Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TV Time Line
Uploaded by
Aj GuanzonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TV Time Line
Uploaded by
Aj GuanzonCopyright:
Available Formats
Television History - A Timeline
1878-2005
1878 William Crookes confirmed the existence of cathode rays by building a tube to display them in. 1897 German scientist Karl Ferdinand Braun constructs the cathode ray tube scanning device. 1900 Russian Constantin Perskyi introduces the word "television" at the 1st International Congress of Electricity at the World's Fair in Paris. Souvenir trading cards are sold at the same fair, two predicting color television and news radio in the year 2000. 1905 Philipp Lenard wins the Nobel Prize in physics for his research on cathode rays. 1907 A.A. Campbell Swinton in England and Boris Rosing in Russia independently propose an electronic scanning system in which a cathode ray tube could produce an image on a phosphorus-coated screen. 1923 Vladimir Zworykin, working for Westinghouse Electric, patents the iconoscope, a television transmission tube and in 1924, patents the kinescope, the receiver tube. 1925 In England, John Logie Baird demonstrates the first moving television pictures via a mechanical system based on Nipkow's disk; they were recognizable human faces in 1925 and moving objects in 1926. He had shown a still image of Felix the Cat in 1924. 1927 Philo Farnsworth transmits the first electronic television image and applies for a patent on the first complete electronic system, the Image Dissector. The first practical demonstration of television is arranged by Bell Labs and AT&T, when Commerce Secretary Herbert Hoover in Washington DC spoke to the president of AT&T in New York. The New York Times reports a clear reception. All About Television, the first serious hobbyist television magazine, is published. The Radio Act, 47 U.S.C. 81-119 (1927) (repealed 1934), regulates programming, sets up a system for issuing licenses, and makes it clear that the airwaves can be used only with the Government's permission. The Federal Radio Commission is established. 1928 GE-owned experimental television station WGY-TV in Schenectady, NY, transmits a 40-minute stage production, The Queen's Messenger, to 4 television sets with a system developed by their engineer, Dr. Ernst
Alexanderson. W2XBS, the RCA experimental television station and lab, begins operations in New York City. The Federal Radio Commission issues the first television license (W3XK) to Charles Jenkins in Wheaton, Maryland, who plans to broadcast "radiomovies." The first mechanical television sets go on sale: GE sells one in a fancy cabinet and in England, Baird sets are available, but only with a license. 1929 Vladimir Zworykin demonstrates the first practical electronic system for both the transmission and reception of images using his improved kinescope tube. RCA's W2XBS begins broadcasting the image of Felix the Cat, placed on a record player turntable, using a mechanical scanning disk and an electronic kinescope receiver. The image was 2" high, in 60 lines (compared to HDTV's 720 or 1,080), and broadcasts lasted around 2 hours a day. Bell Labs demonstrates a mechanical television color television system. 1930 RKO experiments with theater television in Schenectady, NY, bringing in up-to-date news and sportscasts to the movies. Charles Jenkins broadcasts the first television commercial and is promptly fined by the FRC. 1931 CBS begins experimental television programming. Charles Jenkin's mechanical television set, Radiovisor Model 100 sells as a kit for $42.50. 1932 NBC begins experimental television programming. 1933 W9XK, State University of Iowa, makes the first television broadcast from an educational institution. A photo of President W.A. Jessup appeared during the telecast which inaugurated the series of educational programs which featured University of Iowa faculty members. 1934 Experimentation with the cathode ray tube gets results. The Federal Communications Act of 1934 is signed, merging the FRC and parts of the ICC and Postmaster General agencies into the FCC. It is empowered to regulate all non-federal use of the radio spectrum, including radio and television, and all interstate telecommunications. 1936 RCA displays a 343-line TELEVISION for the press as part of NBC's tenth anniversary celebration.
1937 The coronation of King George VI and the Wimbledon tennis tournament are televised in England. Nine thousand sets are sold in London. Electronic television is still slow to come to the United States. The Communications Act of 1937, 47 U.S.C. 315, requires that stations provide equal time to all legal candidates for office if they gave time to any candidate. 1939 RCA's station W2XBS begins the industry's first regular schedule of television service to 4,000 locally-owned sets on April 30, 1939, showing President Roosevelt opening the 1939 New York World's Fair. It later broadcasts the first major league baseball game, a double-header between the Cincinnati Reds and the Brooklyn Dodgers at Ebbets Field, Brooklyn, and the first NFL game, the Brooklyn Dodgers vs. the Philadelphia Eagles. Dumont Company, along with RCA and GE begins producing electronic television sets for consumers. Kits are available for the less affluent. 1940 Dumont gets a license for experimental television station W2XWV in New York City. Dr. Peter Goldmark at CBS develops and demonstrates electronic color television but it is incompatible with the 525-line broadcast standard. The first Peabody Awards for broadcasting excellence are given out. 1941 The FCC authorizes commercial television to begin on July 1. It sets television standards to 525 lines and 30 frames per second, authorizes commercial television stations, and issues the "Report on Chain Broadcasting," which resulted eventually in NBC's sell-off of the Blue network. W2XBS goes commercial as WNBT (NBC) and General Mills sponsors a baseball game between Brooklyn and Philadelphia. Just before the game starts, the first "legal" commercial, for Bulova watches, appears. It lasts 10 seconds and costs $9. Later in the day, Ralph Edwards hosts the first television game show, "Truth Or Consequences," simulcast on radio and television. The station jumped the legal gun by actually beginning its broadcasts the day before. WCBS goes on the air with the first newscast the same day (July 1). Both CBS and NBC have regularly scheduled programming of approximately 15 hours per week. There are approximately 7,000 television sets in the U.S. Americans hear a radio broadcast of the Pearl Harbor attack. CBS broadcasts televised news of the attack. Commercial production of television equipment stops until the end of the war.
