Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DipIFR-Session31 d08 Operating Segments
Uploaded by
Fahmi Abdulla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views0 pagessession 31
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsession 31
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views0 pagesDipIFR-Session31 d08 Operating Segments
Uploaded by
Fahmi Abdullasession 31
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 0
SESSION 31 IFRS 8 OPERATING SEGMENTS
Accountancy Tuition Centre (International Holdings) Ltd 2008 3101
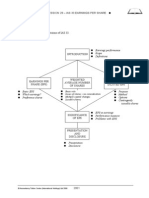
Overview
Objective
To provide users of financial statements with information about the nature
and financial effects of the business activities in which an entity engages and
the economic environment in which it operates.
OPERATING
SEGMENTS
DISCLOSURE
Core principle
General information
Information about profit or loss, assets
and liabilities
Basis of measurement
Reconciliations
Restatement of previously reported
information
Entity-wide disclosures
Scope
Definitions
Reportable segments
SESSION 31 IFRS 8 OPERATING SEGMENTS
Accountancy Tuition Centre (International Holdings) Ltd 2008 3102
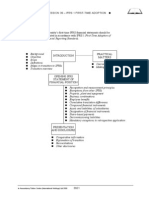
1 Operating segments
1.1 Scope
IFRS 8 applies to the separate financial statements of entities whose debt or equity
instruments are publicly traded (or are in the process of being issued in a public market).
IFRS 8 also applies to the consolidated financial statements of a group whose
parent is required to apply IFRS 8 to its separate financial statements.
Commentary
The scope of IAS 33 has been changed to be consistent with that of IFRS 8.
Where an entity is not required to apply IFRS 8, but chooses to do so, it must
not describe information about segments as segment information unless it
complies with IFRS 8.
Where a parents separate financial statements are presented with consolidated
financial statements, segment information is required only in the consolidated
financial statements.
Commentary
IFRS is applicable to annual financial statements for periods beginning on or
after 1 January 2009. Early adoption must be disclosed.
1.2 Definitions
1.2.1 Operating segment
This is a component that meets the following three criteria:
(1) it engages in business activities from which it may earn revenues and
incur expenses (including intersegment revenues and expenses arising
from transactions with other components of the same entity);
Commentary
Thus a start-up operation not yet earning revenues may be an operating segment, as
revenues would be expected in the future.
(2) its operating results are regularly reviewed by the entitys chief
operating decision maker to make decisions (about resources to be
allocated) and to assess its performance; and
(3) discrete financial information is available.
Commentary
A component, by definition, should meet this last criterion (see IFRS 5).
An entitys post-employment benefit plans are not operating segments.
SESSION 31 IFRS 8 OPERATING SEGMENTS
Accountancy Tuition Centre (International Holdings) Ltd 2008 3103
Corporate headquarters or other departments that may not earn revenues (or
only incidental revenues) are not operating segments.
1.2.2 Chief operating decision maker
This term describes a function (to allocate resources to and assess the
performance of operating segments). This may be a chief executive office, a
board of directors or others.
Commentary
An operating segment will generally have a segment manager who is directly
accountable to and maintains regular contact with the chief operating decision
maker to discuss operating activities, financial results, forecasts, etc.
1.3 Reportable segments
1.3.1 Separate information
Separate information must be reported for each operating segment that:
meets the definition criteria or aggregation criteria for two or more
segments (see 1.3.2); and
exceeds the quantitative thresholds (see 1.3.3).
1.3.2 Aggregation criteria
Two or more operating segments may be aggregated into a single operating
segment if:
aggregation is consistent with the core principle of this IFRS;
the segments have similar economic characteristics; and
the segments are similar in respect of:
the nature of products and services (e.g. domestic or industrial);
the nature of the production process (e.g. maturing or production line);
types or class of customer (e.g. corporate or individual);
distribution method (e.g. door-to-door or web sales); and
the regulatory environment (e.g. in shipping, banking, etc).
Commentary
An operating segment that does not meet a qualitative threshold may be aggregated
with another segment that does only if the operating segments have similar
economic characteristics and share a majority of the above aggregation criteria.
SESSION 31 IFRS 8 OPERATING SEGMENTS
Accountancy Tuition Centre (International Holdings) Ltd 2008 3104
1.3.3 Quantitative thresholds
Separate information must be reported for an operating segment that meets
any of the following quantitative thresholds:
reported revenue (including both external and intersegmental) is
10% or more of the combined revenue (internal and external) of all
operating segments;
profit or loss is 10% or more, in absolute amount, of the greater of:
(i) the combined profit of all operating segments that did not
report a loss; and
(ii) the combined loss of all operating segments that reported a loss;
assets are 10% or more of the combined assets of all operating segments.
