Professional Documents
Culture Documents
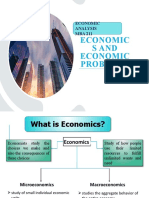
What Is Economics?: Unit - I 2 Marks
Uploaded by
saravmbaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Economics?: Unit - I 2 Marks
Uploaded by
saravmbaCopyright:
Available Formats
SHIVANI SCHOOL OF BUSINESS MANAGEMENT BA9202 Economic Analysis for Business
Unit I 2 marks 1.
ECONOMICS is a social science which deals with human wants and their satisfaction. It is
What is Economics?
mainly concerned with the way in which a society chooses to employ its scarce resources which have alternative uses, for the production of goods for present and future consumption. Economics is the study of how economic agents or societies choose to use scarce productive resources that have alternative uses to satisfy wants which are unlimited and of varying degrees of importance.
2.
What to Produce? capital goods
What are the three fundamental Economic Questions?
consumer goods The choice of product based on scarcity. How to produce? Decision to how to mix technology and scare resources and Partially by man power and machine or fully automated. For whom to produce? The person who actually receives. Who gets maximum satisfaction Who is having the buying power. production.
3.
What is Economic Efficiency? Productive efficiency? Allocative efficiency?
ECONOMIC EFFICIENCY refers to the use of resources so as to maximize the production of goods and services PRODUCTIVE EFFICIENCY (also known as technical efficiency) occurs when the economy is utilizing all of its resources efficiently, producing most output from least input ALLOCATIVE EFFICIENCY is a theoretical measure of the benefit or utility derived from a proposed or actual selection in the allocation or allotment of resources.
4.
What is Stability?
Stability A condition in which national output is growing steadily with low inflation and full employment of resources.
5.
What is PPF?
PRODUCTION POSSIBILITY FRONTIER (PPF) is a graph that shows all of the combinations of goods and services that can be produced if all of societys resources are used efficiently.
6.
What is Micro & Macro Economics?
MICRO ECONOMICS :
Meaning : Micro has been derived from GREEK word MIKROSwhich mean small. It is a study of the individual units of economic system. In other words a small part of economy & not the whole economy. DEFINITION: Prof. Mac cannel, micro economics is a study of the specific economic units and a detailed consideration of the behavior of these individual units. Prof.Boulding, micro economics seeks to explain the working of individuals, firms, households, individual prices, wages, particular industries. MACRO ECONOMICS : MEANING : Macro is been derived from the Greek word MAKROSwhich means LARGE. Macroeconomic is the study of large part of the economy i.E.,The whole economy. The study of economic behaviour of the economy as a whole & not the individual economic units of the economy. DEFINITION : Prof. Boulding, Marco economics deals not only with individual quantities but with the aggregates of these quantities , not with the individual incomes , but with national income , not with individual prices , but with prices level , not with individual outputs but with the national output . Brief out externalities.
Factors whose benefits (called external economies) and costs (called external diseconomies) are not reflected in the market price of goods and services. Externalities are a loss or gain in the welfare of one party resulting from an activity of another party, without there being any compensation for the losing party. Externalities are an important consideration in costbenefit analysis. 16 marks 7. Explain the themes of economics.
ECONOMICS is a social science which deals with human wants and their satisfaction. It is mainly concerned with the way in which a society chooses to employ its scarce resources which have alternative uses, for the production of goods for present and future consumption. Economics is the study of how economic agents or societies choose to use scarce productive resources that have alternative uses to satisfy wants which are unlimited and of varying degrees of importance. THEMES OF ECONOMICS Concepts & Economics Systems Scarcity and Choices,& Decision Making Work, Earnings, and Finance Management Business and Entrepreneurship Economic Interdependence Market and the Functions of Governments
THREE FUNDAMENTAL ECONOMIC QUESTIONS:
1. What To Produce?
capital goods consumer goods The choice of product based on scarcity. 2. How to produce? Decision to how to mix technology and scare resources and Partially by man power and machine or fully automated. 3. For whom to produce? The person who actually receives. Who gets maximum satisfaction Who is having the buying power. production.
8.
