LOGISTICS NETWORK OF DHL
DHL is a global expertise in express, air and ocean freight, overland transport and logistics solutions; DHL combines worldwide coverage with an in-depth understanding of local markets. Below are the global facts and figures that show you the scale of the world's largest express and logistics network.
DHL Express worldwide
Employees Countries and territories Hubs Bases Vehicles Aircraft Pack stations (only Germany) more than 124,000 more than 220 36 4700 72,000 350 900
DHL Logistics in figures
DHL logistics worldwide Employees * DHL Global Forwarding Countries and territories Terminals, warehouses, offices Air freight volume Ocean freight volume TEU ** DHL Excel Supply Chain Countries and territories Centers, warehouses, terminals Storage area sqm DHL Freight Countries and territories Full truckload movements p.a. 150 813 4,409,000 tones 2,764,000 59 2500 23,000,000 more than 30 2,000,000
more than 162,500
7|Page Terminals more than 160
1.3 DHL INDIA CORPORATE PROFILE
DHL Worldwide Express (India) Pvt Ltd is the No.1 international air express services provider in India, a position it has held since it began its India operations in 1979. Today, DHL offers its customers the entire spectrum of express services from international air express to high end logistics solutions including repair and return, strategic inventory management and direct express inventory. DHL India has over 50,000 customers serviced through DHL's national network with its 1,000 strong ground staff, fleet of 400 vehicles and dedicated service centers in Ahmadabad, Bangalore, Chennai, Cochin, Jaipur, Hyderabad, Kolkata, Mumbai, New Delhi, Pune and Tripura. Acknowledged for its innovative solutions and pioneering initiatives, DHL India has many firsts to its credit including India's first and only 24-hour customer service call center, the first to introduce customized solutions such as Jumbo Box, Junior Jumbo, Import Express and Fashion First for customers in the air express industry, as well as the first to provide track and trace services in India via email, via SMS or via the Internet and WAP phones. Facilities: DHL India has an outstanding reputation in the market for providing a reliable, fast and easyto-use service. DHL offersHighly trained and professional staff, committed to being responsive to all customers needs
Customer Service Agents, available round-the-clock, 365 days of the year, to serve customers whenever and wherever they need them Electronic pre-clearance of shipments through Customs Five international gateways providing direct-to-air networks and faster sorting of inbound and outbound shipments
DHL India is a proven facilitator of trade, across the globe. His strength lies in our global network and the know-how of our people. Backed by strategic alliances with world-class partners and the innovative use of technology, they strive to continuously improve the quality of our service. Our services range from fast, responsive and cost effective express deliveries toe-commerce fulfillment and intelligent logistics solutions. DHL Core Services consist of door-to-door air express delivery of documents and parcels of all sizes (and weight), both into and out of the country.
8|Page
9|Page
1.4 PRODUCTS AND SERVICES OF DHL: DHL Document Express (DOX): This service is ideal for shipments that are not subjected to Customs declaration at destinations, or have no commercial value or do not require a license. DHL Express Worldwide Package (WPX) This service is used for shipments with commercial value or those, which must be declared for Customs evaluation. They may be subjected to Customs inspection at destinations and may be taxable or dutiable. Jumbo Pack and Jumbo Junior: This service makes exporting easy. One box dispatched for one flat fee, anywhere in the world. DHL Jumbo Box is for shipments under 25kg and Jumbo Junior for shipments less than 10kg. Import Express: This service is a single window solution for all importing needs. DHL Import Express is a one window, one rate, and one account, one currency service that enables a shipment picked up from the supplier's doorstep overseas and delivered directly to the customer anywhere in the world. And what's more, it allows the customer to maintain total control of your importing costs. Fast Forward: Fast Forward is the revolutionary new service of DHL for moving heavy goods that brings increased efficiency and delivers greater cost savings for Indian importers and exporters. It facilitates the import and export of shipments weighing 20kg and above by providing significant savings with a wide range of innovative and flexible door-to-door solutions. Another feature of Fast Forward is Trade Automated Services (TAS), an online platform that provides comprehensive trade and customs information in 50 key countries worldwide, calculates total landed costs of a shipment (including duty, tax and other customs related charges), generates import and export documentation, screens senders and receivers against government lists pertaining to embargoes and sanctions, and compares an item's export and import clearance costs and regulations to enable qualifying sourcing decision. Fast Forward is specially developed after extensive research and designed to meet the unique needs of industries such as Automobiles, Electronics, Heavy Engineering, Publishing and Textiles.