Commentary
IFRS 8 is the only International Financial Reporting Standard with a
materiality rule.
At least 75% of the entitys revenue must be included in reportable segments.
Thus operating segments that fall below the quantitative thresholds may need
to be identified as reportable.
Commentary
Segments that fall below the threshold may also be considered reportable,
and separately disclosed, if management believes that the information would
be useful to users of the financial statements.
Information about other business activities and operating segments that are
not reportable are combined and disclosed in an all other segments
category.
When an operating segment is first identified as a reportable segment
according to the quantitative thresholds, comparative data should be
presented, unless the necessary information is not available and the cost to
develop it would be excessive.
Commentary
The Standard suggests ten as a practical limit to the number of reportable
segments separately disclosed as segment information may otherwise become
too detailed.
SESSION 31 IFRS 8 OPERATING SEGMENTS
Accountancy Tuition Centre (International Holdings) Ltd 2008 3105
Activity 1
Fireball group has:
three significant business lines which make up about 70% of combined
revenue; and
five small business lines, each of them contributing about 6% to the
combined revenue.
Required:
Explain how many segments Fireball group should report.
Solution
2 Disclosure
2.1 Core principle
An entity must disclose information to enable users of its financial statements
to evaluate:
the nature and financial effects of its business activities; and
the economic environments in which it operates.
This includes:
general information;
information about reported segment profit or loss, segment assets,
segment liabilities and the basis of measurement; and
reconciliations.
Commentary
This information must be disclosed for every period for which an income
statement is presented. Reconciliations of amounts in the statements of
financial position are required for each date at which a statement of financial
position is presented.
SESSION 31 IFRS 8 OPERATING SEGMENTS
Accountancy Tuition Centre (International Holdings) Ltd 2008 3106
2.2 General information
The factors used to identify reportable segments, including:
the basis of organisation (e.g. around products and services,
geographical areas, regulatory environments, or a combination of
factors and whether segments have been aggregated); and
Illustration 1 Basis of organisation
Eparts Cos reportable segments are strategic business units that offer different
products and services. They are managed separately because each business requires
different technology and marketing strategies. Most of the businesses were acquired as
individual units, and the management at the time of the acquisition was retained.
types of products and services from which each reportable segment
derives its revenues.
Illustration 2 Types of products and services
Eparts has five reportable segments: machine parts, lazer, prototyping, waterjet and
finance. The machine parts segment produces parts for sale to aviation equipment
manufacturers. The lazer segment produces lazer cutters to serve the petrochemical
industry. The prototyping segment produces plastics for sale to the pharmaceutical
industry. The waterjet segment produces cutting equipment for sale to car
manufacturers and jewellers. The finance segment is responsible for parts of Eparts
financial operations including financing customer purchases of products from other
segments and car leasing operations.
2.3 Information about profit or loss, assets and liabilities
The following must be reported for each reportable segment:
A measure of profit or loss and total assets.
A measure of liabilities if such an amount is regularly provided to
the chief operating decision maker.
Commentary
Note that segment cash flow information is voluntary (IAS 7) and therefore unlikely to
be produced as it would provide information to an acquirer to value and target for a
takeover bid.
SESSION 31 IFRS 8 OPERATING SEGMENTS
Accountancy Tuition Centre (International Holdings) Ltd 2008 3107
2.3.1 Profit or loss
The following must also be disclosed if the specified amounts are regularly
provided to the chief operating decision maker (even if not included in the
measure of segment profit or loss):
revenues from external customers;
intersegment revenues;
interest revenue;
Commentary
Interest revenue may be reported net of its interest expense if the majority of
the segments revenues are from interest and the chief operating decision
maker relies primarily on reporting of net interest revenue.
interest expense;
depreciation and amortisation;
other material items of income and expense required by IAS 1
Presentation of Financial Statements (i.e. write-downs,
restructurings, disposals, discontinued operations, litigation
settlements and reversals of provisions);
entitys interest in the profit or loss of associates and joint ventures
accounted for by the equity method;
income tax expense or income; and
material non-cash items other than depreciation and amortisation.
Commentary
Impairment losses also have to be disclosed (but as an IAS 36 requirement).
2.3.2 Assets
The following must also be disclosed if the specified amounts are regularly
provided to the chief operating decision maker (even if not included in the
measure of segment assets):
the investment in associates and joint ventures accounted for by the
equity method; and
additions to non-current assets (other than financial instruments,
deferred tax assets and post-employment benefit assets).
