Professional Documents
Culture Documents
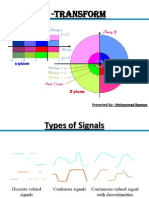
Z Transform
Uploaded by
Moiz RanaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Z Transform
Uploaded by
Moiz RanaCopyright:
Available Formats
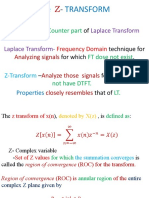
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
The z -Transform
Dr. Muhammad Sarwar Ehsan sarwar.ehsan@ee.uol.edu.pk
Department of Electrical Engineering, The University of Lahore
April 9, 2013
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
Outline
Introduction
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
Outline
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
Outline
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT
Region of Convergence (RoC)
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
Introduction
z -transform of a sequence x[n] is dened as:
X (z ) =
n=
x[n]z n
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
Introduction
z -transform of a sequence x[n] is dened as:
X (z ) =
n=
x[n]z n
z is complex i.e. z = rej
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
Introduction
z -transform of a sequence x[n] is dened as:
X (z ) =
n=
x[n]z n
z is complex i.e. z = rej Powerful tool for analyzing & designing DT systems
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
Introduction
z -transform of a sequence x[n] is dened as:
X (z ) =
n=
x[n]z n
z is complex i.e. z = rej Powerful tool for analyzing & designing DT systems Generalization of the DTFT
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
z -Transform and DTFT
X (z ) =
n=
x[n]z n
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
z -Transform and DTFT
X (z ) =
n=
x[n]z n x[n](rej )n
=
n=
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
z -Transform and DTFT
X (z ) =
n=
x[n]z n x[n](rej )n
=
n=
X (rej ) =
n=
x[n]rn ejn
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
z -Transform and DTFT
X (z ) =
n=
x[n]z n x[n](rej )n
=
n=
X (rej ) =
n=
x[n]rn ejn forr = 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
z -Transform and DTFT
X (z ) =
n=
x[n]z n x[n](rej )n
=
n=
X (rej ) =
n=
x[n]rn ejn forr = 1
X (ej ) =
n=
x[n](ejn )
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
Region of Convergence (RoC)
Critical question: Does summation X (z ) = converge (to ne value)?
n n= x[n]z
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
Region of Convergence (RoC)
Critical question: n Does summation X (z ) = n= x[n]z converge (to ne value)? In general, depends on the value of z
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
Region of Convergence (RoC)
Critical question: n Does summation X (z ) = n= x[n]z converge (to ne value)? In general, depends on the value of z Region of Convergence: Portion of complex z-plane for which a particular X (z ) will converge.
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC Example
Example
Let x[n] = n u[n]
X (z ) =
n=0
n z n =
1 1 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC Example
Example
Let x[n] = n u[n]
X (z ) =
n=0
n z n =
1 1 z 1
converges for |z 1 | i.e. RoC is |z | > ||
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC Example
Example
Let x[n] = n u[n]
X (z ) =
n=0
n z n =
1 1 z 1
converges for |z 1 | i.e. RoC is |z | > || || < 1 (e.g. 0.8)- nite energy sequence
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC Example
Example
Let x[n] = n u[n]
X (z ) =
n=0
n z n =
1 1 z 1
converges for |z 1 | i.e. RoC is |z | > || || < 1 (e.g. 0.8)- nite energy sequence || > 1 (e.g. 1.2) - Divergent sequence, innite energy, DTFT does not exist but still has ZT when |z | > 1.2 (in RoC)
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
About ROCs
ROCs always dened in terms of |z | circular regions on z-plane (inside circles/outside circles/rings)
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
About ROCs
ROCs always dened in terms of |z | circular regions on z-plane (inside circles/outside circles/rings) If ROC includes unit circle (|z | = 1), x[n] has a DTFT
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC Another Example
Example
Let x[n] = n u[n 1] an anti-causal (Left-sided) sequence
1
X (z ) =
n=
()n z n =
1 1 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC Another Example
Example
Let x[n] = n u[n 1] an anti-causal (Left-sided) sequence
1
X (z ) =
n=
()n z n =
1 1 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC Another Example
Example
Let x[n] = n u[n 1] an anti-causal (Left-sided) sequence
1
X (z ) =
n=
()n z n = =
1 1 z 1
n z n
m=1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC Another Example
Example
Let x[n] = n u[n 1] an anti-causal (Left-sided) sequence
1
X (z ) =
n=
()n z n = =
1 1 z 1
n z n
m=1
1 z 1 1 z
1 1 z 1
Same ZT as n u[n], dierent sequence?
