Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electric Forces and Fields Exam 1 Review
Uploaded by
Bob TheBuilderOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electric Forces and Fields Exam 1 Review
Uploaded by
Bob TheBuilderCopyright:
Available Formats
exam 1 spring 06 -kg 1. Two charges, Q1 and Q2, are separated by a certain distance R.
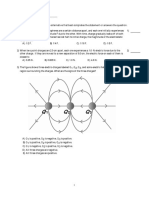
If the magnitudes of the charges are doubled and their separation is also doubled, then what happens to the electrical force between these two charges? A) It is quadrupled B) It changes by a factor of 3 C) It is doubled D) It remains the same E) It changes by a factor of 8 1D 2. Four equal charges are located at the corners of a square of side d. If the magnitude of each charge is doubled, then what happens to the resultant force on each charge? A) It remains the same B) It is doubled C) It is quadrupled D) None of the other choices is correct E) It changes by a factor of 8 2C 3. Three equal charges are at three of the corners of a square of side d. A fourth charge of equal magnitude is at the center of the square as shown in Figure. Which of the arrows shown represents the net force acting on the charge at the center of the square? A) A B) B C) C D) D E) None of them 3B
o 8 .1 . 0 5
10 2
0 1
m 1 .1 6 7 p . 0
7 2
1 9 e K( m, v) . 0 1 .1 6
1. . 2 mv 2
.0 6 Q 616 1 q. . Q .o ( .Four q 61 6 .0 F( Q , , ) q x ( ). i Q 61 point charges of equal magnitude, 4 . .signs arecsarranged 0 4. but varying x
2
s ( i n ). j)
16d 0d 0e e g g 16 F FqQ, 2 ( ,GL 2 e v i, ) n
o on the corners of the square of side d as shown in Figure. Which of the arrows 0 shown represents the net force acting on the charge at the upper right hand corner F F = 1 2 of the square? . 0 4 1 A) A B) B C) C D) D E) None of them 4B
1 d F FqQ, 2 2 e 1 ( , ,L 1 0g )
5. Three identical point charges Q of magnitude +6.0 C each are located at the corners of an equilateral triangle of L = 2 m as shown in Figure. The magnitude of resultant force acting on the upper charge Q (at point P) is given by A) 0.075 N B) 0.094 N C) 0.140 N D) 0.162 N E) 0.266 N 5C
L2
L2
2
.F . 2 =0 11 2 6
Fake
q 1 (x x ) 1
q 2 (x x ) 2
2
x0 1 .
6. Two point charges of magnitudes +8 C, and +10 C are placed along the x-axis at x = 0 cm and x = 100 cm, respectively. Where must a third charge be placed along the x-axis so that it does not experience any net force because of the other two charges? A) 47 cm B) 9 cm C) 4 cm D) 91 cm E) 24 cm 6A
F()0 n 4 i x=. d 7 2
7. Three equal point charges of varying signs are placed on three of the corners of a square of side d as shown in Figure 19-17. Which of the arrows shown represents the direction of the net electric field at the vacant corner of the square? A) A B) B C) C D) D E) none of them 7B
8. Two point charges of +30 C and -9 C are separated by a distance of 20.0 cm. What is the intensity of electric field E midway between these two charges? A) 35.106 N/C directed towards the negative charge B) 35.106 N/C directed towards the positive charge C) 18.8.106 N/C directed towards the negative charge D) 18.8.106 N/C directed towards the positive charge E) 2.7*107 N/C directed towards the negative charge 8A a 9. A proton is placed in an electric field of intensity 500 N/C. What is the magnitude and direction of the acceleration of this proton due to this field? A) 4.8.109 m/s2 B) 4.8.1010 m/s2 C) 3.2.1010 m/s2 D) 9.8.1010 m/s2 E) 7.4.1010 m/s2 9B
10. An electron traveling along the +x-axis enters an electric field that is directed vertically down, i.e., along the negative y-axis. What will be the direction of the electric force acting on the electron after entering the electric field? A) upward B) to the right C) downward D) to the left E) No force is acting because the electron has negative charge 11. Two point charges of +7 C and +10 C are placed inside a cube of edge length 0.1 m. The net electric flux due to these charges is given by A) 3.4.105 Nm2/C B) 1.1.106 Nm2/C C) 7.9.105 Nm2/C D) 9.6.105 Nm2/C E) 1.9.106 Nm2/C 11E
