Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sugar Mills in Pakistan
Uploaded by
Idrees Akbar RajputOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sugar Mills in Pakistan
Uploaded by
Idrees Akbar RajputCopyright:
Available Formats
NTRODUCTION Sugar is one of the essential commodities of life and plays important role in the dietary of human beings.
It is the cheapest food for purchasing energy as an Anna (1/16 of rupees) would buy 545 calorie when laid out on sugar as against 395 for bread, 182 for cheese and 190 for milk. In addition to an essential energy. It is the cheapest and most abundant pure organic chemical available to so many other industries as it is put to a wide variety of industrial use. e.g. in hair tonics, shoe polishes, photographic material explosives, tanning leather and silvering mirrors etc. It serves as a starting material for the synthesis of vitamin B2, also. There are different sources from which sugar is manufacturing, but sugar cane and sugar beets are the main sources of the word sugar supplies. Commercial sugar are also obtained from other plants such as maple, palms, coconuts and apple etc but only in negligible quantities, sugarcane, however, furnished almost two-third of world sugar supplies. Sugarcane, besides sugar, yield many other product like fiber molasses, industrially important acids and valuable maxise.
HISTORY OF SUGAR The origin of English word sugar can be traced back to age old Hindu civilization, when words like Sharkara. In Sansikrat and Sansikrat and Sakkara in prakrit existed to convey the same sense.Then it may be traced through all the Aryana languages, as schaker in Persian, sukkar in Arabic, sincer in Assyrian, zucchero in Italian, sucre in French, zucher in German, saccharum in Latin and ozucarin Spanish etc stand as Testimony for its origin from sharkara. It would thus clear that India is the birth place of the manufacturing of sugar from sugarcane.The history of modern sugar industries in India may be said to begain from 1932. Five factories, however, were started in 1932-1935 but excepting one, at Rahwali, all other enterprises failed due to their uneconomic size. Inadequate sugar cane supplies and inefficient management. At the time of partition we had the only factory at Rahwali in the Punjab. Hence we had to start with a scarth. Punjab is the second largest sugar cane growing province in Indo-Pakistan sub-continent.Now update position of sugar industries in Pakistan is 38 sugar factories in Punjab and 31 in Sindh and 6 in NWFP and Pakistan is now exporting sugar to other countries. DETAIL OF SUGAR MILLS IN PAKISTAN PUNJAB 1. Adam Chishtian Bahawalnagar 2. Ashraf Ashrafabad Bahawalpur 3. Baba Farid Okara Okara 4. Brothers Pattoki Kasur 5. Chanar Tandlianwala Faisalabad 6. Choudary Pensara Road Gojra 7. Chistia Sillianwali Sargodha 8. Crescent Nishatabad Faisalabad 9. Fatima Kot Addu Muzaffarghar 10. Fauji Sheikhupura Sheikhupura 11. Fecto Darya Khan Bhakkar Gojra Sam Gogra Faisalabad 13. Haseeb Waqas Mirajabad Nankana Sahib 14. Husein Jaranwala Faisalabad
15. Hyesons Jetha Bhutta Rahimyar Khan 16. Ittefaq Sahiwal Sahiwal 17. JDW Mouza Sharin Rahim Yar Khan 18. Kamalia Kamalia Tobatek singh 19. Kohinoor Jauharabad Khushab 20. Layyah Layyah Layyab 21. National Sargodha Sargodha 22. Noon Bhalwal Sargodha 23. Pasrur Pasrur Sialkot 24. Pattoki Pattoki Kasur 25. Phalia Karmanwala Gujrat 26. Punjab Man Channu Khanewal 27. Pahirianwali Lalian Jhang 28. Ramzan Chiniot Sargodha 29. Shahtaj Mandi Bahauddin Gujrat 30. Shakarganj Jhang Jhang . Sheikhoo Kot Addu Muzafargarh 32. Tandlianwala Kanjwani Faisalabad 33. United Sadiqabad Rahimyar Khan 34. Indus Kot Bahadur Rajan Pur 35. Madina Chattah Khankah Hafizabad 36. Qand Ghar Shahkot Faisalabad 37. Yousaf Shahpur Sargodha SINDH 38. Al-Abbas Mirwah Gorchani Mirpurkhas 39. Al-Asif Garho Thatta 40. Al-Noor Moro Naushero Feroz 41. Ansari Tando M.Khan Hyderabad 42. Army Welfare Badin Badin 43. Bawany Talhar Badin 44. Dadu Piarogoth Dadu 45. Dewan Budho Talpur Thatta 46. Faran Sheikh Bhirkio Hyderabad 47. Fauji-Kho Khoski Badin 48. Fauji TMK Tando M. Khan Hyderabad Habib Nawabshah Nawabshah 50. Kiran Rohri Sukkur 51. Khairpur Khairpur Khairpur 52. Larr Sajawal Thatta 53. Matiari Matiari Hyderabad 54. Mehran Tando M. Khan Hyderabad 55. Mirpurkhas Mirpurkhas Mirpurkhas 56. Mirza Kadhan Badin 57. Pangrio Deh Rajauri-2 Badin 58. Sakrand Sakrand Nawabshah 59. Sanghar Sindhri Sanghar 60. Shahmurad Jhok Sharif Thatta 61. Sindabadgar Deenpur Hyderabad 62. Thatta Deh Bijoro Thatta
63. Consolidated Ranipur Khairpur 64. Larkana Naudero Larkana N.W.F.P 65. Bannu Sarai Naurang Bannu 66. Chshma D.I. Khan D.I. Khan Frontier Takht-I-Bhai Mardan 68. Khazana Peshawar Peshawar 69. Premier Mardan Mardan 70. Saleem Charsadda Charsadda AZAD KASHMIR 71. Mian Mohammad Mirpur Azad Kashmir
Introduction to Organization:
The company was incorporated in Pakistan on September 19, 1964 as a public limited company and is listed at Karachi and Lahore stock exchanges of Pakistan. The company is principally engaged in the manufacture and sale of sugar. The company has set up a Particle Board unit. It is situated in Darya Khan. SHARE CAPITAL &RESERVES Authorized capital 15,000, 000 SharesOf Rs. 10 each Rs. 150, 000, 000 Issued, subscribed and paid up capital Rs. 50, 297, 280
Main product: The main product of the Chashma Sugar Mills is white crystalline sugar. BY PRODUCT: The by products are following 1 BAGGASSES 2 MALLASSES 3 PRESS MUD
DEPARTMENTS OF the ORGANIZATION There are six main departments in Indus Sugar Mills. i) Cane Department ii) Mechanical Deptt. iii) Chemical Deptt. iv) Electrical Deptt. v) Accounts Deptt. vi) Administration Deptt.
Companys Information:
CHAIRMAN: MR. GHULAM MUHAMMAD A. FECTO BOARD OF DIRECTORS: CHIEF EXECUTIVE MR. MUNAWAR ALI FECTO DIRECTORS MR. KAISER MAHMOOD FECTO MRS. ABIDA BANO DR. ABDUL WAHID MUHAMMAD MR. SAID AHMED MR. YAHAYA AHMED BAWANY MR. JAMES T. RICHARDS MR. FAZLUR REHMAN MR. MUHAMMAD ASEED AKHTAR (SLIC) SECRETARY: MR. MUHAMMED ANWAR NATHANI (ACA) AUDITORS: M/S. HYDER BHIMJI & CO (Chartered Accountants)
M/S. A. R. DIWAN & CO. (Chartered Accountants) BANKERS: MUSLIM COMMERCIAL BANK LTD. HABIB BANKLTD. REGISTERED OFFICE: 1ST FLOOR, PANORAMA CENTRE, RAJA GHAZANFAR ALI KHAN ROAD, KARACHI-75530 ZONAL OFFICE: 1ST FLOOR, NAWA-E-WAQT HOUSE, 4-SHAHRAH-E-FATIMA JINNAH LAHORE. MILLS: DARYAKHAN (DISTT: BHAKKAR)
Part two
Company Management System
ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
CHAIRMAN M.D. (Managing Director) Board of Directors G.M. ---------------------------------------- G.M. G.M. G.M. Manager (Cane) (Tech.) (Production Administration ------------- Technical Commercial Plant Production Electrical Manager Manager Manager Manager Manager Chief Engineer ---------------------------- Shift Engineer Senior Engineer
Administration Department
I worked in this department for 10 days. The head of this department is known as General Manager (Admin). Presently
Ch.M.Safdar is the head of this department. He keeps all the record of the office. There is one senior personnel officer, one security officer and two senior clerk and the other dispatch clerks working in the office. The senior clerk has the duty of keeping personal files of employees. He also keeps some other necessary files, which can be produced on demand. The dispatch clerk has the duty to give dispatch numbers to letters, orders and correspondent of the mill. Timekeeper is supposed to keep record of employees time of entering and leaving the mill. Security officer is responsible for all the security requirements of the company.
ACTIVITIES OF ADIMINISTRATION DEPARTMENT 1RECRUITMENT, SELECTION AND RETRENCHMENT OF EMPLOYEES 2MAINTENANCE OF PERSONAL RECORD 3TIME OFFICE MANAGEMENT 4 Interactions with following govt. department: Social security Employee old age benefit Labor department Liaison with local administration Worker welfare programme programme arrangement for company executives 7. Mail receiving and distribution 8Legal matters 9Supervision of faire price shops 10AUTHORIZING DISPATCH SALES
11. SUPERVISION OF PLANTATION 12. ENTERTAINMENT OF VISITORS Labor and personal department Labor and personal department may be considered as the heart of any organization. The head of this department is called labor officer. This department includes Supervisor Senior officer Junior clerks These employees are under the control of labor officer and are accountable to him. The function of supervisors is to supervise all the activities of the other clerks. They are responsible to maintain all the records of this department. If the labor officer is in need of any old record he produce it to him. I worked in this department for the period of one week and observed all the information in detail.
Functions of Labor and Personal Department 1APPOINTMENT This department has a special policy for the appointment of employees the labor department advertises information of general public. usually the advertisement consists of posts for which the application are required, pay, other allowances if any, qualifications for the candidates, and last date for the receipt of application. On the expiry of the last date for the receipt of application from the candidates at merit list is prepared and only those candidates are called for interview that are considered suitable for the post. On the date of interview managing director of the project, manager, the head of the department in which the vacancy exist conduct the interview. There is also written test and medical test for the candidates to be selected for the post. The candidate who is declared medically fit and also considered suitable for the post is then selected for the post on the terms and conditions decided with the applicant. The labor personal department issues the orders of the appointment with the approval of the project manager.
2 PROMOTION The promotion of employees depends upon the seniority of the employee. When vacancy of higher post occurs the senior most person is promoted first to fill up the vacant post. In this project all permanent employees are provided 50%chance of promotion. For example two posts are lying vacant in any department, the first post is filled up from temporary or the manager selects direct new person for the post. Moreover the seniority of all confirmed employees is considered from the date of regular appointment. In a case of two or more appointments are made at the same date, then their seniority is accounted from the dispatch number of the order of the appointment respectively. In case of vacancy in any department, all the employees of the department are equally considered to be promoted to that post the employees who is the most senior and who have got the necessary qualification for the post promoted to that post. If any employee is the senior most but does not posses the required qualification he is not to be promoted and the next senior one who have the required qualification is
promoted to the post. In case of transfer of employee from one department to the other department or from one section to the other section a seniority of employee for promotion is considered of appointment and confirmation. It is not to be considered from the date on which the employee has been transferred.
3Punishment All the employees are required to obey and abide the rules and regulations of the project. Violation of rules and regulations by the employees is considered as misconduct of the employees and consequently leads to the punishment. The following acts of the employees are considered to be a violation of the law. 1.disobedience to the supervisors 2. refusal to obey the lawful orders of the supervisors 3. taking or giving bribes 3. to damage the property of the factory 5. absence without leave from the factory 6. late arrival in the office 7. found sleeping during the working hours 8. found absence from the work for one or two hours Any employee who is found guilty of the above miss conducts, action may be taken against him, which leads to the following punishments 1. the management will issue a warning to the employees to be careful for future and not to repeat this action or otherwise he will be punished. 2. some time the management makes deduction from the salary. 3. some time the management will hold the increments or promotions for a certain period of time. They not give them increment and promotion during that a period of time 4. some time he his demoted to the lower post 5. in case of serious miss conduct the management will dismiss him from the services.
The head of the department to which the guilty employee is concerned sends the case of employee to the personal department. The personal department will call for his explanation and the employee will explain his position in the light of charge framed against him within a specified period of time. The explanation is received from the employee and then the case of the employee with explanation is forwarded to the project manager for the final decision. If the employee is found guilty he is punished otherwise the case is dropped by the project manager. 4Transfers One of the functions of this department is the transfer of employees. Usually the employees are not
transferred from one department to the other department. But if any employee of a department wants to transfer to another department consent of the department is essential. After positive reply from both departments i.e. the department from which he wants to be transferred and the department to whom he want to be transferred. The case is transferred to the project manager who posses the transfer orders.
Leave procedure The following leaves are allowed to the employees of the mill. 1CASUAL LEAVE 2MEDICAL LEAVE 3LAVE WITHOUT PAY There are special rules and regulations for leaves made be the factory. These rules are applied to each employee of the mill. The explanation of above leaves are as followed a. casual leave ACASUAL LEAVE The project manager grants the casual leave. The leave is allowed only to the permanent employees of the project. Every employee has the right to avail ten days casual leave per annum, Three days at a time is the maximum ceiling for the leave.
BMEDICAL LEAVE This leave is also allowed to the permanent employees. This leave can be granted on the basis of medical certificate issued by any authorized medical officer. In the case of one day no medical certificate is necessary, every employee is allowed ten days medical leave per annum. If the disease of the employee is such that it requires more than a day then the approval of the project manager is necessary. CLEAVE WITHOUT PAY This leave is granted to the employees when leave without pay is exhausted and none of the type of leave is available at his credit, leave without pay is granted by the management of the projection special cases this leave can not be more than one month at a time. But can be extended in special cases. Any employee who is found guilty of the above miss conducts, action is liable to be taken against which it leads to the following punishments 1. the management ill issue a warning to the employees to be careful for future and not to repeat this action or otherwise he will be punished. 2. some time the management makes deduction from the salary. 3. some time the management will hold rhea increments or promotions for a certain period of time. They not give them increment and promotion during that a period of time 4. some time he his demoted to the lower post 5. in case of serious miss conduct the management will dismiss him from the services.
