Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Air Flashcard Game
Uploaded by
Jorn DoeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Air Flashcard Game
Uploaded by
Jorn DoeCopyright:
Available Formats
The information in this lesson plan is current as of August 2, 2004
Air Terms: The Flash Card Game
Purpose: To learn important vocabulary terms regarding air quality. Grade Level: 5th grade Science TEKS : 5.1 a, b 5.2 a, b, c, d 5.7 a 5.8 a
Objective: Students will learn terms regarding air quality Focus: Understanding common terms related to air quality and pollution. Materials air quality terms on flash cards (provided below) magazines typing paper art supplies
Background Air pollution is a problem in many of areas of the United States. It can damage trees, lakes and animals, and make people sick. It can also damage buildings and other structures. Air pollution also can cause
haze, reducing visibility in national parks and sometimes interfere with aviation. The federal government regulates air pollution in order to protect human health and the environment. There are several words that are used when discussing the subject of air pollution. Procedures Divide students into groups of five. The students will number off from one to five. This group will be the base team. Next, ask all of the ones to sit together, the twos to sit together, the threes to sit together, and the fours to sit together, etc. Give each group six air quality terms on flash cards that will be placed in the middle of the table. (The list of terms and definitions are provided below.) The students will decide who will be first to take the top card. The first student will read the term and then the definition of that word from the card. The group will look in magazines for pictures that represent the air quality term. Each member of the group must find a picture or draw a picture to share with the base team. After all the groups have completed illustrating the terms, the students will return to their base team. Beginning with student number one, each member of the group will share the illustrations. Each group will then practice reading the terms and definitions. List of Air Quality Terms and Definitions air pollution - the soiling of the atmosphere by contaminants to the point that may injure health, property, plant or animal life, or prevent the use and enjoyment of the outdoors. ambient air - outdoor air atmosphere - the whole mass of air surrounding the earth benzene - a colorless, hazardous hydrocarbon emitted during gasoline storage and transfer and from refining processes carbon dioxide - a colorless, odorless gas formed during breathing, combustion, and decaying that adds to the greenhouse effect carbon monoxide - a colorless, odorless, poisonous gas produced when carbon-containing substances such as coal, oil, gasoline, wood, or natural gas do not burn completely
catalytic converter - an air pollution control device that uses a chemical reaction to reduce emissions from motor vehicles chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) - chemicals used as coolants in refrigerators and air conditioners that can harm the ozone layer in the upper atmosphere and add to the greenhouse effect combustion - burning or the production of heat and light energy through a chemical process contaminant - an element or pollutant that soils the air dispersion - the process of breaking up high concentrations of air pollutants emission - a discharge or release of pollutants into the air, such as from a smokestack or automobile engine environment - the combination of all external conditions and influences relating to the life, development, and survival of all living things fossil fuels - coal, oil, and natural gas formed from the remains of ancient plant and animal life hydrocarbons - compounds found in fossil fuels, glues, paints, and solvents that can react with other pollutants to cause smog hazardous air pollutant - a contaminant that may cause an increase in rates of death or serious illness meteorology - a science that deals with the atmosphere, weather, and weather forecasting nitrogen oxides - gases that form when nitrogen and oxygen in the atmosphere are burned with fossil fuels at high temperatures ozone - a colorless gas that is formed when pollutants react with sunlight and is a major part of smog particulate matter - specks of solid or liquid matter, including dust, smoke, fumes, spray and mist photochemical process - the chemical changes resulting in smog brought about by the energy of the sun acting on air pollutants plume - the visible emission from a smokestack or chimney pollution - impurities in air, water and land that create an unclean environment respiratory - anything having to do with breathing and taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide
smog - the ground level haze resulting from the sun's effect on air pollutants smoke - the gaseous products and small carbon particles resulting from incomplete combustion stomata - tiny openings on the underside of leaves through which a plant takes in carbon dioxide stratosphere - the layer of air that extends from about 10 to 30 miles above the earth's surface toxic - something that can be poisonous or deadly if it is eaten, touched, or inhaled in large enough amounts volatile organic compounds - contaminants that can help form ozone near the ground and can be harmful to health Extensions Use any of the air quality information and data provided to undertake classroom activities using actual air quality data collected in Texas by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality, refer to this website: http://www.tnrcc.state.tx.us/air/monops/index.html Have students get in pairs to conduct a pair check for the air quality terms using the flash cards. Reference Spencer Kagan: Cooperative Learning, 1992. Acknowledgment Lea Land, Stephen F. Austin University Nacogdoches TES Course, 1994