1942 Television stations' air time requirement is lowered to 4 hours a week from 15. 1943 Edward Noble, owner of Lifesaver candy and station WMCA, buys the NBC Blue Network and turns it into the American Broadcasting Company. Vladimir Zworykin develops a better camera tube - the Orthicon - with enough light sensitivity to record outdoor events at night. WRGB, Schenectady, broadcasts the first complete opera, Hansel and Gretel. The Voice of Firestone Televues documentary series premiers, the first series to feature original programming and the first to go network-wide the following spring. 1944 Dumont's W2XWV goes commercial as WABD and broadcasts the 30-minute Your World Tomorrow, combining news and entertainment features. The FCC opens hearings on postwar allocations for new stations. 1945 Sci-fi author Arthur C. Clarke suggests using geosynchronous satellites for communications in "V2 for Ionospheric Research" in a brief letter to Wireless World. Dumont's first network hookup - Washington to NewYork - announces the dropping of the atomic bomb on Nagasaki. 1946 RCA markets the first post-war designed television, the 630-TS, and nearly 10,000 sets sell for ca. $350. each, a little more than 10% of an average yearly salary. The prime time schedule opens with NBC programming on Sunday, Monday, Thursday, and Friday, and Dumont on Sunday, Tuesday, Wednesday, and Thursday. Dumont's Faraway Hill is the first network television soap opera, the only program on Wednesday nights. James Beard hosts the first network television cooking show, I Love to Eat, a fifteen minute show on Friday nights on NBC. Tokyo Tsushin Kogyo is founded; the name changes to Sony in 1958. 1947 There are approximately 44,000 television sets in homes in the U.S. In March, Dumont premieres the first network children's show, Small Fry Club, at 7 p.m. Monday through Friday. It had originated on radio in 1921.
Harry Truman is the first president to address the nation from the White House via television. It is a plea for food for Europe. Public Prosecutor is the first filmed (not live) series produced for television in Hollywood. It is the first program created for syndication. Meet the Press and The Howdy Doody Show premiere on NBC. Afternoon programming comes to New York City. AT&T Bell Telephone Laboratories scientists invent the transistor. Philco Radio Time, hosted by Big Crosby, is the first taped US radio network program. 1948 Full time evening programming begins for all four television networks and there are 27 stations in 18 cities beaming to an estimated 350,000 sets. Uncle Miltie blows away the competition with Texaco Star Theater. Milton Berle, aka Mr. Television, was said to have sold more televisions than any advertising campaign could have. When the Nielsen's ratings began in 1950, TST had a market share of 61.6 Cable television is introduced in Pennsylvania as a means of bringing television to rural areas. A patent is granted to Louis W. Parker for a television receiver, the "intercarrier sound system," the modern basis for coordinating sound and picture in the television receiver. 1949 Milton Berle hosts the first charity telethon, the Damon Runyon Memorial Fund. Television sets appear in the Sears Roebuck catalog.
