Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Meaning of Staffing
Uploaded by
Adeem AshrafiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Meaning of Staffing
Uploaded by
Adeem AshrafiCopyright:
Available Formats
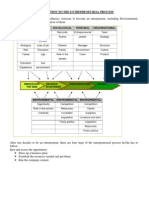
MEANING OF STAFFING Earlier staffing was considered to be a part of organization function of management. It is now recognized as a separate management function.
The reason for separating the staffing from organizing is to give proper emphasis to the actual meaning of managerial roles. Today the staffing function has assumed greater importance because of rapid advancement of technology, increasing the size of the organization and complex behaviour of human beings. The enterprise has to give due importance to human resource planning. It is the tendency in modern enterprises to create a separate department. It is for this purpose medium and large organizations have separate department known as personnel department or human resource department to perform staffing function. The organization structure spells out various positions of the organization. Filling and keeping these positions with right people is the staffing phase of the management function. Staffing involves the determination of manpower requirements of the enterprise and providing it with adequate competent people at all levels. The staffing function performs the following sub functions: (1) Manpower planning. (2) Recruitment (3) Selection of the best qualified from those who seeks job, (4) Training and Development. (5) Performance appraisal and compensation. NATURE AND IMPORTANCE OF STAFFING The staffing function has assumed greater significance these days because of various factors. Staffing is also a pervasive function. Through separate department exist for this yet every manager is engaged in performing the staffing function, when they participate in selection, training and evaluating their subordinates. The various reasons which have increased the significance of staffing functions are discussed below: (1) Increasing size of organization: Advancement in science and technology has given rise to large scale companies employing thousands of employees. The performance of the company depends on the quality and character of the people. This has increased the importance of staffing. (2) Advancement of technology: In order to make use of latest technology, the appointment of right type of persons is necessary. (3) Long-range needs of manpower: In some industries, labour turn-over is high. The management is required to determine the manpower requirement well in advance. Management has also to develop the existing personal for future promotion. The role of staffing has also increased because of shortage of good managerial talents. (4) Recognition of human relations: The behaviour of individuals has become very complicated and hence human aspect of organization has become very important. Employees are to be motivated by financial and non-financial incentives. Right kind of atmosphere should also be created to contribute to the achievement of organizational objectives. By performing the staffing function, management can show the significance it attaches to the man power working in the enterprise.
Man Power Planning Manpower Planning which is also called as Human Resource Planning consists of putting right number of people, right kind of people at the right place, right time, doing the right things for which they are suited for the achievement of goals of the organization. Human Resource Planning has got an important place in the arena of industrialization Steps in Manpower Planning 1. Analysing the current manpower inventory- Before a manager makes forecast of future manpower, the current manpower status has to be analysed. For this the following things have to be noted Type of organization Number of departments Number and quantity of such departments Employees in these work units 2. Making future manpower forecasts- Once the factors affecting the future manpower forecasts are known, planning can be done for the future manpower requirements in several work units. 3. Developing employment programmes- Once the current inventory is compared with future forecasts, the employment programmes can be framed and developed accordingly, which will include recruitment, selection procedures and placement plans. 4. Design training programmes- These will be based upon extent of diversification, expansion plans, development programmes,etc. Training programmes depend upon the extent of improvement in technology and advancement to take place. It is also done to improve upon the skills, capabilities, knowledge of the workers. 1. Importance of Manpower Planning 1. Key to managerial functions- The four managerial functions, i.e., planning, organizing, directing and controlling are based upon the manpower. Human resources help in the implementation of all these managerial activities. Therefore, staffing becomes a key to all managerial functions. 2. Efficient utilization- Efficient management of personnels becomes an important function in the industrialization world of today. Seting of large scale enterprises require management of large scale manpower. It can be effectively done through staffing function. 3. Motivation- Staffing function not only includes putting right men on right job, but it also comprises of motivational programmes, i.e., incentive plans to be framed for further participation and employment of employees in a concern. Therefore, all types of incentive plans becomes an integral part of staffing function. 4. Better human relations- A concern can stabilize itself if human relations develop and are strong. Human relations become strong trough effective control, clear communication, effective supervision and leadership in a concern. Staffing function also looks after training and development of the work force which leads to co-operation and better human relations. 5. Higher productivity- Productivity level increases when resources are utilized in best possible manner. higher productivity is a result of minimum wastage of time, money, efforts and energies. This is possible through the staffing and it's related activities ( Performance appraisal, training and development, remuneration) Need of Manpower Planning Manpower Planning is a two-phased process because manpower planning not only analyses the current human resources but also makes manpower forecasts and thereby draw employment programmes. Manpower Planning is advantageous to firm in following manner: 1. Shortages and surpluses can be identified so that quick action can be taken wherever required. 2. All the recruitment and selection programmes are based on manpower planning. 3. It also helps to reduce the labour cost as excess staff can be identified and thereby overstaffing can be avoided. 4. It also helps to identify the available talents in a concern and accordingly training programmes can be chalked out to develop those talents. 5. It helps in growth and diversification of business. Through manpower planning, human resources can be readily available and they can be utilized in best manner. 6. It helps the organization to realize the importance of manpower management which ultimately helps in the stability of a concern.