Workman compensation In this project compensation is paid to the workers when they receive injuries in the cause of work during accident. If the worker has violated the safety precaution the management is not bound to pay compensation. The management also pays compensation for any kind of diseases, which are caused as a result of the type of duty. Also in this case he must prove that he has suffered disease during the employment. If the disease pertain to preposition period, compensations cannot be claimed. Fringes benefits The employee of this mill is given the following fringe benefits in the form of money or shape of certain facility in addition to their monthly wages. These benefits are mentioned below FUNDS The project maintain a provident fund for the employee under the rule of provident fund every permanent employee of factory who have completed six month continue service in the factory is eligible subscribe towards the fund. Provident fund consists of deductions from the monthly wages of the employees as equal amount is also contributed toward the provident fund by the mills. The total amount of provident fund is deposited in the account of provident fund and separate account is maintained for every employee in the account office of the factory. The total amount alongside interest is paid to the employee in lump sum upon completion of office tenure. During the employment an employee can take loan from the provident fund for the urgent needs. The management sanctioned the required loan upon 50% of the total loan is recovered in easy installment from the monthly salaries. Place allowance Place allowance are given in the following ways 1. those employees whose pay is unto Rs. 300 p.m. is given 205of the basic pay 2. those employees whose pay is up to 301 to 500 per month are allowed Rs. 155of their basic pay. 3 those whose salary is more than R.s. 500 are given 10%of their basic pay. HOUSE RENT The employees are also paid hose rent at the basic pay=claw 405 means cost of leaving allowance up to Rs. 500 = 110 fix Rs. 501/-uptors 735/-=10%of basic pay+25+25 Rs735/-and above 9736)=105 of their basic pay=25
MEDICAL ALLOWANCE Every employee and his family are given free medical facilities. Whenever any employee or any of his family member fall ill, the management is responsible for their medical allowances, payment made as a result of medical treatment are disbursed later on. The medical parishioners prepare the bills of medicine, and these bills are offered to the finance manager for payment.
FACED WASHING ALLOWANCE Washing allowance is given to all the employees at the rate of rs 6 per month.
EDUCATION FACILITIES In the Fecto sugar mills there is special arrangement for the employees children education. Educational facilities are intro under worker children ordinance 1967, under the ordinance each factory should provide free education to the children of the employees. This ordinance applied to all those organizations 29 or more than 20 workers. The employee receiving monthly wages less than Rs.10000 are entitled to avail these facilities. Under the ordinance the education will be free for one child of each employee of the factory. The children of the employee are free from tuition fee school funds and the cast of the books. There is also transportation system for the children of employees. Scholar Ships To Children Of Employees In this mill without free education to the children of the workers scholarship at the rate of rs 15 rs25 rs 30 are awarded to the deserving children of the employees in their 5th 8th and 10th classes CANTEEN FACILITIES The mill has provided the canteen facility to its employees. Adequate furnitures and other facilities are available in the canteen. FAIR PRICE SHOP The mill has provided a fair price shop facility to the employees. In the fair price shop a person can buy the comm. duties of daily use on their prices BONUSES In this mill employees are given the bonus also. The number of bonus usually is divided between the management and workers unions on production basis. / 1 one bonus is given on the production of 1000000 lack bags of sugar 2. The production of 2000000 lack bags of sugar are given the two bonuses 3on additional 50 thousand bags of sugar one bonus is given. The amount of one bonus is equal to one basic pay of the employee, but after up to the present time the required limit for bonus is not attained as the project is running in losses and the production has always been less than the actual capacity.
Employees /Personnel in various section CLASSIFICATIN OF WORKERS The workers of Fecto sugar mills can be classified as under: 1 PERMANENT WORKERS
2 TEMPORARY WORKERS 3.. SEASONAL WORKERS 4.. DAILY WAGE WORKERS 5.. APPRENTICES
Permanent workers Those workers who are engaged on performing their services for the whole year are called permanent workers. They are appointed on those jobs, which are of permanent nature.
Temporary workers Temporary workers are appointed on those jobs, which are of temporary nature. They are likely to be financed in a maximum period of nine months.
Seasonal workers These workers are hired during the cane crushing seasons, when the season is over they are lay off. Daily wage workers These are the workers who worked and get their remuneration on daily bases. They can be hired in any section where they are needed. Apprentices These are the learners. This is a work mean, to which allowances are paid during the training and after the completion of the course.
Designation and number of employees
CANE DEPARTMENT Designation/Department STR CANE DEPARTMENT General Manager 1 Cane Manager 1 Dy. Cane Manager 2 Tr. Cane Officer 1 Sr. Cane Officer (Admn) 1 C.O. (Admin)/ACO (Admin) 1 Office Supdt./Office Supr./ Typist 1 Office Supdt./Office Supr./ Computer I/C. 1 Cane Admin Office Clerks 5 Qasid/Sr. Qasid 2 Tea Boy 1 ---------16
---------Designation/Department STR LOAN OFFICE Loan Supdt./Loan Supr/ Loan Asstt. 1 Clerks 2 Asstt. Fitter/Fitter (Agri) Workshop 1 ---------4 ---------CANE YARD & WEIGHBRIDGES Asstt. Cane Officer (Yard)/ Sr. CO (Yard)/C.O. (Yard) 1 Card Supdt. 1 Shift Supr. 2 Weighment Incharge 4 Parchi Clerk 6 Posting Clerk 6 Line Jemedar 6 Gate Pass Clerk 6 Line Jemedar (Gate pass) 3 ---------35 ---------CANE CARRIER Feeding Incharge 3 Feeding Clerk 9 Line Jemedar 6 ---------18
Designation/Department STR CANE TRANSPORT OFFICE Clerks 3 Line Jemedars 3 ---------6 ---------PROGRAMME OFFICE Programme Officer/Asstt. Programme Officer 1 Programme Supdt./Supr. Programme Clerks 6 Line Jemedar/Qasid 1
Dak Runners/Line Jemedar 5 ---------13 ----------
FIELD OFFICE Sr. Cane Insp./Cane Insp. 3 Fd. Supr./Sr. Fd.Man/Fd. Man 32 ---------35 ---------PURCHASING CENTRES Depot. Incharge (Clerks) 16 Clerks 9 Line Jemedars 16 ---------41 ----------
MECHANICAL DEPARTMENT Designation/Department STR MECHANICAL GENERAL OFFICE General Manager (Technical) 1 Dy. General Manager (Tech) Technical Manager/Chief Engr. 1 Dy. Chief Engr./Sr. Engr. 4 Sr. Shift Engr./Shift Engr. 3 Asstt Engr./Tr. Engr. 1 Drawing Engr/A.D. Engr. 1 Draftsman/A.D. Man/Tracer 1 Typist Clerk 1 Qasid 1 ---------14 ---------MILLS HOUSE Mill Engr/Asstt M. Engr/Foreman 1 Shift Foreman/A.Shift Foreman/Mechanic 5 Sr. Fitter 5 Fitter 8 Asstt/Fitter 8 Helpers 13 Welders Oil man 3 Pump Coolies 5 Tipper Operators 4
Tip. Carrier Operator 2 Cane Carrier Operator 4 Clearing Coolies 18 ---------76 ---------Designation/Department STR BOILER HOUSE Maint. Engr/A.Maint.Engr/Foreman 1 Shift Foreman/A.F.man (Shift)/shift Supr. 4 Asstt. Shift Supr. 3 Fireman/A.Fireman 14 Waterman/A.Waterman 9 Fire Coolies 8 Feed Pump Attd. 3 Feed Tank Attd. 2 Bagges Carrier Attd/Oilman 2 Welders ---------46 ---------BOILING HOUSE Boiling House Engr/ Asstt.Engr/Foreman 1 Shift Foreman/A.Shift Foreman/Mechanic 3 Sr. Fitter 3 Fitters/Fabricators 8 Asst. Fitters/Helpers 9 Sr. Welder/Welder/A.Welder 6 Oilman 4 Pump Cooly/Pump Attd. 18 ---------52 ---------KHALASI GANG Kh. Foreman/Kh.Jem. 1 A.Kh.Jem. 2 Mill House Khalasies 11 Boiling House Khalasies 6 ---------20 ---------MECHANICAL WORKSHOP Workshop Incharge 1 Sr. Engr Wksp/Engr Wksp/Foreman A.Foreman/Mechanic 1 Sr. Fitters 1 Fitters 2
A.Fitter/Helpers 1 Master Turner 1 Sr. Turner/Turner 3 A.Turner 1 Foreman Welder/Hd. Welder 1 Welders 2 Helper Welder/A.Welders 2 Pettern Maker 1 Black Smith 1 Hammerman 1 Moulder/Asstt Moulder Shaperman 1 Plannerman Coolies 3 ---------23 ---------Designation/Department STR AUXILIARY TECH. SERVICES Asstt. Engr./Foreman A. Foreman / Mech. 1 Sr. Fitter / Fitter 1 A. Fitter / Helper / Cooly 2 Diesel Fitter 1 ---------5 ---------TURBINE AND COMPRESSOR Sr. Turbine Engr/Turbine Engr. 1 A.Turbine Engr/Foreman/General Foreman 1 Mechanic/Asstt Foreman 1 Sr. Tur. Operator/Sr. Fitter 1 Tur. Optr/Fitter 9 Asstt. Tur. Optr/Helper 2 Coolies 2 ---------17 ---------CHEMICAL DEPARTMENT Designation/Department STR CHEMICAL OFFICE Process Manager (DGM. (P) 1 Chief Chemist/Dy. chief Chem. 1 Senior Chemist/S.Chemist/Trainee Chem. 6 Office Supdt. 1 Qasid ----------
9 ---------LABORATORY Sr. Lab. Officer/Lab Officer 1 Lab. Chemist 3 Lab. Analyst 9 Asstt. Analyst 3 Lab. Pointsman 3 Sampler 17 ---------36 ---------PROCESS CONTROL Juice Foreman/Asstt.Chem. 1 Juice Supervisor/Asstt. Juice Foreman 3 General/Record Clerk 3 Juice Heater Mate/A.Supp. 2 Juice Heater Cooly 1 General Cleaning Cooly 6 ---------16 ---------Designation/Department STR DEFECATION STATION Def. Attendant 1 Def. Cooly 5 Def. Mate/Asstt. Supp. 3 ---------9 ---------CLARIFIER STATION Mate/Asstt. Supp. 3 Coolies 4 Asstt. Mate. 1 ---------8 ---------VACUUM FILTER STATION Mate/Asstt.Supervisor 3 Coolies 10 ---------13 ---------EVAPORATION STATION Quadman/Asstt. Supervisor 3 Quad Operator 3 ---------6 ----------
Designation/Department STR TALO REFINERY STATION Talo Technician/Operator 3 Coolies 5 ---------8 ---------PAN & CRYSTILLIZER STATION Sr. Pan Chemist/Pan Chemist 1 Head Pan Boiler 3 Head Panman 3 Senior Panman 4 Panman 3 Assistant Panman 3 Pan Mate 3 Assistant Panmate 3 Pan Coolies 16 Cryst. Mate. 4 Cryst. Coolies 4 Pan Apprentices ---------47 ---------CENTRIFUGAL STATION Mate/Asstt Suppr 3 Asstt Mate. 3 Centrifugal Operator 17 Magma/Remelting Coolies 12 ---------35 ---------Designation/Department STR BAGGING HOUSE Bagging Clerk 2 Mate/Asstt Supr 2 Asstt Mate 2 Bagging Filling Optr. 1 Bagging Coolies 21 ---------28 ---------L.S. STATION Attendant Coolies 2 L.S. Mate 3 ---------5 ---------MILL SANITATION
Coolies 3 Records Clerk 1 ELECTRICAL DEPARTMENT Designation/Department STR C.E.E. OFFICE Chief Electrical Engineer 1 Deputy Chief Engineer/ Sr. Inst. & Elect. Engg. 1 Qasid 1 ---------3 ---------POWER HOSUE Supervisor S.B.S.E. 3 Asstt. Switch Board Optr. ---------3 ---------ELECTRICAL SHIFTS Inst. Electrical Engg. 1 Asstt. Engr./Foreman/Supp. 3 Senior Electrician 3 Electrician 9 Junior Electrician Tubewell Operator 2 Helper/Asstt. Elect. 3 Assistant Wireman Coolies 2 ---------23 Designation/Department STR ELECTRICAL WORKSHOP Foreman/Supervisor 1 Asstt. Foreman(H.Winder) Senior Winder/Winder 1 Asstt. Winder/Winder Helper 1 Electrician 1 Wireman/Electrician 1 Assistant Wireman Lineman/Khalasi 1 Welder Asstt. Lineman/Asstt. Khalasi/ Asstt. Electrician Electrical Fitter 1 Cooly ---------7
---------INSTRUMENT WORKSHOP Workshop I/c./Instrument Engr/Assttt. Engr 1 Foreman/Asstt. Foreman 1 Asstt. Supervisor Senior Technician/Tech. 1 Helper/Cooly 1 ---------4 ---------INSTRUMENT SHIFTS Technician/Asstt. Tech. 3 Helper/Asstt. Tech. ---------3 ---------ACCOUNTS DEPARTMENT Designation/Department STR FINANCE DEPARTMENT Finance Manager (Malik Ishfaq Hussain) 1 Chief Accountant (Rana Saeed Akhtar) 1 Store Account Officer (Hafiz Sajid Akhtar) 1 Sr. Accountant (Mr. Sohail Siddiqui) 1 Sr. Accountant (Mr. Mobishir Ahmad) 1 Store Accountant (Mr. Shahid Akhtar) 1 Record clerk 1 (Mr. Qasim) Typist 1 Qasid 1 Dak Runner 1 Tea Boy 1 ---------11 ---------Designation/Department STR SUGAR GODOWN Deputy Manager/Off. I/C. 1 Supervisor 1 Asstt. Store Keeper 4 Godown Boy. 5 Qasid 1 ---------12 ---------CANE ACCOUNTS
Accounts Officer/Asstt. Accounts Officer 1 Accounts Supervisor/Asstt. Accountant 1 Junior Programmer 1 Computer Operator 1 Data Feeding Clerk/Ledger Posting Clerk Clerk (Cash payment) 3 Billing Clerk 1 Checking Clerk 4 Clerk (Bank Payment) 2 TPT Clerk Qasid ---------14 ---------FAIR PRICE SHOP Incharge Fair Price Shop 1 Cooly 1 ---------2 ---------MANAGEMENT OFFICE T.D. OFFICE Technical Director 1 Executive Secretary 1 Qasid 1 ---------3 Designation/Department STR LOCAL PURCHASE OFFICE Purchase Manager (Mr. Daud Shah) 1 Purchase Officer (Mr. Irshad Ahmad) 1 ---------2 ---------STORES SECTION Manager Store/Store Officer 1 Sr. Officer Store/Asstt. Store Officer 1 Store Keeper 1 Asstt. Store Keeper 3 Storeman/Clerk 4 Asstt. Storeman/Store Boy Sr. Store/Boy/Helper 6 Typist/Sr. Typist 1 Qasid 1 ---------18 ---------ADMINISTRATION DEPARTMENT
Designation/Department STR PERSONNEL OFFICE Manager Administration (P.I.R.O) 1 (Malik Ishfaq Hussain) Supervisor 1 (Malik Iqbal Hussain) Officer I/c/Off.Supdt. 1 Steno Typist/Typist 1 Record Clerk/General Clerk 1 Office Attendant 1 Mr. Allah Ditta ---------6 ---------TIME OFFICE Supervisor/Asstt. Supp. 1 Mr. Tariq Clerk 3 Qasid 1 ---------5 ---------DISPENSARY Pharmacist 1 ESTATE OFFICE Estate Officer Plumber 1 Sweepers 6 Mali 1 Carpenter 1 Gardner 2 Cooly ---------11 ---------CIVIL SECTION Sr. Civil Engr./Civil Engr. 1 Sr. Civil Supp./Civil Supp. 1 Clerk/Supervisor 1 Mason (R.F.) 1 Cooly 4 ---------8 ---------SECURITY SECTION Security Officer/Asstt. Sty. Officer 1 Asstt. Security Supervisor 1
Security Jemadar 3 Security Leading 1 Security Man 3 Security Watchman 35 ---------42 ---------M.T. SECTION M.T. Incharge/M.T. Supdt. 1 Mechanic/Sr. Fitter 1 Sr. Driver/Fitter Driver 6 Tractor Driver Cooly/Helper 1 Cleaner ---------11 ---------Designation/Department STR GUEST HOUSE Incharge Guest House 1 Cook 2 Bearer 1 Guest House Keeper 1 ---------5 ---------TELEPHONE EXCHANGE Supervisor/Asstt. Supp. 2 Sr. Telephone Optr. 2 Telephone Optr/Asstt. Optr. 1 Lineman ---------5 ----------