1950 6,132,000 television sets are sold, making a total of 9,735,000, in 9% of U.S. households. Audiences anticipate color television. Converters are offered. Zenith Radio Corporation creates the first television remote control in 1950, the "Lazy Bone." Lazy Bone could turn a television on and off and change channels, but it was attached by a bulky cable. Iowa State College launches WOI, the first television station owned by an educational institution, although it operates commercially. 1951 Lucille Ball and Desi Arnaz negotiate a contract with CBS for the right to film I Love Lucy and get 100% ownership, pioneering the rights to residuals and earning them over $1 million a year by the mid 50s. They
have a 50.9 rating which jumps to 67.3 the following year. Amos 'n Andy is the first prime-time show with an all-black cast. The networks offer 27 hours of children's shows a week, much of it in the early evening, and promote televisions as an educational tool to their parents. CBS' Arthur Godfrey's Talent Scouts edges out Milton Berle with a 53.8 share over his 52.0. 1952 The FCC approves UHF-TV broadcasting. Black-and-white portable television era begins. The Today Show begins, with Dave Garroway as its host. Theater television reaches its peak with the broadcast of the Walcott/Marciano fight. Fifty movie theaters in 30 cities were wired together for the event. The first congressional hearings on television violence are held by the House Interstate and Foreign Commerce Subcommittee. 1953 When Lucy gave birth to Little Ricky forty-four million viewers (72% of all U.S. homes with televisions - half of U.S. homes own televisions) tune in to I Love Lucy, 15 million more than had watched Dwight Eisenhower's inauguration the day before. The first issue of TV Guide features the baby. Color television broadcasting officially begins on The Colgate Comedy Hour after the FCC adopts the RCA system as the standard. The University of Houston signs on the first noncommercial educational television station, KUHT. 1954 NBC broadcasts the first coast-to-coast color program, the Rose Bowl Parade, to the 200 sets able to receive RCA's electronic color system. The first all-electronic color television sets are Westinghouse's and the RCA CT-100, selling for $1,000. Just over half of all American households own televisions. The Tonight Show, the longest running talk show on television, debuts. The first public television station, WQED-TV makes its debut in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The Army-McCarthy congressional hearings are broadcast live and repeated at night, bringing the country face to face with zealot Joe McCarthy's zeal as he tracks down the Commies. 1955
4% of television-owning households own more than one set. Sales of RCA color sets jump from 5,000 in the previous year to 20,000. Quiz shows hit their peak when The $64,000 Question tops the ratings with a 47.5 share. The following year brings questions about fraud and in 1958 they were pulled when a disgruntled contestant on Dotto reveals all. The Mickey Mouse Club and Captain Kangaroo debut. 1956 RCA drops the price of color televisions to $500. Robert Adler invents the first wireless remote control, the Zenith Space Commander. Ampex introduces the first practical videotape system of broadcast quality. Nat King Cole is the first black entertainer to host a network variety show. Elvis Presley appears on the Ed Sullivan Show and scandalizes the nation. 1957 Gunsmoke, the longest running drama (1955-75), tops the charts with a 43.1 share. Ten programs in the top 30 slots are westerns. Perry Mason premieres, ranking 19th the following year and reaching its peak in popularity in 1961 with a fifth place. 1960 The first split screen broadcast occurs on the Kennedy-Nixon debates. The first battery-operated transistorized television is for sale. There are 67,145,000 television sets in the U.S. 1961 FCC chairman Newton Minow, in an address to the National Association of Broadcasters, claims that television is nothing but a "vast wasteland." John F. Kennedy holds the first live televised presidential news conference. The Defenders opens the door for law-inspired social commentary. Moscow welcomes home astronaut Yuri Gagarin in the first western viewing of live television from the USSR in a BBC broadcast. 1962 Justice William O. Douglas presents a special Emmy award to Jackie Kennedy for her televised tour of the White House.
Johnny Carson succeeds Jack Paar as host of the Tonight Show. AT&T launches Telstar, the first satellite to send television signals. The All Channel Receiver Act, Pub. L. No. 87-529, 76 Stat. 150 requires that all television sets sold in the U.S. be able to pick up UHF stations as well as VH. 1963 Walter Cronkite reports "President Kennedy died at 1:00 p.m. central standard time." The on-camera murder of Lee Harvey Oswald by Jack Ruby is telecast live. Television is used on a U.S. manned space flight, the Mercury 9. The low-brow takes over when The Beverly Hillbillies ranks first, with a 36 rating. 1964 The first prototype for a plasma display monitor is invented at the University of Illinois by Professors Donald Bitzer and Gene Slottow, and graduate student Robert Willson. They received an Emmy Award for their invention in 2002. The Beatles appear on the Ed Sullivan Show. 3% of television owning households have color televisions. 1965 "Early Bird," the first international communications satellite, is launched (Intelsat I). The fall season opens with almost all of NBC's prime time schedule produced on color film. CBS follows in 1966, and ABC in 1967. 1967 The Green Bay Packers beat the Kansas City Chiefs, 35-10, in the first Super Bowl game. The Public Broadcasting Act of 1967, P.L. 90-129 (1967), authorizes federal operating aid to public stations through a new agency, the Corporation for Public Broadcasting. 1968 CBS uses a portable minicam for political convention coverage. 60 Minutes, the longest running primetime television program, makes Mike Wallace the eldest statesman of news reporters. Dan Rowan and Dick Martin's Laugh-In changes the style and pace of television comedy, shooting to the top of the ratings within weeks of its debut. Japan's public broadcasting network, NHK, begins research on high definition television.
