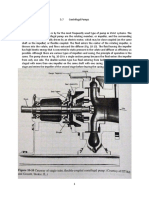
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9A01308 Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery
Uploaded by
sivabharathamurthyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9A01308 Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery
Uploaded by
sivabharathamurthyCopyright:
Available Formats
Code: 9A01308
1
(Electrical and Electronics Engineering)
B.Tech II Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 FLUID MECHANICS & HYDRAULIC MACHINERY Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks *****
1 (a) (b) Differentiate between: (i) Liquids and gases. (ii) Real fluid and ideal fluids. (iii) Specific weight and specific volume of a fluid. Determine the intensity of shear of an oil having viscosity = 1.2 poise and is used for lubrication in the clearance between a 10 cm diameter shaft and its journal bearing. The clearance is 1.0 mm and shaft rotates at 200 r.p.m. Define stream line, path line and streak line. Derive mathematical expressions for each of these lines. A 75 cm diameter uniform pipe bend turns the directions of flow of gasoline of sp.gr. 0.79 through an angle of 120 in the horizontal plane. The constant pressure and velocity through the bend are 90 KPa and 3 m/s respectively. Find the magnitude and direction of the force to be exerted on the bend to achieve the directional change. Derive an expression for the loss of head due to sudden contraction in a pipe. Sketch the flow pattern and show how the hydraulic gradient and total energy line vary as the flow takes place through the contraction. Two reservoirs whose water surface elevations differ by 100 m are connected by a 25 cm diameter pipe 3000 m long. Another pipe of the same diameter is laid parallel with the first pipe and connected to the middle one-third of its length. Calculate the percent increase in discharge. Assume f = 0.01 for all pipes and neglect minor losses. A jet of water of diameter 50 mm having a velocity of 20 m/sec strikes a curved vane which is moving with a 0 velocity of 10 m/sec in the direction of the jet. The jet leaves the vane at an angle of 60 to the direction of motion of the vane at outlet. Determine: (i) The force exerted by the jet on the vane in the direction of motion and (ii) Work done per second by the jet. Define the terms gross head, net head, hydraulic efficiency and overall efficiency. Discuss with neat sketches the classification of hydroelectric plants based on storage characteristics. A Pelton wheel is required to develop 12,000 KW of power under a head of 400 m. The wheel speed is 720 rpm. Assuming Ku = 0.45, CV = 0.98, o = 86% and approximate jet ratio = 8, design the machine and specify (a) bucket circle diameter, (b) number of buckets and (c) size of each bucket. Give a fully dimensioned sketch of a bucket. Where is servo meter used in governing mechanism of turbines? Explain it in detail. A Kaplan turbine is to develop 2400 KW when running at 240 rpm under a net head of 49 m. In order to predict its performance a model of scale 1:5 is tested under a net head of 25 m. At what speed should the model run and what power would it develop. Determine the discharge in the model and in full scale turbine if the overall efficiency of the model is 85%. What is priming? Why is it necessary? Explain in detail. A centrifugal pump discharges 1200 lit/minute against a head of 16.5 m when the speed is 1500 rpm. The diameter of the impeller is 35 cm and the power required is 6 h.p. A geometrically similar pump of 45 cm is to run at 1750 rpm. Assuming equal efficiencies, find. (i) the head developed (ii) the discharge (iii) power developed by 45 cm pump.
