Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SKEMA Biologi
Uploaded by
Loong Wai FamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SKEMA Biologi
Uploaded by
Loong Wai FamCopyright:
Available Formats
Section A 1. A 2. D 3. C 4. B 5. B 6. A 7. A 8. C 9. C 10. D 11. B 12. D 13. B 14. C 15.
Section B Question 16 (a) (i) A mitochondrion and B nucleus (ii) increased surface area Increase cell respiration/enzymes (b) 1 1 1
plasmid/capsule/70S ribosomes/smaller ribosomes/complex cell wall/mesosome/no nucleus 1 use of differential centrifugation 1 First spin at low speed to remove cell wall material/cell debris 1 supernatant re-spun at higher speed / until pellet with chloroplasts is found1 Total 7
(c)
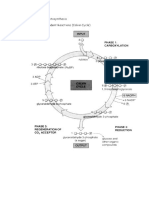
Question 17 (a) (i) X glycolysis Y Krebs / citric acid, cycle (ii) cytoplasm / ground cytoplasm / cytosol (b) removal of hydrogen (ions) from, pyruvate / pyruvic acid to acceptor / to coenzyme 1 1 1
(c) (d)
removal of carbon dioxide / carboxyl group (i) inner membrane of mitochondrion
1 1
(ii) ETC stops/transfer of electrons down the chain stops 1 No (release of) energy, to phosphorylate ADP/stops phosphorylation 1 Krebs cycle stops, no (oxidised) NAD/FAD/oxidised coenzymes 1 Max 2 Total 8
Section C Question 18 (a) 1 cellulose structural compound 2 made of -glucose chain 3 unbranched chains 4 run parallel to each other 5 have cross-linkage of hydrogen 6 that gives stability and strength 7 insoluble 8 fibers laid in layers in different directions adding further strength Max 5 1 starch-storage compound 2 made of -glucose 3 mixture of amylase and amylopectin 4 amylase - unbranched chain forms helix structure 5 amylopectin - branched chains of a-glucose 6 compound stabilized by countless hydrogen bond 7 compact and insoluble 8 readily hydrolysed to form sugar when required Max 5 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
(b)
1 Bipolar / hydrophobic and hydrophilic molecule 1 2 forms bilayer 1 3 Hydrophobic tail repelled by water /hydrophilic head attracted by water; 1 4 Allows movement of lipid soluble / non-polar molecules / water / gases // Prevents movement of water soluble / (named) polar molecules 1 5 Allows membranes to fuse with other membranes / able to form vesicles / exocytosis and endocytosis; 1 6 Unsaturated fatty acids increase fluidity / flexibility / permeability 1 7 Allows compartmentalisation / allows cells to maintain different concentrations of molecules on either side of the membrane 1 8 label diagram 1 Max 5 Total 15
Question 19 (a) 1 graph 2 temp increase, increase in kinetic energy; 3 increase in number of collision ions 4 After optimum temperature, rate of the reaction decrease 5 Enzyme denaturation start 6 breaking of hydrogen bonds 7 permanent change in shape of tertiary structure Max 4 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
(b)
1 enzymes are globular proteins, 2 Tertiary structure 3 Enzyme molecule has an active site 4 with specific shape 5 formed by only a few amino acids 6 Active site is complementary to substrate structure 7 lock and key hypothesis - enzyme has a rigid active site 8 substrate fits exactly into the active site of the enzyme 9 induced fit hypothesis - Enzyme with a flexible active site 10 Enzyme changes shape slightly to enclose substrate in a precise fit 11 enzyme-substrate complex form 12 Diagram showing enzyme & substrate molecule, enzyme- substrate complex, enzyme & products Max 8
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
(c)
1 Enzyme immobilization - binding enzyme to solid medium/support Methods 2 Adsorption 3 Entrapment 4 Covalent coupling Max 3
1 1 1 Total 15
