Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 6 Basic Statistics Definitions
Uploaded by
Asghar AliOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 6 Basic Statistics Definitions
Uploaded by
Asghar AliCopyright:
Available Formats
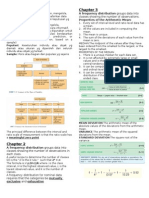
Unit # 6 Basic Statistics Definitions
1. Frequency Distribution:
A frequency distribution is a tabular arrangement for classifying data into different groups and the number of observations falling in each group corresponds to the respective group.
2. Discrete Frequency Distribution:
A frequency distribution formed by a set of values which are of discrete in nature is called a discrete frequency distribution.
3. Continuous Frequency Distribution:
Continuous frequency distribution is an arrangement of the values , that one or more variables take in a sample. It can assume an infinite number of values within a specific range.
4. Class Limits:
The minimum and the maximum values defined for a class or group are called class limits.
5. Lower Class Limit:
The minimum value of a class is called lower class limit.
6. Upper Class Limit:
The maximum value of a class is called upper class limit.
7. Class Boundaries:
The real class limits of a class are called class boundaries. A class boundary is obtained by adding two successive class limits and dividing the sum by 2.
8. Mid-Point or Class - Mark:
For a given class the average of that class obtained by dividing the sum of upper and lower class limits by 2, is called Mid- Point or class mark. Mudassar Nazar Notes Published by Asghar Ali Page 1
9. Size of Class Interval:
The difference between the upper class boundary and the lower class boundary of a class is called the size of class interval.
10. Cumulative Frequency:
The cumulative frequency is the number of observations less than or equal to a value of the variable.
11. Histogram:
A histogram is a graph of adjacent rectangles constructed on XY- plane. Or A histogram is a vertical bar chart in which the rectangular bars are constructed at the boundaries of each class.
12. Frequency Polygon:
Frequency polygon is a graph of the frequency distribution in which the frequencies are plotted against the mid point of the classes. The plotted points are joined together to get the frequency polygon.
13.Cumulative Frequency Polygon Or Ogive:
In cumulative frequency polygon, the cumulative frequencies are plotted against the upper class boundaries. The word ogive polygon is also used for cumulative frequency polygon.
14.Cumulative frequency Distribution:
A table showing cumulative frequencies against upper class boundaries is called a cumulative frequency distribution. It is also called a less than cumulative frequency distribution.
15.Average or Central Value:
An average or a central value is a specific value of the variable around which the majority of the observations tend to concentrate.
Mudassar Nazar Notes Published by Asghar Ali
Page 2
16.Measures of Central Tendency:
The measures or techniques that are used to determine the central value are called measures of central tendency.
17.Arithmetic Mean:
Arithmetic mean ( or simply mean) is obtained by dividing the sum of all the values of the variable by their number of observations. It is denoted by .
18.Median:
Median is the middle most observation in an arranged data set. It divides the data set into two equal parts. It is denoted by .
19.Mode:
Mode is the most frequent occurring observation in the data. It is the observation that occurs maximum number of times in the given data.
20.Geometric Mean:
Geometric mean of a variable X is the nth positive root of the product of the x1, x2, x3, ., xn observations.
21.Harmonic Mean:
Harmonic mean refers to the value obtained by reciprocating the mean of the reciprocal of the x1, x2, x3, ., xn observations.
22.Properties of Arithmetic Mean:
1. 2. 3. 4. Mean of a variable with similar observations say constant K is the constant K itself. Mean is affected by changing origin. Mean is affected by change in scale. Sum of the deviations of the variable X from its mean is always zero. Page 3
Mudassar Nazar Notes Published by Asghar Ali
23.The Weighted Arithmetic Mean:
When numbers x1, x2, x3, ., xn are not equally important , we associate them with certain weight w1, w2, , wn depending on the importance and significance. It is called the weighted arithmetic mean.
24.Moving Averages:
Moving averages are defined as the successive averages ( arithmetic means ) which are computed for a sequence of days/ months/ years at a time.
25.Measures of Dispersion:
The measures that are used to determine the degree or extent of variation in a data set are called measures of dispersion.