JOB DESIGN Job design is the process of defining the way work will be performed and the tasks that will be required in a given job. In other words job design is the process of deciding on the content of a job in terms of its duties and responsibilities; on the methods to be used in carrying out the job, in terms of techniques, systems and procedures and on the relationships that should exist between the job holder and the superiors, subordinates and colleagues.Thus job design is necessary to fulfill the following goals: To Meet the organizational requirements such as higher productivity, operational efficiency, quality of product/service etc To satisfy the needs of the individual employees like interests, challenges, achievement or accomplishment, etc. Integrate the needs of the individual with the organizational requirements. APPROACHES TO JOB DESIGN The four approaches used in job design are: mechanistic approach motivational approach biological approach perceptual-motor approach Mechanistic Approach
Its roots in classical industrial engineering. Focuses on designing jobs around the concepts of task specialization, skill simplification, and repetition.
Scientific management, one of the earliest mechanistic approaches, sought to identify the one best way to perform the job through the use of time-and-motion studies. The scientific management approach was built upon in later years and resulted in a mechanistic approach that calls for the job to be designed very simply. Biological Approach New employees can be trained to perform the job quickly and inexpensively. Comes primarily from the sciences of biomechanics, or the study of body movements
Is referred to as ergonomics, or the concern with examining the interface between individuals' physiological characteristics and the physical work environment. The goal of this approach is to minimize the physical strain on the worker by structuring the physical work environment around the way the body works. Focuses on outcomes such as physical fatigue, aches and pains, and health complaints. Perceptual-Motor Approach
Has their root in the human-factors literature. Focuses on human mental capabilities and limitations. The goal is to design jobs in a way that ensures that they do not exceed people's mental capabilities. Tries to improve reliability, safety, and user reactions by designing jobs in a way that reduces the information processing requirements of the job. Motivational Approach The motivational approach to job design focuses on the job characteristics that affect the psychological meaning and motivational potential of job design. A focus on increasing job complexity through job enlargement, job enrichment, and the construction of jobs around sociotechnical systems. A model of how job design affects employee reaction is the Job Characteristics Model.
FACTORS AFFECTING JOB DESIGN I] Organizational factors :Organizational factors to refer to factors inside the organization which affect job design they are a) Task characteristics :- Task characteristics refer to features of the job that is depending on the type of job and the duties involved in it the organization will decide, how the job design must be done. Incase the company is not in a position to appoint many people; a single job may have many duties and vice versa. b) The process or flow of work in the organization:-There is a certain order in which jobs are performed in the company. Incase the company wishes it could combine similar job and give it to one person this can be done if all the jobs come one after the other in a
sequence. c) Ergonomics:- Ergonomics refers to matching the job with physical ability and characteristics of the individual and in providing an office environment which will help the person to complete the jobs faster and in a comfortable manner. d) Work practices: - Every organization has different work practices. Although the job may be the same the method of doing the job differs from company to company. This is called work practice and it affects job design. II] Environmental factors:Environmental factors which affect job design are as follows a) Employee availability and ability :- Certain countries face the problem of lack of skilled labour. They are not able to get employees with specific education levels for jobs and have to depend on other countries due to this job design gets affected. b) Social and cultural expectations :- The social and cultural conditions of every country is different so when an MNC appoints an Indian it has to take into account like festivals, auspicious time, inauspicious time, etc. to suit the Indian conditions. This applies to every country and therefore job design will change accordingly. III] Behavioral factors:Job design is affected by behavioral factors also. These factors are a) Feedback :-Job design is normally prepared on the basis of job analysis and job analysis requires employee feedback based on this employee feedback all other activities take place. Many employees are however not interested in providing a true feedback because of fear and insecurity. This in turn affects job deign. b) Autonomy :-Every worker desires a certain level of freedom to his job effectively. This is called autonomy. Thus when we prepare a job design we must see to it that certain amount of autonomy is provided to the worker so that he carries his job effectively. c) Variety :-When the same job is repeated again and again it leads to burden and monotony. This leads to lack of interest and carelessness on the job. Therefore, while preparing job design certain amount of variety must be provided to keep the person interested in the job. Methods of job design There are various methods in which job design can be carried out. These methods help to analysis the job, to design the contents of the and to decide how the job must be carried out .these methods are as follows I. Job rotation- Job Rotation is a management approach where employees are shifted between two or more assignments or jobs at regular intervals of time in order to expose them to all verticals of an organization. It is a pre-planned approach with an objective to test the employee skills and competencies in order to place him or her at the right place. In addition to it, it reduces the monotony of the job and gives them a wider experience and helps them gain more insights.Job rotation is a