SESSION 31 IFRS 8 OPERATING SEGMENTS
Accountancy Tuition Centre (International Holdings) Ltd 2008 3108
Illustration 3 Profit or loss, assets and liabilities
Machine Lazer Proto- Water- Finance All Totals
parts typing jet other
$ $ $ $ $ $ $
Revenues from
external customers 7,200 12,000 22,800 28,800 12,000 2,400
(a)
85,200
Intersegment revenues 7,200 3,600 10,800
Interest revenue 1,080 1,920 2,400 3,600 9,000
Interest expense 840 1,440 1,680 2,640 6,600
Net interest revenue
(b)
2,400 2,400
Depreciation and
amortisation 480 240 120 3,600 2,640 7,080
Reportable segment profit 480 168 2,160 5,520 1,200 240 9,768
Other material non-cash items:
Impairment of assets 480 480
Reportable segment
assets 4,800 12,000 7,200 28,800 136,800 4,800 194,400
Expenditures for reportable
segment non-current
assets 720 1,680 1,200 1,920 1,440 6,960
Reportable segment
liabilities 2,520 7,200 4,320 19,200 72,000 105,240
(a) Revenues from segments below the quantitative thresholds are attributable to three operating
segments of Eparts. Those segments include a small warehouse leasing business, a car rental
business and a design consulting practice. None of those segments has ever met any of the
quantitative thresholds for determining reportable segments.
(b) The finance segment derives a majority of its revenue from interest. Management primarily relies on
net interest revenue, not the gross revenue and expense amounts, in managing that segment.
Therefore only the net amount is disclosed.
Commentary
This company does not allocate tax expense or no-recurring gains or losses
to reportable segments. Also, not all reportable segments have material non-
cash items other than depreciation and amortisation.
SESSION 31 IFRS 8 OPERATING SEGMENTS
Accountancy Tuition Centre (International Holdings) Ltd 2008 3109
2.4 Basis of measurement
The amount of each segment item reported is the measure reported to the
chief operating decision maker.
Commentary
Segment information is no longer required to conform to the accounting
policies adopted for preparing and presenting the consolidated financial
statements.
If the chief operating decision maker uses more than one measure of an
operating segments profit or loss, the segments assets or the segments
liabilities, the reported measures should be those that are most consistent with
those used in the entitys financial statements.
Illustration 4 Measurement
The accounting policies of the operating segments are the same as those described in
the summary of significant accounting policies except that pension expense for each
operating segment is recognised and measured on the basis of cash payments to the
pension plan. Eparts evaluates performance on the basis of profit or loss from
operations before tax expense not including non-recurring gains and losses and foreign
exchange gains and losses.
Eparts accounts for intersegment sales and transfers at current market prices, i.e. as if
the sales or transfers were to third parties.
An explanation of the measurements of segment profit or loss, segment assets
and segment liabilities must disclose, as a minimum:
the basis of accounting for intersegment transactions;
the nature of any differences between the measurements of the
reportable segments and the entitys financial statements (if not
apparent from the reconciliations required);
Commentary
Differences could include accounting policies and policies for allocation of
centrally incurred costs, jointly used assets or jointly utilised liabilities.
the nature of any changes from prior periods in the measurement
methods used and the effect, if any, of those changes on the
measure of segment profit or loss;
the nature and effect of any asymmetrical allocations to reportable
segments.
Commentary
For example, the allocation of depreciation expense with the related
depreciable assets.
SESSION 31 IFRS 8 OPERATING SEGMENTS
Accountancy Tuition Centre (International Holdings) Ltd 2008 3110
2.5 Reconciliations
Reconciliations of the total of the reportable segments with the entity are
required for all of the following:
revenue;
profit or loss (before tax and discontinued operations);
assets;
liabilities (if applicable);
every other material item.
All material reconciling items must be separately identified and described
(e.g. arising from different accounting policies).