26.Range:
Range measures the extent of variation between two extreme observations of a data set. Range = Xm - Xo.
27.Variance:
Variance is defined as the mean of the squared deviations of observations from their arithmetic mean. It is denoted by S2.
28.Standard Deviation:
Standard deviation is defined as the positive square root of mean of the squared deviation of observations from their arithmetic mean. It is denoted by S.
29.Data:
The numerical figures obtained from any field of study are known as data.
30.Ungrouped Data:
Numerical facts which are obtained on the first hand and recorded as they stand are known as ungrouped data.
31.Grouped Data:
When the data have gone through some statistical process, classified into certain groups or into rows and columns, it is called grouped data.
Mudassar Nazar Notes Published by Asghar Ali
Page 4
You might also like
- How To Organize DataDocument4 pagesHow To Organize DataMichael YuNo ratings yet
- Collection of Data Part 2 Edited MLISDocument45 pagesCollection of Data Part 2 Edited MLISWhieslyn ColeNo ratings yet
- Wikimama Class 11 CH 15 StatisticsDocument8 pagesWikimama Class 11 CH 15 StatisticsWikimamaNo ratings yet
- Stat Review 2020Document5 pagesStat Review 2020Ruby Ann BaniquedNo ratings yet
- Introduction BS FinalDocument54 pagesIntroduction BS FinalsathravguptaNo ratings yet
- ChandruDocument27 pagesChandruSidhant BhayanaNo ratings yet
- Statistik Mid Rumus1Document5 pagesStatistik Mid Rumus1PurnawanJogjaNo ratings yet
- Stat 106Document26 pagesStat 106Bashar Al-Hamaideh100% (1)
- MATH 6200 Lesson 2 PDFDocument31 pagesMATH 6200 Lesson 2 PDFAldrien S. AllanigueNo ratings yet
- STAT DefinitionsDocument11 pagesSTAT DefinitionsChoodi 200No ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument6 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyCarlo YambaoNo ratings yet
- Research 3: Inferential StatisticsDocument39 pagesResearch 3: Inferential StatisticsHanna nicole JapsayNo ratings yet
- StatDocument44 pagesStatLoreth Aurea OjastroNo ratings yet
- MPC Measures of Central TendencyDocument24 pagesMPC Measures of Central TendencyPaul Carlo GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Module-1 2Document32 pagesModule-1 2Ctrl-Alt-DelNo ratings yet
- Statistics: An SEO-Optimized TitleDocument5 pagesStatistics: An SEO-Optimized TitleVenkataraghavanNo ratings yet
- First Stage: Lecture ThreeDocument14 pagesFirst Stage: Lecture Three翻訳すると、40秒後に死にますOMGITZTWINZNo ratings yet
- Research II Q4 Measures of VariabilityDocument54 pagesResearch II Q4 Measures of Variabilityhrhe heheNo ratings yet
- STA301 Statistics and Probability FAQS AND GLOSSARYDocument33 pagesSTA301 Statistics and Probability FAQS AND GLOSSARYzeeshanbhutta005No ratings yet
- Statistics Review NotesDocument23 pagesStatistics Review NotesMarjun CaguayNo ratings yet
- DADT Report Raw InfoDocument4 pagesDADT Report Raw InfoSwayamNo ratings yet
- Engineering StatisticsDocument10 pagesEngineering StatisticsAhmed SuhailNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation On: "FrequencyDocument36 pagesPowerpoint Presentation On: "Frequencyasaduzzaman asad100% (1)
- Chapter - 14 StatisticsDocument33 pagesChapter - 14 StatisticsYash GoyalNo ratings yet
- Bio Statistics 3Document13 pagesBio Statistics 3Moos LightNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Business Statistics & AnalyticsDocument25 pagesUnit 1 - Business Statistics & Analyticsk89794No ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Mode, MedianDocument30 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency: Mean, Mode, Medianafnan nabiNo ratings yet
- Stats 3Document12 pagesStats 3Marianne Christie RagayNo ratings yet