well-planned practice to reduce the boredom of doing same type of job everyday and explore the hidden potential of an employee.. II. Job enlargement-A job design technique in which the number of tasks associated with a job is increased (and appropriate training provided) to add greater variety to activities, thus reducing monotony.Job enlargement is considered a horizontal restructuring method in that the job is enlarged by adding related tasks. Job enlargement may also result in greater workforce flexibility. III. Job enrichment-A job design technique that is a variation on the concept of job enlargement. Job enrichment adds new sources of job satisfaction by increasing the level of responsibility of the employee. While job enlargement is considered a horizontal restructuring method, job enrichment is a vertical restructuring method by virtue of giving the employee additional authority, autonomy, and control over the way the job is accomplished. Also called job enhancement or vertical job expansion.
Recruitment According to Edwin B. Flippo,Recruitment is the process of searching the candidates for employment and stimulating them to apply for jobs in the organization. The personnel department of a larger business will often have detailed recruitment and selection policies that need to be followed by those responsible for hiring new employees. Thus Recruitment means: Recruitment is the activity that links the employers and the job seekers.
A process of finding and attracting capable applicants for employment
The recruitment process has the following objectives: To ensure that the recruitment is as per the company expectations. (e.g time, skills, etc.,) To attract sufficient applications from potential candidates with the required skills, qualities, experience, and competencies deemed as being necessary to the job To develop and maintain processes which will assist in ensuring the appointment of the most suitable candidate Purpose and importance 1)To determine the present and future requirement of the organization, 2)To increase the pool of job candidates at minimum cost. 3) Helps to increase the success rate of the selection process. 4) Helps to reduce the turnover of the job employees. 5) Helps to meet the organization legal and social obligations. 6) Helps to identify the individual effectiveness in the short term and long term. Factors Affecting Recruitment All organizations, whether large or small, do engage in recruiting activity, though not to the same extent. This differs with: (i) The size of the organization; (ii) The employment conditions (iii) The effects of past recruiting (iv) Working conditions and salary and benefit packages offered by the organization (v) The rate of growth of organization; Sources of Recruitment
Recruitment Process
1. Identify vacancy 2. Prepare job description and person specification 3. Advertising the vacancy 4. Managing the response 5. Short-listing 6. Arrange interviews 7. Conducting interview and decision making
Selection Selection is the process picking the right individuals and offering them job. Selection can be defined as the process of differentiating between applicants in order to identify and hire those with greater likelihood of success in a job. Once the potential applicants are identified, the next step is to evaluate their qualification, qualities, experiences, capabilities,etc..&make the selection. It is the process of offering jobs to the desired applicants.. Need for Selection (i)It ensures that the organization gets the best among the available, and (ii) It enhances the self-esteem and prestige of those selected and conveys to them the seriousness with which the things are being done in the organization Selection Process or Procedures Process of selection varies from organization to organization and even from department to department. The main steps in selection procedure are: 1. Preliminary Interview: does the job of eliminating the totally unsuitable candidates. It saves the time of both employer and applicants. The candidates who pass this screening will be usually asked to fill the application. 2. Employment Tests: Different tests are conducted in order to know the level of candidates ability, the knowledge, the pattern of his interest and aptitudes in detail. The following are some of the tests: a) Intelligence test b) Aptitude tests c) Trade or proficiency test d) Interest test e) Personality tests 3. Employment Interview: Employment test provide a lot of valuables information about the candidate. The main purposes of an employment interview are: 1. To find out the suitability of candidates. 2. To seek more information about the candidate. 3. To give him an accurate picture of the details of terms and conditions and some idea of organization policies. The communication skill of candidate can be judged in the interview. 4. Checking References: Prior to final selection the prospective employment normally makes an investigation on the references supplied by the applicant and undertakes more or less a through search into candidates past employment, education, personal reputation, financial condition etc 5. Medical Examination: A proper medical examination will ensure higher standard of health and physical fitness of the employees and will reduce the rates of accidents, labor turnover, and absenteeism. It serves to ascertain the applicants physical capability to meet the job requirements. 6. Final Selection: After candidates successfully clear all the hurdles in selection procedure, they will be given appointment letter formally. The candidates are not appointed permanently; rather organization will try them for a few months. 7. Evaluation: This step also can be treated as an important step in the selection process, the entire selection process has to be evaluated to ensure the quality of selection process and to perfect it for the next selection. This is also called as selection audit. Difference between Recruitment and Selection Basis Meaning Recruitment It is an activity of establishing contact between employers and applicants. It encourages large number of Candidates for a job. It is a simple process. The candidates have not to cross over many hurdles. Selection It is a process of picking up more competent and suitable employees. It attempts at rejecting unsuitable candidates. It is a complicated process. Many hurdles have to be crossed.
