Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ch-10 WKG Principle UPS Inv
Uploaded by
neeraj kumar singhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ch-10 WKG Principle UPS Inv
Uploaded by
neeraj kumar singhCopyright:
Available Formats
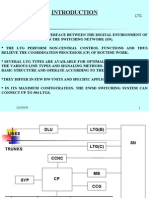
CHAPTER TEN
WORKING PRINCIPLE OF UPS / INVERTER
UPS SYSTEM 1 KVA / 3 KVA INVERTER
5.1 UPS System
UPS System means Uninterrupted Power Supply. As the name indicates, this system
supplies uninterrupted A.C. supply.
• Necessity:- Un-interrupted power supply is very much necessary in BSNL for the
operation of computers, peripherals in O.M.C and for the other telecom equipments.
• Capacity: The Capacity of an UPS is the output power it can deliver and is expressed in
terms of kilo volt-amperes (KVA). Different capacities of UPS systems are available
readily in the market right from 1 KVA onwards.
5.1.1 Principle of UPS System
Rectifier /
/ charger Inverter
AC mains DC DC AC Output
Battery
Fig.1 Block diagram of UPS System
The Block diagram of UPS is given above single phase AC. supply is first rectified to
120V D.C. supply. Across this 2 sets of 40 AH, 120 volts battery sets are floated. The
combined D.C is then fed to the inverter, which converts into A.C of 220 volts.
During the available period of input AC mains, the battery sets will be trickle charged and the
load will be taken by rectifier only. During the absence of input A.C. mains, the battery set
will be taking the load.
Another type of UPS system used in B.S.N.L is designed to work on -48 V D.C
supply fed from the exchange power plant.
RTTC NAGPUR Page 72 of 75
5.1.2 Specifications of UPS systems
a) Input 230V, 1 φ, A.C. supply
b) Input BTY 120V, 40 AH, two sets of Batteries.
c) Output 220 volts, A.C
d) Output current For 5 KVA it is 21.5 Amps.
5.1.3 Alarms in UPS system
1) Low Battery - If the battery voltage falls below a specific voltage.
2) Over load - If the load on UPS is more than its capacity UPS will be tripped
and overload alarm comes
3) Output High - When output voltage becomes high UPS will be tripped and
this alarm comes.
4) Output low :- When output voltage becomes low UPS will be tripped and
this alarm comes.
5) Trip - This LED glows once if the inverter trips.
5.2 Inverters of 1KVA/3KVA Capacities
Inverter is an alternating current (A.C) generating equipment using D.C voltage
source of -48v as its input.
5.2.1 Necessity
Inverters are very widely used in D.O.T network for the operation of peripherals in
CDOT and E-10B exchanges.
5.2.2 Technical Specifications
1) Input
a) Voltage = 44 to57 volts D.C
b) Current = 32A, 96A, 192Amps for 1 KVA, 3KVA, 6KVA
inverters respectively.
c) Power drawn = 1.5KVA/4.5KVA/9KVA for 1 KVA,
3KVA,6KVA inverters respectively.
d) Source = Battery /Float rectifier
e) Source Ripple = Less than 2 %
2) Output
a) Voltage = 220 ± 2% V.A.C
b) Rated KVA = 1, 3, 6 KVAs
RTTC NAGPUR Page 73 of 75
c) Rated Current = 4.3A, 12.9A. 25.8 A for 1 KVA
3KVA, 6KVA inverters respectively.
d) Wave form = Sinusoidal
e) Total Harmonic distortion = 5% Max
f) Frequency = 50 ± 0.1 Hertz
g) Voltage adjustment = 220 to 250 volts
h) Over current trip = 120%
i) Efficiency = 70 % minimum
5.2.3 Inverters (Capacity wise) used in DOT are listed below:
Exchange Make and Capacity Capacity and No. of Inverters used
CDOT up to 1400 lines 1 KVA x 2 Nos
CDOT above 1400 lines 1 KVA x 3 Nos
E10B 6 KVA x 3 Nos
5.2.4 Principle of Operation
Low capacity inverters are designed using integrated circuits, transistors, etc whereas
higher capacity inverters are designed using thyristors.