Max Marks: 70
2 (a) (b)
3 (a) (b)
5 (a) (b) 6
7 (a) (b)
8 (a) (b)
*****
Code: 9A01308
2
(Electrical and Electronics Engineering)
B.Tech II Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 FLUID MECHANICS & HYDRAULIC MACHINERY Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks *****
1 (a) (b) What is meant by vapour pressure? Explain its importance in liquid flow systems. A mist droplet is of 0.06 mm diameter. The atmospheric pressure is 101.04 KPa and the surface tension of water is 0.0736 N/m. Estimate the absolute pressure within the droplet. Derive Eulers equation of motion along a stream line for an ideal fluid stating clearly the assumptions. 3 A pipe of 20 cm diameter conveying 0.20 m /sec of water has a right angled bend in a horizontal plane. Find the resultant force exerted on the bend if the pressure at inlet and outlet of the bend are 22.563 2 2 N/cm and 21.582 N/cm respectively. Define an orifice-meter. Derive an expression for the discharge through an orifice-meter. A horizontal venturimeter with inlet diameter 30 cm and throat diameter 15 cm is used to measure the flow of oil of specific gravity 0.8. The discharge of oil through venturimeter is 50 litres/s, find the reading of the oil-mercury differential manometer. Take Cd= 0.98. Show that in case of jet striking the flat plates mounted on wheels, the efficiency will be maximum when the tangential velocity of wheel is half that of the jet. A jet of water having a velocity of 45 m/s impinges without shock on a series of vanes moving at 15 m/s. 0 The direction of motion of the vanes is inclined at 20 to that of the jet, the relative velocity at outlet is 0.9 times that at inlet, and the absolute velocity of the water at exit is to be normal to the motion of vanes. Find: (i) Vane angles at entrance and exit. (ii) Work done on vanes per unit weight of water supplied by the jet and (iii) Hydraulic efficiency. Describe different aspects that are to be studied in respect of underground power houses. 6 A hydropower plant has an installed capacity of 50 MW. The yearly output of the plant is 25010 KWhr. If the peak load is 40000 KW. Determine: (i) annual load factor (ii) Plant use factor and (iii) Capacity factor. A Kaplan turbine develops 60,000 KW of power under a head of 25 m with overall efficiency of 90%. Taking the value of flow ratio = 0.5, speed ratio = 1.6, the hub diameter as 0.35 times the diameter of the runner, find: (i) the diameter of the runner (ii) the speed of the turbine (iii) the specific speed of the turbine. Define the specific speed of a turbine. Derive an expression for the specific speed. What is the significance of the specific speed? An inward flow reaction turbine has external and internal diameters as 1.2 m and 0.6 m respectively. The velocity of flow through the runner is constant and is equal to 1.8 m/s. Determine: (i) Discharge through the runner, and (ii) Width at outlet if the width at inlet = 200 mm. Discuss the detailed classification of pumps. What precautions are to be taken while starting and closing the pump?
Max Marks: 70
2 (a) (b)
3 (a) (b)
4 (a) (b)
5 (a) (b)
7 (a) (b)
8 (a) (b)
*****
Code: 9A01308
3
(Electrical and Electronics Engineering)
B.Tech II Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 FLUID MECHANICS & HYDRAULIC MACHINERY Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks *****
1 (a) (b) 2 (a) (b) Distinguish between: (i) Standard and local atmospheric pressures. (ii) Barometric pressure and absolute pressure and (iii) Absolute pressure and gauge pressure. Explain the working of a Bourdon pressure gauge. Derive Bernoullis equation for the flow of an incompressible frictionless fluid from consideration of momentum. A 45 reducing bend is connected in a pipe line, the diameters at the inlet and outlet of the bend being 40 cm and 20 cm respectively. Find the force exerted by water on the bend if the intensity of pressure at inlet of bend is 2 21.58 N/cm . The rate of flow of water is 500 litres/s. Explain how the following flow problems are analyzed: (i) series pipe connection and (ii) parallel pipe