Objective Process Hurdles
Approach Sequence Economy Time Consuming
It is a positive approach. It proceeds selection. It is an economical method. Less time is required.
It is a negative approach. It follows recruitment. It is an expensive method. More time is required.
Importance of Recruitment and Selection Helps to get a proper candidate. Help to increase success rate. Helps to get organizations legal and social obligations. Helps to increase organization and individual effectiveness. Training Training as a part of staffing is done to aid employees in improving performance. Training is the act of increasing the knowledge and skills of an employee for doing a particular job. Training is the formal and systematic modification of behavior through learning which occurs as a result of education, instruction, development and planned experience. Objectives of Training The general objectives of any training programme are: 1. To impart the basic knowledge and skill to new entrants and enable them to perform their jobs well. 2. To equip the employee to meet the changing requirements of the job and the organisation. 3. To teach the employees new techniques and ways of performing the job or operations. 4. To prepare employees for higher level tasks and build up a second line of competent managers. Need for Training Training is needed to achieve the following purposes: 1. Newly recruited employees require training so as to perform their tasks effectively. 2. Training is necessary to prepare existing employees for higher-level jobs (promotion). 3. Existing employees require refresher training so as to keep abreast of the latest developments in job operations 4. Training is necessary when a person moves from one job to another (transfer). 5. Training is necessary to make employees mobile and versatile. Advantages of Training: Advantages of Training 1. Leads to improved profitability and/or more positive attitudes toward profits orientation. 2. Improves the job knowledge and skills at all levels of the organization. 3. Improves the morale of the workforce. 4. Helps people identify with organizational goals. 5. Helps create a better corporate image. Disadvantages of training: Disadvantages of training 1. Can be a financial drain on resources; expensive development and testing, expensive to operate 2. Often takes people away from their job for varying periods of time; 3. Equips staff to leave for a better job 4. Bad habits passed on 5. Narrow experience Methods of Training Broadly speaking, there are two methods of training, viz., on-the-job training Job Instruction Training Coaching and Mentoring Apprenticeship Training Job rotation Refresher training Orientation training off-the-job training Role playing Lecture method Conference/ discussion approach Programmed instruction
Development Development refers to formal education, job experiences, relationships, and assessments of personalities and abilities that help employees prepare for the future.Employee development is a necessary component of a companys efforts to: Improve quality Retain key employees Meet the challenges of global competition and social change Incorporate technological advances and changes in work design Approaches to employee development Formal education programs It includes: off-site and on-site programs designed specifically for the companys employees short courses offered by consultants or universities executive MBA programs university programs in which participants actually live at the university while taking classes Assessment It involves collecting information and providing feedback to employees about their behavior, communication style, or skills. Used most frequently to: identify employees with managerial potential measure current managers strengths and weaknesses identify managers with potential to move into higher-level executive positions Work with teams to identify members strengths and weaknesses, and factors that inhibit productivity Job experiences It refers to relationships, problems, demands, tasks, or other features that employees face in their jobs. Most employee development occurs through job experiences. A major assumption is that development is most likely to occur when there is a mismatch between the employees skills and past experiences and the skills required for the job. Interpersonal Relationship Employees can also develop skills and increase their knowledge about the company and its customers by interacting with a more experienced organizational member.Two types of interpersonal relationships used to develop employees: o Mentoring o Coaching The Development Planning Process The development planning process involves: o Identifying development needs o Choosing a development goal o Identifying the actions that need to be taken by the employee and the company to achieve the goal o Determining how progress toward goal attainment will be measured o Establishing a timetable for development