Question 20 (a) 1 two ring of cells 2 surrounding the vascular tissue 3 outer ring columnar mesophyll cells 4 inner ring bundle of sheath cells 5 diagram Max 3 (b) 1 no Krantz anatomy 2 open stomata during night 3 CO2 fixation take place at night 4 PEP combines with CO2 to produce OAA 5 enzyme PEP carboxylase 5. OAA is reduced to malate 6 reduction agent NADPH 7 malate is stored in vacuole of mesophyll cell 8 during the day malate splits into CO2 and pyruvate 9. concentration of CO2 increases in mesophyll cells and photorespiration is prevented 10 CO2 is fixed by RuBP in Calvin cycle 11 pyruvate is reduced to PEP Max 7 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
(c) C3 CO2 fixation - once - In one cell type First CO2 acceptor - RuBP Enzyme - Rubisco / RuBP carboxylase Product - 3C substances - 3-phosphoglycerate Location of calvin cycle mesophyll cells Photorespiration -occurs C4 Twice In two cells type PEP PEP carboxylase 4 C substances Oxaloacetate Bundle sheath cells Occur at minimum level / avoided Max 5 Total 15 mark 1/0 1/0 1/0 1/0 1/0 1/0 1/0 1/0
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
You might also like
- Biology Notes IB Free ResponseDocument26 pagesBiology Notes IB Free ResponseLarry LohNo ratings yet
- Factor Denaturing, Xylem and Pholem Structure and Paper ChromatDocument3 pagesFactor Denaturing, Xylem and Pholem Structure and Paper Chromatpc usageNo ratings yet
- STPM Trials 2009 Biology Answer Scheme (Terengganu) PDFDocument12 pagesSTPM Trials 2009 Biology Answer Scheme (Terengganu) PDFCarolineNo ratings yet
- Biology T4 2013 JWPDocument4 pagesBiology T4 2013 JWPShirmei WangNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 1 & 2 Questions 1996 To 2005 MS PDFDocument97 pagesBiology Unit 1 & 2 Questions 1996 To 2005 MS PDFLeen WaheedhNo ratings yet
- Marking Schemes For Topic 3 Stafford PapersDocument30 pagesMarking Schemes For Topic 3 Stafford Papersrifu91No ratings yet
- Answer Scheme Upp Sem 1 2020 Ssi Kulai Section A (15 Marks) : ConfidentialDocument5 pagesAnswer Scheme Upp Sem 1 2020 Ssi Kulai Section A (15 Marks) : ConfidentialJiaWenTanNo ratings yet
- Selangor AnsDocument4 pagesSelangor AnsChan Yu QianNo ratings yet
- Markscheme HL Paper2Document56 pagesMarkscheme HL Paper2George KoukouvesNo ratings yet
- GEN BIO RevsDocument7 pagesGEN BIO RevsacglianeNo ratings yet
- Answer Scheme Upp Sem 1 STPM 2021 Section A (15 Marks)Document5 pagesAnswer Scheme Upp Sem 1 STPM 2021 Section A (15 Marks)Mi MiNo ratings yet
- Modul Ka f4 2011 Combine (T)Document44 pagesModul Ka f4 2011 Combine (T)Suriati Bt A RashidNo ratings yet
- AS Bio MS Answers PDFDocument34 pagesAS Bio MS Answers PDFGame ZoneNo ratings yet
- AS Bio MS AnswersDocument32 pagesAS Bio MS AnswersryanNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Basis of LifeDocument13 pagesThe Chemical Basis of Lifezulfikarleghari100% (1)
- Cell Respiration ReviewerDocument6 pagesCell Respiration ReviewerEllemer Rose CastañaresNo ratings yet
- OxygenDocument8 pagesOxygenblack00swanNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme (Kedah)Document15 pagesMarking Scheme (Kedah)Rozaini OthmanNo ratings yet
- Week 3 AnswersDocument8 pagesWeek 3 AnswersBenjamin SamaniNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 2Document3 pagesLab Exercise 2Patricia Andrea Alexei FernandezNo ratings yet
- Revision Chapter 6 Photosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)Document6 pagesRevision Chapter 6 Photosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)MOHAMAD SAHIMI BIN MAHAT MoeNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Cell Transport Ans PDFDocument23 pages3.2 Cell Transport Ans PDFtess_15No ratings yet
- Enrichment Activity in BiologyDocument4 pagesEnrichment Activity in BiologyMizzi Nicole Mortel TiuNo ratings yet
- Quizlet Nmat Sample TermsDocument12 pagesQuizlet Nmat Sample TermsPrincesza AngelesNo ratings yet