- Measure of Central Tendency in StatisticsDocument16 pagesMeasure of Central Tendency in StatisticsAnshu SinghNo ratings yet
- MAPC006Document12 pagesMAPC0068158Anshika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Course Code & Number:FET201Document70 pagesCourse Code & Number:FET201Humam Al-DhubhaniNo ratings yet
- Dispersion 1Document32 pagesDispersion 1Karishma ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Probability and StatisticsDocument42 pagesEngineering Probability and StatisticsKevin RamosNo ratings yet
- STA301StatisticsandProbabilityGlossaryBywww Virtualians PK PDFDocument16 pagesSTA301StatisticsandProbabilityGlossaryBywww Virtualians PK PDFBeeBa GujjarNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics 140127003954 Phpapp02Document47 pagesBiostatistics 140127003954 Phpapp02Nitya KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Central Tendency With Partition 16.03.2024Document25 pagesCentral Tendency With Partition 16.03.2024Spider ManNo ratings yet
- Frequency Distribution Graphs & TablesDocument24 pagesFrequency Distribution Graphs & Tablessterling goinNo ratings yet
- Data ManagementDocument48 pagesData ManagementRikki MaeNo ratings yet
- Statistics Chapter IV ReviewDocument3 pagesStatistics Chapter IV ReviewShaira May RitualNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency ExplainedDocument39 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency ExplainedVirencarpediemNo ratings yet
- Prelim Lec 2017Document49 pagesPrelim Lec 2017Marc AlamoNo ratings yet
- 1 Unnamed 04 01 2024Document66 pages1 Unnamed 04 01 2024vanchagargNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in StatisticsDocument40 pagesBasic Concepts in StatisticsJeffrey CabarrubiasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 PDFDocument49 pagesLecture 1 PDFPorkkodi Sugumaran0% (1)
- ShapesDocument36 pagesShapesaue.ponytoyNo ratings yet
- Statistics Chapter-IIDocument66 pagesStatistics Chapter-IIMiley GirmayNo ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument12 pagesDescriptive StatisticsAndrew MwingaNo ratings yet
- Terminologies: Classification of DataDocument6 pagesTerminologies: Classification of Datavraj mishraNo ratings yet
- Basic Statistical TermsDocument27 pagesBasic Statistical TermsPaul MorakinyoNo ratings yet
- Statistical Tools for Cost EngineeringDocument16 pagesStatistical Tools for Cost EngineeringAhmed AbdulshafiNo ratings yet
- PGDISM Assignments 05 06Document12 pagesPGDISM Assignments 05 06ashishNo ratings yet
- Stats week 1 key termsDocument6 pagesStats week 1 key termsAnonymous n0S2m9sR1ENo ratings yet
- Contents UNIT 42Document21 pagesContents UNIT 42zainabasim2003No ratings yet
- Ecs NotesDocument10 pagesEcs Notes55389740No ratings yet
- PPT6 Descriptive StatisticsDocument37 pagesPPT6 Descriptive StatisticsMary De CastroNo ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument7 pagesDescriptive StatisticsShane LiwagNo ratings yet
- Learn Statistics Fast: A Simplified Detailed Version for StudentsFrom EverandLearn Statistics Fast: A Simplified Detailed Version for StudentsNo ratings yet
- Maths McqsDocument14 pagesMaths McqsAsghar AliNo ratings yet
- Matric Result Boys WingDocument2 pagesMatric Result Boys WingAsghar AliNo ratings yet
- Physics 10Document57 pagesPhysics 10Asghar AliNo ratings yet
- 8th Class Islamiat Model Paper Objective PartDocument5 pages8th Class Islamiat Model Paper Objective PartAsghar Ali33% (3)
- The City Grammar Schools, Faisalabad.: 1st Test Timings:8:15am To 9:30am 2nd Test Timings:10:00am To 11:15amDocument3 pagesThe City Grammar Schools, Faisalabad.: 1st Test Timings:8:15am To 9:30am 2nd Test Timings:10:00am To 11:15amAsghar AliNo ratings yet