connection. Kerosene of specific gravity 0.8 flows upwards through a 30 cm diameter by 15 cm diameter vertical venturimeter. The height of the converging cone is 50 cm. A mercury differential manometer connected between the inlet and throat shows deflection of 68 cm in mercury levels. Assuming C = 0.985, calculate the rate of flow. If the inlet pressure is 1.6 bars, what is the throat pressure? Derive an expression for the force exerted by a jet of water on a moving inclined plate in the direction of the jet. A jet of water of 60 mm diameter strikes a curved vane at its center with a velocity of 18 m/s. The curved vane is 0 moving with a velocity of 6 m/s in the direction of the jet. The jet is deflected through an angle of 165 . Assuming the plate to be smooth find: (i) Thrust on the plate in the direction of jet. (ii) Power of the jet, and (iii) Efficiency of the jet. Write short on the: (i) Necessity of storage and pondage and (ii) Stream flow data requirement in hydropower plants. 5 4 The designed capacity of a hydropower plant is 1.32 x 10 KW. If the power generated in the plant is 9 x 10 KW, find the efficiency of the plant. If the peak discharge is 1.5 times the normal discharge, determine the plant capacity, plant factor and total energy produced in a year. What is a draft tube? Why is it used in a reaction turbine? Describe with sketches, two different types of draft tubes. A reaction turbine works at 500 r.p.m. under a head of 100 m. The diameter of turbine at inlet is 100 cm and flow 2 area is 0.35 m . The angles made by absolute and relative velocities at inlet are 15 and 60 respectively with the tangential velocity. Determine: (i) The volume flow rate. (ii) The power developed and (iii) Efficiency. Assume whirl at outlet to be zero. Explain the difference between Kaplan turbine and propeller turbine. Define cavitation. What are the effects of cavitation? Give the necessary precautions against cavitation. Sketch the velocity triangles at the inlet and outlet of a centrifugal pump identifying the various velocity components. A centrifugal pump has an impeller 45 cms in diameter running at 450 rpm. The discharge at inlet is entirely 0 radial. The velocity of flow at outlet is 1.2 m/s. The vanes are curved backwards at outlet at 30 to the wheel tangent. If the discharge of the pump is 0.15 cumec, calculate the impeller horse power and the torque on the shaft.
Max Marks: 70
3 (a) (b)
4 (a) (b)
5 (a) (b)
6 (a) (b)
7 (a) (b) 8 (a) (b)
*****
Code: 9A01308
4
(Electrical and Electronics Engineering)
B.Tech II Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 FLUID MECHANICS & HYDRAULIC MACHINERY Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks *****
1 (a) (b) Distinguish between manometers and mechanical gauges. What are the different types of mechanical pressure gauges? A simple manometer is used to measure the pressure of oil (sp.gr. = 0.8) flowing in a pipe line. Its right limb is open to the atmosphere and left limb is connected to the pipe. The centre of the pipe is 9 cm below the level of mercury (sp.gr.13.6) in the right limb. If the difference of mercury level in the two limbs is 15 cm, determine the 2 absolute pressure of the oil in the pipe in Ncm . Define the following: (i) Steady flow. (ii) Non-uniform flow. (iii) Laminar flow and (iv) Two-dimensional flow. The water is flowing through a taper pipe of length 50 m having diameters 40 cm at the upper end and 20 cm at the lower end, at the rate of 60 litres/s. The pipe has a slope of 1 in 40. Find the pressure at the lower end if the 2 pressure at the higher level is 24.525 N/cm . What do you mean by equivalent pipe? Obtain an expression for equivalent pipe. A pipe of diameter 300 mm and length 1000 m connects two reservoirs, having difference of water levels as 15 m. Determine the discharge through the pipe. If an additional pipe of diameter 300 mm and length 600 m is attached to the last 600 m length of the existing pipe, find the increase in the discharge. Take f = 0.02 and neglect minor losses. A jet of water moving at 12 m/sec impinges on vane shaped to deflect