10 | P a g e
2. INTEGRATED LOGISTICS SYSTEM Logistics is viewed as the competency that links an enterprise with its customers and suppliers. Information from and about customers flows through the enterprise in the form of sales activity, forecasts and orders. As products and materials are procured, a value added inventory flow is initiated that ultimately results in ownership transfer of finished products to customers. Thus the process is viewed in terms of two inter-related efforts, inventory flow and information flow. Inventory flow
Suppliers
Physical distribution
Manufacturing support
Customers
Information flow
11 | P a g e
2.1 Inventory Flow The management of logistics is concerned with the movement and storage of materials and finished products. From the initial purchase of a material or component, the logistical process adds value. By moving inventory when and where needed. Thus the material gains value at each step. For a large manufacturer, logistical operations may consist of thousands of movements, which ultimately culminate in the delivery of the product to an industrial user, wholesaler, dealer or customer. In order to understand logistics it is useful to divide it into three areas:
Physical distribution
Manufacturing support
Procurement
For DHL: DHL is completely service oriented therefore it does not have its own material movement but that of the customers the sender, the receiver and also the intermediateries. That means it only involves physical distribution and procurement. Procurement also includes the material needed for packaging such as paper, moulded trays and boxes, wooden crates, standard containers wraps, plastic inlays etc. The materials or the goods collected from the senders (including papers, documents, physical goods like clothing, household good, chemicals, exotic animals etc) are weighed, checked for condition, and depending upon its various characteristics it is packed. The goods are then dispatched to their destinations. There is no value addition to the material itself but it is done to the service which is provided (e.g. if there has to be a certain package delivered from India to UK the normal services would take about 2 days whereas as a super fast delivery would be done in about 9 hours) 2.2 Information flow Information flow identifies specific locations within a logistical system that have requirements. Information also integrates the three operating areas. The primary objective of developing and specifying requirements is to plan and execute integrated logistical operations. Logistical information involves two major types of flows:
1. Coordination flows 2. Operation flows
12 | P a g e
Planning and coordination flows Coordination is the backbone of the overall information system. Strategic objectives: Strategic objectives detail the nature and location of customers, which are matched to the required products and services to be performed. For DHL It implies estimating the time requires for collecting the goods from the door step of the sender and then estimating the time for the goods to reach the final customer.
Forecasting Forecasting utilizes historical data, current activity levels, and planning assumptions to predict future activity levels. Logistical forecasting is generally concerned with relatively short term predictions. The overall purpose of information planning/coordination flow is to integrate specific activities within a firm and to facilitate overall integrated performance.
For DHL DHLs whole business is dependent on the vital point of timely delivery. Based on the distance to the final receiver, the accessibility, the documentations and procedures that need to be handled etc they have fine tuned the process of delivery. They can accurately gauge how much time it will take for the goods to reach its end destination.
13 | P a g e
Operational flows The second aspect of information requirements is concerned with directing operations to receive, process, and ship inventory as required supporting customer and purchasing orders. Operational requirements deal with
Order management Order processing Distribution operations Inventory management Transportation and shipping Procurement
For DHL: DHL owns its success for the efficiency with which the operations are carried out. Here not only the company but the sender and sometimes the receiver can track the goods through their information center. They are given a certain password which they can use to trace via online or their customer service helpline.
14 | P a g e
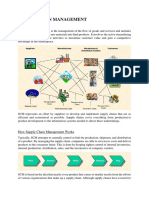
3. SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
Definition for supply chain management Supply chain management is the management of upstream and downstream relationships with suppliers and customers to deliver superior customer value at less cost to the supply chain as a whole. Explanation: The supply chain is the network of organizations that are involved through upstream and downstream linkages, in the different processes and activities that produce value in the form of products and services in the hands of ultimate consumer.( in detail mention above) For DHL: Supply chain Optimization
Good design is at the heart of an effective supply chain solution. DHL has developed a reputation for consistently developing innovative solutions that streamline operations and improve control. Their in-house teams have contributed to the solutions design of some of the world's leading brands and enabled to win key contacts. DHL solutions design team offers a wide portfolio of expertise and services, from logistics network strategy, transport design, warehouse design and simulation, through to operational improvement and inventory analysis
15 | P a g e
3.1 International Supply Chain:
DHLs international supply chain management solutions are focused on helping customers take increased control of international inbound supply chain to maximize the value of international and global sourcing. DHL helps customers: Give visibility of the upstream supply chain, and enable earlier decision making Create a more agile supply chain, better able to respond to changes in consumer demand Reduce lead times, inventories, and associated storage costs Customer-focused solutions are built up from the following core services: Origin management, including: vendor management; supplier collections; customs brokerage; consolidation services and value-added services Global forwarding, including: air/ocean/road/rail freight forwarding and management; European managed transport Destination management, including: port and demurrage management; customs brokerage; de-consolidation and pre-retail services; port to distribution centre transportation; direct store delivery (US only) Supply chain visibility and management, including: purchase order management; RFID product tracking; exception management; planning and forecasting; inventory management. Global forwarding services are provided across all major routes. Logistical services that are offered. Reverse Logistics Services Logistics Inbound to Manufacturing Medical device distribution Distribution to stores Management Engineering Response
16 | P a g e
Reverse Logistics DHLs reverse logistics solutions help customers plan, implement and control flow of materials and manage related information, back up the supply chain to recapture values and ensure the safe disposal of goods. Items include the recovery of obsolete or non-operational white goods such as refrigerators, plus the removal of old furniture on delivery of new or replacement products. Services include: Roll in Management: de-installation of finished goods at the customer's site Returns Management: receiving, sorting, verifying and managing returned products Express Delivery: Exchange of Dead On Arrival product.
Service logistics Service and replacement parts DHLs service and replacement parts service involves the management of manufacturers' replacement parts delivered to and from customers according to pre-defined service levels or warranty agreements on a one, two, four or eight-hour and next-day basis, 24 hours a day, seven days a week. DHL works closely with customers to overcome common issues such as: Poor parts availability High inventory investment Long lead times, accentuated by global sourcing High levels of customer returns Poor visibility, reporting and control Cost control of the demand chain Key services include: International freight forwarding Domestic and regional inbound deliveries Inventory planning, forecasting, procurement and analysis Distribution centre operations Outbound delivery
17 | P a g e
The entire process is underpinned by a web-enabled electronic order processing and order monitoring tool.