12. Gaussian surfaces A and B enclose the same positive charge +Q. The area of Gaussian surface A is three times larger than that of Gaussian surface B. The flux of electric field through Gaussian surface A is A) 3 times larger B) times larger C) the same D) times smaller E) 3 times smaller 12C 13. A charged particle with charge +q = 7 C is initially at rest. It is accelerated through a potential difference of 300V. What is the kinetic energy of this particle after acceleration period? A) 2.10-8 J B) 3.41 J C) 5.107 J D) 0.9 mJ E) 2.1 mJ 13E a 14. The two charges of magnitude 2 C and 3 C are placed at the corners of the base of an equilateral triangle, as shown in Figure. What is the electric potential at the vertex, P, of the triangle due to these charges? A) 2.2.105 V B) 4.7.105 V C) 7.6.105 V D) 1.2.106 V E) .106 V 14A 2.4
15. Two point charges of magnitude +4.0 nC and -4.0 nC are placed as shown in Figure . What is the potential difference between points A and B? A) 0 V B) 48 V C) 72 V D) 96 V E) 120 V 15D
16. Two equal point charges of magnitude 4.0 C are situated along the x-axis at x1 = -2.0 m and x2= 2.0 m . What is the electric potential energy of this system of charges? A) 18.103 J B) 2.2.103 J C) 9 J D) 3.6.10-2 J E) 9.0.10-3 J 16D a 17. When a dielectric material is introduced between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor the capacitance increases by a factor of 4. What is the dielectric constant of the material introduced between the plates? A) 1.41 B) 1.73 C) 2 D) 3 E) 4 17E 18. The potential difference between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor is 24V and the electric field between the plates has a strength of 3000V/m. If the plate area is 40.0 cm2, what is the capacitance of this capacitor? A) 6.6 nF B) 4.4 nF C) 1.48 pF D) 4.4 pF E) 0.012 pF 18D
19. A particle of charge q = 3.1 C is fixed at point P, and a second particle of mass m = 20 mg (milligrams) and the same charge q = 3.1 C is initially held a distance r1 = 0.9 mm from P. The second particle is then released. Determine its speed when it is a distance r2 = 2.5 mm from P. A) 6.10-9 m/s B) 1.9.10-3 m/s C) 0.83 m/s D) 516 m/s E) 2480 m/s 19E a 20. A plastic rod having a uniformly distributed charge q = 3.1 nC has been bent into a circular arc of
radius R = 20cm and central angle 1200. With V = 0 at infinity, what is the electric potential at P, the center of the curvature of the rod? A) 46.4 V B) 139 V C) 292 V D) 418 V E) 1224 V 20B a 21 A 20 F capacitor A is charged to potential 120 V then connected (closing switch S) to 16 F capacitor B and 12 F capacitor C (see fig). Both capacitors B and C were discharged initially. What is the final potential across the three capacitors? A) 30 V B) 50 V C) 70 V D) 90 V E) 110 V
21B
You might also like
- Practice Questions Chs 21-24 1Document40 pagesPractice Questions Chs 21-24 1jevanjunior0% (1)
- Two Small Spheres in MotionDocument12 pagesTwo Small Spheres in MotionharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Prac FinaleDocument14 pagesPrac FinaleadadafasfasNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 review: Electric charge and field concept testDocument16 pagesExam 1 review: Electric charge and field concept testMartin SeungWhan KimNo ratings yet
- Physics 1653 Exam 3 - Review Questions: Sphere A Sphere BDocument39 pagesPhysics 1653 Exam 3 - Review Questions: Sphere A Sphere BPi PoliNo ratings yet
- Review Test 1314Document11 pagesReview Test 1314Hassan AliNo ratings yet
- W2016_PHYS259_Final_booklet_I_answersDocument12 pagesW2016_PHYS259_Final_booklet_I_answersYasmeenNo ratings yet
- Test1 16FDocument8 pagesTest1 16FJasper LuNo ratings yet
- Test 1Document5 pagesTest 1ramNo ratings yet
- 111年下A卷題庫Document10 pages111年下A卷題庫陳奕安No ratings yet
- Electrostatics ExerciseDocument20 pagesElectrostatics ExerciseUtkarsh Mittal86% (7)
- p240w12 Mid1-2Document14 pagesp240w12 Mid1-2shlaeaNo ratings yet
- Previous Exams Questions Ch21-22-With NotesDocument7 pagesPrevious Exams Questions Ch21-22-With NotesaamerbolookiNo ratings yet
- Practice Midterm 1.2 v2Document5 pagesPractice Midterm 1.2 v2golemisgreeaaaatNo ratings yet
- Previous Exams Questions Ch23-24-With NotesDocument11 pagesPrevious Exams Questions Ch23-24-With NotesaamerbolookiNo ratings yet
