Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Ledger
Uploaded by
Anshuman SharmaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
General Ledger
Uploaded by
Anshuman SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
3.
Closing period in GL
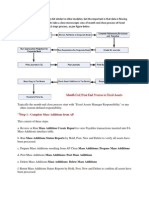
Before starting the discussion about period end closing in GL, You must understand the concept of Primary Ledger. Primary Ledger: A primary ledger is defined as a ledger where all your day-to-day transactions are performed or it can be regarded as a main and record keeping ledger. It is defined by four Cs: a. Chart of Accounts (COA): Chart of Accounts structure is defined based on business, reporting and statutory requirements. b. Accounting Calendar: Accounting Calendar defines an accounting year and the period it contains. c. Currency: Functional currency as well as other currencies can be selected that is used to transact business. d. Convention (Sub-ledger Accounting Method): Convention means accounting method which allows you to assign and manage specific accounting method for each ledger. Before closing the period in Oracle General Ledger, there is a list of activities which needs to be done. The list of activities is listed below: Ensure Next Period is Future Enterable or Open: Ensure the next accounting period status is set to Future Entry. In R12, Import journals to SLA (Sub Ledger Accounting) and then to GL and in 11i directly import to General Ledger. The procedure of importing journals to SLA or directly to GL is as follows: 1.) Upload journals from Web ADI (Application Desktop Integrator) to Oracle GL. 2.) Generate reversal journals. 3.) Generate recurring journals. 4.) Generate mass allocation journals.
5.) Review and verify journal details of un-posted journals. Post journal batches. Run and review journals reports. Run Revaluation : It adjusts asset or liability accounts that may be materially understated or overstated at the end of a period due to a significant fluctuation in the exchange rate between the time the transaction was entered and the end of the period Run Translation: 1) It restates an entire ledgers or balances from functional currency to foreign currency. 2) Translate actual and budget balances from functional to foreign currency for online inquiries, reports and consolidations. Consolidate Ledgers: Consolidation means merging the financial data of all subsidiary ledgers in one parent ledger (ledger is a replacement for sob in R12 with some additional features). It can also be defined as a period-end process of combining the financial results of separate subsidiaries with the parent organization to form a single, combined statement of financial results. Below are the following steps involved for consolidation: 1) Create subsidiary ledgers for all the countries where we operate our business in all currencies. 2) Create parent ledger with reporting currency of organization. 3) Translate all ledger balances to reporting currency. 4) Transfer all the balances from subsidiary ledgers to parent ledger with the help of mapping rules. Mapping rules are of two types: A. Segment Rule: These are used when the Chart of Accounts of subsidiary and parent set of books are same. B. Account Rules: These are used when the Chart of Accounts of subsidiary and parent set of books are different.
Run Final Reports .Some of the reports are listed below: 1) Audit Trail Report: Provides a complete, detailed listing of the transactions that have taken place in each account for a specified time period. 2) Trial Balance Report: Provides a quick check of the balances in each account and verifies that debits equal credits. 3) Balance Sheet Report: Provides current data on the financial condition of the company. Accumulations to asset, liability, and equity accounts are included in this report. 4) Income Statement Report: Shows the relationship between the revenue generated and the expenses paid for a specified range of periods. 5) Revenue and Expense Report (FUND): Shows the relationship between the revenue generated and the expenses paid for a specified range of periods.
