Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ee0403 Power System Operation
Uploaded by
karen dejoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ee0403 Power System Operation
Uploaded by
karen dejoCopyright:
Available Formats
EE0403-POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL
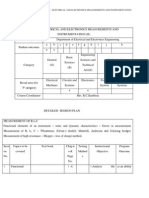
Detailed Session Plan Introduction Necessity for voltage and frequency regulation of power system - P-f and Q-V control loops recent trends in real time control of power system Introduction to load dispatching, load forecasting, unit commitment, load shedding and islanding. Sessio n No. 1 2 Topics to be covered General introduction Power system PS control C7,223 Text book Chap. no & Page No. Testing Instructional Methods Objective CT1,mo 1.To learn the del basics of power CT1,mo system control del Program Outcome
Voltage and frequency C9,229 (a) an ability to apply CT1,mo 3 control, p-f and Q-V knowledge of del loops T1 mathematics, science, and engineering Recent trends in real time R1,C11,654 CT1,mo 4 control del Load dispatching, T2,C3,29 CT1,mo 5 load forecasting del Unit commitment, load T2,C5,131, CT1,mo 6 shedding, islanding del Frequency Control Plant and system level control mathematical model of speed governing system speed load characteristics regulation of two generators in parallel concept of control area LFC control of a single area system static and dynamic response of uncontrolled and controlled system - LFC of two area system static and dynamic response of uncontrolled system tie line with frequency bias control of two area system. Sessio n No. 7 Real power control mechanism-speed governor, hydraulic valve Turbine generator T1 Static performance speed governor of C9,310 C7,223 Topics to be covered Introduction to LFC Text book Chap.no & Page No. T1,C7 221 Testing Methods CT1, ,model Assignm ent Instructional Objective Program Outcome (a) an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering (b) an ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data (e) an ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems
8 9
C9,310
10
11 12
Case A, Case B and Case C Examples, closing LFC loop
C9,313 C9,316
2 .Controlling a power system by controlling system CT1,mod frequency and el system voltage. CT1,mod el CT1, ,model Assignm ent CT1,mod el CT1,mod el
EE0403-POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL
13
14
Block diagram Primary LFC loop Static response primary LFC loop
C9,313 C9,314
15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
Examples Physical interpretation of results Proportional plus integral control Dynamic analysis Two area system Static response of two area system Dynamic response of two area system Tie line bias control Revision
C9,314 C9,322 C9,323 C9,326 C9,329 C9,333 C9,336 C9,339
CT1,mod el CT1, ,model Assignm ent CT1,mod el CT1,mod el CT1,mod el CT1,mod el CT2,mod el CT2,mod el CT2,mod el CT2,mod el
P Voltage Control Type of excitation system Characteristics of excitation system block diagram of excitation system - static and dynamic analysis. Methods of voltage control: OLTC, synchronous condenser, SVC, shunt capacitor Power system level voltage control using tap changing transformer (simple problems). Sessio n No. 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Topics to be covered Text book Chap.no & Page No. C9,302 Testing Methods CT2,mod el CT2,mod el CT2,mod el CT2,mod el CT2,mod el CT2,mod el CT2,mod el Instructional Objective Program Outcome (a) an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering (b) an ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data (e) an ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering
Types of excitation systems Characteristics of C9,304 excitation systems Block diagram of C9,304 excitation system Static and dynamic T1,R C9,306 analysis 1 OLTC, Synchronous R1,C11,672,R1, condenser C11,638 SVC, shunt capacitor R1,C11,631, R1,C11,639 Tap changing R1,C11,678 transformer