Illustration 5 Revenue reconciliation
$
Total revenues for reportable segments 93,600
Other revenues 2,400
Elimination of intersegment revenues (10,800)
______
Entitys revenues 85,200
______
Illustration 6 Profit or loss
$
Total profit or loss for reportable segments 9,528
Other profit or loss 240
Elimination of intersegment profits (1,200)
Unallocated amounts:
Litigation settlement received 1,200
Other corporate expenses (1,800)
Adjustment to pension expense in consolidation (600)
______
Income before income tax expense 7,368
______
Illustration 7 Assets
$
Total assets for reportable segments 189,600
Other assets 4,800
Elimination of receivable from corporate headquarters (2,400)
Other unallocated amounts 3,600
_______
Entitys assets 195,600
_______
SESSION 31 IFRS 8 OPERATING SEGMENTS
Accountancy Tuition Centre (International Holdings) Ltd 2008 3111
Illustration 8 Liabilities
$
Total liabilities for reportable segments 105,240
Unallocated defined benefit pension liabilities 60,000
_______
Entitys liabilities 165,240
_______
Illustration 9
Other material items Reportable Adjustments Entity totals
segment totals
$ $ $
Interest revenue 9,000 180 9,180
Interest expense 6,600 (120) 6,480
Net interest revenue
(finance segment only) 2,400 2,400
Expenditures for assets 6,960 2,400 9,360
Depreciation and amortisation 7,080 7,080
Impairment of assets 480 480
The reconciling item is the amount incurred for the company head office building
which is not included in segment information.
2.6 Restatement of previously reported information
Where changes in the internal organisation structure of an entity result in a
change in the composition of reportable segments, corresponding information
must be restated unless the information is not available and the cost to
develop it would be excessive.
An entity should disclose whether corresponding items have been restated.
If not restated, the entity must disclose the current period segment information on
both the old and new bases of segmentation, unless the necessary information is not
available and the cost to develop it would be excessive.
2.7 Entity-wide disclosures
All entities subject to this IFRS are required to disclose information about the
following, if it is not provided as part of the required reportable segment information:
products and services:
geographical areas; and
major customers.
Commentary
Including those entities that have only a single reportable segment.
SESSION 31 IFRS 8 OPERATING SEGMENTS
Accountancy Tuition Centre (International Holdings) Ltd 2008 3112
The only exemption for not providing information about products and
services and geographical areas is if the necessary information is not
available and the cost to develop it would be excessive, in which case that
fact must be disclosed.
2.7.1 By product and service
Revenues from external customers for each product and service (or each
group of similar products and service) based on the financial information
used to produce the entitys financial statements.
Illustration 10 By product group (extract)
30 PRIMARY SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
(BY PRODUCT GROUP)
2006
%
2005
%
2006
US$m
2005
US$m
Sales revenue
Iron Ore 30.9 28.9 6,938 5,497
Energy 18.1 19.4 4,070 3,693
Industrial Minerals 11.1 12.5 2.501 2,374
Aluminium 15.5 14.4 3,493 2,744
Copper 19.6 18.0 4,396 3,433
Diamonds 3.7 5.7 838 1,076
Other 1.1 1.1 229 216
Consolidated sales revenue 100.0 100.0 22,465 19,033
Share of equity accounted units 2,975 1,709
Gross sales revenue 25,440 20,742
Rio Tinto 2006 Annual report and financial statements
2.7.2 By geographical area
Revenues from external customers attributed to:
the entitys country of domicile;
all foreign countries in total; and
individual foreign countries, if material.
Similarly, non-current assets (other than financial instruments, deferred tax
assets and post-employment benefit assets).
Commentary
Again based on the financial information used to produce the entitys
financial statements.
SESSION 31 IFRS 8 OPERATING SEGMENTS
Accountancy Tuition Centre (International Holdings) Ltd 2008 3113
Illustration 11
Geographical information Revenues
(a)
Non-current
assets
$ $
United States 45,600 26,400
Canada 10,080
China 8,160 15,600
Japan 6,960 8,400
Other countries 14,400 7,200
______ ______
Total 85,200 57,600
______ ______
(a) Revenues are attributed to countries on the basis of the customers location.
2.7.3 Major customers
An entity discloses the extent of its reliance on major customers by stating:
if revenues from a single external customer amount to 10% or more
of the entitys total;
the total revenues from each such customer; and
the segment(s) reporting the revenues.
An entity need not disclose the identity of a major customer or the amount of
revenues that each segment reports from that customer.
Commentary
For the purposes of this IFRS, a group of entities known to be under common
control (including entities under the control of a government) is a single customer.
Illustration 12
Revenues from one customer of Eparts Cos prototyping and waterjet segments
represent approximately $12,000 of the companys total revenues.
SESSION 31 IFRS 8 OPERATING SEGMENTS
Accountancy Tuition Centre (International Holdings) Ltd 2008 3114
Activity 2
Silver is applying IFRS 8 for the first time in financial statements for the financial year
ended 31 December 2007. This will cause changes in the identification of Silvers
reportable segments and require additional disclosures.
Required:
Comment on whether Silver should restate the comparative information.