Explain the concept of Production Possibility Frontier Unit II 2 marks
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
What State What What What
is meaning of Demand? the Law of Demand? is Consumer Surplus? is Market Equilibrium? is Elasticity of Demand? 16 marks
Explain the Factors determining demand Explain the types of Elasticity of Demand Explain Law of Returns to Scale: Unit -III 2 marks
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
What is market? What is Perfect Competition? What are the Factors of Production? What is Oligopoly? What is Monopolistic competition?
6. 7. 8.
16 marks Explain the Features/Characteristics or Conditions of Perfect Competition. Explain the Comparison Between Monopoly and Competitive Equilibrium or Perfect Competition. Explain the three important economic models of Oligopoly. Unit -IV 2 marks
1. 2. 3. 4.
What What What What
is Aggregate Demand? is Macroeconomic equilibrium? are the components of Aggregate Demand? is fiscal policy?
5. 6. 7. 8. 9.
Marginal propensity to save? What is marginal propensity to consume? 16 marks Explain the Methods of Measurement of National Income Explain the important concepts of national income. Explain the Circular Flow of Macroeconomic Activity Unit -V 2 marks
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.
What is Philips Curve? What is money? What is seasonal Unemployment? What are the motives of money? What is monetary policy? 16 marks Explain Explain Explain Explain the the the the types of Inflation. PHILLIPS CURVE in Unemployment. Instruments of Monetary Policy types of Unemployment
You might also like
- Principles of Macroeconomics 10th Edition Solution ManualDocument43 pagesPrinciples of Macroeconomics 10th Edition Solution ManualAhmed GhanimNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Industrial EconomicsDocument18 pagesLecture Notes For Industrial Economicsnv71% (21)
- Lesson 01 Principles of Economics Handout 1Document42 pagesLesson 01 Principles of Economics Handout 1seyon sithamparanathanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Economics - ppt1Document13 pagesIntroduction To Economics - ppt1Akshay HemanthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1& 2Document24 pagesChapter 1& 2Michael GezahegnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Applied EconomicsDocument5 pagesLesson 2 - Applied EconomicsShanna Cielo Jean BerondoNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument0 pagesIntroductionramanagpalNo ratings yet
- Unit I: I Semester / I Year Ba5101 Economic Analysis For BusinessDocument23 pagesUnit I: I Semester / I Year Ba5101 Economic Analysis For BusinessN.SHANKARNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Industrial EconomicsDocument18 pagesLecture Notes For Industrial EconomicsJaga SwainNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Basic Economics 1Document6 pagesLecture Notes - Basic Economics 1lei_sangabrielNo ratings yet
- UNIT I-MG2452-Engineering Economics and Financial Accounting NotesDocument18 pagesUNIT I-MG2452-Engineering Economics and Financial Accounting Notesanon_331279695100% (1)
- Microeconomics Important QuestionsDocument284 pagesMicroeconomics Important QuestionsAkshit JunejaNo ratings yet
- Studying EconomicsDocument26 pagesStudying EconomicsThu PhuongNo ratings yet
- UNIT I-MG2452-Engineering Economics and Financial Accounting NotesDocument18 pagesUNIT I-MG2452-Engineering Economics and Financial Accounting NotesMohammed AsifNo ratings yet
- 1.intro Engg EcoDocument26 pages1.intro Engg EcoadroitdexterNo ratings yet
- Economics&Economic ProblemsDocument22 pagesEconomics&Economic ProblemsRhocel TolenadaNo ratings yet
- Intro to Microeconomics CourseDocument87 pagesIntro to Microeconomics Coursesewanyina muniruNo ratings yet
- ST - Joseph College of Engineering Department of Management Studies Ba5101 Economic Analysis For Business - I Part - ADocument23 pagesST - Joseph College of Engineering Department of Management Studies Ba5101 Economic Analysis For Business - I Part - Ajsc nazeerNo ratings yet