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
RoC is Necessary!
To completely dene a ZT, you must specify the ROC
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
RoC is Necessary!
To completely dene a ZT, you must specify the ROC
n u[n]
1 1z 1
RoC is |z | > ||
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
RoC is Necessary!
To completely dene a ZT, you must specify the ROC
n u[n] n u[n]
1 1z 1 1 1z 1
RoC is |z | > || RoC is |z | < ||
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
RoC is Necessary!
To completely dene a ZT, you must specify the ROC
n u[n] n u[n]
1 1z 1 1 1z 1
RoC is |z | > || RoC is |z | < ||
A single X (z ) can describe several sequences with dierent RoCs
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
RoC is Necessary!
To completely dene a ZT, you must specify the ROC
n u[n] n u[n]
1 1z 1 1 1z 1
RoC is |z | > || RoC is |z | < ||
A single X (z ) can describe several sequences with dierent RoCs
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
RoC is Necessary!
To completely dene a ZT, you must specify the ROC
n u[n] n u[n]
1 1z 1 1 1z 1
RoC is |z | > || RoC is |z | < ||
A single X (z ) can describe several sequences with dierent RoCs
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
RoCs and Sidedness
Two sequences have X (z ) = 1 1 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections
Consider X (z ) = with |1 | < 1 and |2 | > 1 1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections
Consider X (z ) = 1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
with |1 | < 1 and |2 | > 1 Two possible sequences for 1 term ...
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections
Consider X (z ) = 1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
with |1 | < 1 and |2 | > 1 Two possible sequences for 1 term ...
Similarly for 2 ...
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections
Consider X (z ) = 1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
with |1 | < 1 and |2 | > 1 Two possible sequences for 1 term ...
Similarly for 2 ...
4 possible x[n] sequences and RoCs
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections
Consider X (z ) = 1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
with |1 | < 1 and |2 | > 1 Two possible sequences for 1 term ...
Similarly for 2 ...
4 possible x[n] sequences and RoCs
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections
Consider X (z ) = 1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
with |1 | < 1 and |2 | > 1 Two possible sequences for 1 term ...
Similarly for 2 ...
4 possible x[n] sequences and RoCs
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections: Case 1
X (z ) = 1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections: Case 1
X (z ) = Right-sided sequences 1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections: Case 1
X (z ) = Right-sided sequences
n x[n] = n 1 u[n] + 2 u[n]
1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections: Case 1
X (z ) = Right-sided sequences
n x[n] = n 1 u[n] + 2 u[n]
1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections: Case 1
X (z ) = Right-sided sequences
n x[n] = n 1 u[n] + 2 u[n]
1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections: Case 2
X (z ) = 1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections: Case 2
X (z ) = Left-sided sequences 1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections: Case 2
X (z ) = Left-sided sequences
n x[n] = n 1 u[n 1] 2 u[n 1]
1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections: Case 2
X (z ) = Left-sided sequences
n x[n] = n 1 u[n 1] 2 u[n 1]
1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections: Case 2
X (z ) = Left-sided sequences
n x[n] = n 1 u[n 1] 2 u[n 1]
1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections: Case 3
X (z ) = 1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections: Case 3
X (z ) = Two-sided sequence 1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections: Case 3