2. Controlling a power system by controlling system frequency and system voltage.
EE0403-POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL
31 32
Problems Revision
problems
Economic Dispatch & Unit Commitment Incremental cost curve co-ordination equation without loss solution by Lamda iteration method co-ordination equation with loss solution of co-ordination equation using Bmn coefficients (no derivation) base point and participating factors. Unit commitment (UC) problem constraints in UC Solution methods Priority list method (Numerical problems) Economic dispatch controller addeto load frequency control. Sessio n No. 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 Topics to be covered Text book Chap.no & Page No. C8,277 C8,277 C8,283 C8,284 C8,289 Testing Methods CT2,mode l CT2,mode l CT2,mode l CT2,mode l CT2,mode l CT2,mode l model model model model T2,C3,57 Model Instructional Objective Program Outcome
Incremental cost curve Co-ordination equation without loss Lamda iteration method Co-ordination equation with loss Solution of co-ordination equation using Bmn T1,T coefficients 2 Base point and participating factors Unit commitment problem Constraints in UC Priority list method Problems Economic dispatch controller added to LFC Revision
T2,C3,55 T2,C5,131 T2,C5,131 T2,C5,139
3. To learn how to reduce losses and hence the cost of power system operation
(a) an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering (b) an ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data (e) an ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems
COMPUTER CONTROL OF POWER SYSTEM operating states: Normal, alert, emergency, restorative control strategies Energy control center various levels national, regional and state level SCADA system computer configuration function monitoring, data acquisition and controls EMS system System. Sessio n No. 44 Topics to be covered Text book Chap.no & Page No. T2,R2 Testing Methods model Instructional Objective 4. To control the operation of a power system using digital Program Outcome (a) an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and
Unit V Computer Control of Power T2,R Systems 2 Energy control center
EE0403-POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL
45 46 47 48 49 50 51
National, regional and state level SCADA system Computer configuration Data acquisition and control System operating status Control strategies
T2,R2 T2,R2 T2,R2 T2,R2 T1,C7 219 T2,R2
model model model model model model
computers
engineering (e) an ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems (k)an ability to use technique, skills and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice.
Revision
TEXT BOOKS: 1. Olle.I.Elgerd, Electric energy systems theory-An introduction, Tata McGraw Hill publishing company, New Delhi, 2003. 2. Allen J.Wood, Bruce F. Woollenberg, Power generation operation and control, John Wiley and sons, 2003. REFERENCE BOOKS : 1. Kundur.P., Power system stability and control, McGraw Hill publishing company, 1994. 2. Mahalanabis A.K., Kothari.D.P., and Ahson.S.I., Computer aided power system analysis and control, Tata McGraw Hill publishing company, New Delhi, 199
You might also like
- EEE Lesson Plan ReportDocument4 pagesEEE Lesson Plan ReportSaravanan RameshNo ratings yet
- SallyubusDocument61 pagesSallyubusravindra898233No ratings yet
- Eee-Vii-computer Techniques in Power System Analysis (10ee71) - Notes123098Document144 pagesEee-Vii-computer Techniques in Power System Analysis (10ee71) - Notes123098Angsuman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tuning of PID Controller Using Ziegler-Nichols Method For Speed Control of DC MotorDocument6 pagesTuning of PID Controller Using Ziegler-Nichols Method For Speed Control of DC Motoreubis_machado4370No ratings yet