Career ladder??????????????????/
Major Managerial Policies In each and every organization discipline is the key to the stability, efficiency and orderly pursuit of business. For employees guidance and to help them guard aga inst those acts or omissions which are inimical to the interests of the company and those of themselves, certain managerial policies are outlined below. It is
the duty of each and every employee to follow these policies and abide by all the rules and regulations otherwise the violations of these norms of conduct may subject one to disciplinary action commensurate to the gravity or seriousness of the violation in every instance and the incorrigible attitude shown. The disciplinary action may range from a verbal admonition, written reprimand, suspension, and ultimately, separation or termination from employment for just cause. As a general rule, however, offences involving dishonesty or breach of trust will be penalized with dismissal. Conflict Of Interest: The following are examples of conflicts which must be avoided unless specifically authorized by the Chairman and Managing Director or his duly authorized representative:a) Employees may not have ownership interest in suppliers, customers or competitors, except for holding of less than 1% of the outstanding stock of companies with publicity traded stock. b) Employees may not seek to profit from confidential information or business opportunities that are available to them as a result of their position with the Company. c) Employees who purchase or have any influence on the purchase of commodities may not engage in personal investment or speculation in commodity futures. d) Employees may not act as director, officer, partner, employee, agent or consultant for a supplier, contractor, customer or competitor. e) Employees may not receive gifts, loans, or favors from suppliers or others with whom the company does business, except (1) casual entertainment or gifts of small value consistent with accepted business practice and (2) loans from financial institutions on prevailing terms and conditions. f) Employees may not use Company funds, facilities, personnel, or other resources for private purposed. The interests, activities, and associations prohibited by this policy are those of a direct, as well as indirect nature. Thus, those who are acting for an employee or of his spouse or member of his family, may be included where the facts are known to the employee. It should also be stressed that non-adherence to employees responsibilities mentioned in Section. A may also result in violations of the companys policy against conflict of interest. Attendance And Punctuality: All employees are expected to be at work during their official working time, except when on approved leaves of absence or prevented from reporting to work by disabling sickness or other emergency situations beyond their control. When you cannot report for work, you should report your absence to your immediate superior within the day of absence through any means available, such as telephone, telegram, or messenger. Failure to give the required notification will result in your absence being treated as UNEXCUSED. Likewise, employees are required to report for work punctually on their designated starting time. It is not permitted for an employee to compensate for tardiness by working overtime. If you are late for 10 minutes or more, it is discretionary on the part of your superior whether or not to accept you for work. if you are sent home, you will not be paid for the day. Examples of conduct in violation of the above norms are:a) Absence without leave (AWOL) or notification. Being absent without notification and approval of leave from the competent authority for 10 consecutive days or more will be considered as hob abandonment. b) Excessive unexcused absences. c) Excessive unexcused tardiness/under times.
Absence and tardiness/under times will be considered excessive where they are incurred for no valid reasons and in such frequency as to cause serious disruption of your work and that of the department where you are assigned. As a general rule, 3 unexcused absences, and 3 unexcused tardiness/under times in a month will be regarded as excessive. Dishonesty And Breach Of Trust: The relationship between the company and its employees regardless for rank, is of necessity founded on mutual trust and confidence. When an employee commits an act of dishonesty or breach of trust, he give cause for the company to lose trust an confidence in him and justifies his termination from employment. Examples of acts or omission which violate the high standards of honesty expected of employees are:a) Theft of company property or of others within or outside company premises. b) Misappropriation, misuse, or unauthorized use of company funds, money or property. c) Submission of false, padded, tampered or fictitious documents in support of claims for reimbursement or other monetary payments form the company. d) Falsifying, altering and tampering of company records such as spoiled merchandise receipts, employment records, overtime slips, quality control reports, etc. e) Punching or filling in of another employees time card and having ones time card punches or filled in by another. f) Accountable company employees who incur unexplained shortages are presumed to have misappropriated the shortages. g) Similar or analogous acts of dishonesty, fraud and breach of trust.
Misbehavior and Misconduct: Examples of acts which constitute misconduct are:a) Insubordination and disrespect to superiors and other company officials, guests, visitors and other persons dealing with this company. b) Fighting or quarrelling inside company premises. c) Loitering or unauthorized leaving of ones post while on duty. d) Gambling inside company premised, including the making, taking and payment of bets. e) Unauthorized or unreported possession of firearms or other deadly weapons. f) Inflicting physical injuries or manhandling another person inside company premises. g) Possession and use of prohibited drugs. h) Sleeping on duty. i) Drunkenness or reporting for work under the influence of liquor. Drinking of alcoholic beverages is prohibited inside company premises. j) Immorality and indecent behavior. k) Threatening another person with harm or physical injury. l) Engaging in activities which are disruptive of company operations, such as gossiping, intriguing against honor and selling personal goods inside company premises. m) Abuse of company benefits and privileges such as malingering or feigning illness to justify absence.
n) In General, violation of other working rules and regulations which may be issued from time to time such as: I. Leaving the job unattended without permission of the supervisor or entertaining the guests or friends at the place of duty. II. Leaving the premises during duty hours without proper authorization or gate pass duly signed by the Manager of the Department. III. Taking any bags, brief case or any other material in the company premises without proper permission of authorities concerned. It is advisable to leave such things in the custody of security at the Gate Office. IV. Using the telephone for personal calls without permission. V. Entering the factory premises or offices without wearing the Identity Cards or the name badges. VI. Taking away the company property without any proper gate pass or authorization slip issued by the Manager of the Department.
Breach Of Security And Safety: Examples of acts which fall under this category are:a) Causing destruction or damage to company materials or property, deliberately or through negligence. b) Causing wastage of company materials and property, deliberately or through carelessness or negligence. c) Sabotage or deliberate downgrading of company property, materials and products. d) Unauthorized disclosure of confidential company information obtained by reason of ones employment in the company. e) Tampering with fire protection and other safety equipment. f) Substituting or attempting to substitute company equipment or property. g) Refusal to comply with or evasion of security requirements, such as searches by security guards. h) Failure to report any misconduct or dishonest act of a co-employee. i) Smoking fire or exposing. j) Horse playing k) Unauthorized use of company vehicles, machinery and other equipment. l) Refusal to use prescribed personal protective safety or working under unsafe conditions by avoiding goggles, or any safety equipment provide for jobs.
Breach of Cleanliness and Sanitation: Examples of unclean unsanitary acts are: a) Urinating or spitting on floors, walls and other places other than the proper receptacles. b) Littering, throwing cigarette butts and other acts which contribute to poor house keeping. c) Refusal to wear prescribed uniform or footwear inside company premises. d) Abuse or misuse of uniforms other company provided personal equipment. e) Poor personal hygiene such as long hair, dirty fingernails or uniforms etc. f) Improper or abusive use of toilets and other company facilities. g) Failure to comply with other sanitary rules, such as washing hands after coming from toilets.
Just causes for Termination of Employment: The following acts and omissions shall be treated as misconduct:-
a) Willful insubordination or disobedience to any lawful and reasonable order of a superior. b) Theft, fraud, or dishonesty in connection with the employers business or property c) Willful damage to or loss of employers goods or property d) Taking or giving bribes or any illegal gratification e) Habitual late attendance f) Habitual absence without leave or absence without leave for more then ten days g) Habitual breach of any law applicable to the establishment. h) Riotous or disorderly behavior during working hours at the establishment. i) Habitual negligence or neglect of work j) Frequent repetition of any act or omission referred to in clause k) Striking work or inciting others to strike in contravention of the provisions of any law, or rule having the force of law l) Go-slow.
Part Three
ADMINISTRATIVE / MANAGEMENT STYLES
ADMINISTRATIVE / MANAGEMENT STYLES Success or failure of any organization largely depends on the management. Mangers have following four major roles to perform. Planning
Organizing Leading Controlling For effective performance of the above mentioned functions the managers need different skills. Like, effective managers require communication skills, in written, oral and non verbal form. They should be creative and innovative, Should be able to manage time and stress. Motivate and influence the others. They should be able to manage the conflicts etc. There are two major sections of the organization. . 1 Plant. 2 Head office Plant related administration is only up to plant. plant administration administer only the plant. and head office administer only the head office. HRM deals with both plant and head office. here in head office peoples are very well disciplines there is no chain of strike or dispute in head office. Same is the case with the plant. Here both in head office and in plant administrator are very strick by the rules and regulation. Otherwise the here is very friendly. people fell free to talk with each other. Here the administrative style is democratic not the autocratic. Administration styles has its impact on the people here but senior executive here have a combine type of attitude at the time of closing they are really strict but at beginning little relax. But when you talk about the styles on the morale of the people. Then you can take the example of this that After its merger with the lever brother. people are very much frustrated about their future.they are very much cautious that what will be happened in the future with respect to their jobs.and all these things are really effecting the efficiency of the people performance.the is the one vview of the picture but on the other there are a bundle of incentives like hajj ticket,allowances,really incouraged the employee to show there best.and they are showing their best here.because all these activities incouraged the people.here the working envirnment is very friendly mess and tea was the two thing which I am really missing.there is no question that when you provide all these facilities then the morale of employees will automatically rise. READ the above page of mgt styles WITH CARE/????????????????/ Part four
Production facilities
PRODUCTION DEPARTMENT The head of this department is called the Production Manager. The Production Manager is also is called the Deputy Manager of the project. There are four Shift Chemists and one Assistant Chemist under the control of Production Manager. The main function of this department is to produce maximum sugar from the cane available to the factory with minimum possible sugar losses during manufacturing by controlling various units, processes and operations.
Functions Of Production Department Function of production department may be classified as follows 1- PRODUCTION Supervising the process of production in three shifts viz; crushing of about 1500 tons of sugar cane, delousing of juice, its carbonation,sulphitation ,filtration and concentration by operating juice heaters liming gassing etc The process involves washing of filter cloth and press mud, operation of sulphur furnace, vacuum evaporators, steam boilers, pan boiling molasses tanks juice, molasses pumps crystallizers and centrifugal machine etc
2-LABORATORIES Conducting special and routine analysis far quality control in each of three shifts .The laboratory chemist who is independently in charge of a shift prepares about 30 routine analyses per hour and two-lab analyses assisted by lab boys and laboratory samples conduct 10 to 15 analyses per hour.Preparation of daily weekly forth nightly and monthly reports and laboratory charts.