X (z ) = Two-sided sequence
n x[n] = n 1 u[n] 2 u[n 1]
1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections: Case 3
X (z ) = Two-sided sequence
n x[n] = n 1 u[n] 2 u[n 1]
1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections: Case 3
X (z ) = Two-sided sequence
n x[n] = n 1 u[n] 2 u[n 1]
1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections: Case 4
X (z ) = 1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections: Case 4
1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1 Two-sided sequences with no overlap X (z ) =
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections: Case 4
1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1 Two-sided sequences with no overlap X (z ) =
n x[n] = n 1 u[n 1] + 2 u[n]
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections: Case 4
1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1 Two-sided sequences with no overlap X (z ) =
n x[n] = n 1 u[n 1] + 2 u[n]
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections: Case 4
1 1 + 1 1 1 z 1 2 z 1 Two-sided sequences with no overlap X (z ) =
n x[n] = n 1 u[n 1] + 2 u[n]
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections
Two-sided exponential sequences x[n] = n < n < = n u[n] + n u[n 1]
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections
Two-sided exponential sequences x[n] = n < n < = n u[n] + n u[n 1] No overlap in RoCs
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
Introduction z -Transform and DTFT Region of Convergence (RoC)
ROC intersections
Two-sided exponential sequences x[n] = n < n < = n u[n] + n u[n 1] No overlap in RoCs ZT does not exist
Dr. M. Sarwar Ehsan
The z -Transform
You might also like
- 27 Points of Difference Between Personnel Management & HRDDocument2 pages27 Points of Difference Between Personnel Management & HRDMurtaza Ejaz33% (3)
- EENG 5610: Digital Signal Processing: Class 3: The Z-Transform and Its ApplicationsDocument32 pagesEENG 5610: Digital Signal Processing: Class 3: The Z-Transform and Its ApplicationsSantosh BommakantiNo ratings yet
- Portland Cement: Standard Specification ForDocument9 pagesPortland Cement: Standard Specification ForHishmat Ezz AlarabNo ratings yet
- CSCI 123 - Final ExamDocument15 pagesCSCI 123 - Final ExamBrianYoungNo ratings yet
- Module1 ZTDocument35 pagesModule1 ZTShruti KumariNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Z TransformDocument43 pagesLecture 7 Z TransformSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- The Z TransformDocument20 pagesThe Z TransformThivaNo ratings yet
- 03 Ztrans PDFDocument20 pages03 Ztrans PDFlawahedNo ratings yet
- Z - Transform: Presented By-: Mohammad RameezDocument42 pagesZ - Transform: Presented By-: Mohammad RameezMohammad RameezNo ratings yet
- 9 Lec9 DSP Z TransformDocument31 pages9 Lec9 DSP Z TransformAhmed KhalfNo ratings yet
- Z TransformDocument156 pagesZ TransformMohammad Rameez100% (1)
- Z TransformDocument14 pagesZ TransformmarojethyoNo ratings yet
- Transform: of Technique For For Which - For Which That ofDocument119 pagesTransform: of Technique For For Which - For Which That ofsk abdullahNo ratings yet
- Waqas AhmedDocument33 pagesWaqas AhmedpriyanirumaNo ratings yet
- Inverse Z-Transforms and Difference Equations 1 PreliminariesDocument14 pagesInverse Z-Transforms and Difference Equations 1 Preliminariessanjayb1976No ratings yet
- The Z TransformDocument37 pagesThe Z TransformNikhil HosurNo ratings yet
- Z-Transform and ConvolutionDocument9 pagesZ-Transform and ConvolutionMichelle MachimbiraNo ratings yet
- The Z-Transform: IntroductionDocument11 pagesThe Z-Transform: IntroductionCoolshags SinghNo ratings yet
- Z TansformDocument65 pagesZ TansformThe Aviator00No ratings yet
- DSP Classtest AnswerDocument5 pagesDSP Classtest AnswerSougata GhoshNo ratings yet
- Handout - 5 The Z-TransformDocument34 pagesHandout - 5 The Z-TransformFanuel PeterNo ratings yet
- Z TransformDocument15 pagesZ TransformSureshKumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document13 pagesChapter 4Solo NunooNo ratings yet