Inbound to Manufacturing Inbound to manufacturing is the complete end-to-end logistics management of inventories, facilities and labour associated with the inbound flow of materials from vendors and supplier origins to consumption points in manufacturers production lines. The service encompasses: Network, transportation and facility design Inventory optimization Supplier management Transportation management In-plant services Key to the service is integrating manufacturers' forecasting, order management and supply chain execution processes with their component suppliers. DHL implements warehouse management and supply chain event management systems to manage just-in-time deliveries and allow supply chain participants to exchange forecast requirements in real time Value is created for manufacturers and component suppliers throughout the world by: Enabling a robust and cost-effective supply chain Providing the necessary visibility so that the location of all components within the supply chain is known to all supply chain participants Reduce inventory and investment costs Improve delivery times Co-ordinate multiple components more efficiently
Medical Device Distribution DHL country-based warehouses for a number of manufacturers to service a local customer base. This includes the receipt of product from local or global manufacturing sites and downstream distribution to hospitals.
18 | P a g e
Distribution to stores management DHL distributions to store services are focused on helping retailers create efficient and flexible supply chains to deliver product to retail outlets at high levels of service. These solutions are built from several core services: reverse logistics collections; sortation; processing; repair/refurbishment; value recovery; disposal and compliance. Engineering Response Through our Engineering Response services, we manage the materials supply chain from works planning and inbound goods through to on-site works, delivering stock out to engineers, builders and construction workers in the field.
3.2 Extended supply chain services
DHL not only provides physical logistics services but also manages other enhanced supply chain services, improving efficiencies and reducing costs. a.) Order Management Receipt, management, execution, sequencing and dispatch of orders in a timely manner. b.) Call Center Management A Call Centre manages orders, monitors sales activities, provides customer services and functions as a Help-desk. c.) Global Inventory Management DHL gives the customer a global view of inventory, thus enabling informed decisions regarding the disposition of stock. d.) Consolidated Billing Services The creation of a consolidated and categorized invoice, based on all services performed in a specific time-period by more than one service provider, made available in an agreed format. e) Freight & Customs Solutions DHL's many years of experience with international trade requirements and formalities, combined with the European Competence Centre and country expertise, gives customers the leading edge in service, quality and management in cross border transactions.
19 | P a g e
4.2Implementation Services:
a. Implementation and Project Management Implementation starts by defining project aims, setting the targets and describing the deliverables in detail. The major topics in implementation include business processes, engineering, real estate, IT systems, migration, HR, finance and legal considerations. b. Quality Management Total Quality Management is a management strategy that integrates quality orientation into the whole structure and workflow of a company by using methods and techniques of quality management Corporate Policy for Quality, Environment, Health and Safety (QEHS) is based on five corporate values: Customer satisfaction: Providing our customers and their customers with excellent, high value logistics solutions Employee motivation: Building on the know-how and stimulation of individual potential in multi-cultural teams Operational excellence: Continuous improvement of processes and services to fulfill or exceed expectations Corporate citizenship: Acting as a responsible corporate citizen in all countries Shareholder reward: Developing a sustainable business to provide increasing shareholder value Globally, DHL management systems are certified according to the international standard for quality management systems ISO 9000 in almost every operating unit.
20 | P a g e
3.4 Performance Management:
Performance management is a key part of the supply chain. Measured elements are reviewed as a system, as each component interacts with all the other parts around it. Performance measuring not only records historical performance but also provides early indication of any service slippage. In this second role, the measures provide a valuable contribution to DHL's Continuous Improvement Programme.
3.5 Outsourcing Projects
Outsourcing involves DHL taking over and managing previous in-house logistics operations, including:
Distribution centers Transport operations Back-office functions Supply chain management functions After sales services
3.6 Innovative Supply Chain Development
Supply Chain Management services are delivered across industry sectors and provide expertise, knowledge and resources in terms of personnel and supply chain tools. All services are targeted at optimizing logistical operations in both process and strategy, and are aligned to the client's commercial expectations. The services are as follows: Strategic Logistics Consulting Lead Logistics Provider Consulting and providing Transport optimization: Route-Pro and Trans-Pro Consulting and providing Supply Chain Design Consulting and providing Transportation Engineering, optimization and re-engineering Implementation and Project Management Process Management Outsourcing
21 | P a g e
DHLs consulting services also offer re-organization of customer facilities, project management for customers, implementation of new IT Systems, creation of tender documents and tender processing. Supply Chain Re-engineering DHL works with customers to review supply chain efficiencies. One of the main tasks is to evaluate cost efficiency to ensure that costs are being driven down throughout the contract duration. Data analysis allows DHL to provide customers with 'what if modeling' or the impact of changing the business rules. After Sales Optimization Optimizing return logistics and spare parts logistics as well as maintenance and repair services. Vehicle Management Services Our vehicle management services focus on the management of sales and marketing support programmes for automotive manufacturers. Combining a range of services and systems to deliver a global response, they help you overcome challenges at the end of the automotive supply chain. Distribution to Stores Management DHLs distribution to store solutions are focused on helping retailers create efficient and flexible supply chains to deliver product to retail outlets at high levels of services These solutions are built from several core services including reverse logistics: logistics network strategy warehouse design and simulation Transport modeling.
22 | P a g e
3.7 Solution for customized End-to-end logistics
worldwide.
23 | P a g e
Best-in-class solutions that deliver Value to your supply chain.
DHL Solutions offers customized logistics solutions for your entire supply chain. Our complete overview from manufacturer/supplier to retailer to consumer enables you to achieve operational excellence at every stage. Services range from consulting and design to management and execution. They provide industry-specific expertise and long-term experience that add value to your business. DHL Solutions sets the pace in Supply Chain Management with state-of-the-art technologies, delivering customized business solutions. Leading edge IT systems ensure seamless integration and guarantee full transparency and control throughout the entire supply chain.