- MCQ Chapter 1Document3 pagesMCQ Chapter 1sukaina fatimaNo ratings yet
- Cmda Mock Exam Phy 124Document4 pagesCmda Mock Exam Phy 124tajudeenabdullahaNo ratings yet
- Assignment (CHAPTER 1) XIIDocument2 pagesAssignment (CHAPTER 1) XIIsneha guptaNo ratings yet
- 07 08 I FinalDocument9 pages07 08 I FinalMahmoud FariedNo ratings yet
- Physics exam 2 practice problemsDocument7 pagesPhysics exam 2 practice problemsMuhammad Tayyab MadniNo ratings yet
- Phys2 Midterm Exam F2019 20 With NotesDocument12 pagesPhys2 Midterm Exam F2019 20 With NotesaamerbolookiNo ratings yet
- 3 Soln Practice Assignment Ch25Document7 pages3 Soln Practice Assignment Ch25Eng MohammedNo ratings yet
- HomeworkDocument13 pagesHomeworkElen MariNo ratings yet
- Electric Field Forces and PotentialsDocument5 pagesElectric Field Forces and PotentialsTHIÊN LÊ TRẦN THUẬNNo ratings yet
- Svprecis 12th Physics Electrostatic Force Electrostatic Field and Gauss TheoremDocument2 pagesSvprecis 12th Physics Electrostatic Force Electrostatic Field and Gauss Theoremapi-252136290No ratings yet
- Xtut2 2017 PDFDocument10 pagesXtut2 2017 PDFadahrenelleNo ratings yet
- FET Online Tutorial Chapter 1: ElectrostaticsDocument6 pagesFET Online Tutorial Chapter 1: Electrostatics胡宇晟No ratings yet
- Electrostatics ProblemsDocument2 pagesElectrostatics Problemsquasar2138No ratings yet
- 2013 Jee-Advanced Model Paper-1Document19 pages2013 Jee-Advanced Model Paper-1Uttej Arendkar A33% (3)
- MFT Samp Questions PhysicsDocument9 pagesMFT Samp Questions PhysicsBerkan YilmazNo ratings yet
- In Your Name Where Indicated in The Upper Right Corner Then (2) Do The Same With YourDocument12 pagesIn Your Name Where Indicated in The Upper Right Corner Then (2) Do The Same With YouradadafasfasNo ratings yet
- DR - Hannan Saadeh Solved Problems PDFDocument50 pagesDR - Hannan Saadeh Solved Problems PDFAbdNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE - Mains Model Test Paper - 1 (Physics, Chemistry, Maths)Document12 pagesIIT JEE - Mains Model Test Paper - 1 (Physics, Chemistry, Maths)studysteps.in83% (6)
- 2008 Bah Fiz144 Ara2 MDocument6 pages2008 Bah Fiz144 Ara2 MpurseyNo ratings yet
- NDocument4 pagesNBHAAJI0001No ratings yet
- SheetsDocument18 pagesSheetsamralquraishi411No ratings yet
- Final ExamA1-2019-1Document4 pagesFinal ExamA1-2019-1trinh.lenukieuNo ratings yet
- Tutorials On Electric FieldDocument2 pagesTutorials On Electric FieldNkeng100% (1)
- Electrostatics & Capacitance ExplainedDocument1 pageElectrostatics & Capacitance ExplainedrockyNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument17 pagesPhysicspaninikumar0000No ratings yet
- Practice Exam - 1 + Answers Winn F10Document13 pagesPractice Exam - 1 + Answers Winn F10Billy PozehlNo ratings yet
- Final ExamA1Document3 pagesFinal ExamA1LÂN HỒ THANHNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Solved QBPDFDocument75 pagesElectrostatics Solved QBPDFMohammed Aftab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Type 2 PART 2 of 3 ENGDocument20 pagesElectrostatics Type 2 PART 2 of 3 ENGSubhashChandraMishraNo ratings yet
- 02 Electric FieldDocument7 pages02 Electric FieldFirdous ANo ratings yet
- AIEEE Practice Test - 2012: Paper - 1Document14 pagesAIEEE Practice Test - 2012: Paper - 1a2b4c600No ratings yet
- Jee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Magnetic Effects of CurrentDocument10 pagesJee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Magnetic Effects of Currentvarunkohliin100% (1)
- Electric Fields Worksheet SolutionsDocument4 pagesElectric Fields Worksheet Solutionssarcasticb15No ratings yet
- Exercises - Chapter - 21 PDFDocument6 pagesExercises - Chapter - 21 PDFmalonz03No ratings yet
- EME Tutorial - 2 To 5Document5 pagesEME Tutorial - 2 To 5Aditya Gadgil100% (1)
- National University of Singapore PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics II TestDocument11 pagesNational University of Singapore PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics II TestYuhua SunNo ratings yet
- 4.multiple Choice QuestionsDocument8 pages4.multiple Choice QuestionsJatin KumarNo ratings yet