- Syllabus 5th SemDocument21 pagesSyllabus 5th SemAmit SahuNo ratings yet
- Non-Linear Predictive Control of A DC-to-DC ConverterDocument5 pagesNon-Linear Predictive Control of A DC-to-DC ConvertermenguemengueNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation Lecture 1 IntroductionDocument14 pagesModeling and Simulation Lecture 1 IntroductionhassenbbNo ratings yet
- CTPS Syllabus BreakdownDocument144 pagesCTPS Syllabus Breakdownchaitanya0% (2)
- X X X X X X X X X X X V: Necdet Sinan Özbek Engineering Science and Technology, An International Journal 35 (2022) 101212Document1 pageX X X X X X X X X X X V: Necdet Sinan Özbek Engineering Science and Technology, An International Journal 35 (2022) 101212paxesicrado-3649No ratings yet
- Third Year Sem A Sem B UpdatedDocument40 pagesThird Year Sem A Sem B UpdatedArpitNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Model Predictive Control For Electrical Motor DrivesDocument12 pagesDesign and Implementation of Model Predictive Control For Electrical Motor Drivestariq76No ratings yet
- M.Sc. I Electronics 2019-20Document12 pagesM.Sc. I Electronics 2019-20Hemant patilNo ratings yet
- Temperature ControlDocument18 pagesTemperature ControlgopikrishnaraoNo ratings yet
- M Tech Industrial Power Automation SyllabusDocument55 pagesM Tech Industrial Power Automation SyllabusZaher V Abdul RahamanNo ratings yet
- MTech Power Systems program objectives and outcomesDocument41 pagesMTech Power Systems program objectives and outcomesRajesh ChidambaramNo ratings yet
- SVUCE MTech PowerSystemsDocument42 pagesSVUCE MTech PowerSystemsTejaRam AugusthyaNo ratings yet
- Control+system Lesson+planDocument6 pagesControl+system Lesson+planNarasimman DonNo ratings yet
- Transient Stability Analysis of The IEEE 14-Bus Test System Using Dynamic Computation For Power Systems (DCPS)Document6 pagesTransient Stability Analysis of The IEEE 14-Bus Test System Using Dynamic Computation For Power Systems (DCPS)Nirmal mehtaNo ratings yet
- Control Systems and Instrumentation Lab GuideDocument3 pagesControl Systems and Instrumentation Lab GuideskrtamilNo ratings yet
- Ymca College 5 Sem Btech ElectricalDocument12 pagesYmca College 5 Sem Btech Electricalvinit kumarNo ratings yet
- MT Syllabus - M Power System Effective 2012Document7 pagesMT Syllabus - M Power System Effective 2012cheshankarNo ratings yet
- ANNA Univ. 2009 Reg M.E. - Power System EngineerinG SyllabusDocument23 pagesANNA Univ. 2009 Reg M.E. - Power System EngineerinG SyllabuschandueeeNo ratings yet
- Model Predictive ControlDocument42 pagesModel Predictive Controlzohaib319No ratings yet
- Overcurrent Relay Protection ReportDocument3 pagesOvercurrent Relay Protection Reportkalinath41No ratings yet
- Model Predictive Control of A Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor With Experimental ValidationDocument19 pagesModel Predictive Control of A Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor With Experimental ValidationAlimamy KoromaNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. DEGREE Instrumentation and Control Engineering: Syllabus FOR Credit Based CurriculumDocument66 pagesB.Tech. DEGREE Instrumentation and Control Engineering: Syllabus FOR Credit Based CurriculumRajashree RaviNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of DC Motor Using Neural Network ConfigurationDocument4 pagesSpeed Control of DC Motor Using Neural Network Configurationtariq76No ratings yet