Customized Logistics Solutions.
Supply Chain Management Warehousing Value Added Services
Analysis, design and engineering. Lead Logistics Provider (LLP) and Lead Service Provider (LSP) services. Engineering, design and management. Vendor management, just in time. Order management, quality control, outbound fulfillment, reverse and return logistics and other services.
Outsourcing
Industry-specific local and transnational. Network and fleet planning and optimization Take-over and management of inhouse logistics including distribution, transport, back-office, supply chain and after sales.
Distribution
24 | P a g e
4. TRANSPORTATION
4.1 Transportation Functionality
Transportation is the most visible of all functions of logistics and high contributor to logistics cost. We can see trucks, containers and wagonloads of material being moved from place to place as an activity directly associated with trade and business. We should also appreciate that this is an activity that adds highest amount of cost to the activity of making inputs and outputs available to consumers. Transportation function moves the products to meet customer expectations at minimum cost. Transportation is one of the most visible elements of logistics operations. Transportation provides 2 major functions: product movement & product storage. Product Movement Whether the product is in the form of materials, components, assemblies, work-in-process, or finished goods, transportation is necessary to move it to the next stage of the manufacturing process or physically closer to the ultimate consumer. A primary transportation function of product movement is moving up and down the value chain. Since transportation utilizes temporal, financial, and environmental resources, it is important that items be moved only when it truly enhances the product value. Transportation involves the use of temporal resources because product is inaccessible during the transportation process. Such product, commonly referred to as in-transit inventory, is becoming a significant consideration as a variety of supply chain strategies such as just in time and quick response practices reduce manufacturing and distribution center inventories. Transportation uses financial resources because internal expenditures are necessary for private fleets or external expenditures are required for commercial or public transportation. The major objective is to move product from an origin location to a prescribed destination while minimizing temporal, financial and environmental resource costs. Loss and damage expenses must also be minimized. At the same time the movement must take place in such a manner that meets customer demands regarding delivery performance and shipment information availability.
Product Storage: Temporary storage in stationary vehicles or Vehicles kept moving on a circuitous route Product storage is expensive in a transport vehicle. But sometimes keeping overall cost in mind this is adopted. A. When unloading and loading is more expensive than storage B. When storage space is limited. [Situation when inventory levels are very high]
25 | P a g e
4.2 Principles
There are two fundamental principles guiding transportation management and operations. They are economy of scale and economy of distance. Economy of scale refers to the characteristic that transportation cost per unit of weight decreases when the size of the shipment increases. E.g. truckload shipments cost less per pound than less-than-truckload shipments. It is also generally true that larger capacity transportation vehicles such as rail or water are less expensive per unit of weight than smaller capacity vehicles like motor or air. Transportation economies of scale exist because fixed expenses associated with moving a load can be spread over the loads weight. The fixed expenses include administrative costs of taking the order; time to position the vehicle for loading or unloading, invoicing and equipment cost. These costs are fixed because they do not vary with shipment volume. E.g. suppose the cost to administer a shipment is $ 10.00. Then the 1-pound shipment has a per unit of weight cost of $10.00, while the 1,000 pound shipment has a per unit of weight cost of $0.01. Thus, it can be said that an economy of scale exists for the 1000-pound shipment. Economy of distance refers to the characteristic that transportation cost per unit of distance decreases as distance increases. E.g. a shipment of 800 miles will cost less than two shipments (of the same combined weight) of 400 miles. Transportation economy of distance is also referred to a se tapering principle since rates or charges taper with distance. The rationale of distance economies is similar to that for economies of scale. Longer distances allow the fixed expenses to be spread over more miles, resulting in lower overall per mile charge. These principles are important considerations when evaluating alternative transportation strategies or operating practices. The objective is to maximize the size of the load and the distance that is shipped while still meeting customer service expectations.
26 | P a g e
4.3 Transport Infrastructure
Transportation infrastructure consists of the rights-of-ways, vehicles, and carrier organizations that offer transportation services on a for-hire or internal basis. The nature of the infrastructure also determines a variety of legal and economic characteristics for each mode or multimodal system. A mode identifies the basic transportation method or form. RAIL NETWORK Since olden times, railroads have handled the largest number of ton-miles. As a result of the early establishment of a comprehensive rail network connecting almost all the cities and towns, railways dominated the intercity freight tonnage till World War II and in some cases of Europe, Asia and Africa they even connected the countries. This early superiority enabled railways to transport large shipments very economically. MOTOR CARRIERS Highway transportation has increased rapidly since the end of World War II. This is because Motor carrier industry results from door-to-door operating flexibility and speed of intercity movement. They are even flexible because they can operate on each and every kind of roadways. In comparison to railroads, motor carriers have relatively small fixed investments in terminal facilities and operate on publicly maintained highways. Although the cost of license fees, user fees, and tolls are considerable, these expenses are directly related to the number of over-the-road units and miles operated. The variable cost per mile for motor carriers is high because a separate power unit and driver are required for each trailer or combination of tandem trailers. Labor requirements are also high because of driver safety restrictions and the need for substantial dock labor. Motor carriers are best suited to handle small shipments moving short distances. WATER TRANSPORT It is the oldest mode of transportation. First it was the sailing vessels, which was replaced by steamboats in early 1800s and by diesel power in the 1920s. Domestic water transportation involves the Great Lakes, canals, and navigable rivers. In every country, fewer system miles exist for inland water than any other transportation mode. The main advantage of water transportation is the capacity to move extremely large shipments. Water transport employs 2 types of vessels. Deep-water vessels, which are generally designed for Ocean and Great Lakes use, & are restricted to deep-water ports for access. In contrast, diesel-towed barges, which generally operate on rivers and canals, have considerably more flexibility. Water transport ranks between rail and motor carrier in the fixed cost aspect. Although water carriers must develop and operate their own terminals, the right-of-way is developed and maintained by the government and results in moderate fixed costs as compared to railways and highways. The main disadvantage of water transport is the limited range of operation and speed. Unless the origin and destination are adjacent, supplement haul by rail or truck is required. The
27 | P a g e
capability to carry very high cargo at an extremely low variable cost places this mode of transport in demand when low freight rates are desired and speed of transit is a secondary consideration. AIR TRANSPORT Air transport is the newest and the least utilized mode of transport. Its major advantage being its speed, which is accompanied by high costs. A coast-to-coast shipment via air requires only a few hours contrast to days taken by other mean of transportation. The high cost of transport can be traded off for high speed, which allows other elements of logistical design, such as warehousing, inventory to be reduced or eliminated. But still air transport remains more of a potential opportunity than a reality because it is very much underutilized. The high cost of jet aircraft, coupled with erratic nature of freight demand, has limited the assignment of dedicated planes to all-freight operations. However premium carriers provide planes dedicated for freight operations. This premium service started off with documents and has moved onto large parcels, which is an ideal service for firms with a large number of highvalue products and time-sensitive service requirements.
