Professional Documents
Culture Documents
KGSG
Uploaded by
Anonymous V9E1ZJtwoEOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
KGSG
Uploaded by
Anonymous V9E1ZJtwoECopyright:
Available Formats
INTRODUCTION TO KGSG BANK
Mahatma Gandhi , the father of nation, once said "Eighty percent of the Indian population lives in villages and most of them live below poverty line. We should therefore formulate such plans and schemes which are beneficial to weakest person of the society also. If the poor people are not brought into mainstream of development, the total development of India will not be possible." Our Prime Minister Late Mrs. Indira Gandhi initially nationalized 14 commercial banks with the intention that these institutions would float credit in social activities and rural development. But after 06 years of nationalization she realized that nothing concrete could be achieved. She then brought in an ordinance on 2nd October,1975 (Date of Birth of our beloved Bapu and Lal Bahadur Shastri ji) to set up the Regional Rural Banks with the object to accelerate the development of rural economy. The aim was to attain upliftment of the poor, the neglected and the down trodden people by channelising the flow of credit to the rural areas.
The Regional Rural Banks were local in structure and were based at the District level. The Lead Banks were given the responsibility of sponsoring these RRBs. The paid up capital was subscribed by the central government, sponsoring bank and state government in the ratio of 50:35:15.In a slow but steady process 196 RRBs were established in 615 districts across the country. The ordinance of 2nd October,1975 came to be recognized as Regional Rural Banks Act,1976 and there were 15155 branches up to 20th July,2009 with approximately 69000 employees serving the country.
Union Bank of India sponsored 4 RRBs in India of which 3 were in the state of Uttar Pradesh. These three Banks were Kashi Gramin Bank, Gomti Gramin Bank and Samyut Kshetriya Gramin Bank. Samyut Kshetriya Gramin Bank, with its headquarter at Azamgarh was established on January 06, 1976. It covered 4 districts (Azamgarh, Ghazipur, Mau and Ambedkar Nagar) with a network of 168 branches and 5 extension counters. A total of 929 staff members served a population of approximately 9092458 people covering 20 tehsils and 56 development blocks. By the end of March, 2005 there were deposits of Rs.11443674 thousand with 61:39 demand term ratio. The total advances of SKGB stood at Rs.2736661 thousand with CD ratio of 23.91% basic. The bank issued 13422 Kisan Credit Cards to farmers by the end of March, 2005.
Gomti Gramin Bank was established on 30th March, 1981 with its Head Office at Jaunpur. It had 84 branches covering 6 tehsils and 21 blocks. There were 376 employees by the end of March, 2005. The Gomti Gramin Bank set the following vision "Our endeavor: Integrated Development". The bank mobilized deposits worth Rs.5471912 thousand with a demand term ratio of 51:49. By the end of March, 05, the outstanding advances were Rs.1693384 thousand. The bank made a continuous effort to improve credit flow by meeting its financial targets to provide credit to target as well as non target group of borrowers. By the end of March, 05 the CD ratio of the bank was 31.69% and it had issued12558 Credit Cards to the farmers.
Kashi Gramin Bank headquartered in Varanasi was established on 28th July 1981 with a view to cater the needs of rural and downtrodden people of Kashi, the oldest city on the earth. By the end of March, 2005 Kashi Gramin Bank was able to cater to the needs of 65520 customers and had an outstanding of Rs.1971694 thousand of advances. With 82 branches and 368 employees the Bank was able to inculcate the habit of saving among rural and semi urban masses since it had taken its banking services to their door step. By March, 2005 the Bank had deposits worth Rs.5212553 thousand. In 2004 the Kashi Gramin Bank was rated as one of the top SIX RRBs in the country.
With the onset of Globalization and financial reforms all over the world, self dependency became the keyword in banking industry. This scenario put pressure on RRBs also which were hitherto concentrated on social banking. Banking industry was very intensively growing and RRBs had to face extreme competitive environment as soon as they tried to capture the non target group customers. India was rapidly sailing on the tides of financial reforms. The banking industry was trying to make big bases by way of consolidation. There were no choices left to Government of India than to consolidate the RRBs. In this process the government of India embarked upon a process of amalgamation of RRBs which were adjacently situated and sponsored by the same sponsoring bank. Due to this process of amalgamation the number of RRBs has reduced from 196 to 83 with 15155 branches which cover 615 districts of the country. 68476 employees are serving the rural as well as urban mass of the country.