- ECONOMICS GUIDE FOR FILIPINOSDocument71 pagesECONOMICS GUIDE FOR FILIPINOSReggie PalaganasNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Study Guide SamuelsonDocument14 pagesMacroeconomics Study Guide SamuelsonMarjan Arbab100% (1)
- EFM College NotesDocument178 pagesEFM College Notesrahul100% (1)
- Instructional Materials For Microeconomics: Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesDocument10 pagesInstructional Materials For Microeconomics: Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesIan Jowmariell GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics: Module No. 2: Week 2: First QuarterDocument8 pagesApplied Economics: Module No. 2: Week 2: First QuarterGellegani, JuliusNo ratings yet
- Micro 111 C1 by NayemDocument10 pagesMicro 111 C1 by NayemHasibul Hasan NayemNo ratings yet
- Micro Economics NotesDocument18 pagesMicro Economics NotesRonak SudhirNo ratings yet
- Applied Econ L1Document42 pagesApplied Econ L1Marie Christine PajanilNo ratings yet
- CW3301 FUNDAMENTALS OF ECONOMICSDocument16 pagesCW3301 FUNDAMENTALS OF ECONOMICSSUDHAN ANo ratings yet
- Chap 01Document14 pagesChap 01Syed Hamdan100% (1)
- Micro I Notes All ChaptersDocument161 pagesMicro I Notes All Chapterstegegn mogessie100% (1)
- TACN CO GIANGDocument25 pagesTACN CO GIANGnguyenanh9279No ratings yet
- Managerial Economics - Till RevenueDocument77 pagesManagerial Economics - Till RevenueVaibhav ShahNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics: Module No. 2: Week 2: First QuarterDocument7 pagesApplied Economics: Module No. 2: Week 2: First QuarterhiNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction To EconomicsDocument46 pagesModule 1 Introduction To Economicsjenor delatorreNo ratings yet
- Uk Unit I Cse Split UpDocument69 pagesUk Unit I Cse Split UpSun Uday SunudayNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Basic Problems of An Economy and Role of Price MechanismDocument18 pagesUnit 2: Basic Problems of An Economy and Role of Price MechanismPriyanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document6 pagesChapter 1zelalem wegayehuNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Is The Study (N) of / Economics Studies (V) How People Choose To UseDocument34 pagesUnit 1: Is The Study (N) of / Economics Studies (V) How People Choose To UseThanh HàNo ratings yet
- Eco 102 (Chapter 1) NewDocument5 pagesEco 102 (Chapter 1) NewMA. FELICITI IGNACIONo ratings yet
- Understanding Micro and Macro Economics ConceptsDocument11 pagesUnderstanding Micro and Macro Economics ConceptsmaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document21 pagesChapter 1tiffada86No ratings yet
- A. A. The Twin Themes of Economics: Scarcity and EfficiencyDocument19 pagesA. A. The Twin Themes of Economics: Scarcity and EfficiencyIrenej Krayewsky100% (1)
- Micro Economics I NoteDocument161 pagesMicro Economics I NoteBinyam Regasa100% (1)
- Microeconomics 2023 BisDocument223 pagesMicroeconomics 2023 BisEsam IphoNo ratings yet
- 74658bos60481 FND p4 cp1 U2Document23 pages74658bos60481 FND p4 cp1 U2Amit MishraNo ratings yet
- Central Concepts of EconomicsDocument21 pagesCentral Concepts of EconomicsREHANRAJNo ratings yet
- Eco Term PaperDocument27 pagesEco Term PaperKalyaniNo ratings yet
- Economics Grade 11 Lesson Note 2Document10 pagesEconomics Grade 11 Lesson Note 2Eyerusalem solomonNo ratings yet
- 102 EABD CourseNoteDocument55 pages102 EABD CourseNoteDr. Rakesh BhatiNo ratings yet
- The Essence of EconomicsDocument16 pagesThe Essence of EconomicsPatNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Basic Problems of An Economy and Role of Price MechanismDocument14 pagesUnit 2: Basic Problems of An Economy and Role of Price MechanismPrabhakar DashNo ratings yet
- 1 - IB EconomicsDocument100 pages1 - IB EconomicsSeongyoon KimNo ratings yet