the jet through 120 when stationary. If the vane is moving at 5 m/sec, find the angle of the jet so that there is no shock at inlet. What is the absolute velocity of the jet at exit in magnitude and direction and the work done per second? Assume that the vane is smooth. Explain the location and function of the following in a hydroelectric power plant. (i) Intake structure. (ii) Pen stock. (iii) Anchor block. Two turbo generators each of capacity 22,000 KW have been installed at a hydel power station. During a certain period the load on the hydel plant varies from 20,000 to 30,000 KW. Calculate: (i) Total installed capacity (ii) Load factor (iii) Plant factor and (iv) Utilization factor. The following data is given for a Francis turbine: Net head = 70 m, speed = 600 r.p.m., shaft power = 367.875 KW, o = 85%, h = 95%, flow ratio = 0.25, breadth ratio = 0.1, outer diameter of the runner = 2 x inner diameter of runner. The thickness of vanes occupy 10% of the circumferential area of the runner. Velocity of flow is constant at inlet and outlet and discharge is radial at outlet. Determine: (i) Guide blade angle. (ii) Runner vane angles at inlet and outlet. (iii) Diameters of runner at inlet and outlet and (iv) Width of wheel at inlet. Describe different types of surge tanks with neat sketches. A Kaplan turbine model built to a reduced scale of 1:10 develops 25 MHP when run at 400 rpm under a head of 6 m. If its overall efficiency is 85%, what flow rate should be supplied to the model? If the prototype machine works under a head of 40 m, compute the speed, power output and discharge of the machine. Assume the same overall efficiency for the model and prototype. Draw a typical layout and explain the working of centrifugal pump. Also indicate various components. Explain the method of selection of centrifugal pumps with the aid of characteristic curves.
0
Max Marks: 70
2 (a) (b)
3 (a) (b)
5 (a) (b)
7 (a) (b)
8 (a) (b)
*****
You might also like
- Hydraulics and Hydraulic Machinery Exam QuestionsDocument8 pagesHydraulics and Hydraulic Machinery Exam Questionshimabindugvsd71No ratings yet
- CFD Analysis of Pelton TurbineDocument4 pagesCFD Analysis of Pelton TurbineSanam ManutdNo ratings yet
- Assignment-6 Solutions - FinalDocument8 pagesAssignment-6 Solutions - FinalmaheshNo ratings yet
- Pumps TurbinesDocument45 pagesPumps Turbinesapi-19799147No ratings yet
- Francis Turbine Test RigDocument4 pagesFrancis Turbine Test RigAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- Frictional Losses in Circular PipeDocument5 pagesFrictional Losses in Circular PipeVrushiket PatilNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Systems PDFDocument12 pagesVacuum Systems PDFSnigdha YadavNo ratings yet
- Baker - 10Mw: Optional Optimum Head Loss Calculation ModuleDocument1 pageBaker - 10Mw: Optional Optimum Head Loss Calculation ModuleamoghimiNo ratings yet
- Pump Horsepower CalculationDocument5 pagesPump Horsepower Calculationkanpur12345100% (1)
- Hydraulic Design - ScanDocument36 pagesHydraulic Design - ScancjayamangalaNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Breaker ValveDocument2 pagesVacuum Breaker ValveRaghunath YeturiNo ratings yet
- Momentum Transfer Operations ProblemsDocument5 pagesMomentum Transfer Operations ProblemsMOHIT GUPTANo ratings yet
- Fire Pump Relief Valve Model 108FC/108FCA Sizes Features SpecificationsDocument2 pagesFire Pump Relief Valve Model 108FC/108FCA Sizes Features SpecificationsAdil AzizNo ratings yet
- Topic Wise Gme Interview Questions (Great Eastern) : NoteDocument2 pagesTopic Wise Gme Interview Questions (Great Eastern) : NoteAthul P PNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual MEC-325 Thermo Fluid Engineering LaboratoryDocument36 pagesLaboratory Manual MEC-325 Thermo Fluid Engineering LaboratoryArpit Kumar Jain100% (1)
- Centrifugal Pumps: How They Work and Their Performance CurvesDocument8 pagesCentrifugal Pumps: How They Work and Their Performance CurvesSaleem Chohan100% (1)
- Unit 1: Introduction To PPE: A) Power GenerationDocument55 pagesUnit 1: Introduction To PPE: A) Power GenerationArun PatilNo ratings yet