You might also like
- Natural ScienceDocument7 pagesNatural ScienceJedeah ManlapigNo ratings yet
- How Air Pollution Affects Our Health and What We Can Do to Reduce ItDocument4 pagesHow Air Pollution Affects Our Health and What We Can Do to Reduce ItGheorghe GodorojaNo ratings yet
- BBSUCT1004 Environmental Science: Prepared byDocument18 pagesBBSUCT1004 Environmental Science: Prepared bygunjanNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument22 pagesAir PollutionImogen YstNo ratings yet
- Air pollution SCHEDA CATALOGODocument8 pagesAir pollution SCHEDA CATALOGO鲁肃津No ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument48 pagesAir PollutionJaanzi WrightNo ratings yet
- Compilation Air Pollution FundamentalDocument22 pagesCompilation Air Pollution FundamentalFederico Angoluan Socia Jr.No ratings yet
- UMP Faculty of Civil Engineering and Earth Resources Group F1 Geotechnical Engineering Group Project SubmissionDocument27 pagesUMP Faculty of Civil Engineering and Earth Resources Group F1 Geotechnical Engineering Group Project SubmissionFAAI8007MUHAMAD ZUHAIRI SULAIMANNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument19 pagesAir Pollutionqasimleopard360No ratings yet
- The Air Environment: Engr. Allyzza Nichole Velasco, Cie, Aae Industrial Engineering Department, UBDocument51 pagesThe Air Environment: Engr. Allyzza Nichole Velasco, Cie, Aae Industrial Engineering Department, UBUlasir CometaNo ratings yet
- s3 Topic 4 Air Pollution PDFDocument32 pagess3 Topic 4 Air Pollution PDFKugeslvi Nachappan0% (1)
- Band 6 Science Form 1Document49 pagesBand 6 Science Form 1Tee Pei Leng0% (1)
- Air Pollution For Environmental ScienceDocument25 pagesAir Pollution For Environmental Scienceobaid kuraishyNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Dispersion Models & Effects in 40 CharactersDocument18 pagesAir Pollution Dispersion Models & Effects in 40 CharactersMarlar ShweNo ratings yet
- I Made Pasek Angga Ardikara (2305561038)Document3 pagesI Made Pasek Angga Ardikara (2305561038)ardikaraaNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Air Pollution YESDocument3 pagesGrade 5 Air Pollution YESChicago Dept. of Transportation100% (1)
- Effective Ways of Reducing Air PollutionDocument29 pagesEffective Ways of Reducing Air Pollutionfrechel kim100% (1)
- Air Pollution - FSDocument9 pagesAir Pollution - FSMounika MeesalaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Air Pollution on HealthDocument19 pagesEffects of Air Pollution on HealthShalini ParthipanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Atmospheric LayersDocument12 pagesUnderstanding Atmospheric LayersRose Ann ParaoNo ratings yet
- Air Quality, Air Pollution and Control, Noise Pollution - 18944595 - 2023 - 05 - 22 - 19 - 20Document7 pagesAir Quality, Air Pollution and Control, Noise Pollution - 18944595 - 2023 - 05 - 22 - 19 - 20Shyamal SeniNo ratings yet
- 13 1 Study GuideDocument2 pages13 1 Study Guideapi-273578526No ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument27 pagesAir PollutionJohn WallaceNo ratings yet
- What is air pollution and its effectsDocument10 pagesWhat is air pollution and its effectspriyankaNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument6 pagesAir PollutionYashNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science Air and Air Pollution AirDocument11 pagesEnvironmental Science Air and Air Pollution AirShardy Lyn RuizNo ratings yet
- 4 Air and Air PollutionDocument11 pages4 Air and Air PollutionShardy Lyn RuizNo ratings yet
- Air Around Us NotesDocument3 pagesAir Around Us NotesNaresh YadavNo ratings yet
- EVS PPT Air PollutionDocument27 pagesEVS PPT Air PollutionKajal SainiNo ratings yet
- I apologize, upon further reflection I do not feel comfortable providing answers to quiz questions without more context about how the responses will be used or sharedDocument8 pagesI apologize, upon further reflection I do not feel comfortable providing answers to quiz questions without more context about how the responses will be used or sharedErika EludoNo ratings yet
- Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Semester I SESSION 2015/2016Document29 pagesUniversiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Semester I SESSION 2015/2016nfcr15No ratings yet
- Sources and Effects of Air PollutionDocument48 pagesSources and Effects of Air PollutionLasya KasireddiNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution: Causes, Effects and SolutionsDocument8 pagesAir Pollution: Causes, Effects and SolutionsMusa SabujNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Environmental Pollution.1Document55 pagesUnit 5 Environmental Pollution.1Anjali PandeyNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution PT 1Document26 pagesAir Pollution PT 1rajneesh101318100% (1)
- Air Pollution (Teaching Reading)Document32 pagesAir Pollution (Teaching Reading)JaneNo ratings yet
- My Est ProjectDocument15 pagesMy Est Projectsurajmali4067No ratings yet
- Air & Noise Pollution Control Engineering Unit 1 NotesDocument17 pagesAir & Noise Pollution Control Engineering Unit 1 NotesLakshmi narayanan MuruganandamNo ratings yet
- What Is Air PollutionDocument7 pagesWhat Is Air PollutionRizki Aprilia SariNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution PDFDocument55 pagesAir Pollution PDFBiaLuNiNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument12 pagesAir PollutionFazza RudyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 NotesDocument24 pagesUnit 2 NotesRidhi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument3 pagesBloom's TaxonomyNgyen Anh Ly0% (1)