Performance Appraisal Performance Appraisal is the process of deciding how employees do their jobs. According to Newstrom, It is the process of evaluating the performance of employees, sharing that information with them and searching for ways to improve their performance. The main characteristics of performance appraisal may be listed as: The appraisal is a systematic process. It tries to evaluate performance in the same manner using the same approach. It provides an objective description of an employee's job's relevant strengths and weaknesses. It tries to find out how well the employee is performing the job and tries to establish a plan for further improvement. The appraisal is carried out periodically, according to a definite plan. It is certainly not a one-shot deal. Objectives Appraisal of employees serves several useful purposes: (a) Compensation decisions (b) Promotion decisions (c) Training and development programmes (d) Feedback (e) Personal development Steps in performance appraisal Establishing job standards Designing an appraisal programme Appraise performance Performance interview Use appraisal data For appropriate purpose
DIRECTION Direction is the managerial function of guiding, motivating, leading and supervising the subordinates to accomplish desired objectives. Direction is an important managerial function that initiates organiser's action. It is a connecting and activating link between various functions of management. Direction phase of management is the heart of management-in-action. It provides necessary guidance and inspiration to people at work in order to carry out their assigned duties. Direction is the essence of operations. It is a continuous function. Direction is telling people what to do and seeing that they do it to the best of their ability. It is through directing that managers get the work done through people. It consists of: Issuing orders and instructions by a superior to his subordinates (Communication). Guiding, advising and helping subordinates in the proper methods of work (Leadership). Motivating them to achieve goals by providing incentives, good working environment, etc. (Motivation). Supervising subordinates to ensure compliance with plans (Supervision). Thus, the scope of direction is very wide. It includes all those activities which a manager undertakes to influence the actions of his subordinates and achieve goals. Importance The importance of directing function in the process of management may be discussed under the following heads: Initiates action issuing instructions, providing guidance, supervising work, and motivating subordinates to realise goals. Achieves integration Motivates people Facilitates changes Attains balance and stability Principles of Direction Important principles of direction may be summarised thus: Principle of harmony of objectives
Principle of unify of command Principle of direct supervision Appropriate techniques Managerial communication Informal organisation Principle of maximum individual contribution Use of motivation techniques Principle of follow-up
Supervision: Meaning The word supervision consists of two parts super and vision. Super means over and above. Vision is the art of seeing objects, or viewing mental images or looking over. Thus Supervision means overseeing from above by a superior. The term Supervision refers basically to an individual who supervises the operatives. He may be designated as foreman, overseer, gang chief, superintendent, section officer or section incharge.Supervision means overseeing the subordinates at work. It involves a face-to-face contact between the supervisor and his subordinates. The aim of supervision is to ensure that subordinates work efficiently to accomplish the tasks assigned to them. Difference Between Direction and Supervision Direction Direction is a function of instructing, guiding and motivating the subordinates for the achievement of organizational goals. Direction includes communication, leadership, motivation and supervision. Direction is important at all levels of the organization, i.e., from top management to operative level. Supervision Supervision is a function of controlling the subordinates to ensure that work is being done in accordance with the instructions issued. Supervision is only an element of direction function. Supervision is important at the operative level because the activities of workers must be guided and controlled continuously.
