Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Project Hse Plan
Uploaded by
yawarhassanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Project Hse Plan
Uploaded by
yawarhassanCopyright:
Available Formats
2013
SAFETY MANUAL
PROJECT HSE PLAN
A RESEARCH BY YAWAR HASSAN KHAN
YAWAR HASSAN KHAN ACL 1/1/2013
HSE POLICY STATEMENT
Before you operate a machine, ensure that the dangerous part of the machine has been installed with a guard. Avoid going to any area with insufficient lighting as there may be some
We are committed towards protecting the health and safety of all people working at or visiting our site We plan, manage, conduct and supervise all our work in compliance with legislation and best practice We want to ensure that all workers have a clear understanding of their responsibilities along with that of the company
dangerous places which have not been provided with fencing. Keep vigilant all the time and watch out for moving cranes, hooks or other lifting equipment. Before you use any electrical installation or tool, check the condition of its electric cables. Avoid dragging electric cables on the ground or allowing the cables to come into contact with water.
BASIC RULES FOR SAFETY
Tidy up construction sites Keep passages clear all the time. Sort out materials and pile them up safely. The stacks should not be too high. Beware of floor openings and ensure that they are fenced or covered. Remove refuse as soon as possible. Provide sufficient lighting. Familiarize with the location and the operation of fire-fighting equipment.
Use electrical tools installed with an earth leakage circuit breaker. Use and handle chemicals with care.
Personal Safety Wear protective equipment. Do not drink or take drugs while working. Pay attention to personal hygiene. Do not play in the workplace. Report to your supervisor immediately if you notice any unsafe condition.
Safety measures
EMERGENCY RESPONSE TO ACCIDENTS
Tidy up construction sites Keep passages clear all the time. Sort out materials and pile them up safely. The stacks should not be too high. Beware of floor openings and ensure that they are fenced or covered. Remove refuse as soon as possible. Provide sufficient lighting. Familiarize with the location and the operation of fire-fighting equipment.
Put out the fire with a fire extinguisher if it is a small fire. If the blaze is out of control, do not try to extinguish the fire on your own. Call the Fire Services Department right away. Emergency telephone numbers: Always pay attention to the emergency telephone numbers posted on the notice board in the site office FALSE WORK , SCAFFOLDING , FENCE WORK AND LADDER FALSEWORK
When someone is found seriously injured, you should: Keep calm. Seek help immediately. Accompany the injured person. Assist in the immediate rescue work as far as possible. Call the site safety staff. Do not try to move the injured person unless it is really necessary to do so. Do not tamper with the accident scene while waiting for the arrival of the investigation team.
If you are engaged in falsework operation, you should: Check whether the falsework is erected in accordance with the design. Make sure that the falsework is securely erected. Check whether the struts of the falsework are secure. Ensure that the props are erected vertically and arranged at a suitable distance in a row. Report to your supervisor when
When a fire breaks out, you should remember:
any unsafe situation is found.
fencing or the fencing has been SCAFFOLD Do not use scaffolds unless they have been erected by trained workmen and under the supervision of a competent person. Do not use a scaffold unless it has been inspected and certified safe by a competent person before use. Strictly follow the instructions of a competent person. Do not alter the scaffold unless authorized to do so. Do not work on an unfinished scaffold. When it is necessary to work on a mobile scaffold, lock the wheels of the scaffold before you start working. Do not work on a scaffold unless it has been provided with a suitable working platform. Ladder Use a ladder which is of good construction, sound material and adequate strength. Examine the ladder before using it and inspect it at regular intervals. Place the ladder on a level and firm footing. Place the ladder at an appropriate angle. Ensure that the ladder has a sufficient length. The upper end of the ladder should be at least FENCING Do not work in a dangerous place unless its floor edges and openings have been installed with secure fencing. If you notice any dangerous places that have not been installed with 1 metre above the landing against which the ladder leans. Do not use a ladder unless its upper or lower end has been securely fixed or secured by another worker. If there are electrical installations damaged, reinstall or repair the fencing. If this is beyond your capability, inform your supervisor at once.
nearby, do not use metal ladders. If work is carried out 2 metres or more above the floor, use a suitable working platform
of the manufacturer of a lifting appliance. Do not work beneath any suspended load.
Material Hoist Do not ride on a material hoist.
Equipment and Electricity
Do not operate a material hoist without prior proper training. Do not exceed the safe working load of a material hoist. Do not use a material hoist unless it has been examined and certified safe by a competent examiner. Do not use a material hoist unless its gates have been installed with an effective interlocking safety system. The hoist is only operable after all the gates have been closed. Do not use a material hoist unless it has been repaired and maintained by a competent person. No unauthorized repair is allowed. Do not put loose materials into receptacles unless properly secured.
Lifting Appliance and Gear Do not operate a lifting appliance unless trained. In the case of a crane, a certificate is required. Before using lifting gear such as hook, shackle or chain sling, check whether there is any wear and tear. Check the weight of the load to be lifted. Do not exceed the safe working load of a lifting appliance or lifting gear. Adopt the correct lifting method. Do not use a lifting appliance or lifting gear unless it has been examined and certified safe by a competent examiner. Do not use a lifting appliance unless it has been regularly repaired and maintained by a competent person. No unauthorized repair is allowed. Follow the safe working instructions
Ensure good communication with the operator of a material hoist. All signals should be understood and followed.
Portable Power Tool Do not use a portable power tool (such as saw, grinder and drill) unless its dangerous parts have
Loadshifting Machinery Unless you are a worker concerned, do not work in an area where a loader, an excavator, etc. is in operation. Do not operate any loadshifting machinery without training and approval. Operators of forklift trucks, bulldozers, loaders, excavators, trucks or lorries should possess appropriate certificates.
been effectively guarded. Place the electric cable and hose of a tool at an appropriate position to avoid tripping
Compressed Air Use compressed air only for specified purposes. Do not use any compressed air equipment, pipes and relevant devices unless they are of good construction and have been examined and certified safe
Cartridge-operated Fixing Tool Do not operate a cartridgeoperated fixing tool unless you have possessed a valid certificate. Wear suitable eye and ear protectors while operating a cartridge-operated fixing tool. Use a cartridge-operated fixing tool with great care.
by a competent examiner before use. Fix the connectors properly. Do not twist the pipes. Do not abuse the use of compressed air for cleaning purpose. Use a brush or a vacuum cleaner to remove dust from clothing and skin.