- Unit# 4 Algebraic Expressions and Algebraic Formulas DefinitionsDocument3 pagesUnit# 4 Algebraic Expressions and Algebraic Formulas DefinitionsAsghar AliNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument3 pagesDefinitionsAsghar AliNo ratings yet
- Matric Boys' Wing Result 2014-16Document2 pagesMatric Boys' Wing Result 2014-16Asghar AliNo ratings yet
- The City Grammar Schools, Faisalabad.: 1st Test Timings: 8:15am To 9:30am 2nd Test Timings: 10:00am To 11:15amDocument3 pagesThe City Grammar Schools, Faisalabad.: 1st Test Timings: 8:15am To 9:30am 2nd Test Timings: 10:00am To 11:15amAsghar AliNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument2 pagesDefinitionsAsghar AliNo ratings yet
- Model Paper Urdu 8th Class 2015 Objective PartDocument4 pagesModel Paper Urdu 8th Class 2015 Objective PartAsghar AliNo ratings yet
- Model Paper Urdu 8th Class 2015 Subjective PartDocument3 pagesModel Paper Urdu 8th Class 2015 Subjective PartAsghar AliNo ratings yet
- Unit # 2 Theory of Quadratic EquationsDocument36 pagesUnit # 2 Theory of Quadratic EquationsAsghar Ali83% (6)
- Model Paper of Math Class 10thDocument4 pagesModel Paper of Math Class 10thMuhammad UsamaNo ratings yet
- Unit#1 Matrice and Derterminants (Exercise 1.6)Document13 pagesUnit#1 Matrice and Derterminants (Exercise 1.6)Asghar Ali94% (17)
- Unit # 2 Theory of Quadratic EquationsDocument36 pagesUnit # 2 Theory of Quadratic EquationsAsghar Ali83% (6)
- Unit # 2 Theory of Quadratic EquationsDocument36 pagesUnit # 2 Theory of Quadratic EquationsAsghar Ali83% (6)
- Unit#1 Matrice and Derterminants (Exercise 1.6)Document13 pagesUnit#1 Matrice and Derterminants (Exercise 1.6)Asghar Ali94% (17)
- Unit# 3 Variations DefinitionsDocument4 pagesUnit# 3 Variations DefinitionsAsghar AliNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Unit 2Document6 pagesDefinitions of Unit 2Asghar AliNo ratings yet
- Unit# 5 Factorization Exercise # 5.4Document11 pagesUnit# 5 Factorization Exercise # 5.4Asghar AliNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Unit 2Document10 pagesDefinitions of Unit 2Asghar AliNo ratings yet
- Unit# 5 Factorization Reveiw Exercise 5Document4 pagesUnit# 5 Factorization Reveiw Exercise 5Asghar AliNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Unit 2Document10 pagesDefinitions of Unit 2Asghar AliNo ratings yet
- Unit# 5 Factorization Exercise # 5.2Document5 pagesUnit# 5 Factorization Exercise # 5.2Asghar AliNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Exercise # 3: Question # 2Document5 pagesMiscellaneous Exercise # 3: Question # 2Asghar AliNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Unit 2Document10 pagesDefinitions of Unit 2Asghar AliNo ratings yet
- Unit# 4 Algebraic Expressions and Algebraic Formulas Exercise 4.1Document17 pagesUnit# 4 Algebraic Expressions and Algebraic Formulas Exercise 4.1Asghar AliNo ratings yet
- Unit# 3 Variations Exercise# 3.3Document2 pagesUnit# 3 Variations Exercise# 3.3Asghar AliNo ratings yet
- Unit# 3 Variations Exercise# 3.2Document3 pagesUnit# 3 Variations Exercise# 3.2Asghar AliNo ratings yet
- We Don't Eat Our: ClassmatesDocument35 pagesWe Don't Eat Our: ClassmatesChelle Denise Gumban Huyaban85% (20)
- Prayer BuddyDocument42 pagesPrayer BuddyJoribelle AranteNo ratings yet
- Why Narcissists Need You To Feel Bad About Yourself - Psychology TodayDocument51 pagesWhy Narcissists Need You To Feel Bad About Yourself - Psychology Todaytigerlo75No ratings yet
- Elementary Hebrew Gram 00 GreeDocument216 pagesElementary Hebrew Gram 00 GreeRobert CampoNo ratings yet
- Ariel StoryDocument2 pagesAriel StoryKKN Pasusukan2018No ratings yet