- Bchem ReviewDocument37 pagesBchem ReviewJennyNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - Topic 8Document57 pagesQuestion Bank - Topic 8Muliasena NormadianNo ratings yet
- Biology Revision 2017Document62 pagesBiology Revision 2017Katherine O'Neill-RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Biology Life On Earth 11Th Edition Audesirk Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument38 pagesBiology Life On Earth 11Th Edition Audesirk Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFodetteisoldedfe100% (15)
- Outline The Thermal, Cohesive and Solvent Properties of Water. 5 MarksDocument8 pagesOutline The Thermal, Cohesive and Solvent Properties of Water. 5 MarksneaNo ratings yet
- Krebs (Citric Acid) Cycle Steps by Steps ExplanatDocument2 pagesKrebs (Citric Acid) Cycle Steps by Steps ExplanatDesiree Marila Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- NAME: PDG: : AnswersDocument16 pagesNAME: PDG: : AnswersPollyNo ratings yet
- Marking Schemes For Topic 1,2 Stafford PapersDocument57 pagesMarking Schemes For Topic 1,2 Stafford PapersSuha AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 WorksheetDocument2 pagesTutorial 3 WorksheetnonosimapsNo ratings yet
- Þ CC) C' (CC& +C++C: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCDocument12 pagesÞ CC) C' (CC& +C++C: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCgauravNo ratings yet
- 2014PPTBIOT4JWPDocument5 pages2014PPTBIOT4JWPShirmei WangNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper - 4 - Essays - MSDocument141 pagesBiology Paper - 4 - Essays - MSVivian BakerNo ratings yet
- Ap Biology PracticeDocument4 pagesAp Biology PracticeHarun KianiNo ratings yet
- Topic 3Document12 pagesTopic 3Ria AccadNo ratings yet
- Science 9 q1w7Document9 pagesScience 9 q1w7seanfelix07102009No ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Second QTR Module RevisedDocument37 pagesGen Bio 1 Second QTR Module RevisedMichaela CasabaNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Kertas 2 Bio JulaiDocument8 pagesJawapan Kertas 2 Bio Julaizulhariszan abd mananNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Module 1 General Biology 1 SCDocument31 pagesQuarter 2 Module 1 General Biology 1 SCAldrin James DafunNo ratings yet
- Week 7 ScienceDocument4 pagesWeek 7 ScienceKaru GreyNo ratings yet
- 1-Proteins: CH 24 Chemistry of LifeDocument6 pages1-Proteins: CH 24 Chemistry of LifeXIBG21SANIANo ratings yet
- Bioilogy 5 - Marking SchemeDocument21 pagesBioilogy 5 - Marking Schemeclaytondc64No ratings yet
- 2 BGU Pre-AP Biology & Environmental Science CELL RESPIRATION ASSIGNMENTDocument1 page2 BGU Pre-AP Biology & Environmental Science CELL RESPIRATION ASSIGNMENTJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- NScELEC3 WEEK 14 LESSONDocument6 pagesNScELEC3 WEEK 14 LESSONAlyssa Jane AbellonNo ratings yet
- Chapter10 - Membrane Structure - 092408Document64 pagesChapter10 - Membrane Structure - 092408marsagcuaNo ratings yet
- Krebs Cycle: TCA/ Citric Acid CycleDocument24 pagesKrebs Cycle: TCA/ Citric Acid Cyclejahanzeb aliNo ratings yet
- Enzymes ReceptorsDocument2 pagesEnzymes ReceptorsDrew DiosoNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Unit 5: Respiration, Internal Environment, Coordination and Gene TechnologyDocument138 pagesUnit 5: Unit 5: Respiration, Internal Environment, Coordination and Gene TechnologyMovie FlexNo ratings yet
- Exercises Bio f4 c3Document7 pagesExercises Bio f4 c3Azlin ShahNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Summary Notes As BiologyDocument22 pagesUnit 1 Summary Notes As Biologyeyheth50% (2)
- General Biology 1 Quarter 2 Week 6 Answer Sheet: EvaluateDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Quarter 2 Week 6 Answer Sheet: EvaluateSamantha MedranoNo ratings yet
- 9700 s11 QP 11Document16 pages9700 s11 QP 11Faizan SaeedNo ratings yet