- Control SystemsDocument160 pagesControl SystemsPintu DeyNo ratings yet
- Be Electrical Engg 2008 SyllabusDocument40 pagesBe Electrical Engg 2008 SyllabusGaurav sNo ratings yet
- Basic Integrated Modelling: A Case Study: Mario E. Salgado and Diego R. OyarzúnDocument15 pagesBasic Integrated Modelling: A Case Study: Mario E. Salgado and Diego R. Oyarzúnñ=?!2No ratings yet
- Modeling and Control of An Electric Arc FurnaceDocument6 pagesModeling and Control of An Electric Arc FurnaceChristopher LloydNo ratings yet
- Co-Requisite: Prerequisite: Data Book / Codes/Standards Course Category Course Designed by ApprovalDocument2 pagesCo-Requisite: Prerequisite: Data Book / Codes/Standards Course Category Course Designed by ApprovalRajalearn2 Ramlearn2No ratings yet
- Ee2401 Power System Operation and ControlDocument2 pagesEe2401 Power System Operation and Controlsshivakumar98No ratings yet
- TR7 TP133 Full Content Part1 مهمDocument100 pagesTR7 TP133 Full Content Part1 مهمqais652002100% (1)
- Synchronous Generator Output Voltage Real-Time Feedback Control Via StrategyDocument9 pagesSynchronous Generator Output Voltage Real-Time Feedback Control Via Strategydebasishmee5808No ratings yet
- Mechatronics ME5007Document5 pagesMechatronics ME5007Kalum ChandraNo ratings yet
- Buck BoostDocument6 pagesBuck BoostAngel MarianoNo ratings yet
- Control System Unit 1 (5 TH Sem.)Document61 pagesControl System Unit 1 (5 TH Sem.)kishan guptaNo ratings yet
- UAEU Electrical Engineering AGC Project ReportDocument87 pagesUAEU Electrical Engineering AGC Project ReportpadmajasivaNo ratings yet
- Chen4570 Sp00 FinalDocument11 pagesChen4570 Sp00 FinalmazinNo ratings yet
- Power System Stability Enhancement With Genetically Optimized SVC ControllerDocument6 pagesPower System Stability Enhancement With Genetically Optimized SVC ControllertinazdrilicNo ratings yet
- Ee0301 Electrical and Electronics MeasurementsDocument8 pagesEe0301 Electrical and Electronics MeasurementsMaruthu Pandian50% (2)
- Wheelchair Stabilizing by Controlling The Speed Control of Its DC MotorDocument5 pagesWheelchair Stabilizing by Controlling The Speed Control of Its DC Motorowais_36No ratings yet
- Eee-Viii-power System Operation and Control (06ee82) - NotesDocument138 pagesEee-Viii-power System Operation and Control (06ee82) - Noteskeerthanavijaya100% (3)
- IEC 61850 LTC ControlDocument40 pagesIEC 61850 LTC ControldilipelineNo ratings yet
- M.Tech. Electrical Engineering Scheme and SyllabusDocument17 pagesM.Tech. Electrical Engineering Scheme and SyllabusSidali ChaibNo ratings yet
- A PI Controller Based On Gain-Scheduling For Synchronous GeneratorDocument11 pagesA PI Controller Based On Gain-Scheduling For Synchronous GeneratoratirinaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Drives and Embedded ControlDocument35 pagesElectrical Drives and Embedded ControlMahmoud AbuziadNo ratings yet
- Computer Modeling and Simulation of PWM Converter CircuitsDocument27 pagesComputer Modeling and Simulation of PWM Converter CircuitsAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Fast Transient Stability Estimation Using A Novel Dynamic Equivalent Reduction TechniqueDocument7 pagesFast Transient Stability Estimation Using A Novel Dynamic Equivalent Reduction TechniqueMd. Arifur KabirNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- Electronic Systems: Study Topics in Physics Book 8From EverandElectronic Systems: Study Topics in Physics Book 8Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Advanced Control of AC / DC Power Networks: System of Systems Approach Based on Spatio-temporal ScalesFrom EverandAdvanced Control of AC / DC Power Networks: System of Systems Approach Based on Spatio-temporal ScalesNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Power Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignFrom EverandPower Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignBruno AllardNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageNo ratings yet