3-BOGGING HOUSE Packing the good quality sugar, maintaining the stock of new empty bags, pointing the serial no. in the correct manner ,handing over the shift production to the sugar go down, repair of damaged filter cloth and preparation of new filter cloth is done by the bogging house. 4-SUGAR GO DOWN Stocking and dispatch of sugar bags to various government agencies, dealing with the food directorate of N.W.F.P., excise departments, preparing periodical reports of disposal of stock, sticking of damaged bags during off season etc. is done by this department. In this department the following materials are used during manufacturing. 1 Lime Stone
2 Hard Coke 3 Filter Clothe 4 Sugar 5 Cotton Bags 6 Furnace Oil
PRODUCTION PROCESS
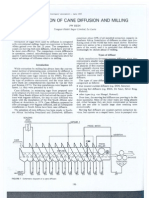
After weightment, cane comes on cane dipper and through the cane carrier it passes through the cane leveler and then reaches at the cane cutter which cut it into small pieces. After it cane passes through cane shredder which cut it into very small pieces. Now the cane is in position to give maximum juice. Then the cane reaches at mill house where the juice is separated from baggage. Baggage go to the boiler house where it is burnt and the heat energy so gained is used for steam and to produce electricity. The juice gathers in a big tank named "mix juice tank". The juice then goes to the process house where it is heated from 25-70C. Then line water (Ca(OH)2) is mixed in it to get rid of impurities. Then it is sent to the clarifier where it is heated from 60-105C and by the Co-agulent, the mud is separated from juice. Then it goes to the evaporators where water evaporators. Here the brix of juice goes from 15-65. This thick juice is named as "syrup". Now the syrup is sent to A-Pan where it is heated so much that it reaches at its supersaturated point. A massecuite is produced by adding small amount of grain in it. Crystals of sugar and molasses is present in A - Massecuite. To separate sugar from molasses, it is sent to A centrifugal. In this way, A - sugar is gained. The molasses separated from A - sugar is sent to B-Pans, where it is heated again and B-Massecuite is produced and the sugar gained from it is known as B-Sugar. C-sugar is also gained by the molasses of B-sugar. The molasses separated from C-sugar has a very little size of sugar in it, so it is sent to the separated thanks and it is called "Final molasses". C-sugar is used for graining purpose while A and B sugars are sent to Talo-house for colouring purpose. Chemicals litre Phosporic Acid, talo-flak, talo float and lime scerate are mixed in it to remove the impurities. This sugar is known as "Liqour" and to get pure sugar from it, it is sent to "refine-pans". Refine massecuite is produced and after passing it from refine centrifugal, sugar is separated from molasses. It is passed through drier to dry it. Then it is passed through grader where "product sugar" is separated from small or big sugar. This small or big sugar is again dissolved in water to get product sugar. Product sugar is sent to godown after packing.
CANE DEPRTMENT This is perhaps the most important department of the establishment outside the factory. Cane department produces the basic raw material which is usually in short supply and for which there are competing forces namely Alternate crops, Gur making crushers and other sugar mills. Therefore, only the effective working of the department can ensure full capacity operation of the mill throughout the crushing season
and thus reduce the fixed costs. This department is considered as the backbone of the mill. The function of this department is as under which are two folded.
1. cane department 2. cane procurement
The head of the Cane Department is known as Cane Manager. There is a Cane Inspector who is under the direct supervision of Cane Manager. The Cane Inspector examines the work and steps that are undertaken for the cane development. Also a large number of Field Men are working under the direct supervision of Cane Manager. The Field Men make crops survey and determine the cane area of the growers. The whole area covered by the production process has been divided into 25 zones. The Field Man supervises each zone. The main reason of dividing the area into zones is to encourage more quantity of cane. Various stages of cane development and procurement are as follows.
Stages Of Cane Development And Procurement The first stage in any development and procurement programme is the correct survey of the sugar cane crops. Each Field Man is responsible to make the first survey in his respective area. If a long-term incentive development programmed is in preview the survey should include the entire area of the zone and cultivated land available in the zone, so that the target for bringing the area under cultivation may be ensures. For the purpose of the cane procurement a survey of the area under sugar cane only is sufficient. For the procurement purpose complete list of the Mohalls under various field staff is to be prepared showing distance of each mahal or village from the mill. Convenient place in consultation with the local people are also to be fixed as loading centers and their accurate distances from the mill be certain and declared which will form the bases of payment of transportation charges. The list of all the loading centers shows their distance from the mills is accurately and carefully prepared. The cane superintendent will provide this to the Cane Accountant for calculation of transport charges where such a calculation is required. While preparing list of villages, each village should be continuous to the other. This list and serial orders will also be followed in the programme register and during the issuance of indents.
SURVEY The field men will commence the survey. Normally the survey should start when the crop is about three feet high as that plot of sugar cane can easily be seen from the distance and no plot is missed during the survey. The field man will prepare a weekly advance programmes of the visit of the villages in his area and also makes an announcement among the sugar cane growers of his visit, so that they may also be able to contact the field man during the visit. Local information has to be collected about the area actually surveyed. Physically, by walking around the plot and counting the number of steps he should do the survey. The surveyor step should be measured
which will give the length of the plot. All survey records should be prepared in the name of the owner of the land and not subtenants unless there are any special circumstances in any particular case. During the survey the Field Man contacts the growers and then takes a note of their demand for seeds sand fertilizers. The field man then prepare the demand schedule for the respective zone and provide it to the department for necessary action.
CHECKING OF THE SURVEY The field man will do the actual field survey. The duty of the Cane Inspector of the area will be to see that the survey is being done is accurate. To achieve this the Cane Inspector will visit these areas along with the Field Man who has surveyed it so that the cane inspector will take up any plot and first see the area noted by the field man and then he himself survey the plot. If any difference is noted it will be immediately checked out. Thus checked out is filled in survey checking (D.D. form) and sent to the cane superintendent every week along with a weekly progress report and explanation of the field man for any discrepancy in his founding during the checking. If facilities are available survey record should also be checked with survey record of the revenue authorities.
Second survey In the month of February and March the field man makes the second survey of his zones. The field man examines whether the grower has shown all the seeds as provided by the mills. They also point out he problem of the grower and try to solve them as son as possible.
Third survey The-Field Man makes the third survey in the month of May and June. During the survey, he makes agreement with the grower. In his agreement the Field Man gives surety of purchases to the growers. The grower also gives surety of supplying his cane to the mill during the incoming season.
Final survey After making the above surveys the Field Man makes an average estimate of cane production of their respective zones. After making all the necessary corrections of the completed survey it should be filled up in the survey form and sent to the cane superintendent. The cane superintendent will then issue instructions for filling up agreement forms with the zamindars
ISSUE OF PASS BOOK (IDENTITY CARDS) Each cane grower whose record is existed will be issued a passbook, which will serve the purpose of a presentation. It will be presented by the grower at the time weightment of the cane in the mills and at the time of payment. When all the passbooks are thus ready they will be handed over to the field staff for the distribution to the zamindar in their areas. Here the programme in charge while handing over the passbook to the field staff for distribution will note down the serial of the passbook having handed over to the Field Man and obtain his signature. The field man while distributing the identity cards will maintain the register. The work of writing and distribution of identity cards should be completed by the end of September. Upon the receipt of the identity cards the grower became responsible to deliver his cane to the Mill within six days. When the identity cards are issued to the grower then cane department makes transportation arrangement for the supply of the cane to the mill The transportation facilities are provided to the growers according to their productive capacity.
WEIGHMENTS When the vehicle arrives at the gross weight bridge the weighment clerk will observe the following procedures THE INDENT The vehicle has a valid indent for that day and there is no over writing or cutting on it. If there is any such thing it should bear the counter signature of an officer. The indent must be accompanied with the identity cards. If any of the documents are not present the cane will not be weighted. PASS BOOK The vehicle got a passbook and has brought the cane according to the movement order. There is no other load on the vehicle except the sugar cane. It must be properly placed on the weight bridge
CANE YARD The whole area from the weightment to the cane carrier (cane yard) includes 1.Gross Weight Bridge 2-. Tare Weight Bridge 3-. Cane carrier After gross weightment, vehicle is processed toward the cane carrier for un-loading. Then without cane
vehicle it is again weighted on the tare weight bridge. Again the tare weight is deducted from the gross weight. Finally the binding material is deducted and net weight of sugarcane is remained. When cane is weighted parchi is prepared in the quadruplicate. This parchi shows the name of the grower name of their zones and the quantity of the cane supplied to the mill The first parchi is given to the grower. The Second copy is sent to the cane account section and the third one is given to the carriage contractor for receiving payments.
Payments All the payments will be made on the bases of the purchasing sheets received by the Cane Accountant from the Cane Superintendent. Any purchi not appearing in the purchasing sheets will not be paid. The procedure for payment is distributed according to the above principle. The cane superintendent after making the necessary checking will forward the posting sheet purchi and duplicate copy of gross and tare register to the cane account. While receiving these the cane accountant will check that all documents have been completed according to the requirement. If any paper is incomplete the cane account will immediately return the paper to the cane superintendent for necessary completion. When received incomplete from the cane accountant ant will check every purchi and entry in the posting sheet particularly the calculations of net weight, cane price and deductions. If any mistake are found the cane accountant will refer this to the cane superintendent for necessary action. The cane accountant may correct the calculation mistake without referring to the cane superintendent Corrections should be made immediately in parches and posting sheets. After having their correct net weight of cane, cane price and deduction in this posting sheet are totaled. These totals should be exactly the same as the total taken of these items from the parches remarks and cutting should be properly initiated erosion and overwriting in the parches and register should not be accepted by the Cane Account and should be referred back to the Cane Superintendent for inquiry and certificate of its correctness. Now the posting sheet will be the basis on which all the payments will be made as well as the daily cane figures. The cane account will also intimate the corrected totaled net weight of the cane to the cane superintendent also so that if necessary he may adjust his daily cane figures also The posting sheet after checking by the cane account will be countersigned by the cane superintendent and then it will be ready for payment. It will also be sent to the cane accountant that will prepare the necessary votures with the managers signature for drawl and payment of the amount of cane price against this posting sheet. Payment will be made of one day of the posting sheet or the posting sheet for Monday may be paid on the next day. If someone fails to turn up and received his payment on Monday or on Sunday then he can again have his payment on the next Monday or Sunday and not between the weeks. While making payment the cashier will take back from the zamidar his copy of the parchee and the acknowledgement or receipt of payment on the reserve side of the account copy of the parchee, which had been checked and corrected, and according to which the payment has been made. The cashier will receive back the parchee from the zamindar one by one from the same serial as entered in purchasing sheet and make the payment immediately after receiving the parchee .Only when one zamindar has been paid the cashier will receive the next person .The cashier should never collect more than one zamindars parchee at a time for payment .Now payment will be made unless the claimant produces the identity card also. Soon as the payment had been made the cashier will put his initial and date on the identity cards in the column provided and stamp paid with his initial and signature on the
posting sheet .The cashier when giving account to the accounting in charge of money advanced to him for payment should also give to the account in support of payment made by him. The zamindars copy of the parchee to against which the payment had been made. These will claimant chances of wrong fictions payment. The accountant in charge may however adopt any other procedure in addition to the above for the accuracy of payment and accounting. Payment through bank In case of payment through bank the procedure of checking the posting sheet will be same except that after checking the posting sheet, it will be handed to the Bank for payment .The bank while claiming reimbursement of amount paid by them should produce the zamindars copy of the parchee of the same value. Under agreement, the bank should not make any payment without production of the identity cards and after payment the band cashier should sign and put his initial on the identity cards in the column provided for.
Facilities provided to the Cane grower The following types of loan are provided to the growers 1 SEEDS LOAN 2 FERTILIZER LOAN 3 PESTICIDES LOAN Each year the project sanctions a fixed amount of loan from A.D.B.P. The amount of loan then is divided into two parts; one part is specified for the seeds and the other for fertilizers and pesticides. Management of the project then inform the grower through their respect field man to contact their programme officer for loan purposes PROCEDURE OF PROVIDING THE LOAN The procedures of providing the loan to the grower is as under: SEED AND FERTILIZER LOAN The grower who wants to acquire seeds and fertilizers from the mill should submit his request through an application. The grower also provides a photo state copy of his national identity card .He also maintained hid land khasra number, which he has specified for seeds in his application After the fulfillment of the above requirement the field man signs on agreement with the grower. After the agreement the application is approved by the cane inspector and then the cane manager give sanction of loan to the grower. When the cane manager sanctions a loan the officer superintendent of the cane department prepare the supply order .In this way seeds and fertilizers loans are provided to the growers. PESTICIDES LOAN Management of the project also provides loan for pesticides to the grower .The procedure of providing pesticides loans is the same as discussed above.
Utilization capacity????????????
Part five is pending ?????????????????
Part Six
Company accounting/finance system
FINANCE DEPARTMENT The head of this department is known as Finance Manager. The Department has two sections. 1Main Account Section 2Cane Account Section There are two Assistant Account Officers under the control of Finance Manager. They supervise the activities of main account section and cane account section respectively. The Finance Manager control all the financial activities of the project along with general administration and make arrangement of funds to meet the requirement of the project
Main account section This section has to supervise all the work of the department. The details of the above section is given as under
1-Finance Section In this era of information technology, Fecto sugar mill is also fully equipped with computer technology in almost all of its sections. The finance section of this department prepares the monthly and annual budget and financial statement bills. The cheques are also prepared in this section. Moreover the following books of account are maintained in this section. AMain cashbook This is a separate book for all kinds of cash receipts and payments known as main cash book .All the cash payments and receipts vouchers are posted to this book. This book is summarized at the end of each month. The transaction in this book is reconciled with the book statement at the end of each month. The final posting from this book are made in the general ledger. B General register All the daily transactions are recorded in the general register .At the end of day the transactions are posted to the general ledger in their respective accounts. CLedger register The ledger register is called the kings of all the registers of different types of accounts. The reason for this is because all the entries from the books for original entry must be posted for various accounts in the ledger. At the end of the day all the transactions are transferred from the general register to the ledger register .The debits and credits columns of the ledger register and these balances are used to prepare the trial balance and financial statements
DPetty cash book The cashier makes all the petty cash payments of miscellaneous bills and post them to the petty cash book and these are summarized at the end of each month and then posted them to the general ledger.