Electric Tool
Before using an electric tool, check the tool and its plug and connecting cable. Do not use a damaged tool. Do not use an electric tool unless its connecting cable is well protected. Do not use an electric tool unless its metal casing is earthed and its power supply is provided with an earth leakage circuit breaker. Do not repair or alter any electrical installation unless competent to do so. If you meet any fault or problem, report it to your supervisor immediately.
working in it.
Gas Welding and Flame Cutting Do not use the equipment for gas welding or flame cutting unless you have attained the age of 18 years and hold a valid certificate. Do not use any gas cylinder unless it has been fitted with flashback arrestors. Wear personal protective equipment. Keep the workplace clean. Place fire extinguishers within reach. Keep gas cylinders in an upright position and secure it properly to avoid overturning.
Excavations Keep the fence on all sides of an excavation intact. Use safe access for ingress and egress. Do not pile soil or any other materials at the edge of an excavation. Make sure that a trench is securely shored before
If gas leakage is detected, report it to your supervisor immediately. Fire Risk There is always a fire risk. However, the chances of fire can be reduced, and you will know what to do when a fire breaks out if you: Always keep the workplace clean and tidy.
Handle machinery and tools that may generate sparks or heat carefully. Do not smoke or use naked flames in any area where flammable and explosive substances are stored. Know where fire extinguishers are located and how they are used. Know the place of assembly for fire evacuation
Dispose all wastes, and unwanted materials must be disposed of at a designated place. Notify your supervisor of the requirement for the separate disposal of chemical or inflammable wastes. Do not leave planks with nails on passageways.
Safety Supervisors Their responsibility is to assist
Public Safety Pay attention to public safety. Members of the public are often unaware of or do not understand the work carried out on construction sites and the risks involved. Take great care to prevent the fall of materials from height. Do not stack materials on floor edges or on scaffolds
others to work smoothly and safely. They have received specific safety training and are important members of the construction team. They have legal responsibility or liability for the overall safety of the construction site. You should get to know your safety supervisor.
Waste Disposal
Eye Protection
A wise worker will certainly take good care of his eyesight. A small fragment may cause serious consequences if it enters one's eyes. When there is a risk of eye injury, such as in concrete breaking or using abrasive wheels, you should wear suitable eye protectors. Take proper care of the eye protectors provided to you. Replace damaged or defective eye protectors immediately. Ensure that eye protectors are comfortable to wear, and keep clean. Use eye protectors for eye protection do not put it on your head or hang it on your neck. Bear in mind that eye protectors are replaceable, but not your eyes.
instructions. Do not reuse disposable ear plugs. Clean ear protectors regularly
Personal Protective Equipment For your own safety and interest, use the personal protective equipment provided by your employer. Wear gloves when handling or contacting chemicals. Remember to wear a mask when working in a dusty environment. Wear eye and ear protectors whenever necessary. Wear a safety harness and secure it to a safe anchorage point when working at height. A bamboo scaffold is not a safe anchorage point, so do not fasten the safety harness to it. Wear safety shoes to prevent foot injury.
Noise Wear ear protectors in areas with high noise levels. Properly wear ear protectors according to the manufacturer's
Consult your supervisor if in doubt.
Safety Helmet Wear a safety helmet on a
construction site. Keep the harness of the helmet clean and make sure that it fits well. Do not drill any holes on the helmet or use it for pounding.
and wear safety boots or shoes to prevent injury to toes by heavy falling objects. Seek assistance from someone in lifting a load if necessary.
Personal Hygiene First Aid If you sustain an injury or feel not well while at work, even if it is minor, go to the first aid room right away for medical treatment and notify your supervisor. Put the case on record. clothing. Alcohol and Drugs Do not drink alcohol, or take drugs, while at work. Manual Handling Operations Avoid manual handling operations as far as possible to minimize the risk of injury. Estimate the weight of the load. Lift an object with a correct posture. Wear suitable protective equipment. Put on gloves as far as possible to protect your hands from any cut, scratch or puncture, If you need to take drugs due to illness, report it to your supervisor. Keep yourself clean. Wash hands before meals and after using the toilet. Dress tidily and in protective
SAFETY MANUAL PROJECT HSE PLAN EFFECTIVE SAFETY COMMITTEES Purpose of safety committee Help protects employee by providing knowledge of safety Helps protect employee by providing a solution to issues Bring together labor and management for health and safety Help the employee give training to manager , supervision and workers for better hazard identification and control and health and safety performance Roles of safety committee Know the feelings and thinking of employee by survey and interview Analyze the behavior of employee by observing Do safety inspections at workplace Do safety audits Control measures and safety improvements measure should be monitored Evaluate quality of safety culture in long terms Develop and submit the written recommendations Functions of safety committee To have knowledge Skills Abilities
Of health and safety Benefits of safety committee Consultant Identify hazards protect employee and employer Communication between labor and management Duties of safety committee members Receive concerns , reports and suggestions by employees and give them to manager level and give the management level response to employees Workplace inspection Receiving training Attending meetings Control measures and safety improvement progress Monitoring Hazard identification communication Benfits of training the safety committee Know their purpose of job Know the role Know the function Know the responsibility Know the skills Know the abilities
Know the information on health and safety Hazard identification profit for company Competition leading Effective audit Lower injury and illness rates Three areas for effective safety committee training Safety committee operations Hazard identification and control Accident investigation procedures Hierarchy of controls Engineering controls Administrative controls Personal protective equipment Accident investigation procedures Write data of accident Know the surface and root causes Make the report Suggest safety measures
Causes of majority injuries Inadequate supervision ,education , accountability , and resources Hazardous conditions
Material Equipment Environment People system System design and implementation Objectives Policy Plan Procedures Processes Budget Report Rules Safety inspection
Causes of accident report failures Surface causes are uncovered but , root causes are not uncovered Hazardous conditions are uncovered Unsafe work practices uncovered Failure in safety management uncovered
In safety inspection we give time to know for a thorough inspection to be conducted to know what is happening Job hazard analysis Employee , managers together solve the problems Problem solving techniques