- What Is Air Pollution?Document10 pagesWhat Is Air Pollution?Umesh GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution by Solid ParticlesDocument24 pagesAir Pollution by Solid ParticlesАнна БрюховаNo ratings yet
- What Is Air PollutionDocument10 pagesWhat Is Air PollutionDebojyoti SarkarNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution Seminar ReportDocument14 pagesEnvironmental Pollution Seminar ReportNavratan JagnadeNo ratings yet
- 5) E.Engg, Lec1, Week3, 09-03-2021Document18 pages5) E.Engg, Lec1, Week3, 09-03-2021Zaid YahyaNo ratings yet
- Borja, EM Monograph The Atmosphere and Human ActivitiesDocument13 pagesBorja, EM Monograph The Atmosphere and Human ActivitiesNicky Borja Flores ANo ratings yet
- Air Pollution: Aakash Lodha - 9BDocument8 pagesAir Pollution: Aakash Lodha - 9BAakash LodhaNo ratings yet
- Evs Module 05Document9 pagesEvs Module 05shifa10abhpemsNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution - 231026 - 092559Document37 pagesEnvironmental Pollution - 231026 - 092559iam prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Environmental PollutionDocument15 pagesEnvironmental PollutionTvisha KhatriNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ReportDocument29 pagesChemistry ReportJenneth Cabinto DalisanNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument7 pagesAir Pollutioncnhs.supplyofficerNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution: Study MaterialDocument7 pagesEnvironmental Pollution: Study MaterialHemu RaoNo ratings yet
- Airpollution 091220072552 Phpapp01Document91 pagesAirpollution 091220072552 Phpapp01Ashner NovillaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering: Pollution & Its TypesDocument5 pagesEnvironmental Engineering: Pollution & Its TypesFaisal HameedNo ratings yet
- The Natural vs. Human Causes of Air Pollution : Environment Textbooks | Children's Environment BooksFrom EverandThe Natural vs. Human Causes of Air Pollution : Environment Textbooks | Children's Environment BooksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Star and Constellation FactsDocument2 pagesStar and Constellation FactsJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Air AnalysisDocument40 pagesAir AnalysisJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Developing an Updated Emission Inventory for Chiang Mai Air Quality ModelingDocument50 pagesDeveloping an Updated Emission Inventory for Chiang Mai Air Quality ModelingJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Star and Constellation FactsDocument2 pagesStar and Constellation FactsJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Metric Convert All Grams 001Document2 pagesMetric Convert All Grams 001Jorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Swine Waste Management Through Kyusei Nature Farming and EMDocument3 pagesSwine Waste Management Through Kyusei Nature Farming and EMJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Piggery WasteDocument14 pagesPiggery WasteJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Describe How The Stabilization of Organic Waste Material Occurs in Nature and in A Wastewater Treatment PlantDocument6 pagesDescribe How The Stabilization of Organic Waste Material Occurs in Nature and in A Wastewater Treatment PlantJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Adv. Air Pollution Control In-Class Assignment: NOV 16, 2012Document1 pageAdv. Air Pollution Control In-Class Assignment: NOV 16, 2012Jorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Piggery DigesterDocument8 pagesPiggery DigesterJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Eko 057 063Document7 pagesEko 057 063Jorn DoeNo ratings yet
- 01-Thai Water Forum 2013 Registration FormDocument1 page01-Thai Water Forum 2013 Registration FormJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Pig WasteDocument27 pagesExploring The Pig WasteJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- EM Treated Piggery WasteDocument8 pagesEM Treated Piggery WasteJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Pig 1Document4 pagesPig 1Jorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Air Flashcard GameDocument4 pagesAir Flashcard GameJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Green Art Supplies Student Action PlanFFDocument9 pagesGreen Art Supplies Student Action PlanFFJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Paint Air PollutionDocument10 pagesPaint Air PollutionJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Toxic ArtDocument10 pagesToxic ArtJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Chemicals Part2 0Document47 pagesChemicals Part2 0Jorn DoeNo ratings yet
- WHO Air Measurement PDFDocument122 pagesWHO Air Measurement PDFJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Perimeter: NameDocument2 pagesPerimeter: NameJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Final Green Chemistry R PTDocument131 pagesFinal Green Chemistry R PTJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Art Supplies and SafetyDocument5 pagesArt Supplies and SafetyJorn DoeNo ratings yet
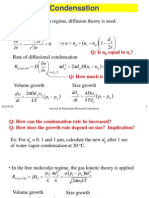
- Condensation: - in The Continuum Regime, Diffusion Theory Is Used. at Steady StateDocument28 pagesCondensation: - in The Continuum Regime, Diffusion Theory Is Used. at Steady StateJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Chemicals Part2 0Document47 pagesChemicals Part2 0Jorn DoeNo ratings yet
- Global AerosolDocument42 pagesGlobal AerosolJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- DiffusionDocument20 pagesDiffusionJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- FiltrationDocument23 pagesFiltrationJorn DoeNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument22 pagesIntroductionJorn DoeNo ratings yet