FOR DHL: DHL uses all the modes of transportations that is Airways roadways waterways rail freight DHL has its own fleet of airplanes and motor vans. Depending upon the final destination where the goods have to finally reach and the type of package the customer has paid for, DHL uses the individual modes of transport or a combination of either of these or all. Once again the geographical location and how fast the goods have to be delivered are the factors for the final selection of modes of transportation. The concept of economies of scale and economies of distance are both taken into consideration in case of larger consignments where DHL provides an appropriate logistical solution which helps in reducing the overall cost for the customers.
28 | P a g e
4.4Optimization of logistics with DHLroad and rail solutions.
DHL Freight is a leader in European overland transport. Our continent-wide network and comprehensive range of products and services guarantee reliable transport. DHL Freight offers you regular services for group age and a full range of transport services for part- and full-load shipments by road, rail and intermodal transportation. They provide special handling and transportation for perishables, furniture, trade fair or event equipment, as well as tailored customs clearance services in more than 350 offices across Europe. State-of-the-art IT systems give you totals shipment visibility and higher delivery efficiency. Our industryspecific expertise and long-term experience can improve your productivity and streamline your operations. A successful, high-caliber partnership with DHL Freight gives you all the advantages you need to optimize your logistics.
29 | P a g e
4.5 Air and ocean freight solutions for a competitive advantage
Whether you need to forward door-to-door, airport-to-airport or port-to-port freight, DHL Danzas Air & Ocean offers a comprehensive range of services no matter the size, weight or dimensions of your goods. Combined with an extensive tool kit of information management systems and a global network of dedicated control towers, our experienced teams around the world can create the right logistics solution for your business. DHL Danzas Air & Ocean is in pole position to
30 | P a g e
Air Freight DHL Danzas Air & Ocean offers a range of fast and cost-effective airfreight services for our most time-sensitive freight with door-to-door or airport-to-airport services, fixed schedules on all main routes and reliable connections to all other destinations.
DHL Air Freight products include:
Air First
Whether door-to-door or airport-to-airport, Air First guarantees priority on the first flight out and forwarding within two days 24hours a day, 7-days a week, and 365-days a
Air Premier
Combines price and time considerations for both door-to-door and airport-to-airport service. Your shipment will arrive at the airport of any major marketplace around the
Air Value
Creative routing solutions via major gateways can save you even more money while adding only 1-2 days over our Air
Sea/Air
Chartering additional airfreight capacity is part of everyday business especially if there is limited commercial lift, for new product launches, during peak seasons or for oversized cargo. Our specialists create solutions to get your goods through on time.
Part and Full Charter
Combine the speed of airfreight and the lower cost of ocean freight and youll benefit from our strength and experience in both. Plus, real-time tracking at every step of the way.