- Basic MicroeconomicsDocument219 pagesBasic Microeconomicsloc dinhNo ratings yet
- Eco Prakash PDFDocument10 pagesEco Prakash PDFPanwar SurajNo ratings yet
- Micro-Economics - IDocument147 pagesMicro-Economics - IWamek NuraNo ratings yet
- Summary Of "Economics, Principles And Applications" By Mochón & Becker: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "Economics, Principles And Applications" By Mochón & Becker: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- Economics in Micro and Macro Consistency: Challenging Old Biases with New InsightsFrom EverandEconomics in Micro and Macro Consistency: Challenging Old Biases with New InsightsNo ratings yet
- The Microeconomics of Wellbeing and Sustainability: Recasting the Economic ProcessFrom EverandThe Microeconomics of Wellbeing and Sustainability: Recasting the Economic ProcessNo ratings yet
- VALUATION COMMON COURSES 13 16.odgDocument7 pagesVALUATION COMMON COURSES 13 16.odgsaravmbaNo ratings yet
- World Trade OrganizationDocument5 pagesWorld Trade OrganizationrudraarjunNo ratings yet
- NTA NET Computer Science Paper 2 July 2018Document24 pagesNTA NET Computer Science Paper 2 July 2018indreshNo ratings yet
- TtestDocument5 pagesTtestsaravmbaNo ratings yet
- I Semester Iv Semester: PhotoDocument3 pagesI Semester Iv Semester: PhotosaravmbaNo ratings yet
- Calculate operating leverage, financial leverage and combined leverage from financial dataDocument12 pagesCalculate operating leverage, financial leverage and combined leverage from financial datasaravmbaNo ratings yet
- Banking TheoryDocument86 pagesBanking TheorysaravmbaNo ratings yet
- VALUATION COMMON COURSES 13 16.odgDocument7 pagesVALUATION COMMON COURSES 13 16.odgsaravmbaNo ratings yet
- EAC Question BankDocument4 pagesEAC Question BanksaravmbaNo ratings yet
- Types of CostDocument4 pagesTypes of CostsaravmbaNo ratings yet
- Calculate operating leverage, financial leverage and combined leverage from financial dataDocument12 pagesCalculate operating leverage, financial leverage and combined leverage from financial datasaravmbaNo ratings yet
- HTTPDocument12 pagesHTTPsaravmbaNo ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonomy Action Verbs-1Document1 pageBlooms Taxonomy Action Verbs-1api-238364969100% (1)
- E BankingDocument7 pagesE BankingsaravmbaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document12 pagesChapter 1saravmbaNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of The ConstitutionDocument4 pagesSalient Features of The ConstitutionNarayanan BhaskaranNo ratings yet
- Cir LTDocument9 pagesCir LTsaravmbaNo ratings yet
- Dr.B.Narayanan: Assistant Professor PG & Research Department of CommerceDocument2 pagesDr.B.Narayanan: Assistant Professor PG & Research Department of CommercesaravmbaNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of The ConstitutionDocument4 pagesSalient Features of The ConstitutionNarayanan BhaskaranNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1.: One Mark Questions One Mark QuestionsDocument53 pagesChapter-1.: One Mark Questions One Mark QuestionssaravmbaNo ratings yet
- EEFA Unit Test 2 QPDocument1 pageEEFA Unit Test 2 QPsaravmbaNo ratings yet
- ECO Cycle IDocument1 pageECO Cycle IsaravmbaNo ratings yet
- Semester-Vi Major Based Elective - Iii - Export Marketing Unit IDocument2 pagesSemester-Vi Major Based Elective - Iii - Export Marketing Unit IsaravmbaNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of The ConstitutionDocument3 pagesSalient Features of The ConstitutionsaravmbaNo ratings yet
- Eco Cycle IIDocument1 pageEco Cycle IIsaravmbaNo ratings yet
- Itf QPDocument2 pagesItf QPsaravmbaNo ratings yet
- Global Branding StrategiesDocument28 pagesGlobal Branding StrategiessaravmbaNo ratings yet
- Marketing ManagementDocument24 pagesMarketing ManagementSaad Mateen AhmedNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Model BM 2014Document1 pageQuestion Paper Model BM 2014saravmbaNo ratings yet