In this process Kashi Gramin Bank, Gomti Gramin Bank and Samyut Kshetriya Gramin Bank sponsored by Union Bank of India in U.P. were amalgamated by GOI vide its notification No.SO-1264(E) on 12th September 2005. Thus came into existence the
"Kashi Gomti Samyut Gramin Bank"
On 12th September 2005, the bank owned a fund of Rs.23250 Crore with deposits to the tune of Rs.2137.87 Corer. Advances of Rs.648.27 Corer and a CD ratio of 30% as on 12th Sep'05. By the end of FY 2010-2011 KGSG Bank was having a total business of 5898 Crore with a 4586.90 Crore of deposits and 1311.31 Crore of advances with CD ratio of 30% and Net profit of Rs.11.36 crore. The bank also achieved the landmark of converting its 100 percent branches on Core Banking Platform. This was a historical event in banking industry that a RRB had achieved such a technical up gradation of its services and that too in a record time. The bank has taken the membership of BCSBI (Banking code & standard Board of India).The bank is also blessed with the achievement of launching Rupay ATM Card.
Branches 1)Region Wise
Azamgarh Bhadohi
Gazipur Jaunpur Varanasi
2)District Wise Ambedkar Nagar Azamgarh Bhadohi Chandauli Gazipur Jaunpur Mau
TECHNOLOGY In the wake of ongoing changes in the financial sector and trends which indicate a move towards globalization and liberalization of the Indian economy, the market environment in the country has undergone a major change.
Reforms in the financial sector and entry of private and foreign banks along with new generation technology have changed the face of Indian banking sector. To respond to the aforesaid challenges, RRBs of Eastern U.P. sponsored by Union Bank of India have been amalgamated and a bigger and stronger bank has emerged.
Embracing technology has become the need of the day. Technology is fast becoming an integral part of banking business. The bank has taken steps to keep pace with the technological changes.
Core Banking Solution
The Bank has been constantly endeavoring to leverage the advancements in Information Technology and Communication network with a view to :
Introduce new techno-centric products Enhance customer convenience Increase efficiency in operations Build up multiple delivery channels
The Bank has embarked upon massive technology based transformation through technology process in the form of implementation of Core Banking Solution. The Bank has engaged M/s Wipro, a leading service provider in IT enabled services for providing end-to-end solution for networking. It is backed by "Finacle" software support from M/s Infosys Technologies Ltd. The Core Banking System bundles a host of customer friendly services.
The Bank has its Data Centre at Prabha Devi, Mumbai and the Disaster Recovery Site at Bengaluru to ensure business continuity. All the branches of the bank are under CBS. Pursuant to the above technological initiative we are focusing on development of new business models that will include formulating new products
and services for serving the banks customer better. Efforts at revitalizing the entire rank and file of the Bank, to give sharper focus to customer satisfaction and delight are also underway.
Following facilities / Services are being provided to the banks customer
Access to customer account from any of our branch. Account Portability RTGS & NEFT - Fund transfer facilities ATM - Inter operable ATM cards to our customers who can use the ATM of Union Bank as their own ATM machine
Rupay enabled ATM Cards acceptable on any ATM in India.
Many more services and products are on the anvil.
