Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aerospace Competency Model - Word
Uploaded by
Ramona PaulaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aerospace Competency Model - Word
Uploaded by
Ramona PaulaCopyright:
Available Formats
/w EPDw ULLTExN
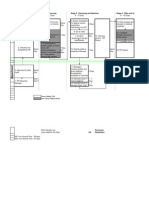
Aerospace Competency Model Tier Name 1 Personal Effectiveness Interpersonal Skills Initiative Reading Engineering & Technology Tier Block Integrity Professionalism
F O U Academic N 2 Competencies D A T I O Workplace N 3 Competencies
Dependability & Reliability Lifelong Learning Writing CommunicationListening & Speaking Planning & Organizing Checking, Examining, & Recording Mathematics Critical & Analytical Thinking Innovation and Invention Science Basic Computer Skills Problem Solving & Decision Making
Teamwork Working with Tools and Technology
Business Fundamentals
I IndustryN Wide D 4 Technical U Competencies S T R Y
Aerospace Fundamentals Project Management & Quality Assurance
Design & Development Aviation Maintenance
Product & Parts Manufacturing Environmental, Safety & Health
Tier Name Tier 1 -Personal Effectiveness Competencies
Block Information Interpersonal Skills: Displaying skills to work with others from diverse backgrounds. Interact appropriately and respectfully with supervisors and coworkers Respect the opinions, perspectives, customs, and individual differences of others Use appropriate strategies and solutions for dealing with conflicts and differences to maintain a smooth workflow Integrity: Displaying accepted social and work behaviors. Accept responsibility for one's decisions and actions Comply with ethical standards for your field
Take responsibility for accomplishing work goals within accepted timeframes Treat others with honesty, fairness, and respect Professionalism: Maintaining a professional demeanor at work. Accept criticism and attempt to learn from mistakes Demonstrate positive attitude towards work Demonstrate self-control by maintaining composure and dealing calmly with stressful situations Dress appropriately for occupation and maintain appropriate personal hygiene Refrain from substance abuse Initiative: Demonstrating a willingness to work. Establish and maintain personally challenging, but realistic work goals Persist at a task despite interruptions, obstacles, or setbacks Pursue work with energy, drive, and effort to accomplish tasks Strive to exceed standards and expectations Take initiative in seeking out new responsibilities and work challenges Dependability & Reliability: Displaying responsible behaviors at work. Behave consistently, predictably, and reliably Comply with organizational rules, policies, and procedures Follow written and verbal directions Fulfill obligations, complete assignments, and meet deadlines Lifelong Learning: Displaying a willingness to learn and apply new knowledge and skills. Broaden knowledge and skills through science fairs, reading publications, job shadowing, and continuing education Demonstrate an interest in personal and professional lifelong learning and development Seek feedback, and modify behavior for improvement Take charge of personal career development by identifying personal interests and career pathways Treat unexpected circumstances as opportunities to learn and adopt new techniques Use newly learned knowledge and skills to complete specific tasks Tier 2 Academic Competencies Reading: Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in workrelated documents. Identify relevant details, facts, specifications, and main ideas Infer or locate meaning of unknown or technical vocabulary Locate, understand, and interpret written technical and non-technical information in documents such as manuals, regulations, procedures,
reports, memos, graphs, charts, tables, schedules, and signs Understand the essential message and purpose of written materials Writing: Using standard English to compile information and prepare written reports. Communicate thoughts, ideas, information, and messages, which may contain technical material, in a logical, organized, and coherent manner Create documents such as letters, directions, manuals, reports, graphs, and flow charts Use correct English spelling, grammar, and punctuation to produce logical and accurate written correspondence, instructions, and documentation Write words, numbers, sentences, reports, and data using technical terminology and notations Mathematics: Using principles of mathematics such as algebra, geometry, and trigonometry to solve problems. Know and apply mathematical principles: Number Systems and Relationships - whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and percentages Number Operations, Computation and Estimation - addition, subtraction, multiplication and division Measurement and Estimation - measurement of time, temperature, distances, length, width, height, perimeter, area, volume, weight, velocity, and speed. Conversion from one measurement to another (e.g., from English to metric) Mathematical Notation - the language of mathematics to express mathematical ideas Mathematical Reasoning and Problem Solving - inductive and deductive reasoning, conjectures, arguments, strategies, and interpretation of results Statistics and Data Analysis - collection, reporting and analysis of data Probability and Predictions - calculating probability to make predictions Algebra and Functions - equations, patterns, and functions Geometry - shapes and using geometric principles to solve problems Trigonometry - triangles and trigonometric functions Calculus - concepts of exponential, logarithmic and trigonometric functions, vectors, complex numbers, conic sections, and analytic geometry Science: Using scientific rules and methods to solve problems. Conduct scientific investigations Describe, explain, predict scientific phenomena