You might also like
- Isys6300 - Business Process Fundamental: Week 8 - The General Ledger and Financial ReportingcycleDocument37 pagesIsys6300 - Business Process Fundamental: Week 8 - The General Ledger and Financial ReportingcycleEdwar ArmandesNo ratings yet
- r12 Sla Slam Asm Ledger Ledger SetDocument5 pagesr12 Sla Slam Asm Ledger Ledger SetSrinivasa Rao AsuruNo ratings yet
- Subledger ReconciliationDocument50 pagesSubledger ReconciliationnimishhshahNo ratings yet
- Month End For FADocument4 pagesMonth End For FAFikadu HaileNo ratings yet
- Budget in OracleDocument21 pagesBudget in Oracleoracleapps R12No ratings yet
- Oracle General Ledger Consolidation RELEASE 11.0: Julie A. Strauch May 30, 2000Document27 pagesOracle General Ledger Consolidation RELEASE 11.0: Julie A. Strauch May 30, 2000Rohan KamatNo ratings yet
- Oracle Advanced Collections: Overview and Implementation Tips and Tricks Session Session ID: TIP1153Document20 pagesOracle Advanced Collections: Overview and Implementation Tips and Tricks Session Session ID: TIP1153Srinivas GirnalaNo ratings yet
- Gotoap: Split ConceptDocument65 pagesGotoap: Split ConceptsureshNo ratings yet
- Subledger AccountingDocument5 pagesSubledger Accountingravi_sri03No ratings yet
- R12.2 Oracle General Ledger Management Fundamentals: DurationDocument3 pagesR12.2 Oracle General Ledger Management Fundamentals: Durationr.n.pradeepNo ratings yet
- AP FunctionalDocument24 pagesAP FunctionaltcsoracleNo ratings yet
- Oracle E-Business Suite R12 Pakistan's WeblogDocument5 pagesOracle E-Business Suite R12 Pakistan's WeblogchinbomNo ratings yet
- Reconciliation Matching RulesDocument3 pagesReconciliation Matching RulesSuneel BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Document On Return To Vendor (RTV) ProcessDocument10 pagesDocument On Return To Vendor (RTV) ProcessSiddharth BiswalNo ratings yet
- Translation Revaluation in GLDocument2 pagesTranslation Revaluation in GLiam_ritehereNo ratings yet
- Use of Secondary Tracking Segment in Oracle FinancialsDocument3 pagesUse of Secondary Tracking Segment in Oracle FinancialsMoh'd AdamNo ratings yet
- AP Suppliers in R12Document51 pagesAP Suppliers in R12Abhilash KarappankuttyNo ratings yet
- Accounting and The Business EnvironmentDocument46 pagesAccounting and The Business EnvironmentSatya JeetNo ratings yet
- AGIS Setup SameLedgerDocument9 pagesAGIS Setup SameLedgernkvasan100% (1)
- EBS GL Interview QuestionsDocument17 pagesEBS GL Interview QuestionsSivakumar KandasamyNo ratings yet
- Oracle Applications - Oracle Accounting Setup Manager (ASM) DetailsDocument11 pagesOracle Applications - Oracle Accounting Setup Manager (ASM) Detailsaruna777No ratings yet
- AR Accounts ReceivableDocument3 pagesAR Accounts ReceivableImran HassanNo ratings yet
- R12 Uploading A Journal Using Web ADIDocument12 pagesR12 Uploading A Journal Using Web ADIdevender143No ratings yet
- CVR Security RuleDocument11 pagesCVR Security RulegopalarajadudduNo ratings yet
- Accounting Key Flexfield - Create Chart of Accounts Key FlexfieldsDocument13 pagesAccounting Key Flexfield - Create Chart of Accounts Key FlexfieldsGopi Krishna Reddy JulakantiNo ratings yet
- SLA Setup R12Document9 pagesSLA Setup R12Muthumariappan21100% (1)
- R12 Sequencing in LedgersDocument9 pagesR12 Sequencing in LedgersaggersainNo ratings yet
- Understanding Supplier Master in FusionDocument13 pagesUnderstanding Supplier Master in Fusionankit131189No ratings yet
- Secondary Tracking SegmentDocument5 pagesSecondary Tracking Segmentrsririshi100% (1)
- Final Implementation GuideDocument52 pagesFinal Implementation GuideSingh Anish K.No ratings yet