You might also like
- OBC Bank Report HistoryDocument38 pagesOBC Bank Report HistoryppschadhaNo ratings yet
- Project On Rural Banking in India 15-01-2023Document74 pagesProject On Rural Banking in India 15-01-2023Praveen ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Rural MantraDocument8 pagesRural MantrajogipaulNo ratings yet
- Bank of Maharashtra ProjectDocument39 pagesBank of Maharashtra Projectchakshyutgupta76% (21)
- Profile State Bank of MysoreDocument5 pagesProfile State Bank of MysoreNagnath B HalgondeNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development of Regional Rural Banks: Case Study of Two Major RrbsDocument16 pagesGrowth and Development of Regional Rural Banks: Case Study of Two Major RrbsProf S P GargNo ratings yet
- Bank of Maharashtra: A History of Service and GrowthDocument51 pagesBank of Maharashtra: A History of Service and GrowthSantosh BarikNo ratings yet
- IBPS RRB CWE III Quick Reference Guide 2014Document58 pagesIBPS RRB CWE III Quick Reference Guide 2014ilakkikarthiNo ratings yet
- State Bank of India: 1.paid Up Capital& Reserve S 2. Deposits 3. Advance S 4. Gross Investme NTDocument5 pagesState Bank of India: 1.paid Up Capital& Reserve S 2. Deposits 3. Advance S 4. Gross Investme NTalansamqlnNo ratings yet
- Customer Satisfaction of J&K BankDocument60 pagesCustomer Satisfaction of J&K BankSabahatRazaNo ratings yet
- Software To Make Cooperaie Banking EasierDocument11 pagesSoftware To Make Cooperaie Banking EasierSIDDARTH BADAJENANo ratings yet
- Indian Banking Industry Profile: Evolution, Key Players & Future OutlookDocument54 pagesIndian Banking Industry Profile: Evolution, Key Players & Future OutlookRhea SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Indian Bank: Profile of The BankDocument16 pagesIndian Bank: Profile of The BankJagan NathanNo ratings yet
- Industry Profile Banking Industry in India:: Study On Agricultural Credit Facility of Canara BankDocument66 pagesIndustry Profile Banking Industry in India:: Study On Agricultural Credit Facility of Canara BankGoutham BindigaNo ratings yet
- About Privet Banking Sector in IndiaDocument11 pagesAbout Privet Banking Sector in IndiaRakesh MalusareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document14 pagesChapter 1Bharat NirmaleNo ratings yet
- Credit Appraisal in Sbi Bank Project6 ReportDocument106 pagesCredit Appraisal in Sbi Bank Project6 ReportVenu S100% (1)
- Punjab State Cooperative Bank 1 (Repaired)Document60 pagesPunjab State Cooperative Bank 1 (Repaired)DeepikaSaini75% (4)
- New Major ProjectDocument50 pagesNew Major Projectgeetumittal65No ratings yet
- Allahabad BankDocument9 pagesAllahabad BankMegha JainNo ratings yet
- State Bank of SaurashtraDocument83 pagesState Bank of SaurashtraHitendrasinh ZalaNo ratings yet
- HUMAN RESOURCE STRATEGIES AT SBIDocument26 pagesHUMAN RESOURCE STRATEGIES AT SBIAmul KapoorNo ratings yet
- Dhanlaxmi Bank: Name ChangeDocument5 pagesDhanlaxmi Bank: Name ChangeSUDEVJYOTHISINo ratings yet
- Hyderabad, Telangana India State Bank of India HyderabadDocument4 pagesHyderabad, Telangana India State Bank of India HyderabadERAKACHEDU HARI PRASADNo ratings yet
- Karur Vysya Bank: Key To SuccessDocument6 pagesKarur Vysya Bank: Key To SuccessShandeep Singh DhanoaNo ratings yet
- Recent Trends in BankingDocument16 pagesRecent Trends in BankingManisha S. BhattNo ratings yet
- 11 Chapter 1Document39 pages11 Chapter 1Divyanshi JainNo ratings yet
- Profile of SBIDocument15 pagesProfile of SBIkarthikrishnaNo ratings yet
- Rural BankingDocument22 pagesRural BankingGungun KumariNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Banking in IndiaDocument41 pagesAn Overview of Banking in IndiaVinay SudaniNo ratings yet
- Project of SyndicaticDocument42 pagesProject of SyndicaticSaad KalaveNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Banking Sector & SbiDocument106 pagesIntroduction To Banking Sector & Sbiaparajitha lalasaNo ratings yet
- Syndicate Bank InterviewDocument17 pagesSyndicate Bank Interviewashishh1327No ratings yet
- State Bank of India: India's Largest BankDocument12 pagesState Bank of India: India's Largest BankpreetighNo ratings yet
- ANUP College 1Document49 pagesANUP College 1NMA NMANo ratings yet