Identify relevant chemical, mechanical, biological, electrical, and physical properties of materials Interpret scientific evidence and draw conclusions Know and apply scientific principles: Scientific Inquiry - Scientific Method (identify problems, collect information, form opinions, draw conclusions) and apply basic scientific research Physical Science (Chemistry and Physics) - properties of matter, structure of atoms, energy, motion and forces Earth and Space Science - origin and evolution of the universe and earth systems, geology, meteorology, astronomy, hydrology, and oceanography Understand the scientific method (identify problems, collect information, form opinions, draw conclusions) and apply basic scientific research Engineering & Technology: Knowledge of the practical application of engineering science and technology. This includes applying principles, techniques, procedures, and equipment to the design and production of various goods and services. Design Attributes of design Artificial intelligence and design Computerized standard test and test bench development Instrumentation Testing models Modeling, control, and tele-operation (operation at a distance) Scientific visualization and animation techniques Automation/robotics Engineering Functions Determine appropriate uses of technology Design, analyze, and construct objects or processes for practical purposes Use mathematics to solve practical work-related problems Use engineering principles for project analysis, design, testing, implementation Use basic design techniques, tools, and principles to produce precision technical plans, blueprints, drawings, and models Formulate mathematical models or other methods of computer analysis to develop, evaluate, or modify design Design, operate, and maintain technological systems and equipment Conduct troubleshooting, research and development, invention and innovation, and experimentation in problem-solving Understand basic principles of circuit boards, processors, chips, electronic equipment, and computer hardware and software
Know and apply engineering principles to material selection and processing method alternatives Communication-Listening & Speaking: Giving full attention to what others are saying and speaking in English well enough to be understood by others. Listening Receive, attend to, interpret, understand, and respond to verbal messages and other cues Apply active listening skills using reflection, restatement, questioning, and clarification Understand and interpret verbal and non-verbal communication Pick out important information in verbal messages Understand complex instructions Speaking/Presenting Speak clearly and confidently using common English conventions including proper grammar, tone, and pace Express information to individuals or groups taking into account the audience and the nature of the information (e.g., explain technical concepts to non-technical audiences) Understand and use non-verbal communication consistent with verbal communication Present ideas in a persuasive manner Critical & Analytical Thinking: Using logic, reasoning, and analysis to address problems. Analyze and break down complex systems into their component parts Draw conclusions from relevant or missing information Explain the relationship and interdependency of the part and the system Organize problems into manageable parts Understand the underlying relationship among facts and connections between issues Use inductive and deductive reasoning to analyze, synthesize, compare, and interpret information Basic Computer Skills: Using a computer and related applications to input and retrieve information. Applications Use word processing programs to compose, organize, and edit simple documents and other business communications Use electronic mail to communicate and Internet applications to search for information Use spreadsheet, database, and presentation software Enter data and type materials quickly and accurately and Double check work carefully and identify/correct typographical errors