- Large Turbine Overhaul ChecksDocument24 pagesLarge Turbine Overhaul ChecksSethuRamalingamNo ratings yet
- Design Shell TubeDocument3 pagesDesign Shell TubeAKSHEYMEHTANo ratings yet
- Water HammerDocument22 pagesWater Hammerparvin_fNo ratings yet
- Literature Review HydroelectricDocument6 pagesLiterature Review HydroelectricCham AmirruddinNo ratings yet
- Reliance Paper On 29th March at New Delhi - 01Document8 pagesReliance Paper On 29th March at New Delhi - 01keyurp_60No ratings yet
- Impeller DesignDocument6 pagesImpeller Design19MECH052 SYED YOUNUS100% (1)
- Levelling Alignment: Levelling, Alignment and Centering of Suspended Type Vertical MachineDocument6 pagesLevelling Alignment: Levelling, Alignment and Centering of Suspended Type Vertical MachineSajid AkhterNo ratings yet
- Agitation and Mixing FlowDocument9 pagesAgitation and Mixing FlowSasitharan MNo ratings yet
- Piping Systems Srac 1994Document6 pagesPiping Systems Srac 1994maheshNo ratings yet
- Pump by BoseDocument26 pagesPump by BoseSonu SinghNo ratings yet
- 909design of High Efficiency Pelton Turbine For Micro-HydropowerDocument13 pages909design of High Efficiency Pelton Turbine For Micro-HydropowerrachidtuNo ratings yet
- Water Hammers PDI PDFDocument38 pagesWater Hammers PDI PDFkarthickNo ratings yet
- PV Array Design Worksheet Determine The Array Size For Your Grid-Connected System.Document6 pagesPV Array Design Worksheet Determine The Array Size For Your Grid-Connected System.موج البحرNo ratings yet
- Study of The Centrifugal Pump Efficiency at Throttling and Speed ControlDocument4 pagesStudy of The Centrifugal Pump Efficiency at Throttling and Speed ControlHassan SouleymanNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Machines LaboratoryDocument27 pagesHydraulic Machines LaboratoryAnonymous f1UCK4No ratings yet
- How VFD Speed Affects Centrifugal Pump HydraulicsDocument6 pagesHow VFD Speed Affects Centrifugal Pump HydraulicsAudrey Patrick KallaNo ratings yet
- Models For Analysis of Water Hammer in Piping With Entrapped Air - Chaiko - 2002 - PPL CorporationDocument11 pagesModels For Analysis of Water Hammer in Piping With Entrapped Air - Chaiko - 2002 - PPL CorporationElias TascaNo ratings yet
- IS 398 Part 2Document16 pagesIS 398 Part 2BharatNo ratings yet
- Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerDocument12 pagesShell and Tube Heat ExchangerZi ChingNo ratings yet
- Pelton Wheel Prac1Document15 pagesPelton Wheel Prac1siphyNo ratings yet
- Increasing The Profits & Production of Mature Fields Through Optimized Jet Pump Design & Operational ConsiderationsDocument9 pagesIncreasing The Profits & Production of Mature Fields Through Optimized Jet Pump Design & Operational ConsiderationsIndra BayuNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Part IIIDocument26 pagesDC Motor Part IIIMohd YasirNo ratings yet
- 2.heat-Exchangers From Ch6 - Mihir's HandbookDocument12 pages2.heat-Exchangers From Ch6 - Mihir's HandbookThế Quang LêNo ratings yet
- Design of Reactor 1Document13 pagesDesign of Reactor 1Nelykah Rianne MartijaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Equipment: Nuclear Training Course 23001 (NEIT 230.1)Document59 pagesMechanical Equipment: Nuclear Training Course 23001 (NEIT 230.1)abuhurairaqaziNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Compressor Design.Document2 pagesCentrifugal Compressor Design.Shoaib AliNo ratings yet
- Selecting An HVAC Pump at HttpsDocument3 pagesSelecting An HVAC Pump at Httpsalone160162lNo ratings yet
- 6 FluidizationDocument40 pages6 FluidizationTenson SichoneNo ratings yet
- Nrel PV String To 3-Phase Inverter With The Highest V CapabilitiesDocument38 pagesNrel PV String To 3-Phase Inverter With The Highest V CapabilitieshaniNo ratings yet
- 908design of High Efficiency Cross-Flow TurbineDocument4 pages908design of High Efficiency Cross-Flow TurbineAdi Setiadi100% (1)
- Fluid Flow AssignmentDocument7 pagesFluid Flow AssignmentPatrickNo ratings yet