Understand the problem Discuss causes Target solutions Sell solutions Implement solutions 5 wh analysis Who is getting hurt ? What actually caused the injury ? When workers are getting hurt ? Where workers are getting hurt ? how workers are getting hurt ? How to conduct a survey Gather a team of trained employees Determine who you are going to sample Decide how will you conduct the survey ? Tell everyone why you are going to conduct survey ? Conduct the survey Summarize result Discuss the result with CEO Characteristics of an effective safety committee Organized meeting Good communication Roles and purposes are understood Standard of behavior
Objectives and completion dates are set Members trained
EFFECTIVE SAFETY COMMITTEE MEETINGS How often do safety committees meet Some once a month and some more often When committee meeting should be held Its most effective if the safety committee conducts a meeting immediately after the inspection What happens in an effective safety committee meeting Discuss findings Ensure identified hazards are reported to responsible supervisors or managers Analyze findings and discuss their possible rootcause Make recommendations to improve safety programs Purpose of safety committee meeting To bring management and labor together Preparing for the meeting Chairperson preparation Recorder must be trained Prepare the agenda and keep it brief Prepare the meeting room
Thank every one for coming
Handle problem situations Disagreement
Call the meeting to order
conflict Evaluate
Note attendence
Meeting process and outcomes Improve
Introduce visitors
Meeting process OSH TRAINING
Review ground rules
SAFETY EDUCATION We become educated in safety in many ways including : personal experience
Review meeting minutes
Review agenda topics
Formal classroom training On the job training
Discuss unfinished business
Effective safety education must tell learners why it is important to use safe procedures and practices Natural consequences Natural consequences are those that naturally occur as a result of what an employee or organization does System consequences System consequences are those actions taken by another person in response to an employees choice and behaviours Technical safety training How to safety training is actually the most common type of safety education
Review observations of conditions and behaviors
Evaluate incident and accident report
Receive safety committee status reports
Conduct safety committee training / education
Conduct a safety inspection
General safety instruction
Is usually conducted using the lecture or discussion method Purpose of training program To provide training professionals for effective safety education Criterea for accepted practices in safety , Health and environmental training Program development Delivery evaluation Program management Suggested training plan core elements Training facility Training director Instructors Course materials Students Ratios Proficiency assessment Course certificate Record keeping Program quality control Safety trainer perform many roles Evaluator Facilitator Counselor Writer Instructors
Manager Marketer Media specialist Analyst Program administrator Designer Strategies Task analysis Theoretician Transfer agent Guidelines for instructor competency Certified person Designated Authorized Competent Qualified Purpose of training evaluation To know the amount of learning achieved by training Whether an employees performance has improved on the job as a result of training RKSAI Evaluate students : Reaction Learning Application
result Guidelines for evaluating training programs How training program is managed Quality of training processes The result of training Suggested program quality control criterea training plan Program management , training director , staff and consultants training facilities and resources Quality control and evaluation Students Institutional environment and administrative support SAFETY MANAGEMENT Top management commitment You should know the benefits of your commitment towards safety You must develop programs , policies , plans and procedures Do commitment to safety because it saves lives , money and you stay out of trouble Safety leadership increases companys potential Coercive ,controlling and caring are the three leadership models out of which caring model is the real commitment approach You must have a vision and mission statement There are two safety strategies: reactive and pro active
In reactive strategy you react after the accident has happened In pro active strategy you make sure that no accident should occur in workplace Labor and management accountability Employees should believe that they are going to be held accountable for their decisions and actions Six elements of effective accountability system : 1.formal standard of performance 2.adequate resources and psychosocial support 3.a system of performance measurement 4.application of effective consequences 5.appropriate application of consequences 6.continous evaluation of accountability system Points to remember: The more Regularly you Recognize and Reward , the more Rarely you will have to Reprimand Training , resources , enforcement , supervision and leadership are 5 obligations of safety Employee involvement Employee is held accountable by the employer for complying with the safety rules , reporting workplace injuries immediately and reporting hazards Rewards are great but , recognition is better Effective communications Its a responsibility to communicate effectively Its not what you say its about how you say it
Hazard identification and control Hazard is state of being leading to illness or injury of a person What can control hazards : 1. Eliminate and substitute hazards 2.Engineering controls 3.administrative controls 4.personal protective equipment Material , people , environment ,system , equipment may be hazardous Do a walk around inspection to see hazards Employee may use his own procedure if not directly supervised Unsafe behaviors lead to 95% cause of accidents Incident and accident investigation Dont go for blame but fix the system You cant afford to relax or be content in safety Incident causes property damage and accident causes life damage too You must know the plan and how to work the plan If accident occurs you must know : 1. background information 2.surface causes and root causes You have to make a report of accident in which you write about findings , recommendations and summary Safety education and training Be trained
We educate to show why We train to show how A simple seven step on the job training includes: 1.introduction 2.trainer shows and tells 3. learner tells trainer shows 4 . Learner shows and tells 5 . Conclusion 6.documentation 7. validate Total quality safety management
Quality and safety are partners in productivity
TQM means to improve performance and process by using coorporate resources
DEMING says about total quality safety management that have a purpose for improvement , adopt a new philosophy , cease dependence on mass inspection , dont go for price tag- go for reducing total cost , improve constantly , give training on job , drive out fear , break down barriers between departments , dont pressurize workforce , give self improvement education and act for transformation PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT THE REQUIREMENT FOR PPE To ensure the greatest possible protection for employees in workplace EMPLOYEE RESPONSIBILITY To wear and maintain PPE
Chemical hazards
FACE AND EYE PROTECTION
Radiological hazards
HEAD PROTECTION
Mechanical hazards WHAT SHOULD NOT BE WORN?