Manage file storage: use functions to store, retrieve, and sort detailed records Basic Computer Knowledge Understand and efficiently use basic computer hardware (e.g. PCs, printers) and software (e.g. word processing software, spreadsheet software) to perform tasks Understand common computer terminology (e.g., program, operating system) and is familiar with the fundamental capabilities of computers Tier 3 Workplace Competencies Teamwork: Working cooperatively with others to complete work assignments. Accept membership in and identify with the goals of a team Be open to considering new ways of doing things and the merits of new approaches to work Collaborate with others to formulate team objectives and develop consensus for best outcome Give and receive feedback constructively Identify roles of team members and effectively communicate with all members of the team Use teamwork skills to achieve goals, solve problems, and manage conflict Work effectively with multi-disciplinary teams Planning & Organizing: Planning and prioritizing work to manage time effectively and accomplish assigned tasks. Adaptability/Flexibility Change gears in response to unpredictable or unexpected events, pressures, situations, and job demands Effectively change plans, goals, actions, or priorities to deal with changing situations Planning & Organizing Approach work in a methodical manner Apply effective organizational skills Develop and implement a plan for a project Keep track of details to ensure work is performed accurately and completely Find new ways of organizing or planning work to accomplish tasks more efficiently Time Management Develop a timeline for sequencing the activities of a project Establish specific goals to accomplish work in a timely manner Prioritize various competing tasks and perform them efficiently according to their urgency
Ensure that others receive needed materials in time Stay on schedule Keep all parties informed of progress and all relevant changes to project timelines Innovation and Invention: Formulating new ideas for and applications of processes and products. Creative Thinking Employ unique analyses and generate new, innovative ideas in complex areas Reframe problems in a different light to find fresh approaches Entertain wide-ranging possibilities to develop unique approaches and useful solutions Understand the pieces of a system as a whole and possess a big picture view of the situation Integrate seemingly unrelated information to develop creative solutions Develop innovative methods of obtaining or using resources when insufficient resources are available Identify Opportunities Identify needs, wants, and problems as they are changing Seek out opportunities to develop and offer new products and services Seek out opportunities to improve, streamline, reinvent work processes Methods for the Creation and Improvement of Products and Processes Understand and apply lean six sigma methods for creation and/or improvement of products/processes Define problems that affect customer value and impact company financially Select and apply appropriate quantitative and qualitative techniques in applications in aerospace Research and Development Analyze the failure of other projects as research for a possible new venture Conduct experiment and application Identify design trends Design a system, product, or service Technology Transfer Identify scientific research which has potential commercial value Analyze the consequences of societal or technological change Develop practical applications for the results of scientific research Apply newly created technology to new, innovative, productive uses Problem Solving & Decision Making: Applying knowledge of STEM
principles to solve problems by generating, evaluating, and implementing solutions. Choose and Implement a Solution Decisively choose the best solution after contemplating available approaches to the problem Consider the technical and cultural (and other non-technical) factors in the decision process Commit to a solution in a timely manner Use strategies, tools, resources, and equipment to implement the solution Observe and evaluate the outcomes of implementing the solution to assess the need for alternative approaches and to identify lessons learned Generate Alternatives Generate a variety of approaches to the problem Think creatively to develop new ideas for and answers to work related problems Use logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions, or approaches to problems Identify criteria and constraints Apply concepts of probability to help make decisions Identify the Problem Anticipate or recognize the existence of a problem Identify the nature of the problem by analyzing its component parts and defining critical issues Identify, obtain, and review information relevant to the problem Working with Tools and Technology: Selecting, using, and maintaining tools and technology to facilitate work activity. Keeping Current Demonstrate an interest in learning about new and emerging tools and technologies Identify sources of information concerning state-of-the-art tools, equipment, materials, technologies and methodologies Seek out opportunities to improve knowledge of tools and technologies that may assist in streamlining work and improving productivity Maintenance Perform routine maintenance on tools, technology, and equipment Determine causes of operating errors and decide what to do about it Troubleshoot maintenance problems in accordance with established procedures Selection & Application Identify, select, and apply tools or technological solutions appropriate