Solution
Focus
You should now be able to:
discuss the usefulness and problems associated with the provision of segment
information;
define an operating segment;
identify reportable segments (including applying the aggregation criteria and
quantitative thresholds);
prepare segment information in accordance with IFRS 8.
SESSION 31 IFRS 8 OPERATING SEGMENTS
Accountancy Tuition Centre (International Holdings) Ltd 2008 3115
Activity solutions
Solution 1 Reportable segments
Commentary
The issue is whether or not it is acceptable to report the three major business lines
separately and to include the rest for reconciliation purposes as all other segments.
Since the reported revenues attributable to the three business lines that meet the
separate reporting criteria constitute less than 75% of the combined revenue, additional
segments must be identified as reportable, even though they are below the 10%
threshold, until at least 75% of the combined revenue is included in reportable
segments.
If at least one of the small segments meets the aggregation criteria to be aggregated
with one of the three reportable segments, there will be four reportable segments
(including all other segments).
Alternatively, two or more of the smaller segments may be aggregated, if they meet the
aggregation criteria. In this case there will be five reportable segments.
If none of the small segments meet the criteria to be aggregated with any of the other
business lines one of them must be identified as reportable, though it does not meet the
10% threshold. In this case there will be five reportable segments also.
Solution 2 Comparative information
Comparative information for all periods presented should be restated (IAS 1)
in conformity with IFRS 8.
If the necessary information is not available and the cost to develop it would
be excessive, this fact should be disclosed.
Commentary
In this case there appears to be no requirement to disclose current period
segment information on both the old and new bases of segmentation (as there
is when there is a change in composition of reportable segments). The
difference, perhaps, being that adoption of IFRS 8 is a mandatory change for
those complying with IFRS, whereas an internal reorganisation is voluntary.
Silver should also disclose early adoption of IFRS 8.
SESSION 31 IFRS 8 OPERATING SEGMENTS
Accountancy Tuition Centre (International Holdings) Ltd 2008 3116
You might also like
- Finance Demo Script - ConsolidationsDocument46 pagesFinance Demo Script - ConsolidationshnoamanNo ratings yet
- Share Based PaymentDocument19 pagesShare Based PaymentFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit CharterDocument15 pagesInternal Audit CharterFahmi Abdulla100% (2)
- Financial Service Business Update PWCDocument90 pagesFinancial Service Business Update PWCRinaasmaraNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Advanced Accounting, 11th Edition - HoyleDocument27 pagesSolution Manual For Advanced Accounting, 11th Edition - HoyleAlmoosawi100% (1)
- Resa Toa 1205 PreweekDocument38 pagesResa Toa 1205 PreweekLlyod Francis Laylay100% (1)
- Welcome To The Presentation On: IFRS 8 - Operating SegmentsDocument21 pagesWelcome To The Presentation On: IFRS 8 - Operating SegmentsMaruf MahadiNo ratings yet
- ICAEW Accounting QB 2023Document322 pagesICAEW Accounting QB 2023diya p100% (1)
- IFRS 8 Operating SegmentsDocument18 pagesIFRS 8 Operating SegmentsrgnrgyNo ratings yet
- FA1 WorkbookDocument243 pagesFA1 WorkbookM C100% (1)
- Business Driven ConfigurationDocument21 pagesBusiness Driven ConfigurationMukul WadhwaNo ratings yet
- Handout 2 - Introduction To Auditing and Assurance of Specialized IndustriesDocument2 pagesHandout 2 - Introduction To Auditing and Assurance of Specialized IndustriesPotato CommissionerNo ratings yet
- Operating Segments PDFDocument12 pagesOperating Segments PDFZahidNo ratings yet
- 9 - Segment ReportingDocument4 pages9 - Segment ReportingCathNo ratings yet
- Adv - Chap 8Document7 pagesAdv - Chap 8Melody LisaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document7 pagesChapter 8suleymantesfaye10No ratings yet
- Ifrs 8 Operating Segments: BackgroundDocument4 pagesIfrs 8 Operating Segments: Backgroundmusic niNo ratings yet
- Kings College of The PhilippinesDocument6 pagesKings College of The PhilippinesIzza Mae Rivera KarimNo ratings yet