1969 Neil Armstrong walks on the moon and a worldwide audience of 720 million watches the event live. In Red Lion Broadcasting Co. v. FCC, 395 U.S. 367 (1969), the Supreme Court holds that the FCC did not violate the First Amendment in requiring a radio or television station to give reply time to people who were the subject of a personal attack or political editorial. 1970 The Public Broadcasting System network is established. Viacom is formed after CBS spins off its television programming arm as a result of the FCC's Fin-Syn rules which limit the financial interest television networks can have in syndicated programming. ABC gets the rights from the National Football League to show their games on Monday Night Football, making Howard "The Mouth" Cosell's career. 1971 All in the Family is the first sitcom to be videotaped but more importantly breaks new ground as it deals openly with the bigotry and narrow-mindedness of its lead character. Episodes treat controversial subjects like prejudice, abortion, and homosexuality and the series makes it to the top of the ratings in its first season, where it stays through 1975. Masterpiece Theatre debuts with "The First Churchills" on PBS. National Public Radio begins service with the live broadcast of Senate hearings on ending the Vietnam War and All Things Considered. Susan Stamberg is the first woman to anchor a daily national broadcast. 1972 Half the televisions in homes are color sets. Boston's WGBH Caption Center prepares the first open-captioned national broadcast, Julia Child's The French Chef. Television and Social Behavior; Reports and Papers, a 5-volume report to the Surgeon General's Scientific Advisory Committee on Television and Social Behavior, concludes that there is a causal link between viewing television violence and subsequent antisocial acts. 1973 Television buying hits a peak with sales of 17,368,000 as older 50s and 60s sets need to be replaced. The Senate Select Committee on Presidential Campaign Activities conducts the Watergate hearings, televised on all networks. 1974 The House Judiciary Committee holds televised hearings on articles of presidential impeachment for Richard Nixon. The Department of Justice files an antitrust suit against AT&T, seeking to break its monopoly.
1975 Sony's Betamax video recorder, goes on the U.S. market for $1300, and more than 25,000 units sell in the first year. A one-hour cassette tape sells for $16. HBO begins program distribution via satellite. PBS launches its first national pledge drive, Festival 75. 1976 VHS home recording format is introduced. Turner Broadcasting's WTCG becomes cable television's first Superstation as it is beamed via satellite to cable homes across the country. 1977 RCA competes with Sony by selling Matsushita-created VHS recorders under the RCA name for $1,000. PBS begins operation by satellite. Roots is the first television mini-series. 1978 Federal Communications Commission v. Pacifica Foundation et al, 438 U.S. 726 (1978) rules that George Carlin's "words you couldn't say on the public airwaves" are indecent. 98% of U.S. households own at least one television. Dallas begins its 13-year run as a low-rated spring show. The episode revealing who shot J.R. (11/21/80) was the most highly viewed program up to that time. 1980 Ted Turner's Cable News Network debuts with 24-hour national news reporting and 1.7 million subscribers. Constant media attention to the Iranian hostage crisis led to Jimmy Carter's defeat by Ronald Reagan in the presidential election. 1981 HDTV is demonstrated in United States by NHK, Japan's government-owned broadcasting service, at the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers meeting in Los Angeles. The MTV network premieres, aiming at the 18-24 age bracket with its music videos and reality programming. 1982 Dolby surround sound for home sets is introduced. David Letterman begins decades of late-night talk show success with Late Night with David Letterman.
1983 The final episode of MASH becomes the most watched television program in history. 1984 Chicagos public WTTW is the first station to air television in stereo sound full-time. The Supreme Court rules in Sony Corporation of America et al. v. Universal City Studios, Inc., et al., 464 U.S. 417 that there is no copyright infringement in videotaping television broadcasts for later viewing in a private setting. 1985 Fox Broadcasting is established. GE acquires NBC as part of a $6.3 billion deal for RCA. The first Blockbuster Video store opens in Dallas. The U.S. Court of Appeals of the D.C. Circuit (Quincy Cable TV v. FCC, 768 F.2d 1434) rules the FCC's "mustcarry" rules requiring cable companies to include local stations are unconstitutional and an FCC inquiry into the "fairness doctrine" concludes the policy no longer serves the public interest. 1986 Scrambling of satellite-fed cable television programming starts; sale of decoders and program subscriptions to home dish owners begins. Stereo sound in television broadcasting is available in all major U.S. population centers. WGBH introduces Descriptive Video Service for vision-impaired viewers. L.A. Law supposedly causes a huge upswing in law school applications. A kinder, gentler audience appreciates Bill Cosby's wide-appeal The Cosby Show, making it number one in the ratings and reflecting the dominance of the sitcom. The FCC breaks up the Spanish International Network because of rules relating to foreign ownership of television stations. It is sold to Hallmark, and becomes Univision, the largest Spanish language network in the U.S. 1989 American National Standards Institute (ANSI) gives final approval to a 1125/60 HDTV production standard. Whittle Communications stirs controversy by offering free satellite dishes and television sets to schools that show the daily Channel One newscast with commercials. 1990
Ninety-nine percent of U.S. households have at least one radio, with the average owning five. More than 200 million VCRs a year are sold worldwide. Ken Burns The Civil War breaks PBS audience records with an estimated national audience of 13.9 million people, far exceeding the 8.7 million people who lived in the Confederacy at the start of the war. The 1990 Children's Television Act, Pub. L. No. 101-437, 104 Stat. 996, is the first congressional act that specifically regulated children's television. One of its requirements was a minimum of 3 hours per week of educational programming. Some stations tried to claim The Flintstones was a history program. The Television Decoder Circuitry Act of 1990 mandates that since July 1993, all televisions manufactured for sale in the U.S. must contain a built-in caption decoder if the picture tube is 13" or larger. 1991 The first generation of direct broadcast satellite systems, Primestar, is launched by a consortium of cable system owners. The first televisions with built-in closed-caption display capability are introduced in the U.S. U.S. testing of HDTV systems begins. Fox Broadcasting is the first network to permit condom advertising on television. 1992 There are 900 million television sets in use around the world; 201 million are in the United States. The Cartoon Network opens, fueled by Ted Turner's acquisition of Hanna-Barbera Cartoons. 1993 Anticipating HDTV, RCA introduces the first widescreen 16:9 aspect television models. 1994 Viacom acquires Paramount Communications for $10 billion and Blockbuster Video for $8.4 billion. RCA puts the Direct Satellite System into service. Ted Turner launches the Turner Classic Movies station. Republicans win a majority in the House and new Speaker Newt Gingrich soon announces plan to zero out CPB funding. 1995 The Walt Disney Company acquires ABC. Westinghouse Corporation buys CBS for $5.4 billion. The first television program ("Computer Chronicles") is delivered via the Internet.
