Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organic Chemistry All Reactions
Uploaded by
Waseem AlkakozCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organic Chemistry All Reactions
Uploaded by
Waseem AlkakozCopyright:
Available Formats
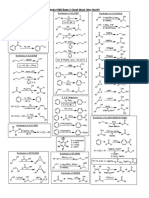
Reactions
Alcohol Reactions
Dehydration H2SO4 R R'' OR R' OH POCl3, pyridine
R R'
R''
(watch for carbocation rearrangements)
R R'
R''
boxed means you will not be responsible for knowing the mechanism
Making alkyl halides H-X, Et2O R OH PBr3, Et2O R OH SOCl2, pyridine R OH TsCl, pyridine R OH R OTs R Cl (for 1 or 2 alcohols) R Br R X (usually 3 alcohols) X = I, Br, Cl
(for 1 or 2 alcohols)
(tosylates behave like halides)
Alcohol Oxidation PCC, CH2Cl2 (1 ) R OH CrO3 H2SO4, H2O R R' (2 ) R OH OH CrO3 H2SO4, H2O R R R' OR O R O water must be absent to stop at the aldehyde stage
OH OR O
K2Cr2O7 H2SO4, H2O
K2Cr2O7 H2SO4, H2O
OR
PCC
R'' (3 ) R' R Not Oxidized by these Cr reagents OH
Ethers Ether Formation 1. NaH 2. R'-X R OH R (subject to the usual considerations for SN2 reactions)
O R'
Williamson ether synthesis
Ether Reactions
(Usually unreactive)
O R'
H-X R X + X R' (X = Cl, Br, I)
Epoxides Epoxide Formation - from alkenes (see below) Epoxide Reactions With strong nucleophiles (basic conditions): O R Nuc R OH Nuc R, etc
Nuc
OR,
attack at the less hindered position (SN2 like)
Under acidic conditions: O R H , NucH R Nuc OH
NucH
H-X, H2O, ROH
attack at the MORE hindered position (SN1 like), inversion of configuration (SN2 like)
Alkene Formation R R' OH R R' X R'' KOH, EtOH R'' H2SO4 R R' R R' R'' R'' dehydration
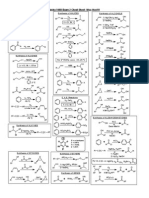
Alkene Reactions HBr R Br2, CH2Cl2 Br R Br R Br2, H2O HO R H2O, H2SO4 HO R Markovnikov Prod. (less useful method) hydration OH R hydroboration/oxidation anti-Markovnikov Prod. (syn-addition) Br halohydrin formation (also with Cl2 or NBS) (anti addition) Br hydrohalogenation (Markovnikov) halogenation (anti addition) (also H-Cl, H-I)
(also Cl2)
1. BH3-THF 2. H2O2, NaOH, H2O
H2, Pd/C, EtOH H2, PtO2, acetic acid R hydrogenation (syn-addition)
1. OsO4, pyridine 2. NaHSO3, H2O
HO R
OH
(syn-addition) dihydroxylation
epoxidation R
H+, H2O
HO R
OH
(overall anti-addition)
m-CPBA, CH2Cl2 R Br2, H2O HO R Br NaOH, H2O R
epoxidation (syn-addition)
R' R
1. O3, CH2Cl2 2. Zn, acetic acid, H2O R
R'
ozonolysis
Me2S may be used for step 2
Alkyne Formation Br R Br KOH, EtOH R 1. NaNH2, NH3 2. X R' R R double elimination or from Br R Base could also be NaH, BuLi Br
R'
alkylation
(only methyl or 1o halides, and epoxides) Alkyne Reactions Br R
H-Br R
H-Br
Br R
Br hydrohalogenation
Br2, CH2Cl2 R R
Br
Br2, CH2Cl2 Br
Br R Br
Br Br
halogenation
1. BH3-THF 2. H2O2, H2O, NaOH R HgSO4, H2SO4, H2O
R O R
anti-Markovnikov hydration Markovnikov DO need to know keto-enol tautomerism mech.