- Dhanalaxmi Bank: A Leading Private Sector Bank in South IndiaDocument4 pagesDhanalaxmi Bank: A Leading Private Sector Bank in South IndiaYkartheek GupthaNo ratings yet
- ZXXZXXDocument14 pagesZXXZXXVishal VishNo ratings yet
- Company Introduction of Punjab Sind BankDocument9 pagesCompany Introduction of Punjab Sind BankHarsh GogiaNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On Non-Performing Assets of Bank of MaharashtraDocument80 pagesA Project Report On Non-Performing Assets of Bank of MaharashtraBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)No ratings yet
- Andhra BankDocument3 pagesAndhra BankAshis karmakarNo ratings yet
- Punjab State Cooperative BankDocument58 pagesPunjab State Cooperative BankRavneet Singh75% (4)
- Rural Banking ProjectDocument55 pagesRural Banking ProjectDelisa Misquitta0% (1)
- Lucknow Model Institute of Management, Lucknow: Summer Training Project Report ONDocument88 pagesLucknow Model Institute of Management, Lucknow: Summer Training Project Report ONManjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- January 2016 1451979191 13Document4 pagesJanuary 2016 1451979191 13amit yadavNo ratings yet
- Main DataDocument59 pagesMain Datachinmay parsekarNo ratings yet
- Upendra Ananth Pai T. M. A. Pai Vaman Srinivas Kudva Government of India Manipal Canara BankDocument5 pagesUpendra Ananth Pai T. M. A. Pai Vaman Srinivas Kudva Government of India Manipal Canara BankrahulNo ratings yet
- Regional Rural BankDocument26 pagesRegional Rural BankVijayeta Nerurkar100% (1)
- Technological Changes in Indian BankingDocument10 pagesTechnological Changes in Indian Bankinganilmourya5No ratings yet
- Rural Banking in India: A Study of Regional Rural BanksDocument10 pagesRural Banking in India: A Study of Regional Rural BanksNaresh KhutikarNo ratings yet
- Industry Analysis On Banking IndustryDocument6 pagesIndustry Analysis On Banking IndustryPulkit JainNo ratings yet
- Institutional Financial ManagementDocument24 pagesInstitutional Financial ManagementPEDAVALLI LAKSHMANNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Banking Sector & SbiDocument107 pagesIntroduction To Banking Sector & SbiTanushreeNo ratings yet
- Banking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingFrom EverandBanking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingNo ratings yet
- T R A N S F O R M A T I O N: THREE DECADES OF INDIA’S FINANCIAL AND BANKING SECTOR REFORMS (1991–2021)From EverandT R A N S F O R M A T I O N: THREE DECADES OF INDIA’S FINANCIAL AND BANKING SECTOR REFORMS (1991–2021)No ratings yet
- Regional Rural Banks of India: Evolution, Performance and ManagementFrom EverandRegional Rural Banks of India: Evolution, Performance and ManagementNo ratings yet
- Financial Inclusion for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises in Kazakhstan: ADB Support for Regional Cooperation and Integration across Asia and the Pacific during Unprecedented Challenge and ChangeFrom EverandFinancial Inclusion for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises in Kazakhstan: ADB Support for Regional Cooperation and Integration across Asia and the Pacific during Unprecedented Challenge and ChangeNo ratings yet
- Access to Finance: Microfinance Innovations in the People's Republic of ChinaFrom EverandAccess to Finance: Microfinance Innovations in the People's Republic of ChinaNo ratings yet
- Asia Small and Medium-Sized Enterprise Monitor 2020: Volume IV: Technical Note—Designing a Small and Medium-Sized Enterprise Development IndexFrom EverandAsia Small and Medium-Sized Enterprise Monitor 2020: Volume IV: Technical Note—Designing a Small and Medium-Sized Enterprise Development IndexNo ratings yet
- Finding Balance 2019: Benchmarking the Performance of State-Owned Banks in the PacificFrom EverandFinding Balance 2019: Benchmarking the Performance of State-Owned Banks in the PacificNo ratings yet