31 | P a g e
5. INVENTORY MANAGEMENT AND WAREHOUSING. Inventory is an unused asset, which lies in stock without participating in value adding process. Unused equipment, raw material, WIP and Finished goods, consumables, spare parts, bought out parts, tools and tackles, gauge and fixtures etc. In India 9 to 12 months of sales quantity lies in the form of Inventory [R/M, WIP, Bought out parts and Finished goods] as against a few days in Japan and a month in the US and Europe. In our country inventory is always viewed as asset [working capital], in fact, though it is called an asset, it is a big liability Warehousing was a customers function conventionally anywhere in the world. Customer to protect himself from shortages at the time of inclement weather always used to store provisions and other utilities in his house. Consumers own stores were underground cellars, smoke houses to store variety of items. Poor communication infrastructure was mainly the cause for this storage by customer. Producers and tradesmen conveniently shrugged off their responsibility for storage and passed it on to the customer who was left with no option. Traditional concept of warehouse as store or godown has undergone major change now. Warehouse is considered a value adding facility now, playing a remarkable role as a function of logistical management. Warehouse Infrastructure Network Warehouse Management Solution Inventory Optimization Special warehouse solution Outsourcing Projects
5.1Warehouse Infrastructure Networks
DHL warehouse service supports inbound logistics, distribution and aftermarket services in a way that improves inventory management, reduces total operating costs and improves cycle times. DHL facilities offer our customers warehousing that is fully integrated into the wider supply chain and meets demanding service levels. This encompasses the design implementation and operation for both dedicated and multi user sites. Benefits include improvements in: Customer service levels Stock accuracy Lead times
32 | P a g e
Redundant stock costs Productivity responsiveness to a company's strategic needs a. Multi User Centers We provide a network of multi-user warehouses, enabling manufacturers to hold inventory at local level, whilst avoiding expensive, dedicated storage solutions. These facilities can receive products from both local and global manufacturing sites, providing downstream distribution. b. Strategic Part Centers (SPC) Our Strategic Part Centers (SPCs) are in-country facilities offering:
1, 2 and 4 hour order fulfillment Stock optimization across the complete network of SPCs Guaranteed performance against agreed business rules
c. Express Logistics Centers (ELC) Our Express Logistics Centers (ELCs) are regional centralized facilities offering: order processing outsourced repair facilities custom final assembly kitting services
5.2 Warehouse Management Solutions:
a) Warehouse Management Systems The Warehouse Management System (WMS) records all events and actions in the receipt, handling and storage of products and orders in a warehouse environment. The WMS also accurately records the location of inventory whilst stored in the warehouse. Our Prologs WMS manages all critical processes in the warehouse, and is also an important support for varied transport and distribution concepts (planning, time controlling, booking of transport capacity, communication with customs and other authorities). b) Strategic Inventory Management Strategic Inventory Management (SIM) has been created to deliver urgent shipments to main business areas within a 2 to 4 hour time frame, usually time critical spare parts with a high value and high impact on business.
33 | P a g e
c) Direct Express Inventory Management Direct Express Inventory (DEI) allows customers to centralize stock in one warehouse and use express distribution to deliver components the next day. Entire management is done by DHL. d) Repair Return Inventory Management Return & Repair Inventory (RRI) manages the physical flows for Return material authorization. In this case, DHL will be responsible for picking up the broken part, sending a new one, bringing the broken part to a repair centre and moving repaired parts back into stock. e) Cross Docking Cross-dock operations are facilities where shipments are received from one mode of transport and transferred to another mode, or where shipments complete one leg of a journey prior to commencement of another journey. Shipments are consolidated or deconsolidated. Product received into the facility is not taken into inventory.
5.3 Inventory Optimization:
Through effective inventory management, inefficiencies can be driven out of the supply chain, overall costs reduced and high service levels achieved. They optimize inventory at a line-item level at every stage of the supply chain. DHL focuses on driving results in: Supplier management Expediting Order replenishment Demand forecasting Safety stock setting Order pipeline monitoring Excess stock management Inventory optimization is supported by inventory management software that calculates 'line item risk profiles' that measure the variability of demand and supply for each line item within a customers inventory.
34 | P a g e
DHL offers: Average of 20% inventory reduction and 8% improvement in product availability Reduced inventory and overhead costs Improved sales, profitability and return on investment High service standards Better matching of supply with demand More streamlined and responsive supply chain
Shared-user Warehousing Our shared-user facilities are designed to meet the needs of organizations of any size. Currently, we provide shared-user services to leading manufacturers and retailers of medical supplies, consumer products, industrial equipment, chemicals and technology. Through sharing of DHL's resources, such as space, labour, equipment and transportation, customers benefit from synergies that considerably reduce supply chain costs. This environment returns significant value to a small business requiring distribution operations without long term lease or capital commitments, or a large enterprise handling a new acquisition, product launches or seasonal overflow. Campus Solutions We pioneered the campus model to provide regional customers with a flexible solution designed to capitalize on similar distribution channels, minimize labour costs, and increase specialized equipment utilization. Campuses are strategically located at key distribution points in North and South America, Europe and select locations in Asia, allowing for expedited transit times to large concentrations of consumers. 5.4 Special Warehouse Solutions Vendor Hubs warehousing and delivery of service parts, based on demand pull. Vendor hubs are usually located in close proximity to the manufacturing facility.
Reverse Centers specially designated facilities for the receipt and handling of returned parts for repair, recycling or disposal.
35 | P a g e
Bonded Warehousing Bonded warehouses provide secure environments in which customers' products can be held without immediate payment of local duties and taxes. Shared-user Warehousing Our shared-user facilities are designed to meet the needs of organizations of any size. Currently, we provide shared-user services to leading manufacturers and retailers of medical supplies, consumer products, industrial equipment, chemicals and technology. Through sharing of DHL's resources, such as space, labour, equipment and transportation, customers benefit from synergies that considerably reduce supply chain costs. Consequently, the customer can increase efficiencies throughout their distribution network and maintain a higher level of service to their customers.
5.5 Outsourcing Projects
Outsourcing involves DHL taking over and managing previous in-house logistics operations, including:
Distribution centers Transport operations Back-office functions Supply chain management functions After sales services
36 | P a g e
6. VALUE ADDED SERVICES
Co packing Product assembly Other value added services
6.1 Co-packing
We offer a comprehensive selection of manufacturing and packaging services through Power Packaging a DHL Company. By integrating manufacturing and packaging operations within their supply chains, our customers can:
Add flexibility Improve service levels Reduce costs Accelerate time to mark Increase asset utilization
In addition to these core packaging services, Power Packaging brings a unique set of services and capabilities for customers that include Beverage manufacturing: Blending, mixing and filling of hot and cold fill beverages and concentrates in the following types of containers:
Plastic bottles (PET) and glass containers (10 oz up to 128 oz) Shelf-stable containers (paperboard, plastic cup and bag-in-a-box)
a.