to the task at hand (e.g., use statistical tools to show reliability of data, use probes and sensors to collect data) Identify potential hazards related to the use of tools and equipment Operate tools and equipment in accordance with established operating procedures and safety standards Use information technology and computer applications as it supports the gathering, storage, manipulation, and transfer of data and information Checking, Examining, & Recording: Entering, transcribing, recording, storing, or maintaining information in written or electronic/magnetic format. Apply techniques for observing and gathering data Complete required maintenance forms, records, and inspection reports Detect and correct errors or inconsistencies, even under time pressure Organize records and files to maintain data Record data with the correct number of significant figures Business Fundamentals: Knowledge of basic business principles, trends, and economics. Business Ethics Demonstrate knowledge of the similarities among and differences between ethics, law, morals, and etiquette Act in the best interest of the company, the community, and the environment Comply with applicable laws and rules governing work and report loss, waste, or theft of company property to appropriate personnel Legal/Financial Maintain privacy and confidentiality of company information, as well as that of customers and co-workers Comply with intellectual property laws Protect trade secrets Situational Awareness Understand trends in the industry and the company's position in the market Recognize one's role in the functioning of the company and understand the potential impact one's own performance can have on the success of the organization Stay current on organizational strategies to maintain competitiveness Sustainability Practice sustainability by using processes that are non-polluting; conserve energy and natural resources; are economically sound; and safe for employees, communities, and consumers
Explain how sustainable practices contribute to economic growth, social objectives, and environmental stewardship Tier 4 Technical Competencies Aerospace Fundamentals: Knowledge of the aerospace industry and its principles, its key sectors, and relevant laws and regulations. Technical Content Areas
Aerospace Sectors Product and Parts Manufacturing Engineering Services Testing Laboratories Space Research and Technology National Defense Customer Service/Support Technical Support/Field Service
Areas of Specialization Avionics Aerodynamics Aeronautics Celestial Mechanics Propulsion Thermodynamics Quality Assurance Training Industry Standards and Certifications Critical Work Functions
Develop understanding of security clearance process and requirements Explain the properties and applications of materials frequently used in the aerospace industry Identify key differences and similarities among aerospace industry sectors
Laws & Regulations Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) maintenance specifications
American Transport Association (ATA) codes Minimum Equipment Lists Federal Acquisition Regulations (FARs) Code of Federal Regulations (CFRs) Airworthiness Directives Advisory Circulars National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) International Air Transport Association (IATA) Import/Export Requirements
Learn and apply appropriate aerospace terminology Locate and comply with relevant local, state, federal, and international laws and regulations that impact the industry
Materials Application Metals Plastics/Polymers Composites Ceramics Fluids
Obtain required security clearance, if necessary Review procedures to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements Understand the requirements for certification in aerospace fields Design & Development: Application of engineering and mathematical principles to design aerospace components. Analyze the impact of engineering from multiple perspectives, such as economic, ethical, health and safety Be familiar with type design certification requirements; designing to comply with applicable aeronautical regulatory agencies (FAA, EASA, etc.)
Conduct tests to determine whether equipment, software, or procedures are operating as expected Demonstrate knowledge of product lifecycle models and acquisition models Develop design criteria for aeronautical or aerospace products or systems, including testing methods, production costs, quality standards, and completion dates Develop new technologies for use in aviation, defense systems, and space exploration, often specializing in areas such as structural design, guidance, navigation and control, instrumentation and communication, or production methods Develop prototypes of aerospace components Technical Content Areas
Engineering & Design Systems Engineering Electrical Engineering Structural Engineering Mechanical Engineering Optical Engineering Chemical Engineering Software Engineering Launch Systems Engineering