- AP M10 Ch9 Respiration Worksheet2Document5 pagesAP M10 Ch9 Respiration Worksheet2Jakie Ubina0% (1)
- Self-Assembly: From Surfactants to NanoparticlesFrom EverandSelf-Assembly: From Surfactants to NanoparticlesRamanathan NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Transition Metal Catalyzed Furans Synthesis: Transition Metal Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesFrom EverandTransition Metal Catalyzed Furans Synthesis: Transition Metal Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal Eps: Instruksi: Hitunglah Earnings Per Share PT. XABIRU!Document3 pagesLatihan Soal Eps: Instruksi: Hitunglah Earnings Per Share PT. XABIRU!Ruth AngeliaNo ratings yet
- Fireman's Fund Insurance Company v. Joseph J. Biafore, Inc., 526 F.2d 170, 3rd Cir. (1975)Document11 pagesFireman's Fund Insurance Company v. Joseph J. Biafore, Inc., 526 F.2d 170, 3rd Cir. (1975)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Agenda: Shoreline City Council Special Workshop Dinner MeetingDocument13 pagesAgenda: Shoreline City Council Special Workshop Dinner MeetingNeal McNamaraNo ratings yet
- "Cannot Be Determined" Isn't The Answer For Any of The QuestionsDocument7 pages"Cannot Be Determined" Isn't The Answer For Any of The QuestionsVirgileOrsotNo ratings yet
- Notes On P-Block ElementsDocument14 pagesNotes On P-Block ElementscurioeNo ratings yet
- Structure of Dna: Components of Nucleic AcidsDocument4 pagesStructure of Dna: Components of Nucleic AcidsVignesh Reddy100% (1)
- 2016 Specimen Paper 4 Mark SchemeDocument6 pages2016 Specimen Paper 4 Mark SchemelolismNo ratings yet
- C1Document19 pagesC1Analys JulianNo ratings yet
- Matriculation Chemistry ThermochemistryDocument54 pagesMatriculation Chemistry ThermochemistryzeemboyzNo ratings yet
- 2010 Nyjc CH h2 p1 Promo SolnDocument17 pages2010 Nyjc CH h2 p1 Promo SolndreamydamselNo ratings yet
- What Are Preliminaries and How To Evaluate ThemDocument11 pagesWhat Are Preliminaries and How To Evaluate Themplanning5No ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Fin622 Short NoteDocument29 pagesCorporate Finance Fin622 Short Notezahidwahla133% (3)
- A NuDocument7 pagesA NuAnusha RamanNo ratings yet
- Leverage Buyout and Junk KbondsDocument31 pagesLeverage Buyout and Junk KbondsChetan VenuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Structure and BondingDocument47 pagesChapter 1 Structure and BondingIzzatiSimaaNo ratings yet
- Inter HWKDocument5 pagesInter HWKMohammed Elias AlamNo ratings yet
- MATH3075 3975 Course Notes 2012Document104 pagesMATH3075 3975 Course Notes 2012ttdbaoNo ratings yet
- Final Exam1-Afternoon SessionDocument40 pagesFinal Exam1-Afternoon SessionJoshua Wright0% (1)
- Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument13 pagesAromatic HydrocarbonsCCNo ratings yet
- Chromium ComplexesDocument3 pagesChromium ComplexesNitty MeYa100% (1)
- The American IllusionDocument11 pagesThe American Illusionsabiont100% (3)
- FNCE2000 Chapter6 Valuing Shares & Bonds QuestionsDocument3 pagesFNCE2000 Chapter6 Valuing Shares & Bonds QuestionsJaydenaus0% (1)
- MFE8812 Seminar Slide 05A (2pg) PDFDocument19 pagesMFE8812 Seminar Slide 05A (2pg) PDFOmkar ChogaleNo ratings yet
- 6-FFGasal1617 YustinaDocument33 pages6-FFGasal1617 YustinasanNo ratings yet
- Sifat-Sifat PolimerDocument185 pagesSifat-Sifat Polimerrifkyrivatra100% (1)
- Experiment 9Document3 pagesExperiment 9cherokeeNo ratings yet
- 2 Water The Solvent For Biochemical ReactionsDocument68 pages2 Water The Solvent For Biochemical ReactionsSiej Go100% (1)
- Chapter 12Document64 pagesChapter 12kgeorges27No ratings yet
- VBTDocument4 pagesVBTJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis & Interpretation 23Document23 pagesData Analysis & Interpretation 23kaushalNo ratings yet