PBS Online debuts. Flat-screen plasma display televisions are introduced at $20,000. By 1997, they are half that price. The WB television broadcast network is launched. 1996 MSNBC is launched as a joint partnership between GE and Microsoft. The FCC approves the Advanced TV Systems Committee's HDTV standard and HDTV is broadcast and received live at WHD-TV in Washington, D.C. There are one billion television sets world-wide. The Telecommunications Act of 1996, Pub. L. No. 104-104, 110 Stat. 56, is passed "To promote competition and reduce regulation in order to secure lower prices and higher quality services for American telecommunications consumers and encourage the rapid deployment of new telecommunications technologies." This allows companies to own more broadcast stations in a given market. 1997 The new television ratings system, similar to that for movies, debuts on both cable stations and broadcast networks. The FCC sets 2003 as the deadline for public television stations to begin DTV simulcasting. 1998 NBC agrees to the highest price ever paid for a television series, over $13 million an episode for the hospital drama ER. Seven public television stations are among first DTV broadcasters and PBS premieres Chihuly Over Venice, the first national broadcast of a program produced and edited in HDTV. DVD technology becomes commercially viable although fewer than 2% of U.S. households have DVD players. 1999 Reality hits hard with Who Wants to Be a Millionaire?-Tuesday, Thursday, and Sunday ranking first, second and third in the Nielsen ratings. Victoria's Secret Super Bowl ad parades scantily clad models across the television screen and a reported 1 million people turn away from the game to log on to the Web address promoted in the ad. Three days later, they webcast their annual fashion show and a record 750,000 comes to watch in spite of slow, if not impossible, connections and a grainy picture worse than that of a 1930 Dumont. Viacom and CBS merge. Tivo enters the market, a hard-disc based personal recorder that allows the viewer to pause a live show, record, and skip over advertisements.
The Recording Industry Assn. of America files a lawsuit against the music website Napster, accusing it of operating as a haven for music piracy on the Internet. 2000 Legal television dramas reach their peak with 9 programs in the top 20 ratings. The AOL/Time Warner agreement becomes the largest corporate merger in history and the world's largest media and entertainment company. 85% of U.S. households own VCRs and 98% own more than one television. Feature film Quantum Project is produced for Internet distribution, not theaters. British "newscaster" Ananova joins other virtual performers on television and the Net. Seven of the top thirty programs are reality shows; Survivor is number one, along with five days of Who Wants to be a Millionaire? 2001 The average American adult watches 4 hours of television daily. Multi-casting begins when WRAL in Raleigh, North Carolina simultaneously broadcasts on one of its digital channels along with its regular CBS programming. Movie box office receipts in U.S. climb to $8.4 billion. 2002 DVD sales surpass VCR sales; 40+ million U.S. homes have DVD capability and there are more than 21,000 titles available. Star Wars: Attack of the Clones is the first big budget film shot with digital cameras. MTV reports that it reaches 250 million homes worldwide. 2003 More DVDs than videotapes are rented, 46.7% of U.S. households own at least one player, and consumers buy more than 1 billion DVD's. Cable television companies offer TiVo-like features: storing programs and skipping commercials. 2004 A little more than 98% of American households have a television and the average home has more than two. Twenty CBS'-owned stations are fined a total of $550,000 by the FCC after a "wardrobe malfunction" during the Super Bowl half-time program Basic cable networks' ratings beat out the no-charge, local broadcast networks in the first week of the fall
season. GE now owns the NBC, Telemundo, Bravo, CNBC, USA, SciFi and Trio networks, as well as Universal Studio, Universal's 5,000 film library, 32,000 television episodes, and 5 theme parks. In addition to ABC, the Walt Disney Company also owns 10 television and 64 radio stations, 12 cable networks, 4 television and 8 movie production and distribution companies, and 15 theme parks. Viacom owns 16 CBS and 18 UPN stations, as well as 5 others. It also owns 15 cable networks, 3 television and production networks (including the largest syndicator, King World), 185 radio stations and Paramount Pictures. There are more than 300 cable networks. It's Betamax all over again with Sony and Disney's Blu-ray versus Toshiba and Paramount's HD DVD technologies for high definition DVDs. Sony buys MGM Studios for $5 billion, gaining the world's largest movie library, over 7,000 titles, and with estimates of the DVD-related value of those titles at over $1 billion per year. More than 30,000 movie titles are available on DVD. Raleigh, NC TV station WRAL is the first television station in the U.S. to provide video news, weather and traffic information to cell-phone users. 2005 Time-Warner/AOL offers telephone service, in addition to cable television and internet access.