FOOT PROTECTION
HAND PROTECTION
The PPE rules requires that rings , wristwatches , earnings , bracelets and other jewelery must not be worn if its possible for it to come into contact with power driven machinery or electric circuitry HAZARD ANALYSIS AND CONTROL BASIC EMPLOYER RESPONSIBILITY
PROTECTIVE CLOTHING
SHIELDS
The employer should see that workers are properly instructed and supervised in the safe operation of any machinery tools , equipment , process or practice which they are authorized to use or apply BASIC EMPLOYEE RESPONSIBILITY All employees should conduct their work in compliance with their employers safety policies and rules. Employees should report all injuries immediately to the person in charge or other responsible representative of the employer .employees should make full use of safeguards provided for their protection SAFETY INSPECTIONS
BARRIERS
RESTRAINTS WHEN AND WHERE PPE IS REQUIRED? Whenever following conditions are encountered :
Process hazards
Environmental hazards
Employers should make sure their workplace are inspected by a qualified person as often as the type of operation or the character of the equipment requires. HAZARDS
Raw materials Toxic chemicals Stationary machinery equipment may not be properly guarded / or in poor working order Tools may not be properly maintained Extreme noise in work environment Poor work station designs Flammable or combustible atmospheres Floors may be slippery and aisles cluttered Guard rails , ladders or floor hole covers may be missing or damage Employees might be fatigued , distracted in some way , or other wise lack the physical / mental way , or working safely HAZARD Unsafe work conditions or practices that could cause injuries or illness to employees Recognized hazards Industry recognition Employee recognition Common sense recognition Exposure Physical Environmental potential Six steps hazard control process
Identifying workplace hazards Analyzing the workplace Developing solution Writing solution Writing recommendations Taking action Evaluating the results Five general hazards Material Equipment Environment People system 13 hazard categories Acceleration Biological Chemical reactions Electrical Ergonomics Explosives and explosions Flammability and fires Temprature Mechanical Pressure Radiation
Toxics Vibration / noise Identifying hazards informal and formal observation programs Comprehensive wide surveys Individual interviews Walk around inspection Documentation review A written record will help ensure Assignment of responsibility for hazard correction Tracking of correction to completion Identification of problems in the control system Identification of problems in the accountability system Identifcation of hazards for which no prevention or control has been planned 4 analysis Job hazard analysis change analysis Process hazard analysis Phase hazard analysis Hierarchy of control Elimination Substitution Engineering controls Administrative controls
Personal protective equipment Solving safety problems-two key strategies Eliminate or reduce the surface cause Eliminate or reduce he root cause Cause effect analysis Every effect is the result of a cause Key steps to develop effective recommendations Write the problem statement Describe the history of problem State the solution options that would correct the problem Describe the consequences as a cost. Vs . Benefit analysis EFFECTIVE ACCIDENT INVESTIGATION What is an accident An accident is the final event in an unplanned process that result in injury or illness to an employee and possibly property damage Accident types STRUCK BY STRUCK AGAINST CONTACT BY CONTACT WITH CAUGHT ON CAUGHT BETWEEN FALL TO SURFACE
FALL TO BELOW OVER EXERTION BODILY REACTION OVER EXPOSURE CAUSE OF ACCIDENT Old theory-worker error :says worker makes a choice to work in an unsafe manner New theory-system approach : says accidents occur due to multiple causes and due to defects in the systems Characteristics of effective incident investigation program Clearly assigned responsibility for accident investigation All accident investigations will be formally trained on accident investigation techniques The purpose is to find fact not fault Dig deep to know hazardous conditions that caused accidents report will make the recommendations to correct the hazardous conditions and work practices Corrective actions must be completed
Determine the solutions Write the report DOCUMENTING THE ACCIDENT SCENE Make personal observations Take photos of accident scene Take video clips of the scene sketch the accident scene Interview records Steves seven rights of interview process Be sure you ask the Right people the Right question at the Right time in the Right place in the Right way for the Right reason to uncover the Right facts WHO NEEDS TO BE INTERVIEWED The victim Co workers
An annual review of accident reports Direct supervisors Six steps for conducting accident investigation Manager Secure the accident scene Training department Conduct interview Personnel department Develop the sequence of events Maintenance department Conduct cause analysis
Emergency responders Medical personal Coroner Police The victims spouse and family Effective interviewing techniques Keep the purpose of investigation in the mind Approach the investigation with an open mind Go to the scene Express concern regarding the accident and desire to prevent a similar occurrence Tell the interviewee that the information they give is important Be friendly , understanding and open minded Be calm and unhurried Single event theory An accident is thought to be the result of a single , one time easily identifiable , unusual , unexpected occurrence that result in injury or illness The domino theory This describes as a series of related occurences which lead to a final event that results in injury or illness Multiple cause theory Accidents are a result of a series of random related and / or unrelated actions that somehow interact to cause the accident Four categories of events
Actual events Assumed events Non events Simultaneous events Developing the sequence of events Once the sequence of events is developed we will study each event to know: Hazardous condition Unsafe behaviors System weaknesses Components of an event Actor: the actor is an individual or object that directly influenced the flow of the sequence of events Action is something that is done by the actor Hazardous conditions Materials Machinery Equipment Tools Chemicals Environment Workstations Facilities People workload Levels of cause analysis
Injury analysis Event analysis System analysis Higher priority strategies that control hazards Elimination Substitution Engineering controls
Evacuation procedures Emergency escape route assignments Procedures to account for all employee after an emergency evacuation has been completed Name or job titles of personas who can be contacted for further information or explanation of duties under the plan. NATURAL DISASTERS Avalanche
Lower priority strategies to control exposure and behavior WARNINGS ADMINISTRATIVE CONTROLS PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT WRITING THE REPORT Background Description Findings Recommendations Summary EMERGENCY ACTION PLANS
Biological Drought Sand storms Earth quakes Extreme heat / cold Fire Flood Hurricane Landslide / Madslide Lightning Snow / Ice / hail Tornando Volcanic eruption