- Ifrs 8: Operating SegmentsDocument15 pagesIfrs 8: Operating SegmentsAANo ratings yet
- Ifrs 8: Operating SegmentsDocument15 pagesIfrs 8: Operating SegmentsMohammad BaratNo ratings yet
- PFRS 8-Operating SegmentsDocument20 pagesPFRS 8-Operating Segmentsrena chavezNo ratings yet
- Operating SegmentDocument6 pagesOperating SegmentsubupooNo ratings yet
- #6 PFRS 8Document2 pages#6 PFRS 8Shara Joy B. ParaynoNo ratings yet
- Segment Reporting: Meaning, Terminology, Need and DisclosuresDocument5 pagesSegment Reporting: Meaning, Terminology, Need and DisclosuresIMRAN ALAMNo ratings yet
- 11 IFRS 8, IAS 24 & Ethical IssuesDocument20 pages11 IFRS 8, IAS 24 & Ethical IssuespesseNo ratings yet
- Ifrs 8 Segment InformationDocument6 pagesIfrs 8 Segment InformationMovies OnlyNo ratings yet
- Ifrs 8: Operating SegmentsDocument12 pagesIfrs 8: Operating SegmentsGere TassewNo ratings yet
- Ifrs 8 and Ias 34-Operating Segments & Interim ReportingDocument46 pagesIfrs 8 and Ias 34-Operating Segments & Interim Reportingesulawyer2001No ratings yet
- Operating Segments: International Financial Reporting Standard 8Document9 pagesOperating Segments: International Financial Reporting Standard 8Imran MustafaNo ratings yet
- AcFN 3151 CH, 7 Segment Reporting and Interim Reporting IFRS 8 andDocument42 pagesAcFN 3151 CH, 7 Segment Reporting and Interim Reporting IFRS 8 andbethelhemNo ratings yet
- 3.3.1 Functions That Are Integral To Business: Financial Reporting SolutionDocument15 pages3.3.1 Functions That Are Integral To Business: Financial Reporting SolutionRITZ BROWNNo ratings yet
- Chapter-08-Ideas On Operating SegmentsDocument12 pagesChapter-08-Ideas On Operating Segmentsmdrifathossain835No ratings yet
- 07 Segment Reporting 1Document4 pages07 Segment Reporting 1Irtiza AbbasNo ratings yet
- Advanced Accounting 10th Edition Hoyle Solutions ManualDocument29 pagesAdvanced Accounting 10th Edition Hoyle Solutions Manualcliniqueafraidgfk1o100% (20)
- 07 Segment ReportingDocument5 pages07 Segment ReportingHaris IshaqNo ratings yet
- Insights Into MFRS 8Document6 pagesInsights Into MFRS 8Ihsan 4102No ratings yet
- Understand Operating Segments with this Accounting GuideDocument3 pagesUnderstand Operating Segments with this Accounting GuideChinchin Ilagan DatayloNo ratings yet
- IFRS 8 Operating SegmentsDocument6 pagesIFRS 8 Operating SegmentsPratima SeedheeyanNo ratings yet
- Ifrs-8 Operating SegmentsDocument8 pagesIfrs-8 Operating SegmentsniichauhanNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Operating SegmentsDocument3 pagesModule 6 - Operating SegmentsChristine Joyce BascoNo ratings yet
- Ca - Bharat Bhushan B-Com, ACA: Presented byDocument23 pagesCa - Bharat Bhushan B-Com, ACA: Presented byEshetieNo ratings yet
- Responsibility Accounting and Transfer Pricing: Management Reporting MAC302Document17 pagesResponsibility Accounting and Transfer Pricing: Management Reporting MAC302jackielyn garletNo ratings yet
- FA Vol.3 Operating SegmentsDocument7 pagesFA Vol.3 Operating SegmentsRyan SanitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Eight: Segment and Interim ReportingDocument30 pagesChapter Eight: Segment and Interim ReportingsoozboozNo ratings yet
- Operating SegmentDocument15 pagesOperating SegmentSrabon BaruaNo ratings yet
- Operating Segments: International Financial Reporting Standard 8Document10 pagesOperating Segments: International Financial Reporting Standard 8Tanvir PrantoNo ratings yet
- Advanced Accounting Hoyle 12th Edition Solutions ManualDocument33 pagesAdvanced Accounting Hoyle 12th Edition Solutions ManualBrentBrowncgwzm100% (89)
- ACTIVITY 8 - Intermediate AccountingDocument2 pagesACTIVITY 8 - Intermediate AccountingMicky BernalNo ratings yet
- Segment and Interim ReportingDocument8 pagesSegment and Interim ReportingKECEBONG ALBINO50% (2)
- 8.0 NFRS 8 - SetPasswordDocument8 pages8.0 NFRS 8 - SetPasswordDhruba AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Operating Segment Reporting Key Financial DataDocument19 pagesOperating Segment Reporting Key Financial DataRainNo ratings yet
- Ifrs 8 Reserrch DocumentsDocument6 pagesIfrs 8 Reserrch Documentssandeep11116No ratings yet
- Operating SegmentsDocument10 pagesOperating SegmentsUdit JindalNo ratings yet
- Ind As 108Document6 pagesInd As 108Khushi SoniNo ratings yet