- Energetic Processes in Follow-Up Electrical Control Systems: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationFrom EverandEnergetic Processes in Follow-Up Electrical Control Systems: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationNo ratings yet
- Ee/Econ 458 Lpopf: J. MccalleyDocument45 pagesEe/Econ 458 Lpopf: J. Mccalleykaren dejoNo ratings yet
- LP Simplex 3Document9 pagesLP Simplex 3karen dejoNo ratings yet
- Ee/Econ 458 Integer Programming: J. MccalleyDocument33 pagesEe/Econ 458 Integer Programming: J. Mccalleykaren dejoNo ratings yet
- Elec LpopfDocument22 pagesElec Lpopfchet_duttsNo ratings yet
- Solving Linear Programs 1.0 Basic Form: C) X (H X FDocument17 pagesSolving Linear Programs 1.0 Basic Form: C) X (H X Fkaren dejoNo ratings yet
- Market SummaryDocument40 pagesMarket Summarykaren dejoNo ratings yet
- Ee/Econ 458 The Simplex Method: J. MccalleyDocument36 pagesEe/Econ 458 The Simplex Method: J. Mccalleykaren dejoNo ratings yet
- LP Simplex 3Document12 pagesLP Simplex 3karen dejoNo ratings yet
- Real-Time Electricity MarketsDocument35 pagesReal-Time Electricity Marketskaren dejoNo ratings yet
- Miso1 2009Document8 pagesMiso1 2009karen dejoNo ratings yet
- LPOPF SettlementsDocument33 pagesLPOPF Settlementskaren dejoNo ratings yet
- LP Simplex 2Document25 pagesLP Simplex 2karen dejoNo ratings yet
- The Power Flow Equations 1.0 The Admittance Matrix: Current Injections at A Bus Are Analogous To Power Injections. TheDocument29 pagesThe Power Flow Equations 1.0 The Admittance Matrix: Current Injections at A Bus Are Analogous To Power Injections. TheJose A. Regalado RojasNo ratings yet
- Miso3 2009Document6 pagesMiso3 2009karen dejoNo ratings yet
- Op Tim Ization BasicsDocument32 pagesOp Tim Ization Basicskaren dejoNo ratings yet
- Payment Vs Bid CostDocument12 pagesPayment Vs Bid Costkaren dejoNo ratings yet
- Market SummaryDocument40 pagesMarket Summarykaren dejoNo ratings yet
- Ee/Econ 458 PF Equations: J. MccalleyDocument34 pagesEe/Econ 458 PF Equations: J. Mccalleykaren dejoNo ratings yet
- Op Tim Ization IntroDocument49 pagesOp Tim Ization Introkaren dejoNo ratings yet
- Real Time PDFDocument7 pagesReal Time PDFKandlakuntaBhargavaNo ratings yet
- PJM ArevaDocument8 pagesPJM Arevakaren dejoNo ratings yet
- Ee/Econ 458 Market Overview: Time-Line and Scuc, Rac, Sced: J. MccalleyDocument10 pagesEe/Econ 458 Market Overview: Time-Line and Scuc, Rac, Sced: J. Mccalleykaren dejoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CPLEX 1.0 OverviewDocument13 pagesIntroduction To CPLEX 1.0 Overviewkaren dejoNo ratings yet
- HW 6 SolutionsDocument11 pagesHW 6 Solutionskaren dejoNo ratings yet
- Unit Commitment,: Jdm@linux3.ece - Iastate.eduDocument33 pagesUnit Commitment,: Jdm@linux3.ece - Iastate.edukaren dejoNo ratings yet
- Ee/Econ 458 Scuc: J. MccalleyDocument42 pagesEe/Econ 458 Scuc: J. Mccalleykaren dejoNo ratings yet
- HW 7 SolutionsDocument9 pagesHW 7 Solutionskaren dejoNo ratings yet
- HW7Document2 pagesHW7karen dejoNo ratings yet
- Intro LPDocument17 pagesIntro LPkaren dejoNo ratings yet
- Ee/Econ 458 Introduction To Linear Programming: J. MccalleyDocument25 pagesEe/Econ 458 Introduction To Linear Programming: J. Mccalleykaren dejoNo ratings yet