You might also like
- Syllabus BACC 8.2Document12 pagesSyllabus BACC 8.2ROMEO DE GUZMAN, JR.100% (1)
- Product Quality Basic ConceptsDocument8 pagesProduct Quality Basic ConceptsHuynhGiangNo ratings yet
- Organizational Development Syllabus at University of LuzonDocument4 pagesOrganizational Development Syllabus at University of Luzontheaa banezNo ratings yet
- Non-Teaching Personnel The Personnel Program Performance EvalDocument45 pagesNon-Teaching Personnel The Personnel Program Performance EvalJoyce Ann RamirezNo ratings yet
- TQM Employee Involvement GuideDocument33 pagesTQM Employee Involvement GuideAli RazaNo ratings yet
- Main Components: Quality Planning, Quality Assurance, QualityDocument6 pagesMain Components: Quality Planning, Quality Assurance, QualityJen gemudianoNo ratings yet
- SQE Vs SQADocument4 pagesSQE Vs SQAEric Fabián Faúndez RubioNo ratings yet
- SMU Mb0049 FullDocument8 pagesSMU Mb0049 FullJimmy JackNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of PerformanceDocument26 pagesA Comparative Study of PerformanceAvijit HiraNo ratings yet
- 2021 PHC - Field Officers Manual - Final - 15.04.2021Document323 pages2021 PHC - Field Officers Manual - Final - 15.04.2021Enoch FavouredNo ratings yet
- 2017 GAD Plans and BudgetDocument4 pages2017 GAD Plans and BudgetQueenie Alicaba BelonioNo ratings yet
- Rights of Teachers and Students Under Philippine Education LawsDocument4 pagesRights of Teachers and Students Under Philippine Education LawsCharles AugustusNo ratings yet
- MINDANAO STATE UNIVERSITY GRADUATE SCHOOL MANAGEMENT CONCEPTSDocument129 pagesMINDANAO STATE UNIVERSITY GRADUATE SCHOOL MANAGEMENT CONCEPTSAnnie Masakal100% (1)
- Recruitment and SelectionDocument26 pagesRecruitment and SelectionnirakhanNo ratings yet
- Org Change and Devt 2Document14 pagesOrg Change and Devt 2Joseph De Vera Ora'aNo ratings yet
- Bpo2 - Module 5Document32 pagesBpo2 - Module 5JeffreyAgdolNo ratings yet
- Unit I SPPMDocument115 pagesUnit I SPPMVenkata Pandu Ranga PrasadNo ratings yet
- Strategic HRM FunctionsDocument26 pagesStrategic HRM FunctionsAasma AasmaNo ratings yet
- Implementing Performance Appraisal Process, Performance Revview Discussion ChangesDocument18 pagesImplementing Performance Appraisal Process, Performance Revview Discussion ChangesamritaNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary: Types of Performance AppraisalDocument21 pagesExecutive Summary: Types of Performance Appraisalumer100% (1)
- Supplier Partnership (Lc-06)Document34 pagesSupplier Partnership (Lc-06)Farhan SaleemNo ratings yet
- Internal Control ElementsDocument19 pagesInternal Control ElementsDayanara VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Controlling (Principles of Management)Document17 pagesControlling (Principles of Management)kiedd_04100% (1)
- The Functions of Human Resources DepartmentDocument14 pagesThe Functions of Human Resources DepartmentGrandpaGyu InSpiRiTNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: Birat Shrestha/ Resta JhaDocument32 pagesStrategic Management: Birat Shrestha/ Resta JhaKhanal NilambarNo ratings yet
- Pay Equity: Internal and External ConsiderationsDocument9 pagesPay Equity: Internal and External ConsiderationsOnline AccessNo ratings yet
- Performance Management and AppraisalDocument29 pagesPerformance Management and AppraisalMoiz AdnanNo ratings yet
- Performance PlanningDocument21 pagesPerformance PlanningJizzle JeennyNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Study OverviewDocument4 pagesFeasibility Study OverviewMrittika MahbubNo ratings yet
- HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT AT NAUBAHAR BOTTLING COMPANYDocument58 pagesHUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT AT NAUBAHAR BOTTLING COMPANYZeeshan GillNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Report on Training & Development at Merino Panel ProductsDocument77 pagesSummer Training Report on Training & Development at Merino Panel ProductsuccvandanaNo ratings yet
- Source and Evaluation of Risks: Learning OutcomesDocument34 pagesSource and Evaluation of Risks: Learning OutcomesNATURE123No ratings yet
- SPMS GuideDocument24 pagesSPMS GuideVidez NdosNo ratings yet
- TQM Performance MeasuresDocument15 pagesTQM Performance MeasuresHaziiMughal100% (1)
- Monitoring and ControllingDocument5 pagesMonitoring and ControllingMohit MalikNo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal Policy and ProcedureDocument6 pagesPerformance Appraisal Policy and ProcedureAndrey MilerNo ratings yet
- MB13204 HRM NotesDocument84 pagesMB13204 HRM NotesAnand RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Knowledge Area 1: Project Integration ManagementDocument27 pagesChapter 4 - Knowledge Area 1: Project Integration ManagementcaprisunNo ratings yet