- Iat21 QP EefaDocument1 pageIat21 QP EefasaravmbaNo ratings yet
- List of Legend ReportsDocument100 pagesList of Legend Reportsapi-137303031No ratings yet
- Not For Profit OrganizationsDocument15 pagesNot For Profit OrganizationsSaravanan Swagger100% (2)
- Authority To Sell Juana Osmena - Amay Ong Vano - BrokerDocument2 pagesAuthority To Sell Juana Osmena - Amay Ong Vano - Brokertom escano100% (1)
- The Effects of Global Connections: DraftDocument17 pagesThe Effects of Global Connections: DraftGina DunggonNo ratings yet
- Fly Emirates HistoryDocument4 pagesFly Emirates HistoryAbody1995100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Unemployment, Inflation, and Long-Run GrowthDocument21 pagesChapter 7 Unemployment, Inflation, and Long-Run GrowthNataly FarahNo ratings yet
- Quillbot Invoice AzZcrCTTpEuxH4aikDocument1 pageQuillbot Invoice AzZcrCTTpEuxH4aiksurinderpal singhNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of DG Khan Cement FactoryDocument12 pagesFinancial Analysis of DG Khan Cement FactoryMuhammad MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Forex - DerivativesDocument5 pagesForex - DerivativesAllyse CarandangNo ratings yet
- Sales Letter (D) Dino Vs CADocument4 pagesSales Letter (D) Dino Vs CAKim Arizala67% (3)
- Report On Demerger - Tube Investment India LimitedDocument8 pagesReport On Demerger - Tube Investment India LimitedMithil DoshiNo ratings yet
- NDT Services Quotation for Dangote Fertilizer ProjectDocument1 pageNDT Services Quotation for Dangote Fertilizer ProjectaakashNo ratings yet
- Analyzing The Marketing EnvironmentDocument9 pagesAnalyzing The Marketing EnvironmentRitesh VarmaNo ratings yet
- 9970 - Africa-Indian Ocean Regional Traffic Forecasts 2010-2030 Seychelles, 20-24 Juin 2011Document48 pages9970 - Africa-Indian Ocean Regional Traffic Forecasts 2010-2030 Seychelles, 20-24 Juin 2011Sambatra KotoNo ratings yet
- How To Make A Trade With BDO Securities Online PlatformDocument13 pagesHow To Make A Trade With BDO Securities Online PlatformJerome Christopher BaloteNo ratings yet
- 6 StudyGuideDocument142 pages6 StudyGuidezohaNo ratings yet
- Buffett On Fire Book - Benjamin Chua FinalDocument136 pagesBuffett On Fire Book - Benjamin Chua FinalJuth LeeNo ratings yet
- Complex Variables and Statistical Methods Exam QuestionsDocument56 pagesComplex Variables and Statistical Methods Exam QuestionsMohan RaoNo ratings yet
- Industrial Pricing Decisions in B2B Marketing: Ravi R Ahuja Roll No:01Document9 pagesIndustrial Pricing Decisions in B2B Marketing: Ravi R Ahuja Roll No:01taru88No ratings yet
- MultifamilyDocument4 pagesMultifamilyKevin ParkerNo ratings yet
- P&L Account NotesDocument6 pagesP&L Account NotesSlicebearNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27 Class WorkDocument10 pagesChapter 27 Class WorkHussain AlmukharreqNo ratings yet
- Example Sale MemorandumDocument6 pagesExample Sale Memorandumflorinj72No ratings yet
- Notes - Timeliness of Reporting and Stock Price Reaction To Earnings AnnoucementsDocument12 pagesNotes - Timeliness of Reporting and Stock Price Reaction To Earnings AnnoucementsChacko JacobNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - CEV633 Tutorial - CHP 1 PDFDocument2 pagesMicrosoft Word - CEV633 Tutorial - CHP 1 PDFmuhammadNo ratings yet
- Demand, Supply, Equilibrium: Managerial Economics Reviewer For Quiz #2Document5 pagesDemand, Supply, Equilibrium: Managerial Economics Reviewer For Quiz #2Kimberly AnneNo ratings yet
- The Contemporary WorldDocument7 pagesThe Contemporary WorldRental System100% (1)
- Department of Management School of Management &business Studies Jamia HamdardDocument2 pagesDepartment of Management School of Management &business Studies Jamia HamdardAmaan ul HasanNo ratings yet
- Expected Profit Analysis of Bolt Motorbike LaunchDocument5 pagesExpected Profit Analysis of Bolt Motorbike LaunchMD Saiful IslamNo ratings yet