2-PAYROLL SECTION This section prepares the salaries of officers and workers on receipt of their attendance from the time office. Moreover payments to employees old age benefit and income tax assessments of the mill officers and workers are also dealt within this section. 3-TIME OFFICE In this office, daily attendance of factory workers is noted. Punch card system is used for the attendance of employees .Two punch cards machines are fixed on the wall of the time office. All the tokens of workers are fixed on the board section wise and employees come and take his token from the board and punch it into the machine and placed it on the box. The in charge of this section is called as Chief Time Keeper. At the end of each month the attendance sheet is prepared and send it to the payroll section .The payroll section prepares the monthly salaries of the workers according to their total attendance as shown by their attendance sheets. 4- STORE ACCOUNT SECTION This section maintains the record of machinery and different parts used in the project .The purchases and consumption of different parts is adjusted monthly and annually. 5 - Suppliers bills The main account section pays all the suppliers bills. When some items are purchased and received in the store, the store in charge prepare the receiving report showing the amount and quantity of items received .the receiving report is sent to the main account section. This section then makes arrangement for payment to the supplier.
Cane account section: The cane or the assistant account section performs the following functions It supervises and checks the cane price bills, sugar bills. Recovery bills of seeds and fertilizers loan from the cane grower and make arrangements for funds to the concern banks for payment. Procedure of payment to the growers: The cane reaching the mill is weighted and voucher is prepared in quadruplicate. The voucher shows the gross weight of cane. The first copy of voucher is given to the grower and second copy is sent to the cane department .The third copy is sent to the cane account section and the last copy is sent to the carriage contactor. After receiving copy of the voucher, cane department makes entry in the gross tire register. Then cash voucher and control ledger posting sheet is prepared and the posting sheet along with the tire register is sent to the main account section. When the posting sheet and gross tire register reaches in the tire account section the gross tire clerks checks the posting sheet and then send it to the loan section .In this section loan is deducted from the actual payment and send it to the voucher checker. The voucher checker then determine the cost of the cane i.e.net payable amount to the grower .The posting sheet is then sent the gross checker who make
super checking of the posting sheet .the gross checker then sent the posting sheet along with the bills in the duplicate. 1 CANE PRICE BILLS 2 SUGAR BILLS 3 CARRIAGE CONTRACTOR BILLS One copy of each of the above bill is sent to the concerned bank for payment .The bank makes the payment after fifteen days of receiving the bill from the cane account section. The project has specified some branches of the scheduled banks in different zones. At the beginning of the season the lump sum amount is deposited with each branch for payment to the grower. Each branch maintains it daily records of payment to the grower and provide it at the end of each month to the cane account section The cane record of payment is checked with the posting sheet of different zones .The cane account section then makes the vouchers of payment to the cane growers and submit it to the main account section. Cane account section therefore plays an important role in the project. This section determines the cost of the cane and makes arrangement for payment to the cane grower and cane carriage contractor.
Analysis of various Accounting Procedures in the company:
Going concern: These accounts have been prepared on going concern basis despite the fact that during the year the company have incurred a net after tax profit of Rs. 0.314 Million and its accumulated loss stood at Rs.41.186 Million, causing erosion in share holders equity. The current ratio is adverse and showing deterioration over preceding year. However the going concern basis is valid as: The company is able to arrange finance for its smooth operations. Repayment of liabilities is being made and arrangements for matured finance have been made and there are not defaults.
Projected cash flows shows better results in future. Accounting convention: These accounts have been prepared under the historical cost convention. Staff retirement benefits: The company operates a defined Contribution Recognized Provident Fund Scheme for its eligible permanent employees who opted for the benefits. Equal monthly contribution are made, both by the company and the employee to the fund at the rate of 10% of basic pay.
Taxation: Current: Provision for current taxation is based on taxable income at the current rates of taxation after taking into account admissible tax credits and rebates, if any.
Deferred: The company accounts for deferred taxation on all significant timing difference using liability method. Fixed assets: Companys owned: Operating fixed assets are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation except freehold land and capital work-in-progress which are stated at cost. Depreciation is computed by applying reducing balance method whereby the cost of an asset is written off over its estimated useful life. Full year depreciation is charged on the assets acquired during the year while no depreciation is charged in the year of the disposal. Maintenance and normal repairs are charged to income as incurred. Major renewals and improvements are capitalized and assets so replaced if any, are retired. Profit or loss on disposal of fixed assets is included in the current years income. Leased assets: The company accounts for plant and machinery under financial lease by recording the asset and related liability. The amount are determined on the basis of discounted value of total minimum lease payments and residual value of the asset at the end of lease period to be paid by the company. Finance charges are allocated to accounting period in a manner so as to provide a constant periodic rate of charge on the out-standing liability. Depreciation is charged at the rates specified in the related note to write off the asset over its estimated use-full life keeping in view of the certainly of the ownership of the asset at the end of lease term. Lease rentals payable on assets held under operating lease are charged to profit and loss account for the year.
Long Term Investment: These are stated at cost, less provision for permanent diminution if any in the value of long term investment. Working of permanent diminution determined on the basis of difference market price prevailing during the year and carrying value of the investment. Inventories: These are valued as follows: Basis: Store and spares -In stock -At cost on FIFO basis. -In transit -At actual cost. Loose tools -At valuation. Work-in-process -At average cost of raw materials. Finished stock -At lower of average cost and net Realizable value. Molasses -At net realizable value
Trade debts: Debts considered irrecoverable are written off and provision is made for the amounts considered doubtful, if any. Revenue recognition: Sales are recorded on dispatch of goods to customers. Income for SNTDs/Profit on bank deposits/COIs and rent is recognized on accrual basis. While income from dividend is recognized when right to received the same is established.
Financial analysis
1. Horizontal + vertical analysis
2. Ratio analysis
INCOME STATEMENTS FOR THE LAST FIVE YEARS
2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 Sales 710380214 916602792 831611332 540572289 528738466 Cost of sale 612248348 824957306 764171721 513867334 451316012 Gross profit 98131866 91645486 67439611 26704955 77422454 Selling expenses 1978790 14330457 1965947 1193813 1495007 Administration expenses 38903083 34034120 28294359 26154434 31024115 40881873 48364577 3260306 27348247 32519122 Operating prfit/(loss) 57249993 43280909 37179305 -643292 44903332 Other income 8916964 3029040 1391158 5595783 2613995 66166857 46309949 38570463 4952491 47517327
Financial charges 60835837 38872986 44085736 42327479 48742830 Other charges 1096662 1042880 211997 893387 358137 61932499 39915866 44297733 43220866 49100967 profit/ (loss) before taxation 4234358 6394083 -5727270 -38268375 -1583640 Taxation 3920008 151069 4687841 508695 1711500 Profit /(loss) after taxation 314350 6243014 -10415111 -38777070 127860 Appropriation Transfer from
general reserve 6000000 Interim dividened (5,029,728) 314350 7213286 unappropriated lossb/f (41,500,778) (48,714,064) -38298953 478117 350257 accumulated profit/ (loss) c/f -48714064 -38298953 478117
Balance sheet
2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 ASSETS: tangible fixed assets: operating assets 721714036 532408169 511617023 552599553 587665901 capital work in progress 11524252 90157171 108655188 7262843 18755571 733238288 622565340 620272211 622862396 606421472 long term investments 20662667 22537900 10037900 10037900 10037900 long term loans 362280 long term deposits 27978541 22334830 12125130 19375130 21884730 CURRENT ASSETS stores spares 63750696 68272304 59379896 63582180 72749612 stock in trade 2254867 407776 89271555 40154151 1094957 trade debts 5654650 short term investments 4113322 loans and advances 13562375 63101972 13615670 13566216 14807087 deposits & prepayments 8634398 4211716 9437510 3025493 6098208 cash and bank balances 69099313 6925345 3722261 6645238 1101494 157301649 142919113 175426896 126973278 105619330 total assets 939181145 810357183 817862137 779248704 744325712
Balance sheet liability side
2000 1999 1998 1997 1996
SHARE CAPITAL AND RESERVES: SHARE CAPITAL: authorized, Rs 10 each 150000000 150000000 150000000 150000000 150000000 issued, subscribed and paid up 50297280 50297280 50297280 50297280 50297280 revenue reserves 6000000 6000000 6000000 accumulated (loss) or profit -41186428 -41500778 -48714064 -38298953 478117 9110852 8796502 7583216 17998327 56775397 subordinated loans 451000000 466000000 466000000 452000000 417000000 long term loans 45750000 30000000 redeemable capital 4000000 19147770 liabilities against assets subject to f. lease 141437404 78669283 37104799 67784794 65702317 Marabaha finance 15264040 deferred liabilities 17488093 27416885 7110410 deferred taxation 6000000 6000000 8300000 CURRENT LIABILITIES current portion of L/T liabilities 127483883 59508341 short term running finance 115035070 72399065 134731755 115625926 55511877 current proportion of redeemable capital 4000000 15147770 20573601 C/T against assets subject to F. lease 30679995 31269316 43848926 current portion of the deferred liabilities 7214970 creditors, accruals and other liabilities 29768462 71177897 92225117 58567469 54611980 provision for taxation 4331434 6318002 4905400 3744692 2853844 276618849 209403305 273757237 224355173 177400228 contingencies and commitments TOTAL 939181145 810357183 817862137 779248704 744325712
FINANCIAL ANALYSIS The process of the financial analysis basically involves viewing the financial position of the organization from different angles. The basic purpose of the making the financial analysis is to see whether the organizations performance is in accordance with the plans of the management and whether the objectives of the organization are being met or not. In short it is the assessment of the firms past, present and the anticipated future financial condition. Because of the financial analysis, firms strengths and weaknesses are highlighted. The financial analysis can be, Internal External INTERNAL ANALYSIS When the analysis is done by the internal employee of the firm then it is called as the internal analysis. EXTERNAL ANALYSIS When the analysis is carried out by the external analyst, then it is known as the external analysis. OBJECTIVES OF FINANCIAL ANALYSIS:
The particular objectives sought to the served by financial analysis determine the type of ratios as well as the extent and depth of ratio analysis to be carried out to draw conclusions. Financial analysis is carried out by; Business Concern: For assessment of profitability of the business. For assessment of stability and financial strength of the business entity. Management: Assessment of efficiency of resources utilization. Assessment of potentials of profitability. Evaluation of different management controls. Investors: Assessment of earnings and divided prospects. Growth in economic value of investments vis--vis risks undertaken. Bankers/Creditors Concern: Assessment of the ability of the business to service its debt obligations. Debt coverage. Proper utilization of assets financed. Government Concern: Evaluation of the economic contributions of the business entity. Determination of the entitys financial strength to carry social and development programs. THE TOOLS USED The tools used by the both internal and the external analysts are the same but the purpose for carrying out the analysis different. The tools commonly used are as follows, 1. Trend analysis 2. Common size analysis 3. Ratio analysis TREND ANALYSIS The word trend normally represents the direction. So in the trend analysis, we see that in which direction i.e. favorable or unfavorable, a particular firm is going. In this analysis, a year is taken as the base and the other years quantities are expressed in term of percentages of the base year. Generally, the first year is taken as the base year; trend analysis involves the computation of the percentage relationship that each figure bears to the same item in the base year. This analysis helps in forming an opinion as to whether the favorable or the unfavorable tendencies are reflected from the data. COMPARABILITY OF THE TREND ANALYSIS
The comparability of the trend analysis is affected by , The accounting principles and the policies followed during the years which are under consideration. Therefore, the accounting policies must remain same during the periods of comparison The prices when these change materially. Therefore for the trend analysis to be effective, the prices must remain unchanged during the period under consideration. Trend analysis for the FECTO SUGAR MILLS LTD. INCOME STATEMENT ANALYSIS SALES From the sales figure we can see that the sales are not going in the favorable direction recently. The trend in the sales, taking year 1996 as base, is as follows, 102.24% in 1997 157.2822 % in 1998 173.3566% in 1999 & 134.3538% in 2000 From the above data we can conclude that the year 1999 was the time of boom for the company. Up to 1999, the sales grew in an increasing pattern but these fell down drastically in the year 2000. It is because of the shortage of the sugar cane in the area. COST OF GOODS SOLD The trend is as follows, 135.6585% in 2000 182.7893% in 1999 169.3208% in 1998 113.8598% in 1997 The same trend was there in the CGS as we found in the sales. The reason being the same for the both. It is not a bad trend because the cost of goods are moving in the same direction as that of the sales. GROSS PROFIT The gross profit has showed the following trend, 126.7486% in 2000 118.3707% in 1999 87.10601% in 1998 34.49252% in 1997 Being closely related to the sales and the cost of sales, the gross profit is also moving in their respective direction. SELLING EXPENSES The trend in the selling expenses shows that the year 1999 was really the year of the selling efforts by the sales department. In this particular year, the selling expenses touched the top as compared to all the other years. The enormous rise in the sales in 1999 was also because of the selling efforts of the department. a few selling contracts were of such nature because of which the sales as well as the sales related expenses rose.
ADMINISTRATIVE EXPENSES
The management of the mills was able to control the management and other administrative expenses up to a great deal. In 1999, these expenses were only 109.7021% of the base year despite the fact that all the other expenses rose in this year. In 1999, there was the implementation of the long planned downsizing policy of the management of the mill. All the redundant posts were vacated by the management. It cut down the salary costs of those who have been employed for nothing. The rise in the sales was also because of the threat to the employees about the managements severe downsizing policy implementation. OPERATING PROFIT The trend shown by the operating profit is quit a successful one. The rise is really a slow one, but it is a favorable one. The trend reflects the managements real efforts towards the improvement of the profits of the company. The trend of 82%, 96% and 127% in the last consecutive years might have really boosted the spirit of the management. OTHER INCOMES This particular area of the company is amazingly improving for the last few years. The reasons for this particular improvement are, The availability of market for the wastes of the mill. Timely disposals of the obsolete machinery The investment of the idle funds in the profitable areas.
FINANCIAL CHARGES It seems the trouble creating area for the company. Almost all the profits of the mill are turned into the losses because of the heavy financial charges. The company must consider its borrowing policy to save all the profits eaten up by the debt servicing charges. OTHER CHARGES In addition to the financial charges, the other charges are also something the company needs to consider seriously. The figures of 291% and 306% in the years 1999 and 2000 respectively, are conveying an alarming condition for the management of the company. NET INCOME Despite the sever fluctuations in the different expenditures of the company, the net income available to the shareholders is satisfactory from its trend point of view. In this area also, the year 1999 took a lead ahead of all the preceding areas. 4882.695% Increase as compared to the base year means a lot of improvement. But as we can see from the other years under consideration, this increase was not because of some permanent nature.