- How to Write Effective Quality ObjectivesDocument51 pagesHow to Write Effective Quality Objectivesdonhan91No ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Performance ManagementDocument22 pagesUnit 1 - Performance ManagementHarini SNo ratings yet
- Performance DocumentDocument71 pagesPerformance DocumentArun KumarNo ratings yet
- BAICS CommunicationsDocument4 pagesBAICS CommunicationsDenmark CostanillaNo ratings yet
- MoneyDocument16 pagesMoneyNighat SaeedNo ratings yet
- Gad'S Justice: Lead, Empower, and Achieve Through Data-Driven DecisionsDocument45 pagesGad'S Justice: Lead, Empower, and Achieve Through Data-Driven DecisionsANNA MARIE LARGADAS MALULANNo ratings yet
- H601 Compensation Management Performance AppraisalDocument42 pagesH601 Compensation Management Performance AppraisalTamim HossainNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit Manual NewDocument26 pagesInternal Audit Manual NewhtakrouriNo ratings yet
- FeasibilityDocument51 pagesFeasibilityRamon C Sager LptNo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal System: Human Resource ManagementDocument22 pagesPerformance Appraisal System: Human Resource Managementdivya_manchandaNo ratings yet
- International Performance ManagementDocument54 pagesInternational Performance ManagementDhanis Ishwar100% (1)
- Succession Planning: Jonathan P. Ruff, P.E. Environmental Manager City of Plattsburgh, NYDocument64 pagesSuccession Planning: Jonathan P. Ruff, P.E. Environmental Manager City of Plattsburgh, NYBelNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Program Development and Evaluation ChapterDocument41 pagesAn Overview of Program Development and Evaluation ChapterMSWDONo ratings yet
- Regular Board Meeting Agenda Package - June 18, 2019 - 1Document42 pagesRegular Board Meeting Agenda Package - June 18, 2019 - 1Jess PetersNo ratings yet
- Project MGMTDocument102 pagesProject MGMTNikhil KhobragadeNo ratings yet
- Project IdentificationDocument89 pagesProject Identificationtadgash4920100% (3)
- Human Resource Development in Dessie WaterDocument61 pagesHuman Resource Development in Dessie Waterkassahun meseleNo ratings yet
- Methods, Process and Practices of Management AuditDocument48 pagesMethods, Process and Practices of Management AuditSana RubabNo ratings yet
- QA Interview Q & ADocument18 pagesQA Interview Q & AMohd RaqeebuddinNo ratings yet
- StaffingDocument11 pagesStaffingHimanshu PatelNo ratings yet
- STAFFINGDocument14 pagesSTAFFINGHimanshu DarganNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 HRM MsDocument23 pagesUnit-3 HRM Msvits20731a3139No ratings yet
- MMDocument2 pagesMMAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Security and Security Market OperationsDocument303 pagesSecurity and Security Market OperationsAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Meaning of LeverageDocument5 pagesMeaning of LeverageAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- PlanningDocument53 pagesPlanningAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Recent Trends in Financial InnovationDocument5 pagesRecent Trends in Financial InnovationAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Risk and UncertainityDocument2 pagesRisk and UncertainityAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Working CapitalDocument15 pagesWorking CapitalAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Job DesignDocument3 pagesJob DesignAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Capital StructureDocument4 pagesCapital StructureAdeem Ashrafi100% (2)
- Capital StructureDocument4 pagesCapital StructureAdeem Ashrafi100% (2)
- Financial Policy and Strategic PlanningDocument294 pagesFinancial Policy and Strategic PlanningAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Meaning of StaffingDocument11 pagesMeaning of StaffingAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Working CapitalDocument15 pagesWorking CapitalAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Barriers To EntrepreneurshipDocument2 pagesBarriers To Entrepreneurshipanas_786No ratings yet
- The Universal BankingDocument5 pagesThe Universal BankingAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Risk and UncertainityDocument7 pagesRisk and UncertainityAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial ProcessDocument2 pagesEntrepreneurial ProcessAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Institutional Support For SSIDocument3 pagesInstitutional Support For SSIAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Hawthorne ExperimentDocument4 pagesHawthorne ExperimentAdeem Ashrafi100% (1)