- S The Big Five Personality TestDocument4 pagesS The Big Five Personality TestXiaomi MIX 3No ratings yet
- A Study On Inventory Management Towards Organizational Performance of Manufacturing Company in MelakaDocument12 pagesA Study On Inventory Management Towards Organizational Performance of Manufacturing Company in MelakaOsama MazharNo ratings yet
- Handout of English For PsychologyDocument75 pagesHandout of English For PsychologyRivan Dwi AriantoNo ratings yet
- Leading a Community Through Integrity and CourageDocument2 pagesLeading a Community Through Integrity and CourageGretchen VenturaNo ratings yet
- Bhaktisiddhanta Appearance DayDocument5 pagesBhaktisiddhanta Appearance DaySanjeev NambalateNo ratings yet
- ADSL Line Driver Design Guide, Part 2Document10 pagesADSL Line Driver Design Guide, Part 2domingohNo ratings yet
- 6 - English-How I Taught My Grandmother To Read and Grammar-Notes&VLDocument11 pages6 - English-How I Taught My Grandmother To Read and Grammar-Notes&VLManav100% (2)
- BUMANGLAG - CLASS D - JEL PlanDocument3 pagesBUMANGLAG - CLASS D - JEL PlanMAUREEN BUMANGLAGNo ratings yet
- Progress Test 5 (Units 13-15) : Complete All Seven Sections. There Are Seventy Marks in TotalDocument7 pagesProgress Test 5 (Units 13-15) : Complete All Seven Sections. There Are Seventy Marks in TotalIlia GviniashviliNo ratings yet
- Neandertal Birth Canal Shape and The Evo PDFDocument6 pagesNeandertal Birth Canal Shape and The Evo PDFashkenadaharsaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15 (91 Slides)Document91 pagesLecture 15 (91 Slides)Hasnain GoharNo ratings yet
- 1022-Article Text-2961-1-10-20200120Document10 pages1022-Article Text-2961-1-10-20200120Zuber RokhmanNo ratings yet
- Lived Experiences of Elementary Teachers in A Remote School in Samar, PhilippinesDocument14 pagesLived Experiences of Elementary Teachers in A Remote School in Samar, Philippinesルイス ジャンNo ratings yet
- Comparative Ethnographies: State and Its MarginsDocument31 pagesComparative Ethnographies: State and Its MarginsJuan ManuelNo ratings yet
- H-1 Nationalism in Europe NotesDocument5 pagesH-1 Nationalism in Europe Noteskanishk kumarNo ratings yet
- Corporation Law Quiz AnswersDocument3 pagesCorporation Law Quiz AnswerswivadaNo ratings yet
- Code of Conduct GuidanceDocument17 pagesCode of Conduct GuidanceMuhammad RidwanNo ratings yet
- Performance AppraisalsDocument73 pagesPerformance AppraisalsSaif HassanNo ratings yet
- General Ledger Journal Import ProcessDocument13 pagesGeneral Ledger Journal Import ProcessMadhavi SinghNo ratings yet
- Vinzenz Hediger, Patrick Vonderau - Films That Work - Industrial Film and The Productivity of Media (Film Culture in Transition) (2009)Document496 pagesVinzenz Hediger, Patrick Vonderau - Films That Work - Industrial Film and The Productivity of Media (Film Culture in Transition) (2009)Arlindo Rebechi JuniorNo ratings yet
- Table Topics Contest Toastmaster ScriptDocument4 pagesTable Topics Contest Toastmaster ScriptchloephuahNo ratings yet
- (Cambridge Series in Statistical and Probabilistic Mathematics) Gerhard Tutz, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität Munchen - Regression For Categorical Data-Cambridge University Press (2012)Document574 pages(Cambridge Series in Statistical and Probabilistic Mathematics) Gerhard Tutz, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität Munchen - Regression For Categorical Data-Cambridge University Press (2012)shu100% (2)
- EY The Cfo Perspective at A Glance Profit or LoseDocument2 pagesEY The Cfo Perspective at A Glance Profit or LoseAayushi AroraNo ratings yet
- Adjustment DisordersDocument2 pagesAdjustment DisordersIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet