Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Domain Name System: Uniform Resource Locator
Uploaded by
swarnimajainOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Domain Name System: Uniform Resource Locator
Uploaded by
swarnimajainCopyright:
Available Formats
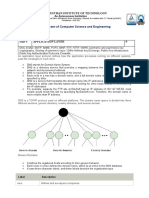
DOMAIN NAME SYSTEM The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical distributed naming system for computers, services,
or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the participating entities. A Domain Name Service resolves queries for these names into IP addresses for the purpose of locating computer services and devices worldwide. By providing a worldwide, distributed keyword-based redirection service, the Domain Name System is an essential component of the functionality of the Internet. An often-used analogy to explain the Domain Name System is that it serves as the phone book for the Internet by translating human-friendly computer hostnames into IP addresses. For example, the domain name www.example.com translates to the addresses 192.0.43.10 (IPv4) and 2620:0:2d0:200::10 (IPv6). Unlike a phone book, however, DNS can be quickly updated and these updates distributed, allowing a service's location on the network to change without affecting the end users, who continue to use the same hostname. Users take advantage of this when they recite meaningful Uniform Resource Locators (URLs) and e-mail addresses without having to know how the computer actually locates the services. The Domain Name System distributes the responsibility of assigning domain names and mapping those names to IP addresses by designating authoritative name servers for each domain. Authoritative name servers are assigned to be responsible for their particular domains, and in turn can assign other authoritative name servers for their sub-domains. This mechanism has made the DNS distributed and fault tolerant and has helped avoid the need for a single central register to be continually consulted and updated. Additionally, the responsibility for maintaining and updating the master record for the domains is spread among many domain name registrars, who compete for the end-user's, domain-owner's, business. Domains can be moved from registrar to registrar at any time. The Domain Name System also specifies the technical functionality of this database service. It defines the DNS protocol, a detailed specification of the data structures and communication exchanges used in DNS, as part of the Internet Protocol Suite. UNIFORM RESOURCE LOCATOR Uniform Resource Locator (URL) it is the global address of documents and other resources on the World Wide Web. The first part of the URL is called a protocol identifier and it indicates what protocol to use, and the second part is called a resource name and it specifies the IP address or the domain name where the resource is located. The protocol identifier and the resource name are separated by a colon and two forward slashes. For example, the two URLs below point to two different files at the domain pcwebopedia.com. The first specifies an executable file that should be fetched using the FTP protocol; the second specifies a Web page that should be fetched using the HTTP protocol:
ftp://www.pcwebopedia.com/stuff.exe http://www.pcwebopedia.com/index.html A URL is one type of Uniform Resource Identifier (URI); the generic term for all types of names and addresses that refer to objects on the World Wide Web. The term "Web address" is a synonym for a URL that uses the HTTP / HTTPS protocol. The Uniform Resource Locator (URL) was developed by Tim Berners-Lee in 1994 and the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) URI working group
You might also like
- Domain Name SystemDocument8 pagesDomain Name SystemAmeer SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Engleza - Domain Name SystemDocument4 pagesEngleza - Domain Name SystemiulianBuhusNo ratings yet
- Domain Name SystemDocument8 pagesDomain Name SystemSrishti AroraNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, Email Verification, Header Analysis, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some SMTP Testing, Email Verification, Header Analysis, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document19 pagesChapter 5minichelagumas143No ratings yet
- Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WP Email Tools: Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WP Email Tools: Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsNo ratings yet
- DNS Server MechanismDocument14 pagesDNS Server MechanismAshesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Internet Technology: Assignment1Document17 pagesInternet Technology: Assignment1Manal FaluojiNo ratings yet
- NSA LO1 - ThabangDocument42 pagesNSA LO1 - ThabangThabang Llyod MompatiNo ratings yet
- 1.1 What Is A Computer Network?Document9 pages1.1 What Is A Computer Network?Mmichael123456789No ratings yet
- CMSCDocument2 pagesCMSCEmmanuel CristobalNo ratings yet
- The Business of Domain Names - Nicolae Sfetcu 2014Document154 pagesThe Business of Domain Names - Nicolae Sfetcu 2014Priscilla Felicia HarmanusNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document65 pagesUnit 1Sweeti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Nomi Lab AssignmentDocument3 pagesNomi Lab AssignmentQasim CheemaNo ratings yet
- Application Layer ProtocolsDocument33 pagesApplication Layer ProtocolsSarah AliNo ratings yet
- Website 1Document51 pagesWebsite 1محمد احمدNo ratings yet
- Domain Name System - Internet PDFDocument8 pagesDomain Name System - Internet PDFp-jornNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 CNDocument28 pagesUnit 5 CNkumargpj7091No ratings yet
- Internet EssentialsDocument37 pagesInternet EssentialsOnel Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- DNS LDocument2 pagesDNS Lruh solNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument22 pagesComputer NetworksRISHINo ratings yet
- Understanding the InternetDocument4 pagesUnderstanding the InternetLokendra Kumar TiwariNo ratings yet
- Domain Name SystemDocument39 pagesDomain Name SystemRavi SrinivasNo ratings yet
- How Domain Name Servers Work: Name Servers Without Even Realizing It. Domain Name Servers, or DNS, Are An IncrediblyDocument5 pagesHow Domain Name Servers Work: Name Servers Without Even Realizing It. Domain Name Servers, or DNS, Are An IncrediblyAzeem AsgharNo ratings yet
- CN Unit V R18Document27 pagesCN Unit V R18Sahithi Priya AttiliNo ratings yet
- IP AddressDocument6 pagesIP AddresssubbavelamaNo ratings yet
- DNSDocument19 pagesDNSAkash BhaiyyeNo ratings yet
- "At The Beginning There Was Nothing, Then Came Internet ": Babu Melepuram Sr. LecturerDocument18 pages"At The Beginning There Was Nothing, Then Came Internet ": Babu Melepuram Sr. Lecturermurali.ts1No ratings yet
- Web System & Development Assignment #2Document1 pageWeb System & Development Assignment #2Kevin LazagaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Application LayerDocument12 pagesUnit 6 Application Layernirjan ghimireNo ratings yet
- Internet Web Programming N Srinibha Rao 19BCI0245: Explain About The Domain Name SystemDocument6 pagesInternet Web Programming N Srinibha Rao 19BCI0245: Explain About The Domain Name SystemSrinibha RaoNo ratings yet
- Application Layer Protocols in Computer Networks 17.01.2024Document8 pagesApplication Layer Protocols in Computer Networks 17.01.2024aloishp36No ratings yet
- Network 5Document20 pagesNetwork 5ranjithdesiganNo ratings yet
- How Fast-Flux Service Networks Work - The Honeynet ProjectDocument1 pageHow Fast-Flux Service Networks Work - The Honeynet ProjectddroNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Fundamentals of Web, XHTML A Brief Introduction About The Internet 1) OriginsDocument58 pagesUnit 1 - Fundamentals of Web, XHTML A Brief Introduction About The Internet 1) OriginsprajakNo ratings yet
- Domain Name System (DNS)Document13 pagesDomain Name System (DNS)suneelkluNo ratings yet
- Unit-1.2 Internet and World Wide WebDocument40 pagesUnit-1.2 Internet and World Wide Webco22352No ratings yet
- CN Unit 5Document37 pagesCN Unit 5chinnupyariNo ratings yet
- Lecture11 - Domain Name SystemDocument7 pagesLecture11 - Domain Name SystemViola NgigeNo ratings yet
- Batrisyia-C-WDD-Research - Server Technologies and Management ServicesDocument3 pagesBatrisyia-C-WDD-Research - Server Technologies and Management ServicesBatrisyia SainiNo ratings yet
- Application ProtocolsDocument28 pagesApplication Protocolsrez habloNo ratings yet
- LeDucAnh - GCS18856-đã chuyển đổi PDFDocument29 pagesLeDucAnh - GCS18856-đã chuyển đổi PDFl1111c1anh-5No ratings yet
- Computer Network Unit-5 NotesDocument44 pagesComputer Network Unit-5 NotessuchitaNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument17 pagesComputer NetworkER Jagdeep GurjarNo ratings yet
- DNS e WINSDocument12 pagesDNS e WINSThone Da Grécia SamuelNo ratings yet
- Lecture5 InternetDocument20 pagesLecture5 InternetEINSTEIN2DNo ratings yet
- ServersDocument5 pagesServersRahul KrNo ratings yet
- W5 - Distributed Naming ServiceDocument31 pagesW5 - Distributed Naming ServiceSabila KaylaNo ratings yet
- FON Unit IV - IoTDocument29 pagesFON Unit IV - IoT21d41a0513No ratings yet
- DRIVE THE WEB WITH A BROWSER TOURDocument11 pagesDRIVE THE WEB WITH A BROWSER TOURRohitToshniwalNo ratings yet
- Domain Name - WikipediaDocument12 pagesDomain Name - WikipediaMati ChalaNo ratings yet
- Definitions of DNS On The WebDocument2 pagesDefinitions of DNS On The WebEr Rahul AnandNo ratings yet
- Name-Shubhankar Kesari Id No - 19BAJMC024 Submitted To-Rishabh ChaudharyDocument5 pagesName-Shubhankar Kesari Id No - 19BAJMC024 Submitted To-Rishabh Chaudharyhardik anandNo ratings yet
- Small Notes Internet ApplicationsDocument4 pagesSmall Notes Internet Applicationsabdoolsaad90No ratings yet
- Domain Name System 8747 Nkl4jkuDocument23 pagesDomain Name System 8747 Nkl4jkumahendrarm2112No ratings yet
- Application Layer Protocols OverviewDocument39 pagesApplication Layer Protocols OverviewBRAHMA REDDY AAKUMAIIANo ratings yet
- Web Design and Devlopment Assignment 1Document16 pagesWeb Design and Devlopment Assignment 1Nurye NigusNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 10 Study of DNS, Remote Login, Use of Nslookup, Dig, FTP, Ping, TracerouteDocument11 pagesAssignment No. 10 Study of DNS, Remote Login, Use of Nslookup, Dig, FTP, Ping, Traceroutesaideep salokheNo ratings yet
- CN - 5Document37 pagesCN - 5SivaRamanNo ratings yet
- Assignment: 17Document12 pagesAssignment: 17Salman RazaNo ratings yet
- Tellabs 8609 PDFDocument3 pagesTellabs 8609 PDFnoe cceñua rupaillaNo ratings yet
- How Do You Add Atom - Link With Rel - Self - To An Rss Document - Stack OverflowDocument4 pagesHow Do You Add Atom - Link With Rel - Self - To An Rss Document - Stack OverflowabeerNo ratings yet
- Aci From Scratch v2Document103 pagesAci From Scratch v2successor169No ratings yet
- Aruba AP-505 SpecDocument2 pagesAruba AP-505 SpecjalenetolasaNo ratings yet
- 13.3.2 Lab - Use Ping and Traceroute To Test Network ConnectivityDocument11 pages13.3.2 Lab - Use Ping and Traceroute To Test Network ConnectivityCao Bằng Thảo NguyênNo ratings yet
- VPC Best Practices BRKDCT-2378 PDFDocument91 pagesVPC Best Practices BRKDCT-2378 PDFHamza AbdelsalamNo ratings yet
- CCNA Exploration 1 Questions Answers BlogDocument15 pagesCCNA Exploration 1 Questions Answers BlogArturGusakNo ratings yet
- Link Layer: Computer Networking: A Top Down ApproachDocument66 pagesLink Layer: Computer Networking: A Top Down ApproachMuhammad FaisalNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument87 pagesUntitledNivlaisoka RomaNo ratings yet
- Cis 185 CCNP Route Chapter 3: Implementing OSPF: Rick Graziani Cabrillo College Graziani@cabrillo - Edu Spring 2015Document172 pagesCis 185 CCNP Route Chapter 3: Implementing OSPF: Rick Graziani Cabrillo College Graziani@cabrillo - Edu Spring 2015Hung Phan ThanhNo ratings yet
- B 1610 Lyr2 9400 CGDocument196 pagesB 1610 Lyr2 9400 CGgarmahis79No ratings yet
- MidsolDocument10 pagesMidsolAmeer El-SayedNo ratings yet
- MST maps VLANs to spanning tree instancesDocument6 pagesMST maps VLANs to spanning tree instancesv711No ratings yet
- Rl8008en Epon Olt User Manual-Cli - 20160513Document63 pagesRl8008en Epon Olt User Manual-Cli - 20160513بُنِي كفاح0% (1)
- Push Log Monitoring and Heartbeat TrackingDocument4 pagesPush Log Monitoring and Heartbeat TrackingTOP 10No ratings yet
- Dell Inspiron 5370 Armani13 MBDocument75 pagesDell Inspiron 5370 Armani13 MBtech kitabNo ratings yet
- SRT Protocol Technical OverviewDocument90 pagesSRT Protocol Technical OverviewgoaltechNo ratings yet
- RFC 6888Document15 pagesRFC 6888NelsonbohrNo ratings yet
- CLI Commands CCNA2Document12 pagesCLI Commands CCNA2Vilas ShahNo ratings yet
- Router Board Performance TestsDocument2 pagesRouter Board Performance TestsedkaviNo ratings yet
- Wireless Simulation Vanet - TCLDocument5 pagesWireless Simulation Vanet - TCLpiyushji125100% (1)
- Advanced Network Routing Algorithms and Protocols - 2022Document57 pagesAdvanced Network Routing Algorithms and Protocols - 2022Jiru MuletaNo ratings yet
- BOOK CiscoPress CCNA 200 301 Official Cert Guide Volume 1Document33 pagesBOOK CiscoPress CCNA 200 301 Official Cert Guide Volume 1usercool setNo ratings yet
- Intrinsically Safe EthernetDocument6 pagesIntrinsically Safe EthernetJairo FlechasNo ratings yet
- RRU BandsDocument15 pagesRRU BandsAdeel MunirNo ratings yet
- FRAGMENTATIONDocument13 pagesFRAGMENTATIONVinayKumarSingh100% (1)
- CT101 IntroductionToNetworkingDocument39 pagesCT101 IntroductionToNetworking2begeniusNo ratings yet
- Huawei Training Day 1 NotesDocument28 pagesHuawei Training Day 1 NotesMutumaNo ratings yet
- 4th-Week 1 and 4 Summative Test g11Document2 pages4th-Week 1 and 4 Summative Test g11Vincent LibreaNo ratings yet