- Z TransformDocument33 pagesZ TransformSomnathNo ratings yet
- Week 6 - Z-TransformDocument15 pagesWeek 6 - Z-TransformRalph Ian CaingcoyNo ratings yet
- Z-Plane Analysis: DR. Wajiha ShahDocument59 pagesZ-Plane Analysis: DR. Wajiha ShahboppanamuralikrishnaNo ratings yet
- Z TransformDocument59 pagesZ Transformsathyasat2001100% (1)
- 6-Structures For DSPDocument54 pages6-Structures For DSPBomber KillerNo ratings yet
- ROC Z TransformDocument15 pagesROC Z TransformMohammad Gulam Ahamad0% (1)
- Z TransformDocument15 pagesZ TransformSN DhakerNo ratings yet
- Ulab Ete 315: DSP LecturesDocument18 pagesUlab Ete 315: DSP Lecturesohenri100No ratings yet
- N U A N X: Definition of The Z-TransformDocument4 pagesN U A N X: Definition of The Z-TransformremyaamalNo ratings yet
- Asansol Engineering College: Topic of The Report: Definition of Z-Transform &Document7 pagesAsansol Engineering College: Topic of The Report: Definition of Z-Transform &Ritoban SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Z TransformDocument59 pagesZ Transformtemkimleang100% (1)
- 4-Z - Transform - ROC-09-01-2024Document51 pages4-Z - Transform - ROC-09-01-2024rupinsgmNo ratings yet
- Z-Transform: Signal Processing IIDocument19 pagesZ-Transform: Signal Processing IIChrispinus ChristianNo ratings yet
- Z TransformDocument20 pagesZ TransformMxaz MyzxNo ratings yet
- Ch3-DSP ZDocument90 pagesCh3-DSP ZtrucquynhtudoanNo ratings yet
- Z TransformDocument59 pagesZ TransformDenise NelsonNo ratings yet
- Frequency Analysis of Signals & Systems: Electrical & Electronics Engineering Department Eastern Visayas State UniversityDocument39 pagesFrequency Analysis of Signals & Systems: Electrical & Electronics Engineering Department Eastern Visayas State Universityryan reasNo ratings yet
- Z TransformDocument56 pagesZ Transformcrux_123No ratings yet
- EE331 - L10 - Signals & SystemsDocument37 pagesEE331 - L10 - Signals & Systemsahmetyasinbulut99No ratings yet
- EEE443 Lect 7Document10 pagesEEE443 Lect 7Mikko Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- The Z-TransformsDocument56 pagesThe Z-TransformsSHAHRIAR MAHMUD SABUJ 1604013No ratings yet
- Z-Transforms 1 DefinitionsDocument7 pagesZ-Transforms 1 DefinitionsGraciele MaeokaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three:Z Transform and Its Application To LTI SystemsDocument52 pagesChapter Three:Z Transform and Its Application To LTI SystemsYimam AlemuNo ratings yet
- IT341 DSP Lec#7Document32 pagesIT341 DSP Lec#7Yousef QuriedNo ratings yet
- Z-Transform - CH 7Document13 pagesZ-Transform - CH 7carmo-netoNo ratings yet
- 5 L L EC533: Digital Signal Processing: The Z-TransformDocument23 pages5 L L EC533: Digital Signal Processing: The Z-TransformDalia Abou El MaatyNo ratings yet
- Signal and System Lecture 22Document20 pagesSignal and System Lecture 22ali_rehman87No ratings yet
- EC 2314 Digital Signal Processing: by Dr. K. UdhayakumarDocument98 pagesEC 2314 Digital Signal Processing: by Dr. K. UdhayakumarSatyam SinghNo ratings yet
- DSP Unit 2Document14 pagesDSP Unit 2KARTHIGA MNo ratings yet
- Z TransformDocument12 pagesZ Transformjasmhmyd205No ratings yet
- IT341 DSP Lec#7 With NotesDocument32 pagesIT341 DSP Lec#7 With NotesYousef QuriedNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Digital Signal Processing - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument13 pagesUnit 2 - Digital Signal Processing - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inRohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Sec. 1.6. Z-TransformDocument12 pagesSec. 1.6. Z-TransformMuhammad Adnan MalikNo ratings yet
- Integral Transforms: DT T K T F GDocument56 pagesIntegral Transforms: DT T K T F GUmer EhsanNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Difference Equations in Normed Spaces: Stability and OscillationsFrom EverandDifference Equations in Normed Spaces: Stability and OscillationsNo ratings yet