- Gender Tool Kit: Micro, Small, and Medium-Sized Enterprise Finance and DevelopmentFrom EverandGender Tool Kit: Micro, Small, and Medium-Sized Enterprise Finance and DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Baba Caterers: To, The Coordinator Refreshment Committee Institute Day Celebration Institute of Science, BHU, VaranasiDocument4 pagesBaba Caterers: To, The Coordinator Refreshment Committee Institute Day Celebration Institute of Science, BHU, VaranasiAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- Attitude of Secondary School Students of Ballia District Towards Online LearningDocument4 pagesAttitude of Secondary School Students of Ballia District Towards Online LearningAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- Summer Training ReportDocument77 pagesSummer Training ReportAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- Housing Finance Services in Kerala: A Study of HDFC and LICDocument1 pageHousing Finance Services in Kerala: A Study of HDFC and LICAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- DLWDocument83 pagesDLWAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement DMPGDocument1 pageAcknowledgement DMPGAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- DLWDocument83 pagesDLWAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- DK'KH Fgunw Fo'Ofo - Ky : Lire Izxfr IzfrosnuDocument9 pagesDK'KH Fgunw Fo'Ofo - Ky : Lire Izxfr IzfrosnuAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- Project Report On Online Examination System: Submitted To Submitted By: Pooja Yadav Pinky Singh Bca Vi SemDocument2 pagesProject Report On Online Examination System: Submitted To Submitted By: Pooja Yadav Pinky Singh Bca Vi SemAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- Usiky Ls ÇDKF'KR Usikyh HKK"KK Ds Çeq (K Nsfud Lekpkj I Ksa DK Vè UDocument2 pagesUsiky Ls ÇDKF'KR Usikyh HKK"KK Ds Çeq (K Nsfud Lekpkj I Ksa DK Vè UAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- Shri Baldev P.G. College - Varanasi: Project On NutritonDocument1 pageShri Baldev P.G. College - Varanasi: Project On NutritonAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- Summer InternshipDocument4 pagesSummer InternshipAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- 1.1 Gaunyle: The Good Will Project Jan.23,2017)Document40 pages1.1 Gaunyle: The Good Will Project Jan.23,2017)Anonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- Working Capital ProjectDocument64 pagesWorking Capital Projectbhawna sonaikar81% (21)
- Patanjali's growth and PESTLE analysisDocument87 pagesPatanjali's growth and PESTLE analysisAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoE80% (20)
- Ananya DissertationDocument33 pagesAnanya DissertationAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- OC-77 Selection LetterDocument4 pagesOC-77 Selection LetterAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- A Study of The Prospective Teachers' Attitude Towaeds 1 Semester Theory Papers of Two Year B.Ed. Programme of Banaras Hindu UniversityDocument7 pagesA Study of The Prospective Teachers' Attitude Towaeds 1 Semester Theory Papers of Two Year B.Ed. Programme of Banaras Hindu UniversityAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- Er BankingDocument1 pageEr BankingAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- University of HyderabadDocument1 pageUniversity of HyderabadAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- Invoice: Address: Phone: Fax EmailDocument2 pagesInvoice: Address: Phone: Fax EmailAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- Investors PerceptionsDocument65 pagesInvestors PerceptionsAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- ZeerasDocument96 pagesZeerasAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- Summer Training at Coca-ColaDocument5 pagesSummer Training at Coca-ColaAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- Ph.D. Thesisi ReportDocument3 pagesPh.D. Thesisi ReportAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
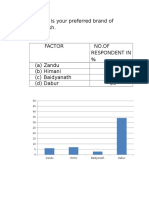
- Q1 What Is Your Preferred Brand of ChawanprashDocument12 pagesQ1 What Is Your Preferred Brand of ChawanprashAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- Resume Anita KumariDocument2 pagesResume Anita KumariAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- Prashant DubeyDocument106 pagesPrashant DubeyAnonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- Combined Defence Services Examination (II) 2016 11636836879 सं यु d땜 र行⊭ा से वा परी行⊭ा (II) 2016Document1 pageCombined Defence Services Examination (II) 2016 11636836879 सं यु d땜 र行⊭ा से वा परी行⊭ा (II) 2016Anonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- Combined Defence Services Examination (II) 2016 11636836879 सं यु d땜 र行⊭ा से वा परी行⊭ा (II) 2016Document1 pageCombined Defence Services Examination (II) 2016 11636836879 सं यु d땜 र行⊭ा से वा परी行⊭ा (II) 2016Anonymous V9E1ZJtwoENo ratings yet