R' H2, Pd/C, EtOH R R' R 1. Na (or Li), NH3 2. H2O H2, Lindlar catalyst, quinoline R R' Lindlar reduction (a hydrogenation) (syn-addition) R dissolving metal reduction (anti-addition) hydrogenation
reduction
R'
1. O3, CH2Cl2 2. H2O
HO O R + O
R' ozonolysis OH
You might also like
- Chem 108 Exam 2 Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesChem 108 Exam 2 Cheat SheetStarrx714100% (2)
- General Chemistry Reference Sheet GuideDocument5 pagesGeneral Chemistry Reference Sheet Guidedadadabababa100% (8)
- Organic Chemistry Cheat Sheet For Midterm2015Document1 pageOrganic Chemistry Cheat Sheet For Midterm2015Norma Leticia Ramos100% (5)
- Organic I Reactions (COMPLETE) PDFDocument10 pagesOrganic I Reactions (COMPLETE) PDFcztinu88% (50)
- Tadashi Okuyama, Mark Maskill - Organic Chemistry - A Mechanistic Approach-Oxford University Press (2013)Document681 pagesTadashi Okuyama, Mark Maskill - Organic Chemistry - A Mechanistic Approach-Oxford University Press (2013)Sooraj Srinivasan100% (12)
- Catch Up Chemistry, second edition: For the Life and Medical SciencesFrom EverandCatch Up Chemistry, second edition: For the Life and Medical SciencesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- 86 Tricks To Ace Organic ChemistryDocument164 pages86 Tricks To Ace Organic Chemistryjinzo8892% (12)
- Ultimate Organic Chemistry Mindmap 9746Document4 pagesUltimate Organic Chemistry Mindmap 9746Kasih Liyana100% (2)
- Experimental Organic Chemistry: Laboratory ManualFrom EverandExperimental Organic Chemistry: Laboratory ManualRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Sterling Test Prep College Organic Chemistry Practice Questions: Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsFrom EverandSterling Test Prep College Organic Chemistry Practice Questions: Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- The Practice of Medicinal ChemistryFrom EverandThe Practice of Medicinal ChemistryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Alkene and Alcohol Reactions OverviewDocument11 pagesAlkene and Alcohol Reactions OverviewPhirun Cheng97% (29)
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Summary of All Reactions For Organic ChemistryDocument4 pagesSummary of All Reactions For Organic Chemistryfoodytang91% (23)
- Organic II Reactions (Complete) BETADocument21 pagesOrganic II Reactions (Complete) BETATheoNo ratings yet
- Advanced Inorganic Chemistry: Applications in Everyday LifeFrom EverandAdvanced Inorganic Chemistry: Applications in Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Undergraduate organic reactions summaryDocument41 pagesUndergraduate organic reactions summaryKathyNo ratings yet
- Go Diane you can do itDocument3 pagesGo Diane you can do itDiane Malaso80% (10)
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry NotesVersiform89% (9)
- Schaums Outline of Organic Chemistry 5/E (ENHANCED EBOOK): 1,806 Solved Problems + 24 VideosFrom EverandSchaums Outline of Organic Chemistry 5/E (ENHANCED EBOOK): 1,806 Solved Problems + 24 VideosRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Organic Chemistry Concepts and Applications for Medicinal ChemistryFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry Concepts and Applications for Medicinal ChemistryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Reagent and The Reactions They CauseDocument3 pagesReagent and The Reactions They CauseChip Timmons100% (8)
- Flow Charts in Organic ChemistryDocument16 pagesFlow Charts in Organic ChemistryJessie McCartney85% (27)
- Organic Chemistry IDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry Iscribblerofnonsense80% (5)
- Cheat Sheet For Organic Chemistry Midterm 1 2015 - 1Document1 pageCheat Sheet For Organic Chemistry Midterm 1 2015 - 1Norma Leticia Ramos33% (3)
- Organic Chemistry II Reactions SummaryDocument8 pagesOrganic Chemistry II Reactions SummaryRicky Fontaine100% (9)
