Professional Documents
Culture Documents
T3 Bab 2
Uploaded by
Mohd ZaidiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
T3 Bab 2
Uploaded by
Mohd ZaidiCopyright:
Available Formats
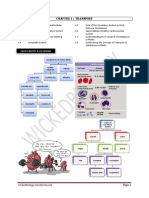
Blood circulation and transportation 1 A B C D 2 Which of the following blood groups is the universal recipient?
Blood group A Blood group B Blood group AB Blood group O (PMR 2004) The table shows two components of blood X and Y. Component Function X Acts as a solvent for digested food Y Helps in blood clotting What are components X and Y? A B C D 3 X Platelets White blood cells Plasma Red blood cells Y Red blood cells Plasma Platelets White blood cells (PMR 2005) The following information shows steps taken during the process of dialysis. L The waste product diffuses out from the blood through pores in the tube M The blood from the artery flows through the tubes which are immersed in salt solution. N The filtered blood flows into the veins of the blood circulation of the patient. Which of the following is the correct sequence for the process of dialysis? A B C D L M N M M L M N N N L L (PMR 2006)
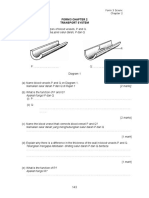
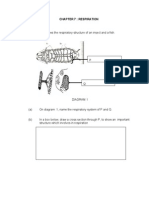
Diagram 18 shows a cross-section of a heart .
Diagram 18 P and Q are blood vessels in the heart. Which of the following is true about P and Q? A B C D p Aorta which carries deoxygenated blood Vena cava which carries deoxygenated blood Pulmonary artery which carries oxygenated blood Pulmonary vein which carries oxygenated blood Q Pulmonary artery which carries oxygenated Pulmonary vein which carries oxygenated blood Aorta which carries deoxygenated blood Vena cava which carries deoxygenated blood (PMR 2006)
Table 4 shows the blood groups of four students. Student R S T U Blood group A B AB O
Student X with blood group O needs a blood transfusion. Which of the following students can donate to student X? A B C D U only S and T only S,T and U only R, S, T and U (PMR 2006)
6.
Diagram 16 shows the blood circulatory system in the body.
Diagram 16 Which of the following statements is true about oxygenated and deoxygenated blood? A B C D 7. Deoxygenated blood flows from the heart to all parts of the body Oxygenated blood flows from the lungs to the heart and to all parts of the body Oxygenated blood flows from the heart to the lungs and to all parts of the body Deoxygenated blood flows from the lungs to the heart and to all parts of the body (PMR 2007) Diagram 16 shows a cross section of a monocotyledon stem with vascular bundles.
Diagram 16 What is the function of X? A B C D Transport water only Transport water and minerals Transport minerals only Transport glucose (PMR 2008)
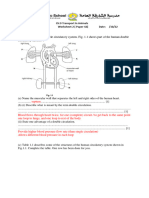
Figure 1 shows the blood circulatory system of a human. ( PMR 2004)
Figure 1 (a) Label one of the following blood circulations in Figure 1. (1 mark)
Systemic Circulation,
Pulmonary Circulation
(b)
The pulmonary vein transports oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart while the aorta transports oxygenated blood from the heart to all parts of the body except the lungs.
In Figure 1, ( i ) Label the position of the lungs and a ventricle. ( ii ) Mark using arrow, (2 marks)
, to show the flow of oxygenated blood. (1 mark)
(c) Figure 2 shows the cross section of blood vessels P and Q.
Thick wall
Thin wall
Figure 2
Explain why there is a difference in the cross section of blood vessels P and Q. . (1 mark) (d) The rate of a students heart beat increases after a vigorous exercise. Explain why. .. .. (1 mark) 2 . a) Diagram 8.1 shows two plants, P and Q (PMR 2008)
Diagram 8.1 P is watered but Q is not watered State one inference about the plants. (1 mark)
b) Diagram 8.2 shows three apparatus set up to study the factors that affect the rate of transpiration. The apparatus was left for three hours in three conditions, J, K, and L.