2000 1999 1998 1997 Sales 134.3538 173.3566 157.2822 102.2381 Cost of sale 135.6585 182.7893 169.3208 113.8598 Gross profit 126.7486 118.3707 87.10601 34.49252 Selling expenses 132.3599 958.5545 131.5009 79.85334 Administration expenses 125.3963 109.7021 91.20118 84.30356 125.7164 148.7266 10.02581 84.09897 Operating profit/(loss) 127.4961 96.38685 82.79854 -1.43262 Other income 341.124 115.8778 53.21961 214.0701 139.2479 97.45908 81.17137 10.42249 Financial charges 124.8098 79.75119 90.44558 86.83837 Other charges 306.213 291.1958 59.19439 249.454 126.133 81.29344 90.21764 88.02447 profit/ (loss) before taxation -267.381 -403.759 361.6523 2416.482 Taxation 229.0393 8.826702 273.9025 29.72217 Profit /(loss) after taxation 245.8548 4882.695 -8145.71 -30327.8
BALANCE SHEET TRENE PERCENTAGES FOR ASSETS
2000 1999 1998 1997 ASSETS: tangible fixed assets: operating assets 122.8103 90.59708 87.05916 94.03294 capital work in progress 61.44442 480.6954 579.3222 38.72366 120.9123 102.6622 102.284 102.7111 long term investments 205.8465 224.528 100 100 long term loans long term deposits 127.845 102.0567 55.40452 88.53264
CURRENT ASSETS stores spares 87.63029 93.84559 81.62229 87.39865 stock in trade 205.932 37.24128 8152.974 3667.19 trade debts 0 0 0 0 short term investments 0 0 0 0 loans and advances 91.59381 426.1606 91.95374 91.61975 deposits & prepayments 141.5891 69.06481 154.7587 49.61282 cash and bank balances 6273.236 628.7229 337.9284 603.2932 148.9326 135.3153 166.0936 120.2178 total assets 126.1788 108.8713 109.8796 104.6919
TREND ANALYSIS FOR LIABILITY SIDE
2000 1999 1998 1997 SHARE CAPITAL AND RESERVES: SHARE CAPITAL: authorized, Rs 10 each issued, subscribed and paid up 100 100 100 100 revenue reserves 0 0 100 100 accumulated (loss) or profit -8614.3 -8680.05 -10188.7 -8010.37 16.04718 15.49351 13.35652 31.70093 subordinated loans 108.1535 111.7506 111.7506 108.3933 long term loans redeemable capital 0 0 0 20.89016 liabilities against assets subject to f. lease 215.27 119.7359 56.47411 103.1696 Marabaha finance deferred liabilities deferred taxation 0 0 72.28916 72.28916 CURRENT LIABILITIES current portion of L/T liabilities short term running finance 207.2261 130.4209 242.708 208.2904 current proportion of redeemable capital 0 0 19.44239 73.62722 C/T against assets subject to F. lease 0 0 69.96749 71.31148 current portion of the deferred liabilities creditors, accruals and other liabilities 54.50903 130.3339 168.8734 107.2429 provision for taxation 151.7754 221.3857 171.8875 131.2157 155.9293 118.04 154.3162 126.4684 Contingencies and commitments TOTAL 126.1788 108.8713 109.8796 104.6919
FIXED ASSETS The trend in the financial position of the company is a very healthy one because the assets have an increasing trend in them which shows the capitalization of the business. In the first two years immediately following the base year, there has been a decrease in the assets i.e.6% in the 1997 and almost 13% in the 1998. but this does not mean any unhealthy sign for the company rather if we look at the capital work in progress, it is continuously at an increase i.e.39% in 1997 and 590% in 1998. it was because of the sale of the obsolete machinery in those years because of which the assets show a decreasing trend. The receipts from the sale were actually capitalized in the acquisition of new assets for the company which is reflected by the increase in the capital work in progress. This capitalization was done very swiftly because we can see the decreasing trend in the capital work in progress figure in the last two years under consideration. LONG TERM INVESTMENTS In 1999 and 2000, the company was also able to invest substantial amount in the long term investments. The management of the company seems to have decided for the long term capitalization process. The increasing trend in the other income is because of the incomes coming from these long term investments. LONG TERM DEPOSITS The long term deposits have increased up to 27% as compared to the base year. From these also, we can conclude the solvency position of the company. Here one thing I would like to add, we have seen in the income statement trends that the company is having substantial earnings from activities other than its major operations because of which, despite having little operating profits, the company was able to gather enough amounts for its shareholders. It is not a bad or ill thing, but what the management should be doing is that they must give greater importance to their main operations instead of having greater income from other sources. No doubt the management has been quite successful in earning funds for the shareholders, but actually they cannot be said to be efficient as they have not been able to show it in the activities for which they have been in the company. CURRENT ASSETS Current assets are basically the key indicators of the efficiency of the management in handling the business. Stores and spares are those current assets which are continuously used by the organization for the daily needs of their plant and machinery. The decrease in the stores and spares mean their utilization in the following period. There has been an almost fixed decrease in the stores in the following years as compared to the base year and this decrease has proved to be the constant one. It shows decreased need for the items of store, probably because of having replaced the worn out machinery. The other thing which can be concluded from this is that the operational workers are well aware of the need for the store items needs which is evident from the constant figure of the store items. STOCK IN TRADE Immediately after the base year, there have been piles of stock at the end of the period and it piled further in the next year. The two figures of the stock in trade i.e.3667% and 8152% in years 1997 and 1998, respectively, show the period of great tension for the management being unable to sell the stock within time. But in the year 1999, the reduction of the stock in trade from 8152% to only 27% is a great achievement of the management who must have worked at their toes to get the market share in the sales
of the sugar. The other reason for this can be the anticipation of a big order in future which made them pile the stock for the period of almost two years. The enormous sales of the year 1999 might also be because of the sale of heavily piled stock.
CASH AND BANK BALANCES The position of the cash and bank balance of the company indicate that the management does not believe in keeping the funds in the form of idle cash either in the bank or at hand. There has been an almost fixed increase in the cash balance of the company in the following years as compared to the base year. In the four years of operations the management has been able to increase the total assets of the company up to 27% of the base year which is a very positive sign for the shareholders. LIABILITIES SIDE OWNERS EQUITY Not being able to earn profits and having been indulged in the payment of the financial and other charges, the company has not been able to generate any profits during the last four years of its operations. It has been accumulating all of its loss due to which the equity of the company has been following a decreasing trend. It is the only sign of great worry for the management and the shareholders. This trend is also putting a very bad impact on the company image in the open market. As discussed earlier, the management should be looking forward to the efficient working of the company instead of making investments in other activities. Looking at the figures for the liabilities, it is really amazing that at one side the management has made huge long-term investments, and has advanced the loans but on the other hand, the trend in the liability position is also an increasing one. The management must try to utilize its own resources in the business so that it may be saved from the heavy interest charges on the borrowed money. It is also advisable because the money earned on investments is much less than the money spent on borrowing the funds.
COMMON SIZE STATEMENT COMMON SIZE ANALYSIS In trend analysis, we see that in which direction the firm is moving by comparing the data of different years. This analysis may be of some value when the comparison of items is made with the same items in the base year. But this method is not beneficial when the comparison is of one company or several companies with the industry. It is because there exists no common base for the different companies. For
such comparisons, the common size statements are used. In common size statements, the items of the financial statements are taken as one grand total .e,g. In case of the income statement, all the items are taken as the percentage of the sales. In the balance sheet, both the assets and the liabilities are taken as the percentages of their grand total of the balance sheet. Because of the above reason, the common size statement is also called as the component percentage or the 100% statement. These are most valuable to the analyst for studying the current financial position and operating results of the company especially in making comparisons with the company in the same industry and the industry standards. COST OF GOODS SOLD The vertical analysis of the company id very attractive so far as the cost of goods sold is concerned. The company has been able to control the cost of goods sold not only up to a constant level but also it has been able to bring it down up to some extent. The picture presented by the vertical analysis is as follows, 86.18601% in 2000 90.00161% in 1999 91.89049% in 1998 95.05987%in 1997 We can easily observe the downward flow of the cost of sales. It might be because of the close supervision of the operations by the management. Ideally, the CGS should have been much less than the percentages which are prevailing in the financial reports of the company. COMMON SIZE ANALYSIS OF THE INCOME STATEMENT
2000 1999 1998 1997 Sales 100 100 100 100 Cost of sale 86.18601 90.00161 91.89049 95.05987 Gross profit 13.81399 9.998386 8.109511 4.940127 Selling expenses 0.278554 1.563432 0.236402 0.220842 Administration expenses 5.476375 3.713072 3.402354 4.838286 5.754928 5.276503 0.392047 5.059129 Operating profit/(loss) 8.059064 4.721883 4.470755 -0.119 Other income 1.255238 0.330464 0.167285 1.035159 9.314288 5.052346 4.63804 0.916157 Financial charges 8.563842 4.240985 5.301243 7.830124 Other charges 0.154377 0.113777 0.025492 0.165267 8.718218 4.354762 5.326735 7.995391 profit/ (loss) before taxation 0.596069 0.697585 -0.6887 -7.07923 Taxation 0.551818 0.016481 0.563706 0.094103 Profit /(loss) after taxation 0.044251 0.681104 -1.2524 -7.17334 So much level of CGS never allows the management to aggressively participate in the other promotional activities to develop the business to some higher level. Anyway, the decreasing pattern of the CGS may be because of the managements awareness of this fact and as a result of the efforts taken by the management in this area.
GROSS PROFIT Gross profit is basically the coushin that any company has for the expenses other than the manufacturing expenses. The companies able to avail a higher level of the GP are in better position to expend the resources in the activities other than the manufacturing activities. From the year 1997 to 2000, there is a very positive sign of increase in the GP which has been increased from a very poor level of only 4% to an acceptable level of 9% in 2000. It is still not up to the mark but the reason of the satisfaction is the trend that we can observe in the GP with the passage of time. As said earlier. The GP provides the cushin to the management for the incurring of the other costs, in the year 1997, where the GP percentage is only 4%, the company has gone into severe loss where it has not even been able to cover its manufacturing costs. It also means that all the other costs have been paid by the company out of its own pocket. In the next years the management has been quite successful in improving in this area and we can see that in the year, 1998, the company has covered all of its manufacturing costs but because of having very little left behind, it fell short of the admin and other expenses. 1999, in contrast to the previous two years, here the company has not only covered its operating costs, but it has also been able to save some amount for its shareholders after paying for all the expenses. 2000, the amount saved for the shareholders has increased which again shows a satisfactory sign for the shareholders. SELLING &ADMIN EXPENSES The management seems to have a firm control over these expenses because at an average these have not shown any significant fluctuations. Only in the year 1999, there have been some tremendous selling activities and as a result, the expenses have gone to a higher level. The admin expenses have increased over these years.