WHAT IS AN EMERGENCY ACTION PLAN An action plan to organize employee and employer action during workplace emergencies COMPONENTS OF AN EFFECTIVE EMERGENCY ACTION PLAN Ways to report fires and other emergencies
Tsunami TECHNOLOGICAL EMERGENCIES Aircraft crash Structural collapse Business interruption
Communication Levee failure Explosion/fire Extreme air pollution Financial collapse Fuel .resource shortage Hazardous material release Power / utility failure Radiological / nuclear accidents Transportation accidents WHAT ARE THE STEPS IN DEVELOPING EAP Development of emergency action plan Establish authority Conduct employee training and plan review Review , coordinate and update the plan Determine specific evacuation routes and exits Make sure EAP meets specific needs Designate someone who will stay to shut down critical operations during an evacuation One policy doesnt fit all situations Address how and when drills and retraining will be conducted Identify how and when the employees will be trained Identify methods to alert employees Develop methods to alert employees
Consider and list potential natural or man made emergencies
Designate evacuation coordinates and workdens
Develop resue and medical assistance strategies Conduct EAP employee training Consider communication Update the EAP regularly Identify methods for reporting fires
INTRODUCTION TO FIRE PREVENTION PLANS
Warning and caution signs Fire detectors
What does the fire prevention plan do for your ORGANIZATION
Pull stations Agent storage containers Purpose of an alarm system The purpose of and employee alarm system is to reduce the severity of work place accidents and injuries by ensuring that alarm systems operate properly and procedures are in place to alert employees to workplace emergencies The fire triangle Enough oxygen to sustain combustion Enough heat to rise the material to its ignition temperature and Some sort of fuel or combustible material Fire extinguisher ratings Class a ordinary combustible Class b flammable liquids Class c electrical equipment Class d combustible metals Class k restaurant kitchens Types of fire extinguishers Dry chemical extinguishers Halon extinguishers Water extinguishers Carbon dioxide extinguishers HOW TO USE A FIRE EXTINGUISHER
Serves to reduce the risk of fires at your workplace Causes of fire Electrical hazards Portable heaters Office fire hazards Cutting , welding and open flame work Flammable and combustible material Smoking in the wrokplace Fixed extinguished system Fixed fire extinguishing systems are commonly used to protect areas containing value able or critical equipment such as data processing rooms , telecommunication switches and process control rooms Components of a fixed system Discharge nozzle Piping Control panel Warning alarm
PASS : PULL AIM SQUEEZE-SWEEP MANAGEMENT TRAINING RESPONSIBLITY
A significant injury or illness diagnosed by a physician or other licensed health care professional
OSHA 300 form is the log of work related injuries and illnesses All managers should be trained and make sure employees are also trained to understand their FFP responsibility.
OSHA 300 A is the summary of work related injuries and illnesses
OSH RECORD KEEPING OSHA FORM 301 or equipment is the workers and employers report of occupational injury or disease The record keeping and reporting rule requires employers to record and report work related fatalities , injuries and illnesses . Its important to record or report a work related injury , illness or fatality
You must involve your employees and their representatives in the record keeping system
An injury or illness meets the general recording criteria and is recordable , if it results in any one of following six conditions :
TOTAL NO. OF INJURIES AND ILLNESSES / NO. OF HOURS WORKED BY ALL EMPLOYEES * 200 , 000 = TOTAL RECORDABLE CASE RATE
Death Days away from work Restricted work or job transfer Medical treatment beyond first aid Loss of consciousness HAZARD COMMUNICATION
The hazard communication rule applies to any chemical which is known to be present in the workplace in such a manner that employees may be exposed under normal conditions of use or in a foreseeable emergency Responsibility Chemical manufacturers and importers must evaluate chemicals produced in their workplaces or imported by them to determine if they are hazardous Employers must assess the hazards of chemicals and develop a written hazard communication plan along with training and information Material safety data sheet Chemical manufacturers and importers must obtain and develop a material safety data sheet for each hazardous chemical they produce or import and must develop appropriate labels that provide hazard warning information Employee training How to Reference the chemical test or hazards Use material data safety sheets Use protective practices including PPE Recognize a release of chemicals Detect over exposure to chemicals Write secondary container labels Hazard communication plan Employers must develop, implement and maintain a written hazard communication plan that contains a list of hazardous chemicals
being used in the workplace, assign responsibilities and describes procedures for: Labeling containers Maintaining and using material safety data sheets Information and training Pipe labeling Non routine tsk procedures Contractor procedures
Hazardous substance Is any chemical which poses a physical or a health hazard? Physical hazards Are chemical reactions that could result in a fire, explosion and/ or toxic gas release which cause physical trauma if chemicals are handled or stored improperly? Health hazards Is health effects caused directly by the chemicals themselves, not an injury resulting from a reaction
Dusts, fumes. Fibres . Mists . Vapors , gases , solids , liquids Chemical effects On various organs of the human body depend on several important factors : solid , liquid or gas ? Ingested , inhaled , absorbed or injected ?
How much chemical makes its ways into the body? How poisonous is the chemical?
HAZWOPER Hazardous waste operations and emergency response covers response to uncontrollable releases CONDUCTING A JOB HAZARD ANALYSIS
Routes of entry Routes of entry of chemicals may take must be known when assessing the workplace for chemical hazards. Alternative labeling methods HMIS ( hazardous material information system) NFPA (national fire protection association ) Material safety data sheet Used to communicate chemical hazard information from the manufacturer to the employee to train and inform on safe use of hazardous chemicals Employers must obtain a MSDS from the chemical manufacturer or import as soon as possible Employers must maintain in the workplace copies of required material safety data sheets Employee must know The hazard communication program The measures to protect themselves Detect the release or presence of hazardous chemical Physical and health hazards When new hazardous chemical is used in organization
JOB HAZARD ANALYSIS :
It focuses on the relationship between the worker , task tools and environment .after you identify uncontrolled hazards , you will take steps to eliminate or reduce them to an acceptable risk level . You can prevent workplace injuries and illnesses.
IMPROVE YOUR EMPOYEES
Get together with your employees and talk about the actual and potential hazards and unsafe behaviors they believe might exist in their current work and surroundings .Discuss the possible accident that might result from the hazards and behaviors . Next come up with ideas to eliminate or control those hazards and behaviors.