You might also like
- History Years in American TelevisionDocument2,202 pagesHistory Years in American TelevisionPcnhs Sal0% (1)
- History of TelevisionDocument23 pagesHistory of TelevisionSheen J PNo ratings yet
- Worldsystem IllustrationDocument1 pageWorldsystem IllustrationEmmanuel Jimenez-Bacud, CSE-Professional,BA-MA Pol SciNo ratings yet
- Evolution of TVDocument28 pagesEvolution of TVdakter esseNo ratings yet
- Q1W1 - WeekDocument99 pagesQ1W1 - WeekjenNo ratings yet
- Philippine TV History: From Mechanical to ElectronicDocument11 pagesPhilippine TV History: From Mechanical to ElectronicDexter CaroNo ratings yet
- History of TelevisionDocument8 pagesHistory of TelevisionHestia NyxiNo ratings yet
- History of BroadcastingDocument47 pagesHistory of BroadcastingLiyana NasarudinNo ratings yet
- Media AssignmentDocument15 pagesMedia AssignmentNoorus SeharNo ratings yet
- Television HistoryDocument5 pagesTelevision HistoryJaider Mercado López100% (1)
- History of TelevisionDocument11 pagesHistory of TelevisionGerald GavinaNo ratings yet
- History of TelevisionDocument18 pagesHistory of TelevisionMyou ChoNo ratings yet
- Gold Age TVDocument14 pagesGold Age TVAnda CruceanuNo ratings yet
- The history of television technology from its origins to modern programmingDocument5 pagesThe history of television technology from its origins to modern programmingChantal ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Televisions Can Be Found in Billions of Homes Around The WorldDocument13 pagesTelevisions Can Be Found in Billions of Homes Around The WorldPriya SelvakumarNo ratings yet
- Broadcast HistoryDocument16 pagesBroadcast HistoryDarrel VeluzNo ratings yet
- History of TV: From Mechanical to ModernDocument6 pagesHistory of TV: From Mechanical to ModernRengeline LucasNo ratings yet
- PartDocument27 pagesPartRasool BhaiNo ratings yet
- History of CommunicationsDocument3 pagesHistory of Communicationsedgardoelijah5No ratings yet
- Project Report On SonyDocument19 pagesProject Report On SonyMadhusudana p n100% (1)
- Communication Using Media Instructor'S Notes: History of TelevisionDocument9 pagesCommunication Using Media Instructor'S Notes: History of TelevisionAlanNo ratings yet
- Science on American Television: A HistoryFrom EverandScience on American Television: A HistoryRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Television 7Document2 pagesTelevision 7funmastiNo ratings yet
- Television: Shair Afgan BuzdarDocument7 pagesTelevision: Shair Afgan BuzdarMuhammad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical TelevisionDocument4 pagesMechanical TelevisionJude FabellareNo ratings yet
- TelevisionDocument60 pagesTelevisionAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Topic 0 History of Electronic CommunicationDocument12 pagesTopic 0 History of Electronic CommunicationRoneline LizadaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of TelevisionDocument18 pagesEvolution of TelevisionArianne AtilasNo ratings yet
- W5 TV and FilmDocument48 pagesW5 TV and Filmgogulamathe shamugamNo ratings yet
- U4 Evidencia 1Document7 pagesU4 Evidencia 1api-299857592No ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle (Television) Amity Business School: MBA (G), Semester 3Document23 pagesProduct Life Cycle (Television) Amity Business School: MBA (G), Semester 3Deeksha RexwalNo ratings yet
- History of Television Sohini GhoshDocument37 pagesHistory of Television Sohini Ghoshrickrock688No ratings yet
- History of TelevisionDocument7 pagesHistory of TelevisionJasmine GamoraNo ratings yet
- History of TV Power PointDocument17 pagesHistory of TV Power Pointapi-334248806No ratings yet
- Republic of The PhillipinesDocument8 pagesRepublic of The Phillipinesnormarie agravanteNo ratings yet
- Presentación Sin TítuloDocument9 pagesPresentación Sin Títulozeki 22psNo ratings yet
- History of Electronic Media and Its ImpactDocument10 pagesHistory of Electronic Media and Its ImpactAhsanFarooqNo ratings yet
- Electronic MediaDocument10 pagesElectronic MediasulaimanNo ratings yet
- 04 Television in AustraliaDocument19 pages04 Television in AustraliaMilena ŠmigićNo ratings yet
- Timeline of Radio HistoryDocument4 pagesTimeline of Radio Historyits yanaNo ratings yet
- Television - Time LineDocument2 pagesTelevision - Time LineDanyelle SantosNo ratings yet