OPERATING PROFIT The operating profit has been managed to increase over the years. This is because of the tight control of the management over the production processes and activities. The cost of goods sold, as explained earlier has been controlled and reduced as compared to the past. It led to an increased gross profit and the increased resultant operating profit. FINANCIAL CHARGES It is really the danger area for the management of the company. We can see that as the operating profit increased, the financial charges have also shown the same trend in them. These charges have been almost equal to the operating income which means that these would not allow the incomes flow to reach the shareholders accounts waiting in the bottom of the income statement. Only an amount less than one percent has been able to flow to the shareholders in the years where there has been some operating profits i.e. 1998, 1999 and 2000.the management of the company must consider their borrowing policies so as to minimize the adverse impact of these financial charges on the financial and the operating performance of the company. BALANCE SHEET VERTICAL ANALYSIS
2000 1999 1998 1997 ASSETS: tangible fixed assets: operating assets 76.84503 65.70043 62.55541 70.9144 capital work in progress 1.227053 11.12561 13.28527 0.932031 78.07208 76.82604 75.84068 79.93114 long term investments 2.200073 2.78123 1.227334 1.288151 long term loans long term deposits 2.979036 2.756171 1.48254 2.486386 CURRENT ASSETS stores spares 6.787902 8.424964 7.26038 8.159421 stock in trade 0.240089 0.050321 10.91523 5.152931 trade debts short term investments loans and advances 1.444064 7.786933 1.664788 1.740935 deposits & prepayments 0.919354 0.519736 1.153924 0.388258 cash and bank balances 7.3574 0.854604 0.455121 0.852775 16.74881 17.63656 21.44945 16.29432 total assets 100 100 100 100 FIXED ASSETS Like a typical manufacturing concern, the company is having most of its investment in the fixed assets. More than 75% of the total assets are in the form of the fixed assets of the company. The company has been involved in the making of the new fixed assets and there has been a continuous exchange between the fixed assets and the capital work in progress but on the whole, the total amount invested in the fixed assets has remained constant over the years. CURRENT ASSETS The current assets investment of the company has remained constant to almost 19% of the total assets. It shows that the company is well aware of the fact that greater the liquid assets, smaller will be the profitability of the company. Looking at the figures, we can see that in the years 1997 and 1998, the major proportion of the current assets were the stock in trade. 2000 1999 1998 1997 SHARE CAPITAL AND RESERVES: SHARE CAPITAL: authorized, Rs 10 each issued, subscribed and paid up 5.35544 6.206804 6.149848 6.454586 revenue reserves 0.73362 0.769972 accumulated (loss) or profit -4.38536 -5.12129 -5.95627 -4.91486 0.970085 1.085509 0.9272 2.309703 subordinated loans 48.02056 57.50551 56.97782 58.00459 long term loans 4.871265 3.702071 redeemable capital 0.513315 liabilities against assets subject to f. lease 15.05965 9.707976 4.536804 8.698737
Marabaha finance 1.62525 deferred liabilities 2.158072 3.352262 0.91247 deferred taxation 0.73362 0.769972 CURRENT LIABILITIES current portion of L/T liabilities 13.57394 7.343471 short term running finance 12.24844 8.934216 16.47365 14.83813 current proportion of redeemable capital 0.48908 1.943894 C/T against assets subject to F. lease 3.751243 4.012752 current portion of the deferred liabilities 0.882174 creditors, accruals and other liabilities 3.169619 8.783521 11.27636 7.515889 provision for taxation 0.461193 0.779656 0.599783 0.480552 29.45319 25.84086 33.4723 28.79122 contingencies and commitments TOTAL 100 100 100 100
In the following two years i.e. 1999 and 2000, the proportion has been shifted to the long term investments than the stocks. The reason being the sale of the stocks in those years and the investment of the receipts in the long term investments. CURRENT LIABILITIES The current liabilities are in the form of the short term running finance availed by the company. The current liabilities made up almost 30% of the total liabilities of the company. Out of the total current liabilities, 15% are in the form of the short term running finance and the 12% are in the form of the current portion of the long term liabilities. The remaining is contributed by the creditors and the taxation provisions and the others. The nominal portion of the creditors in the current liabilities shows that the company pays the cash to its suppliers of sugar cane through the presence of a running finance facility obtained from a bank. Like all the other industries using the agricultural products as their raw materials, the Fecto sugar mills is also dealing with its suppliers through making payment to them in cash. LONG TERM LIABILITIES AND THE EQUITY This area is very poor one for the company as the portion of the equity in the total liabilities is only round about 1% which shows that the company is not at all in a position to give anything to its shareholders if it gets insolvent. 1% means really nothing as equity. The other thing which is very interesting here is the presence of the subordinated loans. The loans provided by the management of the company. From here we can easily conclude that the management of the company is more interested in the company than the shareholders of the company. The portion of the subordinated loans in the total liabilities is 48%. I can even say that the shareholders of this company must have considered their investment as gone wasted and the fact that the company is still in operation is that the management has all the interest in the company for which it is making the organization move in any direction with an anticipation of recovering some thing out of it one or the other day. RATIO ANALYSIS An index that relates two accounting numbers and is obtained by dividing one number by other Ratio Analysis is an important and age-old technique of financial analysis. It simplifies the comprehension
of financial statements. Ratios tell the whole story of changes in the financial condition of business. It provides data fro inter firm comparison. Ratios highlight the factors associated with successful and unsuccessful firm. They also reveal strong firms and weak firms, over- valued and under valued firms. It helps in Planning and forecasting. Ratios can assist management, in its basic functions of forecasting, planning, co-ordination, control and communication. Ratio analysis also makes possible comparison of the performance of different divisions of the firm. The ratios are helpful in decision about their efficiency of otherwise in the past and likely performance in future. Ratios also helps in Investment decisions in the of investors and lending decisions in the case of bankers etc. Types of Ratios Following the main types of ratios that we are going to calculate in this assignment, 1. Liquidity Ratios 2. Leverage Ratios 3. Coverage Ratio 4. Activity Ratios 5. Profitability Ratios
LIQUIDITY RATIOS Liquidity ratios are used to measure a firms ability & solvency of the firm to meet short -term obligations. They compare short-term obligations to short-term resources available to meet these obligations. It consists of two ratios current & acid test ratio. Let us calculate these for Service Industries. We have two types of liquidity ratios, Current ratio Acid test/quick ratio Current Ratio Current ratio is the relationship between current assets and current liabilities. This Ratio is also known as working Capital ratio. It is calculated as Current ratio = Current Assets/ Current Liabilities The current ratio for the Fecto sugar mills is as follows,
INTERPRETATION The current ratios of the company are not very impressive. The acceptable current ratio is 2:1 but the company has never been able to maintain the acceptable level of the current ratio. Having a 1:1 current ratio means that the company has one rupee for the discharge of each one rupee of the current liabilities. The company is not in a good position to meet its current obligations as they will fall due in the recent period of time. The company has a current ratio of less than one in each of the years which shows that the companies short term obligations will not be fulfilled by its current assets rather some of the long term assets will also be needed for the discharge of the current liabilities. The other thing which this ratio
signifies is that some of the fixed assets of the company have also been financed through the short term liabilities. QUICK/ACID TEST RATIO: Quick or Acid Test Ratio is the ratio of liquid assets to current Liabilities. True liquidity refers to the ability of a firm to pay its short-term obligations as when they become due. Quick Ratio is equal to Quick or Acid test ratio = Quick Assets/ Current liabilities
INTERPRETATION This ratio basically shows the ability of the company to pay off its short term obligations as they become due without going for anything else. For this ratio, the current assets are reduced by the amount of the slow moving items like the stocks and the prepayments. The acceptable or the ideal ratio is 1:1 which means that the firm must have one rupee in quick assets to pay off its current liabilities as they become due. Like the current ratio, the company has never been able to achieve the desirable figure in this area also. As shown in the above table, the average ratio maintained by the company in the last five years is less than 1 which means that the company will be forced to do some thing else to pay off its current obligations. LEVERAGE RATIOS We all know that the firms are financed through two main sources, Internal sources External sources Internal sources include the shareholders contribution in the total financing of the company and the external sources include the debts which have been obtained by the management to finance the company. Leverage ratios can be defined as, The ratios which show the extent to which the firm has been financed by the debts. These include, Debt to equity ratio Debt to total assets ratio Long term debt to total capitalization DEBT TO EQUITY RATIO: Debt to equity ratio indicates the relationship between the external equities or outsider finds and the internal equities or shareholder fund. It is calculated to assess the extent to which the firm is using borrowed money. In other words, we can say that the debt to equity ratio answers the following question, How the firm has financed its assets? It gives us the sources of finance and their percentages in the total financing of the company. Debt to equity is simply calculated as Debt to equity ratio = Total Debts / Shareholders equity Where as: Total debts = current liabilities + long-term debts
INTERPRETATION We can see that the company has been consistently relying on the external debts to finance its operations. The ratio has an increasing trend in it since 1996 up to year 2000; the debt amount has gone beyond the equity. It means that for financing the activities of the firm, each rupee invested by the shareholders has been accompanied by, 0.12 rupee in year 1996 0.47 rupee in 1997 1.42 rupees in 1998 0.97 rupee in 1999 & 1.13 rupees in 2000 of the external lender. It is not a good sign at all as the firm would not be able to get more funds from other lenders because the coushin in its equity for the lenders has already been exhausted. DEBTS TO TOTAL ASSETS RATIO: The Debts to total assets Ratio tells us how much portion of assets is a debt. This ratio serves a similar purpose to debts to equity ratio. It highlights relative importance of debt financing to the firm by showing the percentage of the firms that is supported by debts financing. This ratio is calculated as Debts to Total Assets ratio = Total Debts / Total Assets
INTERPRETATION This ratio gives us the view about the amount invested in the total assets of the company. The above figures of the company are not very good. We can see that for the last five years, the c ompanys assets have been predominantly financed by the external debts. The ratios of 1.05, 1.11, 1.33, 1.067, and 1.11 for the years 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999 and 2000 respectively show that for all of these years, the each rupee of the shareholders had been accompanied by more than one rupee of the external lenders. LONG TERM DEBT TO TOTAL CAPITALIZATION This ratio tells us about the amount of the long term debt in the total capitalization of the firm. It is calculated by the following relation, Long term debt to total capitalization = LT debt/ (LT debt + share holders equity)
INTERPRETATION We can see that the long term debt has always been equal to the total financing of the company. As already discussed the equity is very nominal in the total financing of the company. Out of the total long term debt, we have seen that the portion of the debt provided by the management of the company is very much. COVERAGE RATIO
The Ratio that relates the financial charges of a firm to its ability to serve or cover them. This ratio tells us about how much earning is available for the servicing of the interest payable on the debts. In other words, we can say that this ratio shows that whether the income of the company is sufficient to bear the interests and other charges or not. INTEREST COVERAGE RATIO: Interest Coverage ratio is designed to relate the financial charges of a firm to its ability of pay/cover them from its earning. Interest Coverage ratio is calculated as Interest Coverage Ratio = Earning before Interest & Tax / Financial charges
INTERPRETATION This ratio again is not a very good one because we can see that for each rupee to be paid as the interest, the company only has an amount a little over one rupee for the payment of interest. Here, I am not saying that the company will not be able to pay its interest charges; the point of tension is that it would be left with only the nominal amount to be distributed among its shareholders or even it would not have anything to pay to its shareholders after the payment of the taxation expenses for the year. This was the picture in the years 1999 and 2000, the condition was even worse in the years 1998, 1997 and 1996 where the company was not even able to pay its financial charges fully. ACTIVITY RATIOS Activity ratios are also known as efficiency or turnover ratios, measure how effectively the firm is using its assets. Some of the aspects of activity analysis are closely related to liquidity analysis. In this session we will primarily focus on how effectively the firm is managing tow specific groups receivables and inventories and its total assets in general. The two main activity ratios are, Receivable turnover ratio Payables turnover ratio Inventory turnover ratio RECEIVABLE TURNOVER RATIO: Debtor turnover ratio indicates the velocity of debts collection of a firm. In simple words, it indicates the number of times average debts are turned over during a year. Higher the value of debts turnover, more efficient is the management of debts or more liquid the debtors are and vice versa. Receivable turnover ratio is calculated as Receivable/debtors turnover ratio = Annual credit sale / Trade debtors There have been no trade debts in the company after the year 1996, probably because of the low performance of the company or because of the strict debt policy of the company. PAYABLE TURNOVER RATIO: This ratio is against to Debtors turnover ratio. It compares the creditors with the total credit purchase. It
signifies the credit period enjoyed by the firm in paying off debts. In payable turnover ratio less the results better for the company. It is calculated as Payable Turnover ratio = Annual Credit Purchase / Creditors INVENTORY TURNOVER RATIO: Inventory Turnover ratio, also known as Stock Turnover, is the relationship between Cost of Goods Sold during the period and average inventories. It measures the velocity of conversion of stock into sales. Usually higher inventory turnover, stock velocity, indicates efficient management because more frequently stocks are sold lesser the amount of money required to finance the inventory. It is calculated as Inventory Turnover = Cost of Goods Sold / Average Inventory PROFITABILITY RATIOS Profitability ratios are of two types Those showing profitability in relation to sale and Those showing profitability in relation to investment. To gather these ratios indicate the overall effectiveness of operation PROFITABILITY IN RELATION TO SALES It consists of the following ratios, Gross profit ratio Net profit ratio GROSS PROFIT RATIO Gross profit is the amount which a company has after the deduction of the operating expenses from the total revenue of the firm. It basically provides the coushin for the expenses other than the operating expenses. Gross profit ratio, which is also called Profitability in relation to sales, is the ratio of gross profit to new sales expressed as a percentage. This ratio tells us the profit of the firm relative to sales after we deduct the producing the goods. It is a measure of the efficiency of the firm operation. Higher the gross profit ratio better it is. It is calculated as Gross Profit Margin = Gross Profit / Net Sales
INTERPRETATION As discussed earlier, the GP ratio provides the management with the funds to expend on the other business activities than the manufacturing expenses. The above calculations of the GP ratio indicate that the management of the Fecto sugar mills have to be very much reluctant in making the expenses because the margin for the expenses is very little i.e. 13.81% in 2000 9.998% in 1999
8.109% in 1998 4.94% in 1997 14.64% in 1996 The margin earned by the company is so much less that the shareholders might have no chance of receiving anything from the company because there are other admin and selling expenses which need to be paid off before anything comes to the shareholders lying at the bottom of the income statement.
NET PROFIT AFTER TAX TO SALE: The net profit margin is a measure of the firms profitability of sales after taking accoun t of all expenses and income tax. This ratio also indicates performance during the financial year. Simply high the ratio better the firm performance and efficiency. It is calculated as, Net Profit Margin = Profit after tax / Sales
INTERPRETATION The net profit ratios gives the picture of what the company is actually paying to its share holders after paying all the expenses incurred in the activities of the business. The above calculations are really very much depressive for the Fecto sugar mills. The firm has never been able to pay the shareholders some amount which can justify their investment in the company. The nominal profits earned in the years 1999 and 2000 went in setting off the accumulated profits carried forward by the company. This fact is also evident from the income statement of the company. PROFITABILITY RATIOS IN RELATION TO INVESTMENT In this head, we have two ratios, Return on equity Return on total assets RETURN ON EQUITY: Return on equity is another measure of overall firms performance. It compares net profit after tax to the equity that share holders have invested in firm. This ratio tells the earning power on shareholders book value. Higher the return on equity ratio often reflects the firms acceptance of strong investm ent opportunities and effective expense management. It is calculated as Return on Equity = Net profit After Tax / Shareholders Equity x100
INTERPRETATION
This ratio is also a very bad one for the company because the return on the equity is negative in the years 1997 and 1998. in the other years when the return is positive, it is so meager that the shareholders might have repented on investing in the company. The amount invested in the company might have earned much greater amount if it had been invested some where else. In the years where it is in positive figures, only the year 1999 is a good one when the company gave 70% return on the equity while in the year 2000, the return was only 3%. TOTAL ASSET TURNOVER: Total Asset turn over shown the sale revenue per dollar of assets invested. This total asset turnover ratio tells us the relative efficiency with which firm utilizes its total assets to generate sale. It is calculated as Total Asset Turnover = Net Sales / Total Assets x 100
INTERPRETATION The assets have been earning at an average of 80% in the form of the profits. This ratio is also not a very great one as compared to the industry average.
Part seven Training programme ????????????????????????????
Part eight Coclusions and recommendations
Conclusion: Specific Recommendations For The Organization:
There should be a safety department in the company to assure the safety of the workers. A regular training programme should be a permanent policy of the management so as to provide not
only the required skill to employees but also to help them keeping their skills up to date. Balance should be at a distance of 5 kilo-meters from the cutters There should be card system for every employee from helper to manager for punctuality. Wages of workers should not be less than Rs3000 per month. There should be family quarters for all married workers. There should be a high school and a college as well for boys and girls in the factory area. There should be transport facility for workers within the district. All the employees especially those associated with production should be encouraged, and should be involved in decision making and empowered to make innovative decisions. In this way employees can add to the organization, a lot. e.g. a new cost effective production technique can result in comparatively huge profits.