- Mbes L16Document9 pagesMbes L16Moiz RanaNo ratings yet
- Prosthetic Hand Project ProposalDocument11 pagesProsthetic Hand Project ProposalMoiz Rana100% (1)
- Project Procurement ManagementDocument11 pagesProject Procurement ManagementMoiz RanaNo ratings yet
- Important: Always Connect The Batteries First. Use For 12V Battery System Only 12V (36 Cells) SolarDocument14 pagesImportant: Always Connect The Batteries First. Use For 12V Battery System Only 12V (36 Cells) SolarMoiz RanaNo ratings yet
- ECE 2222-Digital Design Lab: Course Instructor: Ms. Saba Zia Lab 2: Gate Level ModelingDocument7 pagesECE 2222-Digital Design Lab: Course Instructor: Ms. Saba Zia Lab 2: Gate Level ModelingMoiz RanaNo ratings yet
- Stack N HeapDocument22 pagesStack N HeapMoiz RanaNo ratings yet
- 96 Dec2018 NZGeoNews PDFDocument139 pages96 Dec2018 NZGeoNews PDFAditya PrasadNo ratings yet
- Editorial WritingDocument38 pagesEditorial WritingMelanie Antonio - Paino100% (1)
- Successful School LeadershipDocument132 pagesSuccessful School LeadershipDabney90100% (2)
- BS EN 50483-6-2009 EnglishDocument27 pagesBS EN 50483-6-2009 EnglishДмитро Денис100% (2)
- Beginning Cosmetic ChemistryDocument1 pageBeginning Cosmetic ChemistrySergio Rugerio0% (1)
- Konsep Negara Hukum Dalam Perspektif Hukum IslamDocument11 pagesKonsep Negara Hukum Dalam Perspektif Hukum IslamSiti MasitohNo ratings yet
- EHVACDocument16 pagesEHVACsidharthchandak16No ratings yet
- OMN-TRA-SSR-OETC-Course Workbook 2daysDocument55 pagesOMN-TRA-SSR-OETC-Course Workbook 2daysMANIKANDAN NARAYANASAMYNo ratings yet
- Description - GB - 98926286 - Hydro EN-Y 40-250-250 JS-ADL-U3-ADocument6 pagesDescription - GB - 98926286 - Hydro EN-Y 40-250-250 JS-ADL-U3-AgeorgeNo ratings yet
- TakeawaysDocument2 pagesTakeawaysapi-509552154No ratings yet
- Neural Computing and ApplicationsDocument49 pagesNeural Computing and ApplicationsLine PhamNo ratings yet
- Asugal Albi 4540Document2 pagesAsugal Albi 4540dyetex100% (1)
- MT Im For 2002 3 PGC This Is A Lecture About Politics Governance and Citizenship This Will HelpDocument62 pagesMT Im For 2002 3 PGC This Is A Lecture About Politics Governance and Citizenship This Will HelpGen UriNo ratings yet
- 10 - SHM, Springs, DampingDocument4 pages10 - SHM, Springs, DampingBradley NartowtNo ratings yet
- Video Course NotesDocument18 pagesVideo Course NotesSiyeon YeungNo ratings yet
- Parts List 38 254 13 95: Helical-Bevel Gear Unit KA47, KH47, KV47, KT47, KA47B, KH47B, KV47BDocument4 pagesParts List 38 254 13 95: Helical-Bevel Gear Unit KA47, KH47, KV47, KT47, KA47B, KH47B, KV47BEdmundo JavierNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of ProbabilityDocument12 pagesBasic Concept of Probability8wc9sncvpwNo ratings yet
- BIO122 - CHAPTER 7 Part 1Document53 pagesBIO122 - CHAPTER 7 Part 1lili100% (1)
- Application of A HAZOP Study Method To Hazard Evaluation of Chemical Unit of The Power StationDocument8 pagesApplication of A HAZOP Study Method To Hazard Evaluation of Chemical Unit of The Power Stationshinta sariNo ratings yet
- Blackstone The Dash Model #1610 Owner's ManualDocument53 pagesBlackstone The Dash Model #1610 Owner's ManualSydney Adam SteeleNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Literature Review SampleDocument6 pagesCivil Engineering Literature Review Sampleea442225100% (1)
- Tripura 04092012Document48 pagesTripura 04092012ARTHARSHI GARGNo ratings yet
- Study On The Form Factor and Full-Scale Ship Resistance Prediction MethodDocument2 pagesStudy On The Form Factor and Full-Scale Ship Resistance Prediction MethodRaka AdityaNo ratings yet
- GT-3000 PrintDocument3 pagesGT-3000 Printmanual imbNo ratings yet
- Python Cheat Sheet-1Document8 pagesPython Cheat Sheet-1RevathyNo ratings yet
- Projected Costs of Generating Electricity (EGC) 2005Document233 pagesProjected Costs of Generating Electricity (EGC) 2005susantojdNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 3 Module 1Document9 pagesProf Ed 3 Module 1alexa dawatNo ratings yet