- 2.short Answer Type IIDocument3 pages2.short Answer Type IIJohn WickNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of CurrentDocument31 pagesMagnetic Effects of CurrentMohammed Aftab Ahmed100% (3)
- Classroom Assignment 3 With AnswersDocument3 pagesClassroom Assignment 3 With AnswersBishoy EmileNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Workbook Answers: Exercise 1.1Document2 pagesWorkbook Answers: Exercise 1.1Akhmad NurNo ratings yet
- Engineering Geology: IntroductionDocument14 pagesEngineering Geology: IntroductionLyn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Pv-Wind Hybrid PowerDocument49 pagesPv-Wind Hybrid PowerHAIMANOT100% (1)
- Mc3 Chapter 1Document7 pagesMc3 Chapter 1Lorraine RiegoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Aspects and Impacts Assessment Guide: PTS 60.3202 June 2006Document34 pagesEnvironmental Aspects and Impacts Assessment Guide: PTS 60.3202 June 2006enviroNo ratings yet
- HKUST CIVIL ENGINEERING FOUNDATION PROJECT REPORTDocument12 pagesHKUST CIVIL ENGINEERING FOUNDATION PROJECT REPORTJun KangNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer From Fin SurfacesDocument25 pagesHeat Transfer From Fin SurfacesAizaz HabibNo ratings yet
- 4th Generation BiofuelsDocument5 pages4th Generation BiofuelsKricel MaqueraNo ratings yet
- Listen and understand important details from conversations and passagesDocument3 pagesListen and understand important details from conversations and passagesHa TranNo ratings yet
- TOEFL Readings 28Document4 pagesTOEFL Readings 28Seni Dan OlahragaNo ratings yet
- Project SynopsisDocument6 pagesProject Synopsislive userNo ratings yet
- Sizing According To ASME Code Sect VIII and API RP 520 and API 521Document31 pagesSizing According To ASME Code Sect VIII and API RP 520 and API 521matrix69No ratings yet
- BuildingstoneDocument20 pagesBuildingstoneAlexander AsonkeyNo ratings yet
- LTV - Thi Thu Vao 10 Lan 1 - 2019Document5 pagesLTV - Thi Thu Vao 10 Lan 1 - 2019Thùy Linh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Grid Connect PV Design Guidelines CEC Issue 5 - 1Document22 pagesGrid Connect PV Design Guidelines CEC Issue 5 - 1Lakshmi NarayananNo ratings yet
- 3 Global Plate TectonicsDocument29 pages3 Global Plate TectonicsIvan Bazilije BuhovacNo ratings yet
- Franco, Reinier M.: Me 405 - Alternative Sources of Energy - Me41S1 Topic: Biomass EnergyDocument2 pagesFranco, Reinier M.: Me 405 - Alternative Sources of Energy - Me41S1 Topic: Biomass EnergyReinier FrancoNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Air Track: Name: Akshat Date:12/15/20Document9 pagesStudent Exploration: Air Track: Name: Akshat Date:12/15/20Akshat Pant100% (8)
- Experiment 8 - Report - Specific HeatDocument3 pagesExperiment 8 - Report - Specific HeatRami HammoudNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficient School DesignDocument31 pagesEnergy Efficient School DesignXando FredericoNo ratings yet
- 6.26 Transient Analysis Depressurising and Venting (Pipeline)Document54 pages6.26 Transient Analysis Depressurising and Venting (Pipeline)shivajireturnsNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: PHYSICS 1050 Mid-Term Test 2Document8 pagesAnswer Key: PHYSICS 1050 Mid-Term Test 2hey_hopNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 BDocument32 pagesChap 3 BMike BelayNo ratings yet
- Negative Mass Exotic MatterDocument3 pagesNegative Mass Exotic MattertechzonesNo ratings yet
- 3540660208Document223 pages3540660208Iswahyudi AlamsyahNo ratings yet
- EcologyDocument50 pagesEcologyKipi Waruku BinisutiNo ratings yet
- How Is The Philippines Affected by Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesHow Is The Philippines Affected by Climate ChangeQueenie SantosNo ratings yet
- Bremsstrahlung X-RayDocument2 pagesBremsstrahlung X-RayYuda FhunkshyangNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Scientific Investigation - Chapter 1 Thinking Like A ScientistDocument2 pagesUnit 1 Scientific Investigation - Chapter 1 Thinking Like A ScientistKayla OsbornNo ratings yet
- Physics NET/JRF Practice QuestionsDocument44 pagesPhysics NET/JRF Practice QuestionsSibadatta MaharanaNo ratings yet