- Organic Reactions Summary SheetDocument2 pagesOrganic Reactions Summary Sheetthacheee64% (11)
- Problems in Organic ChemistryDocument408 pagesProblems in Organic ChemistryGowri Shankar100% (11)
- Summary of Organic ReactionsDocument6 pagesSummary of Organic ReactionsAbudi Alsagoff100% (5)
- Chemistry - Organic Chemistry Reaction SchemeDocument19 pagesChemistry - Organic Chemistry Reaction Schemehelixate94% (16)
- Organic ChemistryDocument334 pagesOrganic ChemistryCristiano Hamdiansyah Sempadian100% (16)
- Organic I Reactions (Complete) PDFDocument10 pagesOrganic I Reactions (Complete) PDFStarrx714No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Notes PDFDocument58 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notes PDFAzadnikov94% (16)
- Chemistry - Harvard's Advanced Organic Chemistry 2003Document717 pagesChemistry - Harvard's Advanced Organic Chemistry 2003ramik100% (23)
- Organic Chemistry - Reactions and MechanismsDocument120 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Reactions and MechanismsLoveena Steadman100% (8)
- Chemistry - Overview of Aliphatic Organic ChemistryDocument1 pageChemistry - Overview of Aliphatic Organic Chemistryhelixate100% (5)
- Organic Chemistry Question BankDocument92 pagesOrganic Chemistry Question BankGpg Subhash100% (7)
- Laboratory Manual of Organic ChemistryDocument305 pagesLaboratory Manual of Organic ChemistryKasraSr100% (23)
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument15 pagesIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compoundsapi-1986055092% (24)
- Organic ChemistryDocument39 pagesOrganic ChemistryAurora JimenezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Cheat Sheet (2010RR)Document3 pagesChemistry Cheat Sheet (2010RR)JethroKuan100% (1)
- Analytical ChemistryDocument55 pagesAnalytical ChemistryMarnel Roy Mayor100% (1)
- Organic ChemistryDocument1,254 pagesOrganic Chemistryayushka100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry Study Guide: Key Concepts, Problems, and SolutionsFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry Study Guide: Key Concepts, Problems, and SolutionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- Student's Solutions Manual to Accompany Organic Chemistry: Organic Chemistry by Weininger and StermitzFrom EverandStudent's Solutions Manual to Accompany Organic Chemistry: Organic Chemistry by Weininger and StermitzRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (12)
- Stereochemistry: Basic Concepts and ApplicationsFrom EverandStereochemistry: Basic Concepts and ApplicationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Organic Syntheses Based on Name Reactions: A Practical Guide to Over 800 TransformationsFrom EverandOrganic Syntheses Based on Name Reactions: A Practical Guide to Over 800 TransformationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Exam 1 Math 220 Summer 11Document9 pagesExam 1 Math 220 Summer 11Waseem AlkakozNo ratings yet
- Calc I Practice ProblemsDocument7 pagesCalc I Practice ProblemsWaseem AlkakozNo ratings yet
- Multiculturalism 0001Document10 pagesMulticulturalism 0001Waseem AlkakozNo ratings yet
- Stading WavesDocument4 pagesStading WavesWaseem AlkakozNo ratings yet
- Women and Gender in IslamDocument21 pagesWomen and Gender in IslamWaseem Alkakoz33% (3)
- Chapter 6 Summary of AFASDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Summary of AFASWaseem AlkakozNo ratings yet
- Women and Gender in IslamDocument21 pagesWomen and Gender in IslamWaseem Alkakoz33% (3)
- Agilent Passivation For ILCDocument4 pagesAgilent Passivation For ILCRaf RafNo ratings yet
- Halpin Et Al Rocky Cape Group GeochronologyDocument1 pageHalpin Et Al Rocky Cape Group GeochronologyPeter McGoldrickNo ratings yet