- 2.lockbox ApproachDocument7 pages2.lockbox Approachmks210100% (1)
- GL Changes - R12 Vs 11iDocument19 pagesGL Changes - R12 Vs 11iPooja PatelNo ratings yet
- Oracle Automatic Receipts and Remittance in R12Document24 pagesOracle Automatic Receipts and Remittance in R12Praveen MallikNo ratings yet
- 19D Receitables v551 PDFDocument63 pages19D Receitables v551 PDFFernanda Gerevini PereiraNo ratings yet
- EBS GlossaryDocument28 pagesEBS GlossarySUMITFORBIZNo ratings yet
- Hyperion® Financial Management - System 9: Library of FunctionsDocument34 pagesHyperion® Financial Management - System 9: Library of Functionsligiamolguin9426No ratings yet
- Unit-I: SVD & SGL College of Management and Technology: RajahmundryDocument38 pagesUnit-I: SVD & SGL College of Management and Technology: RajahmundryHappyPrinceNo ratings yet
- GL Cross Validation RulesDocument6 pagesGL Cross Validation RulesSingh Anish K.No ratings yet
- Oracle Iexpenses FlowDocument25 pagesOracle Iexpenses FlowVivekanand Pandey100% (1)
- Bank Acct Trans White PaperDocument30 pagesBank Acct Trans White Paperyoursashok_giriNo ratings yet
- CV RahulDocument8 pagesCV RahulIbtissem BenaichaNo ratings yet
- The Following Is The Enterprise Structure Which We Would Be ImplementingDocument48 pagesThe Following Is The Enterprise Structure Which We Would Be ImplementingKuladeep PNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Review of The Accounting Cycle 1.1.1 Journalizing Transactions in The General JournalDocument11 pages1.1 Review of The Accounting Cycle 1.1.1 Journalizing Transactions in The General JournalgabNo ratings yet
- Manage Journal Line Rules in Fusion Receipt Accounting PDFDocument8 pagesManage Journal Line Rules in Fusion Receipt Accounting PDFBayo JekayinfaNo ratings yet
- How To Configure and Use Procurement Card (P-Cards) in Fusion Self Service ProcurementDocument6 pagesHow To Configure and Use Procurement Card (P-Cards) in Fusion Self Service Procurementmiba_2025No ratings yet
- PPR PrimerDocument49 pagesPPR PrimerjrparidaNo ratings yet
- Accruals and Accounting FaqDocument3 pagesAccruals and Accounting Faqandrew_bw100% (1)
- R12Projects White Paper Part IIDocument137 pagesR12Projects White Paper Part IIrahuldisyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Collections 11iDocument53 pagesAdvanced Collections 11iShelly Dixit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- How Many Key Flexfields Are There in Oracle Financials?: EBS GL Interview QuestionsDocument15 pagesHow Many Key Flexfields Are There in Oracle Financials?: EBS GL Interview QuestionsSreekanthNo ratings yet
- Vishal TyagiDocument9 pagesVishal Tyagityagi.vishal8323No ratings yet
- Oracle Cash Management SystemDocument36 pagesOracle Cash Management SystemAbdulsayeedNo ratings yet
- PO - Accounting - Flow in Encumbrance EnvironmentDocument16 pagesPO - Accounting - Flow in Encumbrance EnvironmentKapil KarwalNo ratings yet
- AIM OverviewDocument22 pagesAIM OverviewSaqib RahatNo ratings yet
- Period-End Process in Receivables r12Document9 pagesPeriod-End Process in Receivables r12devender143No ratings yet
- Financial Reporting andDocument58 pagesFinancial Reporting andJohn PaulNo ratings yet
- AIS PaperDocument8 pagesAIS PaperTarra AuliaNo ratings yet
- FAR Summary NotesDocument53 pagesFAR Summary NotesVeronica BañaresNo ratings yet
- Receivables To Ledger Reconciliation-Note IDDocument8 pagesReceivables To Ledger Reconciliation-Note IDJanardhanNo ratings yet