- Operating Segment: Pfrs 8Document28 pagesOperating Segment: Pfrs 8Giellay OyaoNo ratings yet
- Operating Segment: Intermediate Accounting 3Document51 pagesOperating Segment: Intermediate Accounting 3Trisha Mae AlburoNo ratings yet
- Advanced Accounting 13th Edition Hoyle Solutions ManualDocument32 pagesAdvanced Accounting 13th Edition Hoyle Solutions ManualKatieElliswcze100% (35)
- PFRS 8 - Operating SegmentsDocument11 pagesPFRS 8 - Operating SegmentseiraNo ratings yet
- Pfrs 8 Operating SegmentsDocument2 pagesPfrs 8 Operating SegmentsJimuel ImbuidoNo ratings yet
- 31 Pfrs 8 - Operating Segments: Scope 1. What Is The Scope of The Standards?Document6 pages31 Pfrs 8 - Operating Segments: Scope 1. What Is The Scope of The Standards?Chris Sevilla BurhamNo ratings yet
- Ifrs 8Document3 pagesIfrs 8kadermaho456No ratings yet
- IFRS-8-Operating-SegmentsDocument15 pagesIFRS-8-Operating-SegmentsNichole Angel LeiNo ratings yet
- PAS 8 Operating SegmentsDocument4 pagesPAS 8 Operating SegmentsAlex OngNo ratings yet
- Far 3 (Final Topics) - Ma'Am JannaDocument68 pagesFar 3 (Final Topics) - Ma'Am JannaAndrea FernandoNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Mod 6 SegmentDocument7 pagesChap 1 Mod 6 SegmentShouvik NagNo ratings yet
- Operating Segments: Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 108Document14 pagesOperating Segments: Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 108Bathina Srinivasa RaoNo ratings yet
- MFRS 8Document31 pagesMFRS 8Anas AjwadNo ratings yet
- Basics of Segment ReportingDocument3 pagesBasics of Segment ReportingNathoNo ratings yet
- 297 303 PDFDocument7 pages297 303 PDFFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- 09 Quang Linh Huynh-PDocument13 pages09 Quang Linh Huynh-PFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- DipIFR-Session26 d08 Investment in AssociatesDocument0 pagesDipIFR-Session26 d08 Investment in AssociatesFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- DipIFR-Session29 d08 Earnings Per ShareDocument0 pagesDipIFR-Session29 d08 Earnings Per ShareFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- DipIFR-Session30 d08 Statement of CashflowsDocument0 pagesDipIFR-Session30 d08 Statement of CashflowsFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- 2012.ethical Investment Study Chapt Islamic FinanceDocument17 pages2012.ethical Investment Study Chapt Islamic FinanceFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- 1Document10 pages1Fahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- BFM132 Islamic Economics Ness & Finance Apr11Document7 pagesBFM132 Islamic Economics Ness & Finance Apr11Fahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- DipIFR-Session25 d08 Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDocument0 pagesDipIFR-Session25 d08 Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive IncomeFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- DipIFR-Session18 d08 Employee BenefitsDocument0 pagesDipIFR-Session18 d08 Employee BenefitsFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- DipIFR-Session27 d08 Interest in JVsDocument0 pagesDipIFR-Session27 d08 Interest in JVsFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- DipIFR-Session31 d08 Operating SegmentsDocument0 pagesDipIFR-Session31 d08 Operating SegmentsFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- DipIFR-Session30 d08 Statement of CashflowsDocument0 pagesDipIFR-Session30 d08 Statement of CashflowsFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- DipIFR-Session33 d08 Events After Reporting PeriodDocument0 pagesDipIFR-Session33 d08 Events After Reporting PeriodFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- DipIFR-Session32 d08 Discontinued OperationsDocument0 pagesDipIFR-Session32 d08 Discontinued OperationsFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- DipIFR-Session34 j08 Related Party DisclosureDocument0 pagesDipIFR-Session34 j08 Related Party DisclosureFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- DipIFR-Session32 d08 Discontinued OperationsDocument0 pagesDipIFR-Session32 d08 Discontinued OperationsFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- DipIFR-Session35 j08 Interim Financial ReportingDocument0 pagesDipIFR-Session35 j08 Interim Financial ReportingFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- DipIFR-Session36 j08 First Time AdoptionDocument0 pagesDipIFR-Session36 j08 First Time AdoptionFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Acca p1 NotesDocument67 pagesAcca p1 NotesAsis KoiralaNo ratings yet