- F.L.A.S.H. The Formation and Characterization of Floating Self-Assembling Super-Hydrophobic Nano-Particle MembranesDocument1 pageF.L.A.S.H. The Formation and Characterization of Floating Self-Assembling Super-Hydrophobic Nano-Particle MembranesSarthak ShivhareNo ratings yet
- El Suelo, Regulador Fisicoquímico de Elementos Traza para Las PlantasDocument14 pagesEl Suelo, Regulador Fisicoquímico de Elementos Traza para Las PlantasKelly Marian BautistaNo ratings yet
- + 2 Chemistry 1 Mark Repeated Qs EM Upto Sept - 2016Document38 pages+ 2 Chemistry 1 Mark Repeated Qs EM Upto Sept - 2016Raison ThomasNo ratings yet
- The Hydrogen-Oxidizing Bacteria: M. P. Starr Et Al. (Eds.), The Prokaryotes © Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 1981Document2 pagesThe Hydrogen-Oxidizing Bacteria: M. P. Starr Et Al. (Eds.), The Prokaryotes © Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 1981SabrinaNo ratings yet
- Nucleophilic Substitution at Saturated CarbonDocument46 pagesNucleophilic Substitution at Saturated CarbonAhmed AtefNo ratings yet
- Renderoc LaxtraDocument2 pagesRenderoc LaxtraAlexi ALfred H. TagoNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Understanding of Carbon Black Feedstock (CBFS)Document31 pagesFundamental Understanding of Carbon Black Feedstock (CBFS)SDawNo ratings yet
- DS 939 Rev5 1207Document1 pageDS 939 Rev5 1207mohdluthfiNo ratings yet
- "Chemical Pulping" Edited by Johan Gullichsen and Carl-Johan FogelholmDocument15 pages"Chemical Pulping" Edited by Johan Gullichsen and Carl-Johan FogelholmrdLuis1No ratings yet
- Corrosion of Cast Aluminum Alloys - A Review - 20201013Document29 pagesCorrosion of Cast Aluminum Alloys - A Review - 20201013Wei YaoNo ratings yet
- Drilling Fluid 1Document98 pagesDrilling Fluid 1Aisyah NingsihNo ratings yet
- Surfactants - Fundamental Properties and Applications (1) (Autosaved)Document28 pagesSurfactants - Fundamental Properties and Applications (1) (Autosaved)SHRAWAN KUMAR JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Paper Organic Chemistry "Soap": Arranged By: Andi Ria Indahsari Asik 1913442004Document11 pagesPaper Organic Chemistry "Soap": Arranged By: Andi Ria Indahsari Asik 1913442004Andi RiaNo ratings yet
- Science 11 ReviewerDocument10 pagesScience 11 ReviewerArgie MabagNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic QuantitiesDocument16 pagesThermodynamic QuantitiesMawin ArabesNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Lesson 7Document17 pagesPhysical Science Lesson 7GLADYS SARAELNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Scope of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument11 pagesIntroduction and Scope of Anatomy and PhysiologyPrathiNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment Answers 19 Asal Chem CBDocument3 pagesSelf Assessment Answers 19 Asal Chem CBRonit KhannaNo ratings yet
- SN1 ReactionDocument9 pagesSN1 ReactionSharyproNo ratings yet
- Grevillea RobustaDocument6 pagesGrevillea RobustaJeyabalaganesh GNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Control Che 311Document43 pagesCorrosion Control Che 311Jaison JoseNo ratings yet
- CrystalDocument2 pagesCrystalAduchelab AdamsonuniversityNo ratings yet
- DEGAROUTE® Designing Safe TrafficDocument9 pagesDEGAROUTE® Designing Safe TrafficMilagros MorantesNo ratings yet
- Test4 ch19 Electrochemistry Practice-answers-MarkedDocument13 pagesTest4 ch19 Electrochemistry Practice-answers-MarkedEga SukmaNo ratings yet
- MontepuezDocument19 pagesMontepuezJoão José SeveneNo ratings yet
- Module 13: Industrial Chemistry ProcessesDocument195 pagesModule 13: Industrial Chemistry Processesabderrahimn100% (2)
- Problem - Chapter18 - 2Document19 pagesProblem - Chapter18 - 2張湧浩No ratings yet
- Facile Synthesis of 3-Nitro-2-Substituted ThiophenesDocument5 pagesFacile Synthesis of 3-Nitro-2-Substituted ThiophenesDiogo DiasNo ratings yet