LOOK FOR HAZARDOUS CONDITIONS AND UNSAFE BEHAVIOURS
Material safety data sheets Experienced workers Accident and incident reports
First aid statistical record Behavior based safety reports Safety committee meeting minutes Safety inspection reports Previous JHAs Existing work procedures Equipment manuals Preventive /corrective maintenance records
Basic job step Hazard present Preventive measures GOALS WHILE CONDUCTING A JHA What can go wrong What are the consequences ? How could the hazard arise ? What are the other contributing factors ? How likely is that hazard will occur ?
HIGH RISK BEHAVIOURS Working at evaluation , no matter what job is Lifting , lowering , pushing , pulling and other manual handling operations Other working above or below the work area Use of bridge cranes man lifts , or other heavy equipment Working on or near energized equipment /components Working alone or in isolated workplaces Operating vehicles Working within a confined space or under temp extremes RISK ANALYSIS Risk = probability*severity JHA FORMAT JHA includes three columns:
TIPS Write safe job procedure Hire professionals to conduct JHA Improve the JHA process by taking a team approach RISK ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEEMNT
SAFETY MANUAL
HOW TO ASSESS THE RISK The risk score is determined by multiplying the consequence and likelihood scores you have recorded for each hazard To assess the risk associated with hazards you have identified, ask the following questions:
How likely is the hazard to cause harm to someone?
What is the worst possible damage the hazard could cause in terms of human suffering and cost if you don't resolve the problem? How many people are exposed to the risk? Sometimes it may be the amount of time workers spend on an activity that creates the safety risk, rather than the nature of the work task itself. Everyone is different. A hazard may also pose more risk to some people more than others because of differences in physical strength, experience, training etc. HOW TO MANAGE THE RISK The risk score is determined by multiplying the consequence and likelihood scores you have recorded for each hazard To assess the risk associated with hazards you have identified, ask the following questions: How likely is the hazard to cause harm to someone? What is the worst possible damage the hazard could cause in terms of human suffering and cost if you don't resolve the problem? How many people are exposed to the risk? Sometimes it may be the amount of time workers spend on an activity that creates the safety risk, rather than the nature of the work task itself.
Everyone is different. A hazard may also pose more risk to some people more than others because of differences in physical strength, experience, training etc.
THE END THANK YOU PLEASE GIVE YOUR FEEDBACK : yawarhassankhan@hotmail.com 03442271438
You might also like
- HSE PlanDocument49 pagesHSE Plankadarmukkam100% (8)
- CCAD - Project HSE PlanDocument187 pagesCCAD - Project HSE Plansergio1234567890100% (7)
- Hse PlanDocument163 pagesHse PlanEnabulele Osakpamwan100% (10)
- Hse PlanDocument62 pagesHse Plannsadnan91% (11)
- HSE Capability AssessmentDocument5 pagesHSE Capability Assessmentsjmpak78% (18)
- HSE Monthly Report For XXXX2 ProjectDocument30 pagesHSE Monthly Report For XXXX2 ProjectAhmed Hassan Sabry80% (5)
- Health Safety & Environmnetal ChallengesDocument13 pagesHealth Safety & Environmnetal ChallengesSantosh Mhatre88% (8)
- Job Procedure FOR: Hse PlanDocument48 pagesJob Procedure FOR: Hse PlanJatin V Paliwal90% (39)
- HSE PlanDocument40 pagesHSE Plansira4sana93% (15)
- Project Hse Plan Rev2 - ScribdDocument35 pagesProject Hse Plan Rev2 - ScribdPaulSwinbank94% (36)
- HSE ManualDocument33 pagesHSE Manualhasan_676489616No ratings yet
- ToolBox TalkDocument86 pagesToolBox TalkAhmad Imran100% (6)
- HSE InductionDocument16 pagesHSE InductionChethan100% (4)
- Safety Culture Improvement through Consistent MessagingDocument28 pagesSafety Culture Improvement through Consistent MessagingRahmat Adi Saputra100% (4)
- Contractor Risk Assessment FormDocument5 pagesContractor Risk Assessment FormRoger Simbhoo100% (1)
- Tool Box SubjectsDocument70 pagesTool Box Subjectsrajeshsabitha80100% (5)
- Contractor HSE Management ProcedureDocument9 pagesContractor HSE Management ProcedureWinnie Eldama100% (1)
- HSE PlanDocument120 pagesHSE Planfararg82% (11)
- Contractor Safety ManagementDocument80 pagesContractor Safety Managementsafety.eng100% (5)
- HSE Manual - V3Document81 pagesHSE Manual - V3Thanh Nguyen100% (3)
- Generic Risk AssessmentDocument8 pagesGeneric Risk Assessmentmorgojoyo100% (3)
- HSE Auditors TrainingDocument66 pagesHSE Auditors Trainingparadigman100% (4)
- Site Activities Risk AssessmentDocument50 pagesSite Activities Risk Assessmentjamie542393% (41)
- Health & Safety Staff Induction PresentationDocument39 pagesHealth & Safety Staff Induction PresentationAhmad Ali100% (2)
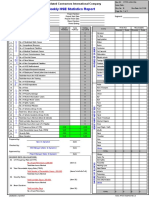
- Hse StatisticsDocument1 pageHse Statisticskrissregion100% (1)
- Hse Plan - Kaia Project - SBGDocument164 pagesHse Plan - Kaia Project - SBGMehmet Alper Sahin75% (4)
- HSE HandbookDocument53 pagesHSE Handbookmuthuswamy77No ratings yet
- Safety PlanDocument45 pagesSafety PlanBspeedman17564100% (3)
- HSE PLAN For UploadDocument18 pagesHSE PLAN For UploadOladimeji Taiwo71% (7)
- Construction HSE Management Plan Final DS PM 00 506Document43 pagesConstruction HSE Management Plan Final DS PM 00 506李君100% (2)
- HSE Manual - 1 0 HSE Management SystemDocument3 pagesHSE Manual - 1 0 HSE Management Systemabinadi92% (12)
- HSE Inspection PlanDocument35 pagesHSE Inspection PlanXozan100% (3)
- Sidenco Engineering HSE ManualDocument16 pagesSidenco Engineering HSE ManualAndika Apish67% (3)
- Hse PolicyDocument1 pageHse PolicysushantvatsaNo ratings yet
- Safety Documentation SystemDocument165 pagesSafety Documentation SystemPieter HerbstNo ratings yet
- RA 020 Risk Assessment - Risk Assessment - Installation of Cables in Ducts & TrenchesDocument11 pagesRA 020 Risk Assessment - Risk Assessment - Installation of Cables in Ducts & Trenchesthomson100% (1)
- Construction HSE ProcedureDocument39 pagesConstruction HSE ProcedureAli Hajirassouliha100% (1)
- Hse Plan L & TDocument69 pagesHse Plan L & TNarayanasami Kannan50% (2)
- HSE Monthly ReportDocument11 pagesHSE Monthly ReportAlfredo Medina Cano100% (7)
- Hse Plan - ArkDocument109 pagesHse Plan - Arkjiks_i4u100% (2)
- HSEManagementsystem PDFDocument48 pagesHSEManagementsystem PDFSyazreen ErinazNo ratings yet
- Policy and Strategic ObjectivesDocument4 pagesPolicy and Strategic ObjectivesKhuda BukshNo ratings yet
- HSE Pre-Qualification ChecklistDocument11 pagesHSE Pre-Qualification ChecklistSri Dharan74% (39)
- Hse PlanDocument62 pagesHse Plannsadnan70% (10)
- Project HSE PlanDocument71 pagesProject HSE Planabdul jabbar100% (1)
- 05 Project Safety PlanDocument32 pages05 Project Safety Planrudiawan100% (3)
- Hse Statistics Report Pp701 Hse f04 Rev.bDocument1 pageHse Statistics Report Pp701 Hse f04 Rev.bMohamed Mouner100% (1)
- Abraj HSE PolicyDocument1 pageAbraj HSE PolicyShahid AlamNo ratings yet
- HSE PolicyDocument1 pageHSE PolicyOnaFajardoNo ratings yet
- Project HSE Plan PDFDocument31 pagesProject HSE Plan PDFWaelBou100% (3)
- Constrution SiteDocument20 pagesConstrution Site101arNo ratings yet
- Aibel's Absolute Safety RulesDocument12 pagesAibel's Absolute Safety RulesRaven AlfieNo ratings yet
- CMPMDocument60 pagesCMPMDonna Grace PacaldoNo ratings yet
- Medicaps University: Civil Presentation OnDocument23 pagesMedicaps University: Civil Presentation OnItika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Warehouse Employee Safety OrientationDocument66 pagesWarehouse Employee Safety OrientationRalph CastilloNo ratings yet
- Construction Site Safety RulesDocument3 pagesConstruction Site Safety RulesshollyeshoNo ratings yet
- Effective Accident InvestigationDocument23 pagesEffective Accident Investigationyawarhassan100% (1)
- Safety and Health in ConstrcutionDocument13 pagesSafety and Health in ConstrcutionyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Cranes SafetyDocument12 pagesCranes SafetyyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Effective Accident InvestigationDocument23 pagesEffective Accident Investigationyawarhassan100% (1)
- Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Management: Yawar Hassan KhanDocument11 pagesHazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Management: Yawar Hassan KhanyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Scissor Lift SafetyDocument8 pagesScissor Lift SafetyyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Trenching Safety: Yawar Hassan KhanDocument11 pagesTrenching Safety: Yawar Hassan KhanyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Work Place ViolenceDocument14 pagesWork Place ViolenceyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Welding and Cutting SafetyDocument22 pagesWelding and Cutting SafetyyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding SafetyDocument15 pagesScaffolding SafetyyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Stairways Safety: Yawar Hassan KhanDocument6 pagesStairways Safety: Yawar Hassan Khanyawarhassan0% (1)
- PermitsDocument10 pagesPermitsyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Tool Box TalksDocument11 pagesTool Box TalksyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Slings SafetyDocument8 pagesSlings SafetyyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Safety ManagementDocument15 pagesSafety ManagementyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Safety and Health Rules and RegulationsDocument21 pagesSafety and Health Rules and Regulationsyawarhassan0% (1)
- Introduction To Osh TrainingDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Osh TrainingyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Lock Out Tag Out ProceduresDocument9 pagesLock Out Tag Out ProceduresyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Yawar Hassan Khan: Monday, March 04, 2013Document8 pagesYawar Hassan Khan: Monday, March 04, 2013yawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fire Prevention PlansDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Fire Prevention PlansyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Personal Protective EquipmentDocument20 pagesPersonal Protective EquipmentyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Lead and SilicaDocument11 pagesLead and SilicayawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Hse Supervision SkillsDocument32 pagesHse Supervision SkillsyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Hse Policy Statement and DescriptionDocument7 pagesHse Policy Statement and DescriptionyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Cranes SafetyDocument12 pagesCranes SafetyyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Site Workers' TrainingDocument10 pagesSite Workers' TrainingyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Managers' TrainingDocument23 pagesManagers' TrainingyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Hse Polciy Statement and DescriptionDocument3 pagesHse Polciy Statement and DescriptionyawarhassanNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Sulfide (0.0001% - 0.05%), Oxygen (19.5 - 23.5%) in Balance NitrogenDocument10 pagesHydrogen Sulfide (0.0001% - 0.05%), Oxygen (19.5 - 23.5%) in Balance NitrogenpcatruongNo ratings yet
- Safety Data SheetDocument7 pagesSafety Data SheetGermanYPNo ratings yet
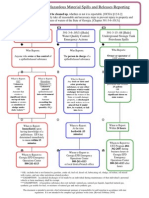
- Georgia Spill Release Reporting FlowchartDocument1 pageGeorgia Spill Release Reporting FlowchartfweNo ratings yet
- Transmission Substation Work Practice Manual 2016-07-22Document499 pagesTransmission Substation Work Practice Manual 2016-07-22Edmund YoongNo ratings yet
- Sika Grout 215Document9 pagesSika Grout 215Sri EkoNo ratings yet
- Lead-Acid Battery Safety Data SheetDocument4 pagesLead-Acid Battery Safety Data SheetNur Cholis HadiNo ratings yet
- Msds Mustang 25 EcDocument8 pagesMsds Mustang 25 EcAmman BilleNo ratings yet
- Msds Bezaprint Red CC-GDocument9 pagesMsds Bezaprint Red CC-GunisourcceeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Spill Prevention, Assessment, Reporting and CleanupDocument28 pagesChemical Spill Prevention, Assessment, Reporting and CleanupAdela Dea PerdaniNo ratings yet
- MSDS ThievesDocument11 pagesMSDS ThievesATOMY KESEHATANNo ratings yet
- Guide NFPA 1072 1706652425Document13 pagesGuide NFPA 1072 1706652425akram benguessoumNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Mass Fatality Management During Terrorist Incidents Involving Chemical AgentsDocument46 pagesGuidelines For Mass Fatality Management During Terrorist Incidents Involving Chemical AgentsBunga MustaqiymahNo ratings yet
- Legal RegisterDocument111 pagesLegal RegisterGlen StrakerNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: DexamethasoneDocument9 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Dexamethasonehadeer YoussriNo ratings yet
- The Storage and Handling of Flammable and Combustible LiquidsDocument10 pagesThe Storage and Handling of Flammable and Combustible Liquidsمحمود من فارس للبترول0% (1)
- Psguide 2015Document83 pagesPsguide 2015laacostam93No ratings yet
- Sds Sh30042 Us enDocument8 pagesSds Sh30042 Us enJaviera FerradaNo ratings yet
- Waste Profile SheetsDocument56 pagesWaste Profile Sheetshitm357No ratings yet
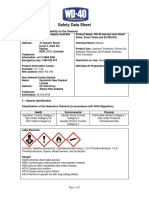
- WD 40 Aerosol AUNZ GHS SDS 7 23 15 With EZ REACH AdditionDocument8 pagesWD 40 Aerosol AUNZ GHS SDS 7 23 15 With EZ REACH AdditionMatt LNo ratings yet
- Training Needs Analysis Questionnaire PDFDocument5 pagesTraining Needs Analysis Questionnaire PDFbbking44No ratings yet
- Premium Brake Fluid MSDSDocument9 pagesPremium Brake Fluid MSDSElías VillegasNo ratings yet
- Legal Register PDFDocument28 pagesLegal Register PDFAnkurNo ratings yet
- SDS FES 200223 SH Synthetic 46 Compressor LubricantDocument16 pagesSDS FES 200223 SH Synthetic 46 Compressor LubricantRP INGENIERIA Y SERVICIOSNo ratings yet
- UN Dangerous Goods Brochure 2014Document17 pagesUN Dangerous Goods Brochure 2014Troy Theboy Mcnamara100% (3)
- TRS 957 (2010) - Annex 3 - WHO GMP For Pharmaceutical Products Containing Hazardous SubstancesDocument17 pagesTRS 957 (2010) - Annex 3 - WHO GMP For Pharmaceutical Products Containing Hazardous SubstancesQuang Hiếu NgôNo ratings yet
- PFM HSE Compliance ChecklistDocument3 pagesPFM HSE Compliance Checklistnoorullah siddiqueNo ratings yet
- HDAX 5200 Low Ash Gas Engine Oil-MSDSDocument6 pagesHDAX 5200 Low Ash Gas Engine Oil-MSDSAlin AspiryeNo ratings yet
- Dettol Antiseptic Wound Spray SDS Safety Data SheetDocument6 pagesDettol Antiseptic Wound Spray SDS Safety Data SheetHana AlghamdiNo ratings yet
- Houghto-Safe 620 e - CLP Sds-EnDocument13 pagesHoughto-Safe 620 e - CLP Sds-EnAnh Tuấn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Msds Methyl OrangeDocument6 pagesMsds Methyl OrangeMuhammad ArdanNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementNo ratings yet
- Safety Critical Systems Handbook: A Straight forward Guide to Functional Safety, IEC 61508 (2010 EDITION) and Related Standards, Including Process IEC 61511 and Machinery IEC 62061 and ISO 13849From EverandSafety Critical Systems Handbook: A Straight forward Guide to Functional Safety, IEC 61508 (2010 EDITION) and Related Standards, Including Process IEC 61511 and Machinery IEC 62061 and ISO 13849Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyFrom EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- A Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesFrom EverandA Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsFrom EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesFrom EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Incidents That Define Process SafetyFrom EverandIncidents That Define Process SafetyNo ratings yet
- Safety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryFrom EverandSafety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryNo ratings yet
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationFrom EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationNo ratings yet
- Inherently Safer Chemical Processes: A Life Cycle ApproachFrom EverandInherently Safer Chemical Processes: A Life Cycle ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersFrom EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeFrom EverandThe Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- One Health: Integrated Approach to 21st Century Challenges to HealthFrom EverandOne Health: Integrated Approach to 21st Century Challenges to HealthJoana C. PrataNo ratings yet
- Radium Girls: Women and Industrial Health Reform, 1910-1935From EverandRadium Girls: Women and Industrial Health Reform, 1910-1935Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Fire Fighting Pumping Systems at Industrial FacilitiesFrom EverandFire Fighting Pumping Systems at Industrial FacilitiesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Handbook of Fire and Explosion Protection Engineering Principles: for Oil, Gas, Chemical and Related FacilitiesFrom EverandHandbook of Fire and Explosion Protection Engineering Principles: for Oil, Gas, Chemical and Related FacilitiesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Electrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70EFrom EverandElectrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70ERating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (6)
- The Safety Critical Systems Handbook: A Straightforward Guide to Functional Safety: IEC 61508 (2010 Edition), IEC 61511 (2015 Edition) and Related GuidanceFrom EverandThe Safety Critical Systems Handbook: A Straightforward Guide to Functional Safety: IEC 61508 (2010 Edition), IEC 61511 (2015 Edition) and Related GuidanceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Process Safety in Bioprocess Manufacturing FacilitiesFrom EverandGuidelines for Process Safety in Bioprocess Manufacturing FacilitiesNo ratings yet
- Establishing an occupational health & safety management system based on ISO 45001From EverandEstablishing an occupational health & safety management system based on ISO 45001Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)