Diagram of 1 KVA Inverter
The diagram of 1 KVA Inverter is given above. In this Q1 to Q4 are four power
transistors arranged in full bridge configuration. This combination acts as a push-pull
amplifier gives AC O/P.
Main transformer T1 provides input output isolation. Radio frequencies are filtered at
the output with the help of RF I suppresser. Regulation and frequency stabilization is done by
the control circuit.
RTTC NAGPUR Page 74 of 75
5.2.5 Method of Connection of Inverters in CDOT Exchanges
In C-DOT exchanges all the peripherals are divided into two or three groups and
connected across the output of individual inverters separately. But in case of failure of any
inverter there is a provision for the connection of the group of peripherals connected to the
faulty inverter to another inverter.
5.2.6 Method of Connection of Inverters in E10B exchanges
In E10B exchanges, the main computer works on the output supply of the inverter.
The inverter system comprises of two 6KVA inverter units and a control cubicle. Normally
the total load is shared equally by both the inverters (each operating at half the full load
capacity). In case of failure of any inverter unit, the total load will be supplied by the other
unit.
This inverter system is most unique in nature because of the following.
a) sharing the system load equally.
b) having ability to be in phase synchronization even in the event of failure of master
oscillator, which normally synchronizes them.
c) able to lower overall distortion.
d) well protected against different fault conditions.
with minimum inter cubicle circulary currents over a wide range of input voltage.
RTTC NAGPUR Page 75 of 75
You might also like
- Voip TechnologyDocument64 pagesVoip TechnologySherry HenryNo ratings yet
- Handbook On Good Building Design and ConstructionDocument100 pagesHandbook On Good Building Design and Constructionmujati100% (3)
- Ccna InterviewDocument29 pagesCcna Interviewvijaysingh100% (6)
- SDHDocument47 pagesSDHneeraj kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Transmission PlanDocument17 pagesTransmission Planneeraj kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Ug CablesDocument183 pagesUg Cablesneeraj kumar singhNo ratings yet
- V5 EwsdDocument79 pagesV5 Ewsdneeraj kumar singh100% (3)
- TrafficDocument31 pagesTrafficneeraj kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Ocb CSNDocument118 pagesOcb CSNneeraj kumar singh100% (1)
- Ocb LoadDocument74 pagesOcb Loadneeraj kumar singh100% (2)
- PCMDocument54 pagesPCMneeraj kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Ocb DataDocument102 pagesOcb Dataneeraj kumar singh100% (3)
- OfcDocument58 pagesOfcneeraj kumar singh100% (1)
- System Panel1Document30 pagesSystem Panel1neeraj kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Ocb 283 AppDocument180 pagesOcb 283 Appneeraj kumar singh100% (5)
- OcbDocument95 pagesOcbneeraj kumar singh100% (2)
- In Arch& ServicesDocument16 pagesIn Arch& Servicesneeraj kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Signalling in TelecommunicationDocument54 pagesSignalling in TelecommunicationBiju NarayananNo ratings yet
- MWDocument46 pagesMWneeraj kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Mtce PhilosphyDocument5 pagesMtce Philosphyneeraj kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Dlu V13Document102 pagesDlu V13neeraj kumar singh100% (1)
- LTGDocument51 pagesLTGneeraj kumar singhNo ratings yet
- IVRSDocument18 pagesIVRSneeraj kumar singhNo ratings yet
- NNP 2003Document124 pagesNNP 2003neeraj kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Mntce PhilosDocument15 pagesMntce Philosneeraj kumar singhNo ratings yet
- InternetDocument351 pagesInternetneeraj kumar singhNo ratings yet
- FeeDocument38 pagesFeeneeraj kumar singhNo ratings yet
- EWSD FeaturesDocument11 pagesEWSD Featuresneeraj kumar singhNo ratings yet