You might also like
- Brown Sugar Icumsa 600-1200 Specification SheetsDocument3 pagesBrown Sugar Icumsa 600-1200 Specification SheetsTerra Merra100% (2)
- Ingredient Substitution ChartDocument2 pagesIngredient Substitution ChartLbmoore100% (5)
- Jaggery Making ProcessDocument12 pagesJaggery Making ProcessSugar Technology100% (4)
- SugarcaneDocument37 pagesSugarcaneImroz MahmudNo ratings yet
- SDCE Industrial Visit Report Sayan Sugar FactoryDocument7 pagesSDCE Industrial Visit Report Sayan Sugar FactoryPrateekBansalNo ratings yet
- Study of Centrifugal Sugar by Electrical MachinesDocument64 pagesStudy of Centrifugal Sugar by Electrical MachinesMohan Raj100% (1)
- Sorbitol manufacturing process guideDocument6 pagesSorbitol manufacturing process guideRenzo Cadag MacasilNo ratings yet
- Gafta - 130Document4 pagesGafta - 130tinhcoonline100% (1)
- Bannu Sugar MillDocument20 pagesBannu Sugar Millyaqoob008No ratings yet
- Production: Santosh Kr. Paswan Roll No 138510 ME3 YearDocument21 pagesProduction: Santosh Kr. Paswan Roll No 138510 ME3 YearEricMargateNo ratings yet
- Angel Rajput 2 Sem - Sugar IndustryDocument29 pagesAngel Rajput 2 Sem - Sugar IndustryMayank jain100% (1)
- Sugar Plant Project ReportDocument5 pagesSugar Plant Project ReportBryan TanNo ratings yet
- Sugarcane Composition and ProcessingDocument7 pagesSugarcane Composition and Processingpacoto livingstoneNo ratings yet
- Fresh Refined Suger-Meghna Group of IndustriesDocument16 pagesFresh Refined Suger-Meghna Group of Industriesiphone nokiaNo ratings yet
- Davanagere Sugar Company ProfileDocument68 pagesDavanagere Sugar Company ProfilenaglikarNo ratings yet
- Mysore Sugar Company ProfileDocument17 pagesMysore Sugar Company ProfileChetan Maski80% (10)
- Sugar Manufacturing Process - Brief Introduction SlidesDocument52 pagesSugar Manufacturing Process - Brief Introduction Slideskiller120No ratings yet
- Sugar Mill Short DescriptionDocument2 pagesSugar Mill Short DescriptionAnindya Vikram SinghNo ratings yet
- Sugar Mill HiDocument46 pagesSugar Mill HiSaravanapriya KarthikNo ratings yet
- Sagar Final ProjectDocument74 pagesSagar Final Projectkeremanevi100% (1)
- Sugar IndustryDocument50 pagesSugar Industryzohaib ul hassanNo ratings yet
- Role of sugars, gur, liquid sweeteners in candy makingDocument10 pagesRole of sugars, gur, liquid sweeteners in candy makingBharath Jaganathan100% (1)
- Ratio Analysis SNJDocument72 pagesRatio Analysis SNJGopi Nath100% (1)
- Sugarcane Processing Technologies: by Md. Akram HossainDocument16 pagesSugarcane Processing Technologies: by Md. Akram HossainDeva Mk100% (1)
- Manufacture of SugarDocument79 pagesManufacture of SugarAhmed Ali100% (2)
- PROCESS in RAW SUGAR Production of FFHCDocument27 pagesPROCESS in RAW SUGAR Production of FFHCTenebroso Pevie Anne100% (1)
- Sugar Production ProcessDocument2 pagesSugar Production ProcessedmarkNo ratings yet
- Sugar IndustriesDocument46 pagesSugar Industriesshine king100% (1)
- Sugarcane Manufacturing ProcessDocument3 pagesSugarcane Manufacturing Processdante224No ratings yet
- 9.transportation of MilkDocument3 pages9.transportation of MilkdairyNo ratings yet
- Cebu Institute of Technology - University: Production of Raw Sugar and Activated Carbon from SugarcaneDocument181 pagesCebu Institute of Technology - University: Production of Raw Sugar and Activated Carbon from SugarcaneChristine FernandezNo ratings yet
- Sugar Factory ProjectDocument75 pagesSugar Factory Projectkalaivani100% (1)
- Sugar Factory DefinitionDocument8 pagesSugar Factory Definitiontsrinivasan5083100% (1)
- Operations at Daurala Sugar ComplexDocument2 pagesOperations at Daurala Sugar ComplexShubhamNo ratings yet
- Term Paper: Master of Buisness ApplicationDocument28 pagesTerm Paper: Master of Buisness Applicationashishsuman50% (2)
- Sugar Industry Case Stdy FNL PDFDocument46 pagesSugar Industry Case Stdy FNL PDFpraneeth bmNo ratings yet
- Factors For Site SelectionDocument4 pagesFactors For Site SelectionHiren AjwaniNo ratings yet
- Percentage Replacement of Bitumen With Sugarcane Waste MolassesDocument10 pagesPercentage Replacement of Bitumen With Sugarcane Waste MolassesIAEME Publication100% (1)
- KPMG Report Exec SummaryDocument19 pagesKPMG Report Exec SummaryNawin KumarNo ratings yet
- Jaggery Plant Powered by Free of Cost SteamDocument4 pagesJaggery Plant Powered by Free of Cost SteamMichael Odiembo100% (1)
- Pakistan Sugar Industry AnalysisDocument34 pagesPakistan Sugar Industry AnalysisMuhammad Irteza Sultan100% (1)
- Airtech's Production Process and Marketing StrategyDocument75 pagesAirtech's Production Process and Marketing StrategyMonica ThakurNo ratings yet
- SugarcaneDocument83 pagesSugarcaneabrahanNo ratings yet
- Organic JaggeryDocument7 pagesOrganic JaggeryPushpender HoodaNo ratings yet
- JDW - FinalDocument28 pagesJDW - Finalmishori2008No ratings yet
- Refining and Processing SugarDocument4 pagesRefining and Processing SugarRocío CapuñayNo ratings yet
- Sugar IndustryDocument35 pagesSugar IndustryJames Laurent75% (4)
- SSP Pumps in Sugar ProcessingDocument44 pagesSSP Pumps in Sugar Processingverderusa100% (1)
- SUGARCANE WASTEWATER TREATMENT PROPOSALDocument49 pagesSUGARCANE WASTEWATER TREATMENT PROPOSALFrancis RobertNo ratings yet
- Mango Pulp RefinerDocument7 pagesMango Pulp RefinerAmzad DPNo ratings yet
- World: Cashew Nuts - Market Report. Analysis and Forecast To 2020Document9 pagesWorld: Cashew Nuts - Market Report. Analysis and Forecast To 2020IndexBox Marketing100% (2)
- Sugar ProcessingDocument46 pagesSugar ProcessingChristian Jay Baliling Sablada100% (1)
- The Soft Drink IndustryDocument21 pagesThe Soft Drink IndustrySelva GanapathyNo ratings yet
- Sweet Sorghum Ethanol ProductionDocument8 pagesSweet Sorghum Ethanol ProductionTri Wijaya PurnamaNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of Cane Diffusion & MillingDocument5 pagesA Comparison of Cane Diffusion & MillingRicardo Albino100% (1)
- 06 - Sugar Industry (B)Document35 pages06 - Sugar Industry (B)waleed chNo ratings yet
- Performance indicators for sugar processing efficiencyDocument3 pagesPerformance indicators for sugar processing efficiencyJavier Manuel IbanezNo ratings yet
- Intern GuidelineDocument36 pagesIntern Guidelinechaman shresthaNo ratings yet
- Chervil Agritech Jaggery Powder ReportDocument11 pagesChervil Agritech Jaggery Powder Reportabhijitpaymal0% (1)
- Sugarcane Biorefinery, Technology and PerspectivesFrom EverandSugarcane Biorefinery, Technology and PerspectivesFernando SantosNo ratings yet
- Zahid CH, Internship Report of Ayub Agriculture Research Institute FaislabadDocument70 pagesZahid CH, Internship Report of Ayub Agriculture Research Institute Faislabadsamreen50% (2)
- Report Sugar MillDocument51 pagesReport Sugar MillMuhammadAyyazIqbal100% (1)
- Fauji Cement Job Openings for Manager Marketing & SalesDocument1 pageFauji Cement Job Openings for Manager Marketing & SalesIdrees Akbar RajputNo ratings yet
- SamplePaper (OG 2 YPIP 5thbatch)Document6 pagesSamplePaper (OG 2 YPIP 5thbatch)Jitesh MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- 6a - The New Digital Age - Building A Brand Experience and Phygital Marketing - 2Document17 pages6a - The New Digital Age - Building A Brand Experience and Phygital Marketing - 2Idrees Akbar RajputNo ratings yet
- Skype and MISDocument8 pagesSkype and MISIdrees Akbar RajputNo ratings yet
- 4 Pass Form1Document1 page4 Pass Form1Idrees Akbar RajputNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Full FormateDocument9 pagesStrategic Management Full FormateIdrees Akbar RajputNo ratings yet
- Lahore Business School Feeguide V2Document2 pagesLahore Business School Feeguide V2Idrees Akbar RajputNo ratings yet
- Cheat CodesDocument5 pagesCheat CodesIdrees Akbar RajputNo ratings yet
- CPM of PepsiDocument3 pagesCPM of PepsiIdrees Akbar RajputNo ratings yet
- Strength and Weaknesses: StrengthsDocument2 pagesStrength and Weaknesses: StrengthsIdrees Akbar RajputNo ratings yet
- DaewooDocument2 pagesDaewooIdrees Akbar RajputNo ratings yet
- Team #:01 Group (A) MBA M2 4: Coconut VallayDocument8 pagesTeam #:01 Group (A) MBA M2 4: Coconut VallayIdrees Akbar RajputNo ratings yet
- Bajaj Hindusthan Limited (BHL) history and operationsDocument19 pagesBajaj Hindusthan Limited (BHL) history and operationsMohd Ashraf BakshNo ratings yet
- Comparison of The Concentration of Phenolic Constituents SugarcaneDocument7 pagesComparison of The Concentration of Phenolic Constituents SugarcaneMolly0630No ratings yet
- How To Make Urea Molasses Blocks Umb and PDFDocument10 pagesHow To Make Urea Molasses Blocks Umb and PDFryanNo ratings yet
- Sugar Sector PDF - 1608046711Document29 pagesSugar Sector PDF - 1608046711Mustafa Farooq100% (1)
- Noon Sugar Mills ReportDocument81 pagesNoon Sugar Mills ReportLion HeartNo ratings yet
- Mba Operations Project in Process ManagementDocument66 pagesMba Operations Project in Process ManagementVidhiya AmbigapathyNo ratings yet
- Production of Edible Syrup From Molasses (17412.en)Document9 pagesProduction of Edible Syrup From Molasses (17412.en)VishnuNo ratings yet
- Blackstrap MolassesDocument9 pagesBlackstrap MolassesKenny100% (1)
- Articulo Me Laz AsDocument10 pagesArticulo Me Laz AsGonzaloCalvoRomeroNo ratings yet
- Dried Molasses PLDocument3 pagesDried Molasses PLyousria.ahmed46No ratings yet
- EAS 16 2009 Plantation (Mill) White Sugar SpecificationDocument11 pagesEAS 16 2009 Plantation (Mill) White Sugar SpecificationFelix MwandukaNo ratings yet
- Back To Baking - Anna OlsonDocument1,678 pagesBack To Baking - Anna OlsonCristoff Castillo100% (1)
- Lactic Acid Production from Concentrated Raw Sugar Beet JuiceDocument6 pagesLactic Acid Production from Concentrated Raw Sugar Beet JuiceRahma Endah SyafitriNo ratings yet
- Living The Good Life With Helen and Scott NearingDocument17 pagesLiving The Good Life With Helen and Scott Nearingnidavan100% (3)
- Bread and Pastry: 1. The Repertoire Is Lengthy, Dehydrated Vegetables Salt, Assorted Herbs, Spice and SaltDocument5 pagesBread and Pastry: 1. The Repertoire Is Lengthy, Dehydrated Vegetables Salt, Assorted Herbs, Spice and SaltEm Israel Jr.No ratings yet
- Sugar Plant - Cost - 2 PDFDocument23 pagesSugar Plant - Cost - 2 PDFSanjay PatelNo ratings yet
- 30 Natural Remedies You Need To Know AboutDocument38 pages30 Natural Remedies You Need To Know AboutMaria BarbaliaNo ratings yet
- Back To Baking Anna Olson PDFDocument636 pagesBack To Baking Anna Olson PDFAnnelis Vásquez de Contreras100% (1)
- Manufacture of White Sugar from Sugar CaneDocument98 pagesManufacture of White Sugar from Sugar CanemgajenNo ratings yet
- A Project Report ON Remuneration System in Nayagarh Sugar Complex LimitedDocument42 pagesA Project Report ON Remuneration System in Nayagarh Sugar Complex LimitedNarayana PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Sugar Industry PrimerDocument38 pagesSugar Industry PrimerDody IrawanNo ratings yet
- Neutral Alcohol: Process TechnologyDocument6 pagesNeutral Alcohol: Process TechnologyBruno Damião100% (1)
- Optimum Bacillus subtilis Growth for Probiotic ProductionDocument31 pagesOptimum Bacillus subtilis Growth for Probiotic ProductionBethel Grace TalhaNo ratings yet
- Fermentation Process: Key Components and Types of BioreactorsDocument114 pagesFermentation Process: Key Components and Types of BioreactorsyoganandaNo ratings yet
- The Feeding Value of Sugar Cane Molasses in Broiler DietsDocument63 pagesThe Feeding Value of Sugar Cane Molasses in Broiler DietsThienNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Employment Law For Human Resource Practice 6th Edition David J Walsh PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Employment Law For Human Resource Practice 6th Edition David J Walsh PDF Full Chapterasiatic.arterym39s6100% (16)
- Properties and Components of Basic Baking PresentationDocument40 pagesProperties and Components of Basic Baking PresentationKhalid P. BataraNo ratings yet