- British TV: Andrés Felipe Chaparro RosasDocument15 pagesBritish TV: Andrés Felipe Chaparro RosasFelipe ChaparroNo ratings yet
- History of Television: American Family Watching TV, 1958Document7 pagesHistory of Television: American Family Watching TV, 1958Hà OhlalaNo ratings yet
- bvp1 2 History of Televisionkey2 1Document5 pagesbvp1 2 History of Televisionkey2 1api-267803318No ratings yet
- Adventures in Cybersound: Trevor BlakeDocument4 pagesAdventures in Cybersound: Trevor BlakeMaciej JüngstNo ratings yet
- Trabalho Da TelevisãoDocument11 pagesTrabalho Da TelevisãoyollandargNo ratings yet
- BBC's History as Public Broadcaster in UKDocument6 pagesBBC's History as Public Broadcaster in UKBEeNaNo ratings yet
- Ev 2 Ut4Document5 pagesEv 2 Ut4api-299857592No ratings yet
- RADIO: The Hits Keep ComingDocument30 pagesRADIO: The Hits Keep ComingAtiqah NadirahNo ratings yet
- 1843-1923: From Electromechanics To ElectronicsDocument11 pages1843-1923: From Electromechanics To ElectronicsSheeraz MemonNo ratings yet
- The History of Radio in 40 CharactersDocument29 pagesThe History of Radio in 40 CharactersMarvie Caleon Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Electronic television historyDocument3 pagesElectronic television historyfunmastiNo ratings yet
- History of Philippine Radio StationDocument3 pagesHistory of Philippine Radio StationAngelica LeybaNo ratings yet
- Review of Wayne Tomasi's "Electronic Communications SystemDocument16 pagesReview of Wayne Tomasi's "Electronic Communications Systemtsk2230No ratings yet
- 1920 - Who Invented The TelevisionDocument1 page1920 - Who Invented The TelevisiondestrysullivanNo ratings yet
- Evolution of TV From Early Broadcasting to HDTVDocument2 pagesEvolution of TV From Early Broadcasting to HDTVHanz Tebelin100% (1)
- History of BroadcastingDocument9 pagesHistory of BroadcastingChris Angelo Tan JamandreNo ratings yet
- Thelma and Millet (25th Year)Document74 pagesThelma and Millet (25th Year)Lian Las PinasNo ratings yet
- COL Application FormDocument1 pageCOL Application FormAj GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Carpio's Dissenting Opinion On Poe vs. Comelec, Et Al.Document55 pagesCarpio's Dissenting Opinion On Poe vs. Comelec, Et Al.Jojo Malig100% (1)
- Revenue Regulation No. 16-2005Document0 pagesRevenue Regulation No. 16-2005Kaye MendozaNo ratings yet
- Garcia Vs ThioDocument11 pagesGarcia Vs ThioAj GuanzonNo ratings yet
- List of Analgesics and Antipyretics DrugsDocument1 pageList of Analgesics and Antipyretics DrugsAj Guanzon86% (7)
- Sources of MoralityDocument3 pagesSources of MoralityAj Guanzon100% (1)
- Bureau of Internal Revenue: Deficiency Tax AssessmentDocument9 pagesBureau of Internal Revenue: Deficiency Tax AssessmentXavier Cajimat UrbanNo ratings yet
- ADR ReviewerDocument29 pagesADR ReviewerferosiacNo ratings yet
- Sublimation and Melting Point Determination of Benzoic AcidDocument3 pagesSublimation and Melting Point Determination of Benzoic AcidAj Guanzon100% (1)
- Republic Act No 9679 PAG IBIGDocument17 pagesRepublic Act No 9679 PAG IBIGJnot VictoriknoxNo ratings yet
- Land Acquisition OFWs.070605Document5 pagesLand Acquisition OFWs.070605Jai CarungayNo ratings yet
- RA9485 Anti-Red Tape ActDocument17 pagesRA9485 Anti-Red Tape ActVinz G. VizNo ratings yet
- TB NegoDocument30 pagesTB NegoAj GuanzonNo ratings yet
- SSS LawDocument29 pagesSSS LawnonecoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 7640: Chan Robles Virtual Law LibraryDocument2 pagesRepublic Act No. 7640: Chan Robles Virtual Law LibraryAj GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Kerkvliet - Toward A More ComprehensiveDocument19 pagesKerkvliet - Toward A More ComprehensiveAj GuanzonNo ratings yet
- 8 49 AP Garb Vs Carp OkDocument6 pages8 49 AP Garb Vs Carp OkAj GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Rules Implementing Code of Conduct for Public OfficialsDocument18 pagesRules Implementing Code of Conduct for Public OfficialsicebaguilatNo ratings yet
- Revisiting The MonopolyDocument3 pagesRevisiting The MonopolyAj GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Pidspn 0908Document6 pagesPidspn 0908Aj GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Problem Set #2: Multiple ChoiceDocument8 pagesProblem Set #2: Multiple ChoiceAj GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Problem Set #4 Multiple Choice on Supply and DemandDocument16 pagesProblem Set #4 Multiple Choice on Supply and DemandAj GuanzonNo ratings yet