Evaluate and improve the producibility, reliability, safety, and maintainability of alternate product and process designs Evaluate product data and design from inspections and reports for conformance to design criteria, engineering principles, customer requirements, safety, and quality standards Formulate conceptual design of aeronautical or aerospace products or systems Know and apply new product and process development methods Plan and conduct experimental, environmental, operational, and stress tests on models and prototypes of aircraft and aerospace systems and equipment
Tools and Technology Computer-aided design (CAD) software Robotics Lasers Advanced electronic optics Mathematical models Analytical or scientific software Compliance software Development environment software Data base user interface and query software Graphics or photo imaging software Industrial control software Communications systems Drafting and design Desktop publishing Electronics communication Graphic communications Multimedia technology Networking systems
Product & Parts Manufacturing: Assembly, installation, inspection, and repair of aerospace components. Critical Work Functions
Carry out procedures for producing, assembling, and installing aerospace components Technical Content Areas
Industrial Planning Shop floor control models Manufacturing resource planning Change management Improvement methods Bills of Materials Safety principles Schematic drawings, diagrams, blueprints, specifications, work orders, and reports Aircraft, missiles, or space vehicles component manufacturing Aerospace engines, propulsion units, auxiliary equipment or parts
Aircraft conversion (i.e., major modifications to systems) Complete aircraft or propulsion system overhaul and rebuilding Non-destructive testing methods
Interpret schematic drawings, diagrams, blueprints, specifications, work orders, and reports in order to determine materials requirements and assembly instructions Manage raw materials/consumables Operate and control production/lab equipment
Production, Assembly, and Installation Aerospace component assembly procedures Laser materials processing Friction stir processing High speed machining Abrasive slurry cutting Composites manufacturing Electronics material processing Joining, welding, and assembly processes
Use state-of-the-art tools and assembly techniques to create and assemble aerospace products and parts Project Management & Quality Assurance: Management of projects to ensure products and processes meet quality system requirements as defined by the industry and customer specifications. Analyze project requests and proposals and engineering data to determine feasibility, producibility, cost, safety, and production time of aerospace or aeronautical product Technical Content Areas
Continuous Improvement Benchmarking and best practice Business process reengineering
Data analysis Performance improvement strategies Systems analysis
Correct the product and process to meet quality standards Employ audits and inspections to maintain the quality and continuous improvement process Meet and maintain certification requirements Monitor production for product and process quality, cost and schedule Prepare and submit budget estimates and progress and cost tracking reports Prepare contracts and negotiate revisions, changes and additions to contractual agreements
Project Management and Execution Strategic planning/global competitiveness Project management tools and techniques (e.g. Deming Cycle) Product lifecycle management (PLM) software Lean manufacturing/Six Sigma Contract management Procurement cycle Supply chain logistics Material and resource management Organizational design and management Operations research, analysis, and forecasting Personnel management methods Labor relations Accounting/finance/economics Social responsibility
Quality Management Quality requirements and inspection methods Internal and external auditing procedures International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 9000 Supplier and sub-tier quality assurance relationships First article inspections Warehousing requirements to support lot traceability
Review and approve purchase orders Schedule the project in logical steps and budget time required to meet deadlines Support and maintain quality systems Use quality and continuous improvement processes to improve safety, quality, cost and schedule performance Aviation Maintenance: Inspection, servicing, and repair aircraft components and systems. Technical Content Areas
Airframe Structures, Systems, & Components Wood structures Aircraft covering Aircraft finishes Sheet metal and non-metallic structures Aircraft landing gear systems Hydraulic and pneumatic power systems Cabin atmosphere control systems Aircraft instrument systems Communication and navigation systems Aircraft fuel systems Aircraft electrical system Position and warning systems Ice and rain control systems Fire protection systems Adhesives; substrate preparation, mixing and application, shelf-life Manufacture of composite parts Corrosion control Metal processing including welding, annealing, heat treating
Critical Work Functions
Communicate to appropriate personnel possible discrepancies and defects that could affect airworthiness of aircraft Conduct work in a safe manner Identify and select appropriate nondestructive testing methods