- IMM Value Creation in MarketsDocument12 pagesIMM Value Creation in MarketsAnshuman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dhaval SpintrpnicsDocument19 pagesDhaval SpintrpnicsAnshuman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Final Seminar Synopsis (Ishant)Document3 pagesFinal Seminar Synopsis (Ishant)Anshuman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Printers and Its TypeDocument2 pagesPrinters and Its TypeAnshuman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Concepts and ConventionsDocument6 pagesAccounting Concepts and ConventionsAMIN BUHARI ABDUL KHADER100% (6)
- We Can Classify Audit Reports in Number of Ways But Usually Audit Reports Are Classified N TWO Broad Categories Which Are Then Further Classified As FollowsDocument4 pagesWe Can Classify Audit Reports in Number of Ways But Usually Audit Reports Are Classified N TWO Broad Categories Which Are Then Further Classified As FollowskalaswamiNo ratings yet
- David OgilvyDocument5 pagesDavid OgilvyNiranjana ChandranNo ratings yet
- BoldData Sample Company Database Belgium1Document22 pagesBoldData Sample Company Database Belgium1Anupriya Roy ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument4 pagesCase StudyAnju PuthanamkuzhiNo ratings yet
- Token Sale AgreementDocument8 pagesToken Sale AgreementAdiyaMaulidilAliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CSR 1Document18 pagesIntroduction To CSR 1JagrityTalwarNo ratings yet
- Central Systems: Installation, Operation and MaintenanceDocument32 pagesCentral Systems: Installation, Operation and MaintenancelatrancaNo ratings yet
- BSP and Dof Floor Plan GFDocument1 pageBSP and Dof Floor Plan GFKarl Anton ClementeNo ratings yet
- Sats Ar 2011-12Document180 pagesSats Ar 2011-12Francisco2105No ratings yet
- Rbi Inspection of BanksDocument94 pagesRbi Inspection of BanksGsr MurthyNo ratings yet
- TB (Service)Document14 pagesTB (Service)Jerric CristobalNo ratings yet
- Business LettersDocument36 pagesBusiness Lettersapi-3713116No ratings yet
- CitibankDocument4 pagesCitibankUmma Eugenio AgustinNo ratings yet
- Business Contacts Bulletin - May Sri LankaDocument19 pagesBusiness Contacts Bulletin - May Sri LankaDurban Chamber of Commerce and IndustryNo ratings yet
- Dungeons & Dragons Drizzt #3 PreviewDocument12 pagesDungeons & Dragons Drizzt #3 PreviewGraphic Policy100% (2)
- Sswot: A Sustainability SwotDocument24 pagesSswot: A Sustainability SwotNikita AroraNo ratings yet
- Resume 2Document4 pagesResume 2edzNo ratings yet
- 2008 Bar Questions and AnswersDocument15 pages2008 Bar Questions and AnswersimoymitoNo ratings yet
- ACCT 897/297 Prof. Jennifer Blouin - Spring 2015: Taxes and Business StrategyDocument6 pagesACCT 897/297 Prof. Jennifer Blouin - Spring 2015: Taxes and Business StrategyTariqul IslamNo ratings yet
- FT Lauderdale-Q3 2010 ReportDocument11 pagesFT Lauderdale-Q3 2010 ReportKen RudominerNo ratings yet
- 42 47 ListDocument6 pages42 47 ListMartha DewaNo ratings yet
- CIR v. BOAC (1987, 149 SCRA 395)Document20 pagesCIR v. BOAC (1987, 149 SCRA 395)KTNo ratings yet
- IA Role in Sox Compliance PDFDocument30 pagesIA Role in Sox Compliance PDFrbshah86100% (2)
- 3935 A722-43007 - Rev00 - 01Document55 pages3935 A722-43007 - Rev00 - 01Elena CucerNo ratings yet
- Accounting Fraud Auditing and The Role of Government Sanctions in China 2015 Journal of Business ResearchDocument10 pagesAccounting Fraud Auditing and The Role of Government Sanctions in China 2015 Journal of Business ResearchAquamarine EmeraldNo ratings yet
- Pro Forma Deed of AssignmentDocument2 pagesPro Forma Deed of AssignmentjamesethanNo ratings yet
- RE KV SathasivamDocument12 pagesRE KV SathasivamAw Jyh JingNo ratings yet