- The Failure of The Philippine Presidential System - 2004Document13 pagesThe Failure of The Philippine Presidential System - 2004Aj GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Charter Change ArticleDocument12 pagesCharter Change ArticleAj GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 3019 (RA 3019) - Anti-Graft LawDocument5 pagesRepublic Act 3019 (RA 3019) - Anti-Graft LawJun RinonNo ratings yet
- ps1 Eco110Document9 pagesps1 Eco110Chitrakalpa SenNo ratings yet
- Chua V Mesina PDFDocument7 pagesChua V Mesina PDFAj GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Phonological ProcessesDocument1 pagePhonological ProcessesAj GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Problem Set #3 MCQsDocument5 pagesProblem Set #3 MCQsAj Guanzon100% (1)
- Language: Derakuruzu, Guanzon, YumulDocument61 pagesLanguage: Derakuruzu, Guanzon, YumulAj GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Underplate GroutingDocument1 pageUnderplate GroutingminedataNo ratings yet
- Revison 5 - Adverbs of TimeDocument50 pagesRevison 5 - Adverbs of Timeluis fernandoNo ratings yet
- Travelstar 25GS, 18GT, & 12GN: Quick Installation GuideDocument2 pagesTravelstar 25GS, 18GT, & 12GN: Quick Installation Guidebim2009No ratings yet
- Laser Light PriceDocument5 pagesLaser Light Priceluis palominoNo ratings yet
- Curso AutoturnDocument66 pagesCurso AutoturnMiorga88No ratings yet
- Challenges of Deep Excavation for KVMRT StationsDocument85 pagesChallenges of Deep Excavation for KVMRT StationsAlwin AntonyNo ratings yet
- EN 1090 White Paper17 119019 PDFDocument24 pagesEN 1090 White Paper17 119019 PDFZaza PokumbaNo ratings yet
- Crane Company Within SingaporeDocument4 pagesCrane Company Within SingaporeRash AcidNo ratings yet
- Organization Management and LeadershipDocument26 pagesOrganization Management and LeadershipOtilia BadeaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2: Quarter 1 - Module 1Document35 pagesPractical Research 2: Quarter 1 - Module 1Alvin Sinel Belejerdo90% (10)
- Casey Cannon: EducationDocument1 pageCasey Cannon: Educationapi-355305449No ratings yet
- Process Validation - SDF - 1 - FDA PDFDocument111 pagesProcess Validation - SDF - 1 - FDA PDFdipakrussiaNo ratings yet
- Katalog Ag-700 To Ag-800Document1 pageKatalog Ag-700 To Ag-800Iqbal AbugindaNo ratings yet
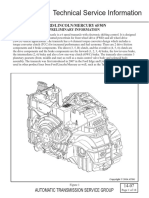
- Technical Service Information: Ford/Lincoln/Mercury 6F50NDocument18 pagesTechnical Service Information: Ford/Lincoln/Mercury 6F50NPlanta Damiana2No ratings yet
- 2.5 PsedoCodeErrorsDocument35 pages2.5 PsedoCodeErrorsAli RazaNo ratings yet
- Fugacity CoefficientDocument4 pagesFugacity Coefficientsigit1058No ratings yet
- Analysis of Wood Bending PropertiesDocument11 pagesAnalysis of Wood Bending Propertiesprasanna020391100% (1)
- Management Quality ManagementDocument7 pagesManagement Quality ManagementJasmine LimNo ratings yet
- Fostering Innovation Through Experiential LearningDocument14 pagesFostering Innovation Through Experiential LearningAndrew TranNo ratings yet
- The Nigerian Marketing System Its Development - Problems and ProspectsDocument8 pagesThe Nigerian Marketing System Its Development - Problems and ProspectsNwakor Maco Sochi100% (1)
- LP Fuel Gas SystemDocument6 pagesLP Fuel Gas SystemAnonymous QSfDsVxjZNo ratings yet
- Snowden Documents Demand 14 0714 PDFDocument4 pagesSnowden Documents Demand 14 0714 PDFSander BelouNo ratings yet
- KaduwaDocument34 pagesKaduwaRohini WidyalankaraNo ratings yet
- Anlage C DQC III-18 La DQC IV-18 LaDocument5 pagesAnlage C DQC III-18 La DQC IV-18 LaPEDRONo ratings yet
- Uncertainty in Measurements - Lab ReportDocument4 pagesUncertainty in Measurements - Lab ReportStaniaNo ratings yet
- BS en 13035-9-2006 + A1-2010Document24 pagesBS en 13035-9-2006 + A1-2010DoicielNo ratings yet
- India: 1UBK7-470E1Document67 pagesIndia: 1UBK7-470E1harish kumar100% (1)
- Odato G-7 LP HomonymsDocument11 pagesOdato G-7 LP HomonymsIvy OdatoNo ratings yet
- ST 30 PDFDocument2 pagesST 30 PDFafiffathin_akramNo ratings yet
- ESDIS05161 DMP For DPs Template PDFDocument15 pagesESDIS05161 DMP For DPs Template PDFneerajshukla246829No ratings yet