Dedicated facility services: Turnkey manufacturing solutions including: Site selection/development Facility and systems design New facility start-up and operation
37 | P a g e
c. Other services:
Packaging and raw material sourcing, procurement and assembly Batch/quality control tracking via digital easy-to-trace coding system Full range of secondary packaging services
6.2 Product Assembly
Postponement, quick response and mass customization are breakthrough business strategies enabled via packaging services. Integrating packaging operations into distribution centers streamlines fulfillment reducing cost, enhancing product visibility and control, and improving speed-to-market and flexibility in the supply chain. Packaging services include:
Postponement packaging - primary, secondary and specialty components Co-packing, kitting, assembly and repackaging Retail-ready, point-of-purchase displays Lot control via variable digital and laser printing Machinery system engineering - labeling, bagging, carton filling, club store packs, clamshells and printed and unprinted film over-wraps Make-to-order pallets Product rework/redress
6.3 Other Value Added Services
a. Kitting/Pre-Assembling Kitting is the addition of items such as accessories and batteries to the product pack. Preassembling is completion of a finished product from component parts or preprogramming of products.
b. Re-Working/Re-Packing Repacking for a specific customer can include repalletisation. Reworking is the modification of products to suit a local market.
38 | P a g e
c. Packaging/Bundling Packaging includes packing of products into suitable media for transportation and retail display. Bundling is the assembly of a number of pre-packaged products to make up an integrated product offering.
d. QA Control Quality control ensures that product is received into and dispatched from the warehouse in a suitable condition, free from faults and defects. e. Labeling/Merchandising The application of labels either to the product or to the packaging. Merchandising can include the addition of price stickers or promotional items ready for retail display.
6.4 External Performance Measurement
While internal measures are important for detailed organizational monitoring, external performance measures are also necessary to monitor, understand and maintain a focused customer perspective and to gain innovative insights from other industries. The topics of customer perception measurement and best practice benchmarking, which address these requirements, are discussed and illustrated below.
6.5 Customer Perception Measurement
To succeed in any activities of business one has to always cater to and satisfy the needs of the customer. To do so, it is essential for one to know how the customer thinks in order to meet his needs in a more satisfying manner. Therefore, an important component of leading edge logistical performance is the regular measurement of customer perceptions. Such measures can be obtained through surveys or by systematic order follow up. These surveys can be company - or industry sponsored. Such surveys ask questions regarding the firms and the competitors performance in general or for a specific order in particular. Most of the surveys incorporates measurement of customer perceptions regarding availability, performance-cycle time, information availability, problem resolution and product support. The survey may be developed and administered by the firm itself or by consultants, delivery agents or industry organizations.
39 | P a g e
7. RECOMMENDATION
1. ENHANCE THE SMART-TRUCK PROJECT Because of the stage of recession and high competition, the companies need to make difference to have new customers and increase their market share. To invent completely new product can be very expensive and take very much time. So, making little difference on the current product or service can be better. At this time, we need to talk about innovation. As a CEO of DHL Logistics, enhancing the Smart-Truck Project is going to be my first strategy. This project will allow our company to deliver faster and cut cost by using less fuel.To achieve this goal, we will follow some steps: a. Increase the budget of R&D 10%. b. Prepare an office for a new innovation team and assign a leader to work on this project. c. Also pay premium for new and creative ideas whoever gives it (even juniors). So this will provide us innovative atmosphere
2. AQUIRE SMALL - SIZE LOGISTICS COMPANIES: By acquiring small local companies in different countries like China, India, USA, will give us precense in that countries. Also, this will decrease the threat of restrictions in those companie. Even they are small companies, they can have creative solutions to different problems. So we are acquiring new brains at the same time. We can get some ideas from them to improve our skills. I mean we are not firing people who were working there actually, we are hiring them to work with us.
40 | P a g e
8. CONCLUSION
Logistics is one the most important and integral part of any organisations strategy and function. When the logistical process is carried out accurately then not only the company reduces the production cost but also improves the efficiency and customer satisfaction. Overall logistics management is very important for todays highly competitive and cut- throat corporate world. DHL has the worlds largest express and logistics Network. Over the past decades it had turned delivering goods into a finely oiled process. Be it a book, pen, WIP material, drugs, hazardous chemicals, clothes, documents, wild animals and any other thing under the sun DHL delivers it. With a network spanning 200 countries and with its private fleet of airplanes, mobile vans, cargo ship carriers & even rail way automotives in some countries DHL can handle any type of goods. Not only has that with international network there come the hassle of documentation and paperwork, standard packaging and other formalities to adhere to. But DHL has its own department which looks into the international laws and other formalities. In the end what matters is delivering well in good condition at the door step of the customer. A happy and satisfied customer makes the business grow. Competitors have come and gone but DHL has been able to keep its No 1 position intact. This is because of its dynamic nature and attitude of maintaining good customer relations. Logistics management is important for every organization but more so DHL. We have tried to incorporate all the facets of logistics which propel DHL to be the best delievery and carriage-service around the world. No wonder that DHL is head and shoulders above all of its competitors!