Diagram 8.2
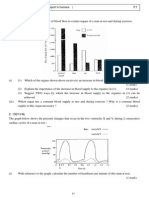
Table 8.3 shows the positions of the air bubbles in J and K. Condition J K L Position of the air bubble/cm 6.6 7.8
Table 8.3 Based on the Diagram 8.2 and Table 8.3: i) ii) Record the position of the air bubble in L in Table 8.3 (1 mark)
Use the graph provided to answer this part of the question. Based on the readings in Table 8.3, draw a bar chart to show the positions of the air bubble in the three condition (2 mark)
iii)
Based on the bar chart drawn in 8 (b) (ii), state the relationship
between the positions of the air bubbles and the conditions. (1 mark) iv) State the manipulated variables involved in this experiment. (1 mark) v) State what happens to the position of the air bubbles readings when the apparatus in K is left for more than three hours. (1 mark) . vi) Table 8.4 below shows the positions of the air bubble under a moving fan of different speeds in one hour. Speed of fan 1 2 3 4 Table 8.4 a) Predict the position of the air bubble if the speed of the fan is 4. Write the prediction in table 8.4 (1 mark) b) State one hypothesis relating the speed of the fan and the position of the air bubble. (1 mark) vii) Define operationally the rate of transpiration (1 mark) Position of air bubble/cm 6.6 6.8 7.0
Blood circulation
PAPER 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. D C B B A B B
PAPER 2 1) a. Lungs
Pulmonary circulation Ventricle
Systemic circulation
b. i) and ii) refer 4a. c) Rate of blood flow is rapid and irregular at high pressure d) The blood carries more oxygen
2. a) Plant Q has wilted because it is not watered and Plant P is turgid because it was watered. b) i) 5.4
ii)
iii) The air bubble is iv) Condition of the apparatus v) The position of the air bubble will continue moving towards left. vi) a) 7.2
b) The higher the speed of fan the further the position of the air bubble. vii) The rate of transpiration increases as the speed of moving air increase.
You might also like
- Blood Circulation and TransportationDocument11 pagesBlood Circulation and TransportationDinesh CidocNo ratings yet
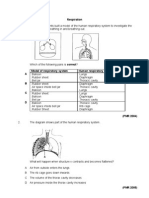
- Exercise - 6 Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesExercise - 6 Respiratory SystemTravel UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory Systems ChapterDocument7 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory Systems ChapterDarren Ng100% (2)
- Form 3 Chapter 2Document9 pagesForm 3 Chapter 2Mariana AhmadNo ratings yet
- CH 9, 10 - Questions - TRANSPORT IN ANIMALS, DISEASES AND IMMUNITYDocument22 pagesCH 9, 10 - Questions - TRANSPORT IN ANIMALS, DISEASES AND IMMUNITYPranitha RaviNo ratings yet
- Hkcee Biology - 4.6 Transport in Humans - P.1Document13 pagesHkcee Biology - 4.6 Transport in Humans - P.1irisyyy27No ratings yet
- This Question Paper Consists of 3 Sections and Answer All QuestionsDocument12 pagesThis Question Paper Consists of 3 Sections and Answer All QuestionsKhusyairy Daeng Sailendra0% (1)
- Latihan Cuti Sekolah PMR t3Document7 pagesLatihan Cuti Sekolah PMR t3sheh8758No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Blood Circulation & TransportDocument2 pagesChapter 2: Blood Circulation & TransportintanNo ratings yet
- Questions Class 10 - Science CBSEDocument9 pagesQuestions Class 10 - Science CBSEViolet TsirblouNo ratings yet
- T3 Bab 1Document8 pagesT3 Bab 1myraeNo ratings yet
- CirculationDocument10 pagesCirculationMohd Azrul DsevenNo ratings yet
- Bio Revision Exercise - Answer KeyDocument11 pagesBio Revision Exercise - Answer Keynmhk89100% (1)
- Heart Structure and Cardiac Cycle Questions: Bournemouth School 1Document9 pagesHeart Structure and Cardiac Cycle Questions: Bournemouth School 1Shermer100% (1)
- Perfect Score Module WebsitesDocument106 pagesPerfect Score Module Websites林雯No ratings yet
- 4th Term - G8 Daily Test (Biology) - MSDocument17 pages4th Term - G8 Daily Test (Biology) - MSMatthew EdbertNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument19 pagesBIOLOGYAnum ObaidNo ratings yet
- Transport of Substances in Humans (LQ)Document13 pagesTransport of Substances in Humans (LQ)Wan Ching ChanNo ratings yet
- 05 Circulatory System-1Document6 pages05 Circulatory System-1dysonjonas269No ratings yet
- Answer All Questions.: Sains Pt3 Tingkatan 3 Set 1Document9 pagesAnswer All Questions.: Sains Pt3 Tingkatan 3 Set 1Wan NazrinaNo ratings yet
- Soalan Sains PMRDocument121 pagesSoalan Sains PMRFazil Jay100% (2)
- Exercise PDFDocument12 pagesExercise PDFAmsyidi Asmida100% (1)
- Biology 2Document15 pagesBiology 2PHANG QI ZHI MoeNo ratings yet