- DipIFR-Session37Index d08Document0 pagesDipIFR-Session37Index d08Fahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- DipIFR-Session01 d08 IFRSDocument0 pagesDipIFR-Session01 d08 IFRSFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Paper 2.4 - ATC InternationalDocument0 pagesPaper 2.4 - ATC InternationalFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- DipIFR-Session03 d08 Presentation of Financial StatementsDocument0 pagesDipIFR-Session03 d08 Presentation of Financial StatementsFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- F 5 CKTQNSPDFDocument9 pagesF 5 CKTQNSPDFFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- DipIFR-Session00 d08Document0 pagesDipIFR-Session00 d08Fahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Manage Transition To Ifrs WhitepaperDocument19 pagesManage Transition To Ifrs WhitepaperAnushree SinghNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 3 - IAS 1 - Paper For Discussion PDFDocument23 pagesPertemuan 3 - IAS 1 - Paper For Discussion PDFSlamet RaharjoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-Accounting Concepts, Principles and ConventionsDocument20 pagesUnit 2-Accounting Concepts, Principles and Conventionsanamikarajendran441998No ratings yet
- Essentials of Accounting: Prof: Mr. Allan Jay Evangelista, CPADocument32 pagesEssentials of Accounting: Prof: Mr. Allan Jay Evangelista, CPAFrances Nicole MuldongNo ratings yet
- Need For Sector Specific Materiality and Sustainability Reporting StandardsDocument10 pagesNeed For Sector Specific Materiality and Sustainability Reporting StandardsALBERTO GUAJARDO MENESESNo ratings yet
- MBA DissertationDocument46 pagesMBA DissertationEmrin StarsNo ratings yet
- Afm - l2 - I-Gaap Vs Us GaapDocument10 pagesAfm - l2 - I-Gaap Vs Us GaapanujNo ratings yet
- Understanding Financial StatementsDocument30 pagesUnderstanding Financial StatementsTeh PohkeeNo ratings yet
- Rules-Based and Principles-Based Accounting Standards and Earnings ManagementDocument32 pagesRules-Based and Principles-Based Accounting Standards and Earnings ManagementJ Satya SarawanaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Lesson 1 Overview of AccountingDocument10 pagesWeek 1 - Lesson 1 Overview of AccountingRose RaboNo ratings yet
- ACCA P2Int Mock1 Answers June2018 PDFDocument24 pagesACCA P2Int Mock1 Answers June2018 PDFsabrina006No ratings yet
- NIIF Completas 2019 Libro Rojo Ilustrado Parte C PDFDocument2,602 pagesNIIF Completas 2019 Libro Rojo Ilustrado Parte C PDFvagonet21No ratings yet
- SIBL Annual Report 2018 PDFDocument369 pagesSIBL Annual Report 2018 PDFShishir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Sadia KhanDocument3 pagesSadia KhanNaveed Abdul WaheedNo ratings yet
- Psak Vs Ifrs 2022Document11 pagesPsak Vs Ifrs 2022kiswonoNo ratings yet
- The Real Effects of A New Accounting Standard The Case of IFRS 15 Revenue From Contracts With CustomersDocument31 pagesThe Real Effects of A New Accounting Standard The Case of IFRS 15 Revenue From Contracts With Customersaccount.oswald.o.20No ratings yet
- United Arab Emirates IFRS ProfileDocument5 pagesUnited Arab Emirates IFRS ProfileabcdNo ratings yet
- International Variations in IFRS Practices: and How Spain Differs From Other Major CountriesDocument60 pagesInternational Variations in IFRS Practices: and How Spain Differs From Other Major CountriesCindyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial Accounting and Reporting in MalaysiaDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Financial Accounting and Reporting in MalaysiaDINIE RUZAINI BINTI MOH ZAINUDINNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 1Document2 pagesPractice Test 1Khail GoodingNo ratings yet
- OLC Chapter 01Document16 pagesOLC Chapter 01Satarupa MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Creative Accounting: A Literature ReviewDocument13 pagesCreative Accounting: A Literature ReviewthesijNo ratings yet
- Bistrat UASDocument32 pagesBistrat UASTegar BabarunggulNo ratings yet
- The Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingDocument40 pagesThe Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingRinaNo ratings yet