41 | P a g e
9. BIBLIOGRAPHY
a) Logistics and Supply Chain Management- Written by Martin Christopher b) Indian Logistics Industry (2008) published by Cushman & Wakefield c) Business logistics Bardi d) Elements of Logistics Management- S.D.Aphale
Websites:
1. www.logisticmanagement.com 2. www.dhl.com
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Operations Startegy in Global EnvironmentDocument28 pagesOperations Startegy in Global EnvironmentCindy Ortiz Gaston100% (2)
- Solution Manual For Marketing Management 3rd Edition Greg Marshall Mark JohnstonDocument21 pagesSolution Manual For Marketing Management 3rd Edition Greg Marshall Mark JohnstonJustinPricetfoq100% (42)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Presentation On Supply Chain Management of CocaColaDocument25 pagesPresentation On Supply Chain Management of CocaColaSyed R Monjur76% (17)
- Global Supply Chain Control TowersDocument16 pagesGlobal Supply Chain Control TowersTebaterror100% (2)
- Startup ReportDocument84 pagesStartup ReportReshanth Vangalapudi0% (1)
- Value Chain NikeDocument13 pagesValue Chain NikeDebeta Indra Utama100% (1)
- Sap Bw-Apo System Landscape and Interface Considerations: Global ASAP For BW AcceleratorDocument30 pagesSap Bw-Apo System Landscape and Interface Considerations: Global ASAP For BW AcceleratorHarit Parikh100% (1)
- Toyota's Crisis Management ResponseDocument21 pagesToyota's Crisis Management Responsevan_1234100% (1)
- Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource Managementvan_1234No ratings yet
- Toyota's Crisis Management ResponseDocument21 pagesToyota's Crisis Management Responsevan_1234100% (1)
- ToyotaDocument23 pagesToyotavan_1234No ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource Managementvan_1234No ratings yet
- Budgeting and Budgetary ControlDocument18 pagesBudgeting and Budgetary ControlchandasumaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Online Shopping ProjectDocument12 pagesEvolution of Online Shopping Projectvan_1234No ratings yet
- Published Corporate Annual ReportsDocument33 pagesPublished Corporate Annual Reportsvan_1234No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship - Industrial SicknessDocument62 pagesEntrepreneurship - Industrial Sicknessvan_1234100% (1)
- SSFDocument2 pagesSSFvan_1234No ratings yet
- International Finance: Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange RatesDocument8 pagesInternational Finance: Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Ratesvan_1234100% (1)
- Personnel ManualDocument5 pagesPersonnel Manualvan_1234No ratings yet
- New PPT kfc-2Document36 pagesNew PPT kfc-2van_1234No ratings yet
- Foreign Trade PolicyDocument23 pagesForeign Trade Policyvan_1234No ratings yet
- Foreign Trade PolicyDocument23 pagesForeign Trade Policyvan_1234No ratings yet
- Employees: Stakeholder AnalysisDocument3 pagesEmployees: Stakeholder AnalysisSamrin HassanNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Coordination Models: A Literature Review: Burra Karuna Kumar, Dega Nagaraju and S. NarayananDocument16 pagesSupply Chain Coordination Models: A Literature Review: Burra Karuna Kumar, Dega Nagaraju and S. NarayananAhmad1986 RawashdehNo ratings yet
- Coca ColaDocument11 pagesCoca ColaKushal BajracharyaNo ratings yet
- Entrep q4 All LessonsDocument14 pagesEntrep q4 All LessonsANDREI ESCOTILLONNo ratings yet
- Literature SurveyDocument11 pagesLiterature SurveyNAGANo ratings yet
- Darshankumar Patil: Material Procurement & Supply Chain Management GroupDocument2 pagesDarshankumar Patil: Material Procurement & Supply Chain Management GroupRohit ShedaleNo ratings yet
- En Slimstock RetailDocument2 pagesEn Slimstock RetailDinesh PatilNo ratings yet
- The Eight Essential Supply Chain Management Processes2004Document10 pagesThe Eight Essential Supply Chain Management Processes2004kallepalliNo ratings yet
- PBO - Lecture 02 - Value Chains and Global OperationsDocument32 pagesPBO - Lecture 02 - Value Chains and Global OperationspreeyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter Twelve: Marketing Channels: Delivering Customer ValueDocument15 pagesChapter Twelve: Marketing Channels: Delivering Customer ValueAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Booz&Co 2012 Oil & Gas Industry PerspectiveDocument7 pagesBooz&Co 2012 Oil & Gas Industry PerspectiveHuiJooHweeNo ratings yet
- 19BSP3167 Varun Kumar Itc Supply ChainDocument4 pages19BSP3167 Varun Kumar Itc Supply Chainvarun kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- Walmart 4Document14 pagesWalmart 4Mus Andey ShahNo ratings yet
- Phase 3 - Porter's Five Forces AnalysisDocument3 pagesPhase 3 - Porter's Five Forces AnalysistheNo ratings yet
- Inbound Logistics Study of Prema Engineering WorksDocument67 pagesInbound Logistics Study of Prema Engineering WorkssNo ratings yet
- Offshore Wind Turbine Cost Structure Analysis: High Technology Letters October 2020Document16 pagesOffshore Wind Turbine Cost Structure Analysis: High Technology Letters October 2020Mohammed AzarudeenNo ratings yet
- Business Simulation With Professional Development - EditedDocument19 pagesBusiness Simulation With Professional Development - EditedKELVIN OKELLONo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument5 pagesSupply Chain ManagementSwarnim DobwalNo ratings yet
- Strategic Supply-Chain For S4HANA - Jan - 2020Document54 pagesStrategic Supply-Chain For S4HANA - Jan - 2020venkay1123100% (1)
- Group AssignmentDocument7 pagesGroup Assignmentwishways srinivasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - San JoseDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 - San JoseJulia San JoseNo ratings yet
- Value Chain ApproachDocument7 pagesValue Chain ApproachkimlengtycoonNo ratings yet
- FEASIB - Flower ShopDocument22 pagesFEASIB - Flower ShopALTHEA ALANONo ratings yet