- IsdnDocument9 pagesIsdnneeraj kumar singhNo ratings yet
- FeexchDocument114 pagesFeexchneeraj kumar singhNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Manual ApexDocument4 pagesManual Apexjhon jairo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- NPCC Dir 4 - Directory 4 - TFSP - Rev - 20151001 - GJDDocument38 pagesNPCC Dir 4 - Directory 4 - TFSP - Rev - 20151001 - GJDj_viditoNo ratings yet
- EC - Unit 1 - Power SupplyDocument17 pagesEC - Unit 1 - Power Supplynanobala15No ratings yet
- Kyoritsu 2009 Full Line Test Equipment CatalogueDocument84 pagesKyoritsu 2009 Full Line Test Equipment CatalogueRadio Parts100% (1)
- ATV 320 Schneider Manual BookDocument345 pagesATV 320 Schneider Manual BookIbrahim Hadi100% (1)
- Electrical Interview Questions Answers EEE KenyaDocument14 pagesElectrical Interview Questions Answers EEE KenyaAnonymous m8oCtJBNo ratings yet
- 8830 Hardware Installation GuideDocument132 pages8830 Hardware Installation GuideHamza_yakan967No ratings yet
- Sci10 TG U2 PDFDocument264 pagesSci10 TG U2 PDFJastin D. Delector100% (3)
- EE6365 – ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY MANUALDocument58 pagesEE6365 – ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY MANUALjk100% (1)
- Inverters for AC Motor Drives: PWM-VSI drivesDocument17 pagesInverters for AC Motor Drives: PWM-VSI drivesAslam SdNo ratings yet
- Masoneilan - SVI-II AP IOM Manual Quick Start Guide PDFDocument69 pagesMasoneilan - SVI-II AP IOM Manual Quick Start Guide PDFSad LiveNo ratings yet
- Emerson Rect PDFDocument28 pagesEmerson Rect PDFIbrahim Mubark IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Experiment.4. Load Characteristics of D.C Series GeneratorDocument2 pagesExperiment.4. Load Characteristics of D.C Series Generatorمحمد الحديNo ratings yet
- Bender IRDH275 Manual - 07-04Document78 pagesBender IRDH275 Manual - 07-04MojamethNo ratings yet
- Ncer Unit1 WTRMRK PDFDocument5 pagesNcer Unit1 WTRMRK PDFshylaja9No ratings yet
- Solar Photovoltaic Power For IndiaDocument74 pagesSolar Photovoltaic Power For IndiaH Janardan PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Fluxus Build Manual DiyDocument8 pagesFluxus Build Manual DiyEyeVeeNo ratings yet
- Door Locking Security System Using GSMDocument130 pagesDoor Locking Security System Using GSMAnsumanNath100% (1)
- LS-VINA EHV Cable's CatalogueDocument36 pagesLS-VINA EHV Cable's CatalogueDjar Ndoeth0% (1)
- Series Capacitor Compensated AC Filterless Flexible LCC HVDC With Enhanced Power Transfer Under Unbalanced FaultsDocument12 pagesSeries Capacitor Compensated AC Filterless Flexible LCC HVDC With Enhanced Power Transfer Under Unbalanced FaultsTRIAD TECHNO SERVICESNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument14 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentSURAJ GAUTAMNo ratings yet
- SMPS - (Switch Mode Power Supply)Document20 pagesSMPS - (Switch Mode Power Supply)Karthi Keyan VeeraNo ratings yet
- UT351Document90 pagesUT351Marcelo ArtolaNo ratings yet
- Bonitron Portable Capacitor FormerDocument2 pagesBonitron Portable Capacitor FormerfghjfghjNo ratings yet
- SP 1103 Electrical Engineering GuidelinesDocument22 pagesSP 1103 Electrical Engineering Guidelinesabdou0% (2)
- Thyristor Switch ApplicationsDocument6 pagesThyristor Switch ApplicationsThilina Jayaweera75% (4)
- Difference Between DC Power and AC PowerDocument4 pagesDifference Between DC Power and AC PowerJanine Jade Setias100% (1)
- Apc 208-480V UpsDocument109 pagesApc 208-480V UpsAnil KolekarNo ratings yet
- Electrical System Presentation: A318/A319/A320/A321 General Familiarization Course Electrical PowerDocument42 pagesElectrical System Presentation: A318/A319/A320/A321 General Familiarization Course Electrical PowervvNo ratings yet
- Hindalco School of Excellence: Trainer: - Abhisek PagadDocument15 pagesHindalco School of Excellence: Trainer: - Abhisek PagadAbhisek PagadNo ratings yet