- Pentair Intellibrite 5g Color Led Pool Installation ManualDocument32 pagesPentair Intellibrite 5g Color Led Pool Installation ManualZahidul HasanNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Diagram of A Plate and Frame Heat Exchanger02Document9 pagesConceptual Diagram of A Plate and Frame Heat Exchanger02sai thesisNo ratings yet
- 1 Kidde Interruptor de Baja PresiónDocument1 page1 Kidde Interruptor de Baja PresiónTatiana RomeroNo ratings yet
- AHM060 2 Ramp Handling PDFDocument15 pagesAHM060 2 Ramp Handling PDFNarablues Indonesia100% (1)
- Civil Engineer Seeks Water Resources RoleDocument2 pagesCivil Engineer Seeks Water Resources Roleimmanuel ketarenNo ratings yet
- Et101 - Electrical TechnologyDocument78 pagesEt101 - Electrical TechnologyNurhidayah JamaluddinNo ratings yet
- ECE6014 Modern-Satellite-CommunicationDocument2 pagesECE6014 Modern-Satellite-Communicationnikhil yamasaniNo ratings yet
- Eff FormulaDocument59 pagesEff FormulaVenkateswara Rao DoodalaNo ratings yet
- SL 4030 PDFDocument2 pagesSL 4030 PDFmekelewengNo ratings yet
- Cross-Board: Instruction Manual - Spare Parts BookDocument18 pagesCross-Board: Instruction Manual - Spare Parts BookMessi EmetievNo ratings yet
- Certification Handbook - LinkedinDocument14 pagesCertification Handbook - LinkedinVinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Inspecting ammonia storage tank welds with non-intrusive ultrasonic robotDocument13 pagesInspecting ammonia storage tank welds with non-intrusive ultrasonic robotMechNo ratings yet
- The Neurally Controlled Animat: Biological Brains Acting With Simulated BodiesDocument6 pagesThe Neurally Controlled Animat: Biological Brains Acting With Simulated BodiessdfoiuhjwerNo ratings yet
- Knowl AssDocument9 pagesKnowl AssEmente Emente100% (2)
- Maneuvers Multi-EngineDocument1 pageManeuvers Multi-EngineELAC2No ratings yet
- Operating Instructions Terex HML 42 PDFDocument136 pagesOperating Instructions Terex HML 42 PDFJMNo ratings yet
- Huawei OTA V100R001 Product DescriptionDocument25 pagesHuawei OTA V100R001 Product DescriptionNguyen Anh QuanNo ratings yet
- Commissioning Switches, Automatic TransferDocument44 pagesCommissioning Switches, Automatic Transferbookbum100% (5)
- ASME B16.36-96 Bridas de OrificioDocument11 pagesASME B16.36-96 Bridas de OrificioLuis MoralesNo ratings yet
- Genetic AlgorithmsDocument41 pagesGenetic Algorithms1balamanian100% (2)
- Difference Between A Computer Science & Information Technology DegreeDocument7 pagesDifference Between A Computer Science & Information Technology DegreeOvidiu Costinel DanciuNo ratings yet
- Irc 11 1962Document14 pagesIrc 11 1962LokeshNo ratings yet
- Final Project at NucsoftDocument97 pagesFinal Project at NucsoftmainasshettyNo ratings yet
- Astm E10-15 PDFDocument32 pagesAstm E10-15 PDFVCNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics I Cee 305: 2.0 Consistency Limit (Atterberge Limit)Document6 pagesSoil Mechanics I Cee 305: 2.0 Consistency Limit (Atterberge Limit)ABUBAKAR SANI HABIBUNo ratings yet
- Thinking Education Through PhilosophyDocument36 pagesThinking Education Through PhilosophyZorayma NavarroNo ratings yet
- Resonant Automation Company Overview and Areas of ExpertiseDocument2 pagesResonant Automation Company Overview and Areas of ExpertiseJohan ConradieNo ratings yet
- In-House Training SyllabusDocument6 pagesIn-House Training SyllabusJokoo Prast SetyooNo ratings yet
- WREN MW54 Gas Turbine Engine CAD ModelDocument141 pagesWREN MW54 Gas Turbine Engine CAD ModelThomas Dickinson67% (3)
- Hadeco Bidop ES-100V3 Operating ManualDocument45 pagesHadeco Bidop ES-100V3 Operating ManualsambadeeNo ratings yet