- Merger of HDFC and Centurion Bank of Punjab Motives and Deal StructureDocument2 pagesMerger of HDFC and Centurion Bank of Punjab Motives and Deal Structureanant ashwaryaNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Accounting Process and RulesDocument14 pagesUnit-2 Accounting Process and RulesSameer XalkhoNo ratings yet
- Global Reciprocal College Receivable Financing DocumentDocument10 pagesGlobal Reciprocal College Receivable Financing Documentsharielles /No ratings yet
- Attra Infotech PVT LTD: Ratings Reaffirmed Summary of Rating ActionDocument7 pagesAttra Infotech PVT LTD: Ratings Reaffirmed Summary of Rating ActionCharan gowdaNo ratings yet
- What Is The CIMB Lazada Prepaid Mastercard Account?Document7 pagesWhat Is The CIMB Lazada Prepaid Mastercard Account?Daniel LowNo ratings yet
- MMW Finals ReviewerDocument4 pagesMMW Finals ReviewerChicken PizzaNo ratings yet
- Account StatementDocument2 pagesAccount Statement4pryh89mg4No ratings yet
- Project Report On Punjab National Bank AakashDocument68 pagesProject Report On Punjab National Bank Aakashaakash_saxena8235356681% (16)
- Summery: Conventional Branches 421Document22 pagesSummery: Conventional Branches 421Malik Talha AhmadNo ratings yet
- Application Form For Project FinancingDocument5 pagesApplication Form For Project FinancingVrds GunturNo ratings yet
- Pretest - Cash and ReceivablesDocument5 pagesPretest - Cash and ReceivablesMycah AliahNo ratings yet
- Environmental Factors Idbi - Bank - FinalDocument47 pagesEnvironmental Factors Idbi - Bank - FinalPramod ShawNo ratings yet
- BK Form II Format 2022Document256 pagesBK Form II Format 2022ALE MEDIANo ratings yet
- Essentials of Investment 1Document12 pagesEssentials of Investment 1tahrimafaruqNo ratings yet
- Central bank financial strength and credibilityDocument2 pagesCentral bank financial strength and credibilityManavNo ratings yet
- Farhan ReportDocument73 pagesFarhan ReportFurkan BelimNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument95 pagesProject ReportPragya DixitNo ratings yet
- Problems CceDocument4 pagesProblems CceajkoywatanabeeexxNo ratings yet
- Administer Financial AccountDocument14 pagesAdminister Financial Accountsadiya AbrahimNo ratings yet
- Porter'S Five Forces (Banking and Finance)Document2 pagesPorter'S Five Forces (Banking and Finance)Tanu SinghNo ratings yet
- Statement of account summaryDocument4 pagesStatement of account summaryShaikh MohammedNo ratings yet
- CBDC For Commercial Banks - Part 2Document5 pagesCBDC For Commercial Banks - Part 2amul_muthaNo ratings yet
- IBF Time Value Problems With SolutionsDocument41 pagesIBF Time Value Problems With SolutionsasaandNo ratings yet
- History of Trade and Commerce - 11th CBSE - TutelageAllTimeDocument10 pagesHistory of Trade and Commerce - 11th CBSE - TutelageAllTimeTutelagealltimeNo ratings yet
- Loan EMI Table: Loan Number Loan Booked Date Loan Type Principal Amount Interest Rate Tenure O/S PrincipalDocument1 pageLoan EMI Table: Loan Number Loan Booked Date Loan Type Principal Amount Interest Rate Tenure O/S PrincipalBalamurugan ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Banking Services of Prabhu BankDocument10 pagesBanking Services of Prabhu Bankशिवम कर्णNo ratings yet
- Payment Methods - Cheques: Clearing SystemDocument2 pagesPayment Methods - Cheques: Clearing SystemCephas PanguisaNo ratings yet
- VISA Classic: Getting Yourself StartedDocument3 pagesVISA Classic: Getting Yourself Startedkarely jackson lopez100% (1)
- (Xii) 2023 Solved Sample Target Paper Bank, C.G, PST, Acc, Stats by Sir IrfanDocument34 pages(Xii) 2023 Solved Sample Target Paper Bank, C.G, PST, Acc, Stats by Sir IrfanMosa AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document5 pagesChapter 7Jesther John VocalNo ratings yet