- Modul DC Emer LangDocument13 pagesModul DC Emer LangNorshamsiah SamsudinNo ratings yet
- Term Test 2Document12 pagesTerm Test 2languagetuitionlabzNo ratings yet
- WBI IAL - Unit 1 RevisionDocument18 pagesWBI IAL - Unit 1 RevisionFathimathshaahaNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 8 Exercise 4Document3 pagesBiology Chapter 8 Exercise 4QueeineNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions PT 2 XI BIODocument6 pagesPractice Questions PT 2 XI BIOpratyushpradhan929No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BIO-F5Document9 pagesChapter 1 BIO-F5adele30No ratings yet
- Edexcel GCSE: Physical EducationDocument6 pagesEdexcel GCSE: Physical Educationmuchamad mahmudiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 F4Document5 pagesChapter 7 F4riyashreeNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 Cardiovascular RDocument31 pagesBio 11 Cardiovascular Rjhilmilkhan100% (1)
- Test 1 Biology F4Document12 pagesTest 1 Biology F4Nurfatin JamaludinNo ratings yet
- WS On Circulatory System PDFDocument5 pagesWS On Circulatory System PDFthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Biology Predictions Part 7Document58 pagesBiology Predictions Part 7hp 7junNo ratings yet
- Past Paper: Biomedical Admissions Test 4500/02Document20 pagesPast Paper: Biomedical Admissions Test 4500/02hirajavaid246No ratings yet
- New PaperDocument12 pagesNew PaperkajuNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange WorksheetDocument2 pagesGas Exchange Worksheetnoddy_noddy100% (1)
- CH 9 Transport in Animals Worksheet 2 Answer KeyDocument8 pagesCH 9 Transport in Animals Worksheet 2 Answer KeyMohamed AlyNo ratings yet
- Breathing Classwork SheetDocument4 pagesBreathing Classwork Sheetshimaa youssifNo ratings yet
- SMK Datuk Menteri. Science Paper Monthly Test February 1 HourDocument11 pagesSMK Datuk Menteri. Science Paper Monthly Test February 1 HourWinnie WenNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Chapter 1 QuestionsDocument11 pagesForm 3 Chapter 1 QuestionsCheah Foo Kit50% (2)
- תרגול עצבים לב ונשימהDocument15 pagesתרגול עצבים לב ונשימהdodbenNo ratings yet
- Hoppensteadt and Peskin - Chapter 1 - Student VersionDocument30 pagesHoppensteadt and Peskin - Chapter 1 - Student VersionchristiansassoNo ratings yet
- Trend (K7) :: Able To State The Pattern of Change in The DataDocument14 pagesTrend (K7) :: Able To State The Pattern of Change in The Dataalyn_haslinda8035No ratings yet
- Blood Circulation and TransportDocument15 pagesBlood Circulation and TransportSENSNo ratings yet
- Combined Past Paper Questions On Excretion and HomeostasisDocument76 pagesCombined Past Paper Questions On Excretion and HomeostasisRamesh Iyer81% (26)
- Biomed Part-B QuestionsDocument4 pagesBiomed Part-B QuestionsNirmal KumarNo ratings yet
- Neet Iv-Test Body Fluids and CirculationDocument8 pagesNeet Iv-Test Body Fluids and CirculationYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Bio Medical ModerateDocument5 pagesBio Medical ModerateRohit BhamuNo ratings yet
- Latih Tubi T1Document17 pagesLatih Tubi T1nurlisa2010No ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Transport In HumansFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Transport In HumansNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 MCQ IG BioDocument19 pagesChapter 9 MCQ IG BioAdanam käûñg khåṇṭ kÿāw šwãrNo ratings yet
- Practice Worksheet-1Document6 pagesPractice Worksheet-1Maryam KhanNo ratings yet
- DPP_BPT - Body Fluids and CirculationDocument2 pagesDPP_BPT - Body Fluids and CirculationDr-Atin Kumar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Ujian Penilaian 1 Biologi Ting. 4 2013 1 Jam Jawab Semua Soalan / Answer All QuestionsDocument5 pagesUjian Penilaian 1 Biologi Ting. 4 2013 1 Jam Jawab Semua Soalan / Answer All QuestionsHayatiArshadNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In HumanFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In HumanNo ratings yet
- Surgical Critical Care and Emergency Surgery: Clinical Questions and AnswersFrom EverandSurgical Critical Care and Emergency Surgery: Clinical Questions and AnswersForrest "Dell" MooreNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Tahunan Sciencef3-2011Document2 pagesRancangan Tahunan Sciencef3-2011Cikgu SamsidarNo ratings yet
- Nota Ringkas Tip Exam Sains Cgu ZaidiDocument12 pagesNota Ringkas Tip Exam Sains Cgu Zaidiman leeNo ratings yet
- T3 Bab 1Document8 pagesT3 Bab 1myraeNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Chapter 1 - Respiration (Notes)Document4 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 1 - Respiration (Notes)Autumn JJ40% (5)