- Dividend DecisionDocument4 pagesDividend DecisionAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Family VentureDocument5 pagesFamily VentureAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Types of Business Entities in IndiaDocument5 pagesTypes of Business Entities in IndiaAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Institutional Support For New VenturesDocument8 pagesInstitutional Support For New VenturesAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- DEPARTMENTATIONDocument1 pageDEPARTMENTATIONAdeem Ashrafi100% (1)
- Operations Managemen1Document1 pageOperations Managemen1Adeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Choosing Your Business Organizational StructureDocument3 pagesChoosing Your Business Organizational StructureAdeem Ashrafi100% (1)
- DEPARTMENTATIONDocument1 pageDEPARTMENTATIONAdeem Ashrafi100% (1)
- TechnicallyDocument5 pagesTechnicallyAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- BusinessesDocument4 pagesBusinessesAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Interpret Electrical Signs & SymbolsDocument2 pagesInterpret Electrical Signs & Symbolsnoy83% (6)
- Domain 1 ReflectionDocument6 pagesDomain 1 Reflectionapi-281499206No ratings yet
- Testing and Assessing Final Presentation PDFDocument46 pagesTesting and Assessing Final Presentation PDFRahhal Ajbilou0% (1)
- TPR Asher PDFDocument67 pagesTPR Asher PDFjorostrNo ratings yet
- Resume - Ibrahim Moussaoui - Updated 2016Document2 pagesResume - Ibrahim Moussaoui - Updated 2016api-228674656No ratings yet
- Xavier Alumni Times - August 2013Document28 pagesXavier Alumni Times - August 2013Martin GomezNo ratings yet
- MODULE ZERO Rzl110Document7 pagesMODULE ZERO Rzl110Jazztine Andrei GecoleaNo ratings yet
- Module (Group 5)Document24 pagesModule (Group 5)LeighNo ratings yet
- CAES9540 17-18 Unit 01Document14 pagesCAES9540 17-18 Unit 01Chungyin YuNo ratings yet
- Cb-Past Form 1: Appendix A Cb-Past Form 1 Competency-Based Performance: Appraisal System For Teachers (CB-PAST)Document7 pagesCb-Past Form 1: Appendix A Cb-Past Form 1 Competency-Based Performance: Appraisal System For Teachers (CB-PAST)Carmelagrace De Luna BagtasNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument51 pagesNarrative ReportDizabelle Anteojo Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Organogram of Pakistan Railways.: Federal MinisterDocument26 pagesOrganogram of Pakistan Railways.: Federal MinisterFarrukhupalNo ratings yet
- 2013 Church Business PlanDocument72 pages2013 Church Business PlanNenad MarjanovicNo ratings yet
- PortfolioDocument35 pagesPortfolioKa Yan Anita HessNo ratings yet
- Onyeji Thecla Onyemauche: Personal InformationDocument2 pagesOnyeji Thecla Onyemauche: Personal Informationonyeji theclaNo ratings yet
- INFJ CareerDocument2 pagesINFJ Careervaruntyagi100% (1)
- Teacher Training Needs Assessment in ICTDocument1 pageTeacher Training Needs Assessment in ICTNieves SantosNo ratings yet
- Developmental Screening Using The: Philippine Early Childhood Development ChecklistDocument30 pagesDevelopmental Screening Using The: Philippine Early Childhood Development ChecklistGene BonBonNo ratings yet
- Let's move on to the next section. Our time is best spent practicing conversational skillsDocument418 pagesLet's move on to the next section. Our time is best spent practicing conversational skillspasinNo ratings yet
- What Does The Lateralization of The Brain Imply About Language Learning?Document6 pagesWhat Does The Lateralization of The Brain Imply About Language Learning?Rhedamei PalmesNo ratings yet
- Childselfdescription - SDQ I MarshDocument7 pagesChildselfdescription - SDQ I MarshwinazhonniwaNo ratings yet
- Single Subject Credential Program EDSC Lesson Plan Template: Precious Daileg, Estefani Bautista, Brit Brown BiologyDocument7 pagesSingle Subject Credential Program EDSC Lesson Plan Template: Precious Daileg, Estefani Bautista, Brit Brown Biologyapi-257666656No ratings yet
- Assessment LearningDocument1 pageAssessment LearningmilkoviciusNo ratings yet
- MG330-Engineering Management Final VersionDocument3 pagesMG330-Engineering Management Final VersionShadan ArshadNo ratings yet
- 345 8773 PDFDocument6 pages345 8773 PDFRiya RajNo ratings yet
- Philosophy and Art at Bard CollegeDocument388 pagesPhilosophy and Art at Bard CollegeTaku Mark MagondeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Cordova VidalDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 Cordova Vidalapi-257908691No ratings yet
- Week 9Document3 pagesWeek 9Kristell PungtilanNo ratings yet
- Future Career ExplorationDocument5 pagesFuture Career ExplorationAmin MofrehNo ratings yet
- CBT Procedures ManualDocument20 pagesCBT Procedures ManualEdgar G. Dela Rosa88% (8)