Identify general types of aircraft, engines, propellers, and rotors Know and apply inspection procedures involved in testing aircraft and missile systems under simulated operational conditions Perform systems readiness tests and pre- and post-operational checkouts Perform troubleshooting on faulty systems and components Plan and conduct routine maintenance checks and incorporate unscheduled, non-routine tasks
Powerplant Systems & Components Engine instrument systems Engine fire protection systems Engine electrical systems Lubrication systems Ignition and starting systems Fuel metering systems Engine fuel systems Induction and engine airflow systems Engine cooling systems Engine exhaust and reverser systems Propellers Turbine powered auxiliary power units
Recognize, detect, and classify defects using common techniques Record and interpret test data on parts, assemblies, and mechanisms to diagnose malfunctions Understand and apply improvement methods Understand and be able to use Automated and Built In Test equipment/features Understand and comply with aerospace standards and regulations Understand concepts of troubleshooting systems and components Understand operation of major aircraft/aerospace systems such as conditioned air, hydraulics, pneumatics, engines, fuel, etc Use aircraft drawings, symbols, and system schematics Write descriptions of work performed including aircraft discrepancies
and corrective actions using typical aircraft maintenance records Environmental, Safety & Health: Practices and procedures necessary to ensure a safe and healthy work environment. Achieve and maintain environmental certifications Identify unsafe conditions and take appropriate action Know and comply with federal and state laws related to emissions Observe rules and regulations to comply with personal and jobsite safety standards Operate safely on the shop and/or hangar floor Participate in safety training and emergency drills Technical Content Areas
Personal Safety Personal protective equipment Foreign Object Debris (FOD) Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) requirements Safety Management System (SMS) policies and procedures
Properly handle and dispose of hazardous materials and commercial and industrial waste according to regulations Recognize Foreign Object Debris (FOD) and mitigate FOD damage Report unsafe conditions or accidents
Waste Management Resource Conservation and Recovery Act Clean Air Act Clean Water Act Toxic Substances Control Act Material Safety Data Sheets National Emissions Standards for Aerospace Manufacturing and Rework Facilities Environmental Certifications (ISO 14000)
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Pregnancy Shopping ListDocument1 pagePregnancy Shopping ListRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- Learn Norwegian - FSI Headstart CourseDocument115 pagesLearn Norwegian - FSI Headstart Course101_languages75% (4)
- Saipem UKDocument0 pagesSaipem UKRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- PWC Change TrifectaDocument12 pagesPWC Change TrifectaRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- Faculty & Research: Working PaperDocument0 pagesFaculty & Research: Working PaperRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- PWC Driving High Performing Shared Services OutsourcingDocument0 pagesPWC Driving High Performing Shared Services OutsourcingRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- Faculty & Research: Working PaperDocument0 pagesFaculty & Research: Working PaperRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- HR TranshormationDocument20 pagesHR TranshormationRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- PWC Change TrifectaDocument12 pagesPWC Change TrifectaRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- Growth Reimagined The Talent Race UsDocument16 pagesGrowth Reimagined The Talent Race UsRamona Paula100% (1)
- US TalentEdge2020January2012Document20 pagesUS TalentEdge2020January2012Ramona PaulaNo ratings yet
- Are You Getting The Most From Your Talent PM Piece FinalDocument12 pagesAre You Getting The Most From Your Talent PM Piece FinalRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- PWC Delivering Results Through TalentDocument28 pagesPWC Delivering Results Through TalentyagayNo ratings yet
- HR Innovation Spring 2013Document34 pagesHR Innovation Spring 2013Ramona PaulaNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Model FinalDocument70 pagesAerospace Model FinalRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- PWC Nextgen Summary of FindingsDocument16 pagesPWC Nextgen Summary of FindingsRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- Updating Flexibility StrategiesDocument8 pagesUpdating Flexibility StrategiesRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- PWC Internal Change CapabilityDocument14 pagesPWC Internal Change CapabilityRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- Ibm Case StudyDocument29 pagesIbm Case StudyRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- Recruitment Lean Process FlowDocument3 pagesRecruitment Lean Process FlowRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- Ibm Case StudyDocument29 pagesIbm Case StudyRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- Faculty & Research: Working PaperDocument0 pagesFaculty & Research: Working PaperRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- US TalentEdge2020January2012Document20 pagesUS TalentEdge2020January2012Ramona PaulaNo ratings yet
- Global Talent PoolDocument51 pagesGlobal Talent PoolRamona Paula100% (1)
- Talent Mobility 2020Document36 pagesTalent Mobility 2020Ramona Paula0% (1)
- Mending Gap LeadersDocument0 pagesMending Gap LeadersRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- Building Critical TalentDocument14 pagesBuilding Critical TalentRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- Updating Flexibility StrategiesDocument8 pagesUpdating Flexibility StrategiesRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- Mending Gap LeadersDocument0 pagesMending Gap LeadersRamona PaulaNo ratings yet
- PWC Delivering Results Through TalentDocument28 pagesPWC Delivering Results Through TalentyagayNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Observer-Based Monitoring of Heat ExchangersDocument10 pagesObserver-Based Monitoring of Heat ExchangersMiguel LópezNo ratings yet
- APEGBC Eng Syllabus MechanicalDocument22 pagesAPEGBC Eng Syllabus MechanicalbaljinderNo ratings yet
- Vortex-Induced Oscillation-A Selective ReviewDocument18 pagesVortex-Induced Oscillation-A Selective ReviewWade ZhouNo ratings yet
- Voltage and Frequency Control of Inverters Connected in Parallel Forming A Micro-GridDocument6 pagesVoltage and Frequency Control of Inverters Connected in Parallel Forming A Micro-GridShad Rahman100% (1)
- Tarea 1 MunsonDocument4 pagesTarea 1 MunsonAlexander JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2: Slider Crank MechanismDocument6 pagesExperiment No. 2: Slider Crank MechanismLovekeshNo ratings yet
- Design, Analysis and Fabrication of Split Braking SystemDocument6 pagesDesign, Analysis and Fabrication of Split Braking Systemhabib nawazNo ratings yet
- 13C NMR Spectroscopy of Coumarin DerivativesDocument18 pages13C NMR Spectroscopy of Coumarin DerivativesGeorge MoshiashviliNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To DC Generator Using Matlab/Simulink: Debabrata PalDocument4 pagesAn Introduction To DC Generator Using Matlab/Simulink: Debabrata PalMohammad H Al-QaisiNo ratings yet
- Surface Area of A Semi-Cylinder WorksheetDocument1 pageSurface Area of A Semi-Cylinder WorksheetvirtualmathsNo ratings yet
- Lang SethDocument52 pagesLang Sethrrmerlin_2No ratings yet
- Higher efficiency synchronous motors for industrial applicationsDocument6 pagesHigher efficiency synchronous motors for industrial applicationsAmirNo ratings yet
- Moment of Inertia of FlywheelDocument3 pagesMoment of Inertia of FlywheelFinney WilsonNo ratings yet
- Lake Ridge Academy 9 - 12 Curriculum GuideDocument2 pagesLake Ridge Academy 9 - 12 Curriculum GuidevanermedusaNo ratings yet
- New Regulations For Geotech GermanyDocument10 pagesNew Regulations For Geotech GermanySâu HeoNo ratings yet
- Asignment 2Document3 pagesAsignment 2EngrAneelKumarAkhaniNo ratings yet
- DC CircuitDocument142 pagesDC CircuitBela FirmantoyoNo ratings yet
- Project Avoidance MEMS Dielectric ChargeDocument17 pagesProject Avoidance MEMS Dielectric ChargeNguyễn Viết HuyNo ratings yet
- Astm D1250 Table 56Document7 pagesAstm D1250 Table 56Frankie Nguyen100% (4)
- Energies: Exergy Analysis and Process Optimization With Variable Environment TemperatureDocument19 pagesEnergies: Exergy Analysis and Process Optimization With Variable Environment TemperatureFranco Camacho CanchariNo ratings yet
- Math 2280 - Lecture 4: Separable Equations and Applications: Dylan Zwick Fall 2013Document8 pagesMath 2280 - Lecture 4: Separable Equations and Applications: Dylan Zwick Fall 2013Kawsar MobinNo ratings yet
- Internal Flows (Laminar Flow) : Lecture - 04Document25 pagesInternal Flows (Laminar Flow) : Lecture - 04غيث منعمNo ratings yet
- Day 266 Solution: Ashmit DuttaDocument2 pagesDay 266 Solution: Ashmit DuttaObama binladenNo ratings yet
- Degree of Freedom PDFDocument13 pagesDegree of Freedom PDFAnasNo ratings yet
- Mechanics and Free Fall - FIDPDocument4 pagesMechanics and Free Fall - FIDPAustin Capal Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Experiment 3 (A) : Cc205 Lab Mechanic of StructuresDocument5 pagesExperiment 3 (A) : Cc205 Lab Mechanic of StructuresZol HasNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Atom Position on X-Ray Diffraction IntensitiesDocument29 pagesThe Effect of Atom Position on X-Ray Diffraction IntensitiesJorge De Jesus Torres ReyesNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument3 pagesDaftar PustakaAwaliyatun Fhathonatuz ZuhriyahNo ratings yet
- Moisture and Total Solids AnalysisDocument44 pagesMoisture and Total Solids AnalysisNicholas BoampongNo ratings yet
- 2018 Experimental and CFD Analysis of Solar Air Heater With Rectangular ShapedDocument5 pages2018 Experimental and CFD Analysis of Solar Air Heater With Rectangular ShapedaliNo ratings yet