Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Technically
Uploaded by
Adeem AshrafiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Technically
Uploaded by
Adeem AshrafiCopyright:
Available Formats
Women Entrepreneurship as agent of Social Change Technically, a "women entrepreneur" is any women who organizes and manages any
enterprise, esp. a business, usually with considerable initiative and risk. However, quite often the term "women-owned business" is used relative to government contracting. In this instance, the entrepreneur (a woman) owns (more than 50%), controls and runs the enterprise. It is estimated that presently women entrepreneurs comprise about 10% of the total entrepreneurs in India. It is also clear that this percentage is growing every year. Indian Women have come a long way with changing time. Interestingly issues related to women in India India has the worlds largest number of professionally qualified women. India has more female doctors, surgeons, scientists and professors than the United States. India has more working women than any other country in the world. This includes female workers at all levels of skill from the surgeon and the airline pilot to bus conductors and menial labourers. As per definition proposed by the Government of India in 1988. Women Entrepreneur was defined as an enterprise owned and controlled by women having a minimum financial interest of 51% of the capital and giving at least 51% of employment generated in the enterprise to women. Criteria of Employment was dispersed in the year 1991.Currently, womens enterprise is defined as A small scale industrial unit / industry related service or business enterprise managed by one or more women entrepreneurs in proprietary concerns in which she / they individually or jointly have a share of capital of not less than 51% as partners / shareholders / directors of private limited companies. Evolution of Women Entrepreneurship Evolution and growth of Woman Entrepreneur in India The glass ceilings are shattered and women are found indulged in every line of business. The entry of women into business in India is traced out as an extension of their kitchen activities, mainly 3Ps, Pickle, Powder and Pappad. But with the spread of education and passage of time women started shifting from 3Ps to modern 3Es i.e., Energy, Electronics and Engineering. Skill, knowledge and adaptability in business are the main reasons for women to emerge into business ventures. Women Entrepreneur is a person who accepts challenging role to meet her personal needs and become economically independent. A strong desire to do something positive is an inbuilt quality of entrepreneurial women, who is capable of contributing values in both family and social life. With the advent of media, women are aware of their own traits, rights and also the work situations. The challenges and opportunities provided to the women of digital era are growing rapidly that the job seekers are turning into job creators. Many women start a business due to some traumatic event, such as divorce, discrimination due to pregnancy or the corporate glass ceiling, the health of a family member, or economic reasons such as a layoff. But a new talent pool of women entrepreneurs is forming today, as more women opt to leave corporate world to chart their own destinies. They are flourishing as designers, interior decorators, exporters, publishers, garment manufacturers and still exploring new avenues of economic participation.
Growth of Women Entrepreneurs Women Entrepreneurs in India When woman moves forward, the family moves, the village moves and the nation moves.Women have set up their enterprises and the reasons can be enlisted as below. Motivational Factors Facilitating Factors Motivating Factors 1. Economic Security 2. Self Actualization 3. Independence of Action 4. Self Identity and social status 5. Utilization of education and skills 6. Role model to others 7. Employment generation 8. Continuation of family occupation Facilitating Factors 1. Financial facilities resources 2. Government policies and programs 3. Support of family members 4. Network of contacts 5. Experienced and skilled people at work In recent years the entrepreneurship has gained wide popularity on the whole globe. The rate of becoming entrepreneurs in women is more compared to men. In north America 38 percent & small businesses are owned by women.The growth rate in women owned enterprises in some of the developing countries are higher as compared to the developed countries. According to ILO Statistics the growth rate is 24% in Malaysia, 30% in Thailand & 36% in Philippines & 42% in Indonesia. The growth rate was highest in the Tamil Nadu state of India. It was 18% in 2001. Promotional Efforts Supporting Women Entrepreneurs in India The concern to develop more women entrepreneurs emerges from the fact that women represent 50% of world population, but receive only 10% of the world income and less than 1% of the worlds assets. Yet, research has shown that women entrepreneurs are no different from men in terms of their personality cognition, achievement motivation, dependency and other related attitudes. Development of women has been a policy objective of the government since independence. Women were given priorities in all the sectors including SSI sector. Government and non-government bodies have paid increasing attention to womens economic contribution through self-employment and industrial ventures. The First Five-Year Plan (1951-56) envisaged a number of welfare measures for women. Establishment of the Central Social Welfare Board, organization of Mahila Mandals and the Community Development Programmes were a few steps in this direction. In the second Five-Year Plan (1956-61), the empowerment of women was closely linked with the overall approach of intensive agricultural development programmes. The Third and Fourth Five-Year Plans (1961-66 and 1969-74) supported female education as a major welfare measure. The Fifth Five-Year Plan (1974-79) emphasized training of women, who were in need of income and protection. The Sixth Five-Year Plan (1980-85) saw a definite shift from welfare to development. The Seventh Five-Year Plan (1985-90) emphasized the need for gender equality and empowerment. The Eight Five-Year Plan (1992-97) focused on empowering women, especially at the Grass Roots Level, through Panchayati Raj Institutions. The Ninth Five-Year Plan (1997-2002) adopted a strategy of Womens Component Plan, under which not less than 30 percent of funds/ benefits were earmarked for women related sectors. The Tenth Five-Year Plan (2002-07) aims at empowering women through translating the recently adopted National Policy for Empowerment of Women (2001) into action and ensuring Survival, Protection and Development of women and children through rights based approach. At present, the Government of India has over 25 schemes for women operated by different departments and ministries. Some of these are: 1. Integrated Rural Development Programme (IRDP) 2. Khadi And Village Industries Commission (KVIC) 3. Training of Rural Youth for Self-Employment (TRYSEM) 4. Prime Ministers Rojgar Yojana (PMRY) 5. Entrepreneurial Development programme (EDPs) 6. Management Development progammes 7. Womens Development Corporations (WDCs) 8. Marketing of Non-Farm Products of Rural Women (MAHIMA) 9. Assistance to Rural Women in Non-Farm Development (ARWIND) schemes 10. Trade Related Entrepreneurship Assistance and Development (TREAD) 11. Working Womens Forum 12. Indira Mahila Yojana 13. Indira Mahila Kendra
14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25.
Mahila Samiti Yojana Mahila Vikas Nidhi Micro Credit Scheme Rashtriya Mahila Kosh SIDBIs Mahila Udyam Nidhi Mahila Vikas Nidhi SBIs Stree Shakti Scheme NGOs Credit Schemes Micro & Small Enterprises Cluster Development Programmes (MSE-CDP). National Banks for Agriculture and Rural Developments Schemes Rajiv Gandhi Mahila Vikas Pariyojana (RGMVP) Priyadarshini Project- A programme for Rural Women Empowerment and Livelihood in Mid Gangetic Plains
Problems Faced By Women Entrepreneur The problems and constraints experienced by women entrepreneurs have resulted in restricting the expansion of women entrepreneurship. The major barriers encountered by women entrepreneurs are: 1. The greatest deterrent to women entrepreneurs is that they are women. A kind of patriarchal- male dominant social order is the building block to them in their way towards business success. Male members think it a big risk financing the ventures run by women Male chauvinism is still prevalent in many parts of the country yet. In a male dominated society, women are not treated equal to men that act as a barrier to womans entry into business. Women entrepreneurs have to face a stiff competition with the men entrepreneurs who easily involve in the promotion and development area and carry out easy marketing of their products with both the organized sector and their male counterparts. Lack of self-confidence, will-power, strong mental outlook and optimistic attitude amongst women creates a fear from committing mistakes while doing their piece of work. Women in India lead a protected life. They are even less educated, economically not stable nor self-dependent which reduce their ability to bear risks and uncertainties involved in a business unit, The old and outdated social outlook to stop women from entering in the field of entrepreneurship is one of the reasons for their failure. Women's family obligations also bar them from becoming successful entrepreneurs in both developed and developing nations. Indian women give more emphasis to family ties and relationships. Married women have to make a fine balance between business and family. Womens family and personal obligations are sometimes a great barrier for succeeding in business career. Only few women are able to manage both home and business efficiently, devoting enough time to perform all their responsibilities in priority. The educational level and family background of husbands also influences women participation in the field of enterprise. Absence of proper support, cooperation and back-up for women by their own family members and the outside world people force them to drop the idea of excelling in the enterprise field Many women take the training by attending the Entrepreneurial Development programme without an entrepreneurial bent of mind. Women who are imparted training by various institutes must be verified on account of aptitude through the tests, interviews, etc. High production cost of some business operations adversely affects the development of women entrepreneurs. Women controlled business are often small and it is not always easy for women to access the information they need regarding technology, training, innovative schemes, concessions, alternative markets, etc. Lack of awareness about the financial assistance in the form of incentives, loans, schemes etc. by the institutions in the financial sector. So the sincere efforts taken towards women entrepreneurs may not reach the entrepreneurs in rural and backward areas.
2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12.
13. 14. 15.
SUGGESTIONS FOR THE GROWTH OF WOMEN ENTREPRENEURS Right efforts from all areas are required in the development of women entrepreneurs and their greater participation in the entrepreneurial activities. Entrepreneurship basically implies being in control of ones life and activities and women entrepreneurs need to be given confidence, independence, and mobility to come out of their paradoxes. The following measures are suggested to empower the women to seize various opportunities and face challenges in business. 1. There should be a continuous attempt to inspire, encourage, motivate and co-operate women entrepreneurs. 2. An Awareness programme should be conducted on a mass scale with the intention of creating awareness among women about the various areas to conduct business. 3. Attempts should be there to enhance the standards of education of women in general as well making effective provisions for their training, practical experience and personality development programmes, to improvise their over-all personality standards. 4. Vocational training to be extended to women community that enables them to understand the production process and production management. 5. Skill development to be done in women's polytechnics and industrial training institutes. Skills are put to work in training-cumproduction workshops. 6. Educational institutes should tie up with various government and non-government agencies to assist in entrepreneurship development mainly to plan business projects. 7. International, National, Local trade fairs, Industrial exhibitions, seminars and conferences should be organized to help women to facilitate interaction with other women entrepreneurs.
8. 9. 10. 11. 12.
13.
14. 15.
16.
Women in business should be offered soft loans & subsides for encouraging them into industrial activities. The financial institutions should provide more working capital assistance both for small scale venture and large scale ventures. Making provision of micro credit system and enterprise credit system to the women entrepreneurs at local level. The weaker section could raise funds through various schemes and incentives provided by the government to develop entrepreneurs in the state. E.g. the Prime ministers Rozgar Yojana, The Khadi and Rural village industries scheme, etc. In the initial stages women entrepreneurs may face problems but they must persevere, believe in themselves and not give up midway. Attempts by various NGOs and government organizations to spread information about policies, plans and strategies on the development of women in the field of industry, trade and commerce. Women entrepreneurs should utilize the various schemes provided by the Government. Women should try to upgrade themselves in the changing times by adapting the latest technology benefits. Women must be educated and trained constantly to acquire the skills and knowledge in all the functional areas of business management. This can facilitate women to excel in decision making process and develop a good business network Self-help groups of women entrepreneurs to mobilize resources and pooling capital funds, in order to help the women in the field of industry, trade and commerce can also play a positive role to solve this problem. Womens entrepreneurship must be examined both at the individual level (i.e. the choice of becoming self-employed) and at the firm level (the performance of women owned and managed firms) in order to fully understand the differences between mens and womens entrepreneurship. To establish all India forums to discuss the problems, grievances, issues, and filing complaints against constraints or shortcomings towards the economic progress path of women entrepreneurs and giving suitable decisions in the favor of women entrepreneurs and taking strict stand against the policies or strategies that obstruct the path of economic development of such group of women entrepreneurs.
Thus by adopting the following aforesaid measures in letter and spirit the problems associated with women can be solved. Entrepreneurship is not a bed of roses to women. Women participation in many kinds of economic activities to complement to their family income, their participation in no way reduces their family duties. The task of women has become more tedious and full of challenges. Let us all make efforts to help women rediscover her. Role of Self Help Groups The definition of SHG as approved by National Bank For Agriculture and Rural Development [NABARD] the apex banking body in India, is An SHG is a small, economically homogeneous and affinity group of rural poor voluntarily formed to save and mutually agree to contribute common fund to be lent to its members as per group decision for their socio-economic development. As the name indicates, self-help group is an informal group of about 15-20 people from a homogeneous class, who come together for addressing their common problems. Group itself becomes a base to convey necessities and sort out social economical problems of their group members.Main aim of SHG is to make group members self sufficient and self reliant [independent] by self-employment and empowerment through group dynamics.Self-help group is a best way to get strengthen. Characteristics of an ideal SHG: SHG should have following structural features: An ideal SHG comprises 15-20 members. All the members should belong to the same socio-economic strata of society. Rotational leadership should be encouraged for the distribution of power and to provide leadership opportunities to all the members. Member should regularly attend meetings, save money and participate in all activities VOLUNTARILY. The procedure of decision-making in SHG should democratic in nature. The group frames rules and regulations, which are required in its effective functioning. Transparency in account keeping and accounts should be maintained and updated regularly. An SHG should be socially viable institution. Role of Self Help Groups in empowering women: The self-help groups empower women and train them to take active part in the socio-economic progress of the nation and make them sensitized, self-made and self disciplined. 1. The SHGs have inculcated great confidence in the minds of rural women to succeed in their day-to-day life. 2. SHGs enhance the quality of status of women as participants, decision makers and beneficiaries in the democratic, economic, social and cultural spheres of life. 3. The SHGs bring out the capacity of women in molding the community in right perspective and explore the initiative of women in taking the entrepreneurial ventures. 4. SHGs also organize women to cope with immediate purposes depending on the situation and need. 5. It also helps to bring about awareness among rural women about savings, education, health, environment, cleanliness, family welfare, social forestry, etc. 6. Self Help Group is able to overcome most of the practical problems encountered in the implementation of the various income generating programmes for the economic empowerment of women. 7. SHGs have also been organized during last decade under various programmes of the government, e.g.- District Poverty Eradication Programme, Aapni yojna, Development of Women and Children in Rural Areas, Krishi Vigyan Kendra, etc.
The SHGs are a viable alternative to achieve the objectives of rural development and to get community participation in all rural development programes. The possible outcomes of womens entrepreneur through SHGs at household level are self employment, sustainable livelihoods, enhanced social dignity and better status of women. SHG would lead to benefits not only to the individual women and womens groups but also for the family and community as a whole through collective action for development. Empowerment is not just for meeting their economic needs but also for more holistic social development.
Rural Women Entrepreneurship The most appropriate definition of entrepreneurship that would fit into the rural development context is the one which defines entrepreneurship as: "a force that mobilizes other resources to meet unmet market demand", "the ability to create and build something from practically nothing", "the process of creating value by pulling together a unique package of resources to exploit an opportunity". Challenges Faced by Rural Women Entrepreneurs The main challenges faced by rural women in business are educational & work background. They have to balance their time between work & family.=Some of the challenges faced by rural entrepreneurs are as follows:1. Growth of Mall culture The greatest deterrent to rural women entrepreneurs is that they are women. India is a kind of patriarchal male dominant society. Male members think it is a big risk financing the ventures run by women. 2. Illiteracy The literacy rate of women in India is found at low level compared to male population. The rural women are ignorant of new technology or unskilled. They are often unable to do research & gain the necessary training.. 3. Low Ability to Bear Risk Women in India lives protected life. She is taught to depend on male members from birth. She is not allowed to take any type of risk even if she is willing to take and has ability to bear. Economically they are not self dependent. 4. Lack of Infrastructure and Rampant Corruption These are also the other problems for the rural women entrepreneurs. They have to depend on office staffs and intermediaries to get the things done, especially the marketing and sales side of business. Here is the more probability for business fallacies like the intermediaries take major part of the surplus or profit. 5. Lack of Finance The financial institutions discourage women entrepreneurs on the belief that they can at any time leave their business. Therefore, they are forced to rely on their own savings, loan from their relatives and family friends. 6.Rural women is Indian Society have got restricted mobility. The carrier of women is limited in four walls of kitchen. The women confined themselves to three KS-Kitchen, kids & knitting. There is hardly any opportunities to cross this boundary Opportunities for rural Entrepreneurs. 1. Integrated rural development programme:- The main objectives of Integrated rural development Programme is to increase the income generating power of family who are below the poverty line to alleviate the poverty. They impart technical & entrepreneurial skills & raise the income level of the poor. Some of the major employment & anti-poverty programme are a)IRDP (Integrated Rural Development Programme):- and its allied programmes i. TRYSEM (Training Rural Youth for Self Employment) ii. DWCRA (Development of women and Children in Rural Areas.) b) JRY (Jawahar Rozgar Yojna):- It is wage Employment programme. Implemented by Panchayats at Village, Block & District level. 2. Regional Rural Development Centres. 3. Technology for Bank. 4. Fund for Rural Innovation. 5. Social Rural entrepreneurship 6. Entrepreneurship Development Institute of India. SUGGESTION Right efforts on from all areas are required in the development of women entrepreneurs. Role of rural women entrepreneurs in economic development is inevitable. The following efforts can be taken into account for effective development of women entrepreneurship 1. Training Programme on management skill should be provided to women community. 2. Counselling through the aid of committed NGOS, Psychologists, managerial experts & technical personnel should be provided. 3. Making provisions of marketing & sales assistance from Govt. part. 4. Making provisions of micro credit system & enterprise credit system to the women entrepreneurs at local level. 5. A women entrepreneurs guidance cell set up to handle the various problems of women entrepreneurs all over the state. 6. Training entrepreneurial attitudes should be given at the High School level through well designed course.
You might also like
- MMDocument2 pagesMMAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Security and Security Market OperationsDocument303 pagesSecurity and Security Market OperationsAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Risk and UncertainityDocument2 pagesRisk and UncertainityAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Capital StructureDocument4 pagesCapital StructureAdeem Ashrafi100% (2)
- The Universal BankingDocument5 pagesThe Universal BankingAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- PlanningDocument53 pagesPlanningAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Meaning of StaffingDocument11 pagesMeaning of StaffingAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Meaning of LeverageDocument5 pagesMeaning of LeverageAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Working CapitalDocument15 pagesWorking CapitalAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Capital StructureDocument4 pagesCapital StructureAdeem Ashrafi100% (2)
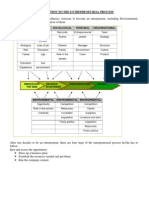
- Entrepreneurial ProcessDocument2 pagesEntrepreneurial ProcessAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Barriers To EntrepreneurshipDocument2 pagesBarriers To Entrepreneurshipanas_786No ratings yet
- Job DesignDocument3 pagesJob DesignAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Recent Trends in Financial InnovationDocument5 pagesRecent Trends in Financial InnovationAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Financial Policy and Strategic PlanningDocument294 pagesFinancial Policy and Strategic PlanningAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Types of Business Entities in IndiaDocument5 pagesTypes of Business Entities in IndiaAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Working CapitalDocument15 pagesWorking CapitalAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Institutional Support For SSIDocument3 pagesInstitutional Support For SSIAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Dividend DecisionDocument4 pagesDividend DecisionAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Operations Managemen1Document1 pageOperations Managemen1Adeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Institutional Support For New VenturesDocument8 pagesInstitutional Support For New VenturesAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Family VentureDocument5 pagesFamily VentureAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- DEPARTMENTATIONDocument1 pageDEPARTMENTATIONAdeem Ashrafi100% (1)
- Meaning of StaffingDocument11 pagesMeaning of StaffingAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Choosing Your Business Organizational StructureDocument3 pagesChoosing Your Business Organizational StructureAdeem Ashrafi100% (1)
- Risk and UncertainityDocument7 pagesRisk and UncertainityAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Hawthorne ExperimentDocument4 pagesHawthorne ExperimentAdeem Ashrafi100% (1)
- DEPARTMENTATIONDocument1 pageDEPARTMENTATIONAdeem Ashrafi100% (1)
- BusinessesDocument4 pagesBusinessesAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Figures of Speech Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesFigures of Speech Lesson PlanMarylin Tarongoy100% (1)
- 1 - Method-and-Approaches of HPDocument63 pages1 - Method-and-Approaches of HPPutri EsaNo ratings yet
- MTICDocument27 pagesMTICKaran MalhotraNo ratings yet
- 2011 Walmart Diversity and Inclusion ADocument20 pages2011 Walmart Diversity and Inclusion ASarah MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Community Mobilization Training Manual PDFDocument2 pagesCommunity Mobilization Training Manual PDFRachel100% (4)
- Top 10 Areas in The Philippines That Are Considered PoorDocument10 pagesTop 10 Areas in The Philippines That Are Considered PoorKarl CabaneroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document43 pagesChapter 1arun neupaneNo ratings yet
- RB Cagmat Review Intong Community Organizing LeaDocument24 pagesRB Cagmat Review Intong Community Organizing LeaPhoebe O. TumammanNo ratings yet
- GM in Sustainable Land Management UndpDocument10 pagesGM in Sustainable Land Management UndpSimon OpolotNo ratings yet
- Citizen Participation, Perceived Control, and Psychological Empowerment.Document26 pagesCitizen Participation, Perceived Control, and Psychological Empowerment.Ray LaiNo ratings yet
- 2010 Annual Report FinalDocument12 pages2010 Annual Report FinalKristy DownerNo ratings yet
- Developing Indicators To Assess Women S Empowerment in VietnamDocument17 pagesDeveloping Indicators To Assess Women S Empowerment in VietnamNicole P. MukledNo ratings yet
- Concept Paper PagalDocument7 pagesConcept Paper PagalHannahclaire DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Hbse II Policy Paper FinalDocument11 pagesHbse II Policy Paper Finalapi-637050088No ratings yet
- Back To The Future Revisiting Kotters 1996 ChangeDocument21 pagesBack To The Future Revisiting Kotters 1996 Changefareha riazNo ratings yet
- Adamawa State CSDA - Draft Report2Document261 pagesAdamawa State CSDA - Draft Report2Justice OnuNo ratings yet
- Gender Manual: A Practical Guide For Development Policy Makers and PractitionersDocument46 pagesGender Manual: A Practical Guide For Development Policy Makers and Practitionersluv_y_kush3575No ratings yet
- Servant Leadership Assessment InstrumentDocument17 pagesServant Leadership Assessment InstrumentFrancis WongNo ratings yet
- Engaging Youth in A Connected WorldDocument53 pagesEngaging Youth in A Connected WorldChicago Learning ExchangeNo ratings yet
- Disability and Mental Health EssayDocument12 pagesDisability and Mental Health EssayNicholas MartinNo ratings yet
- CSR Report Infosys - Psda 2Document11 pagesCSR Report Infosys - Psda 2Aman vijayNo ratings yet
- Participatory Methodology: Rapid Care AnalysisDocument32 pagesParticipatory Methodology: Rapid Care AnalysisOxfamNo ratings yet
- Complaints Handling Guide For Partners - CAFODDocument25 pagesComplaints Handling Guide For Partners - CAFODIrene AnastasiaNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior Managing People and Organizations 11th Edition Griffin Solutions Manual 1Document10 pagesOrganizational Behavior Managing People and Organizations 11th Edition Griffin Solutions Manual 1wendy100% (48)
- Leadership Agility - 5 Levels Short SummaryDocument16 pagesLeadership Agility - 5 Levels Short SummaryAnssi BalkNo ratings yet
- Ucsp EducationDocument17 pagesUcsp Educationteresita barrioNo ratings yet
- Advocacy Action Plan PacketDocument12 pagesAdvocacy Action Plan Packetapi-118575087No ratings yet
- Modernity and Gender A Critique of Modernization TDocument16 pagesModernity and Gender A Critique of Modernization TNabih ShehataNo ratings yet
- Realizing The Existence of Multiple Forms of Knowledge: A Strategy Towards Seeing Education For Rural TransformationDocument16 pagesRealizing The Existence of Multiple Forms of Knowledge: A Strategy Towards Seeing Education For Rural TransformationSagar SunuwarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: NSTP Community Immersion As Foundation of National Development ObjectivesDocument3 pagesLesson 1: NSTP Community Immersion As Foundation of National Development ObjectivesRheeanne AmilasanNo ratings yet