- 9A01308 Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulic MachineryDocument4 pages9A01308 Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulic MachinerysivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A01402 Hydraulics and Hydraulic MachineryDocument4 pages9A01402 Hydraulics and Hydraulic MachinerysivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Ajay Kumar Garg Engineering College, Ghaziabad: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument3 pagesAjay Kumar Garg Engineering College, Ghaziabad: Department of Mechanical EngineeringMradul GuptaNo ratings yet
- FMHM Regular Jntu Question Papers 2008Document8 pagesFMHM Regular Jntu Question Papers 2008anjaneyulud100% (1)
- FM &HM Old PapersDocument4 pagesFM &HM Old Paperssai leenaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Machinery Systems Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesHydraulic Machinery Systems Exam QuestionswirelessandlessNo ratings yet
- FM Question Model 2Document8 pagesFM Question Model 2aadhanNo ratings yet
- MFHM Code No: 07A3EC02Document2 pagesMFHM Code No: 07A3EC02rafikhanpathanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery (Electrical and Electronics Engineering)Document7 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery (Electrical and Electronics Engineering)29viswa12No ratings yet
- Control Systems (CS) Notes As Per JntuaDocument203 pagesControl Systems (CS) Notes As Per Jntuasivabharathamurthy100% (3)
- SSC Telugu (FL) (AP)Document232 pagesSSC Telugu (FL) (AP)sivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- SSC Social Textbook (AP)Document100 pagesSSC Social Textbook (AP)sivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7312301 Transport Phenomena in BioprocessesDocument1 pageR7312301 Transport Phenomena in BioprocessessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7311205 Distributed DatabasesDocument1 pageR7311205 Distributed DatabasessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 07A4EC01 Environmental StudiesDocument1 page07A4EC01 Environmental StudiessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7410506 Mobile ComputingDocument1 pageR7410506 Mobile ComputingsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A05707 Software Project ManagementDocument4 pages9A05707 Software Project ManagementsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7410407 Operating SystemsDocument1 pageR7410407 Operating SystemssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R5410201 Neural Networks & Fuzzy LogicDocument1 pageR5410201 Neural Networks & Fuzzy LogicsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A13701 Robotics and AutomationDocument4 pages9A13701 Robotics and AutomationsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7311506 Operating SystemsDocument1 pageR7311506 Operating SystemssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7310106 Engineering GeologyDocument1 pageR7310106 Engineering GeologysivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7310506 Design & Analysis of AlgorithmsDocument1 pageR7310506 Design & Analysis of AlgorithmssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Code: R7311306: (Electronics & Control Engineering)Document1 pageCode: R7311306: (Electronics & Control Engineering)sivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A10505 Principles of CommunicationsDocument4 pages9A10505 Principles of CommunicationssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7311006 Process Control InstrumentationDocument1 pageR7311006 Process Control InstrumentationsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7310406 Digital CommunicationsDocument1 pageR7310406 Digital CommunicationssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A15502 Digital System DesignDocument4 pages9A15502 Digital System Designsivabharathamurthy100% (1)
- R7310206 Linear Systems AnalysisDocument1 pageR7310206 Linear Systems AnalysissivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R5310406 Digital CommunicationsDocument1 pageR5310406 Digital CommunicationssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7310306 Heat TransferDocument1 pageR7310306 Heat Transfersivabharathamurthy100% (1)
- R5310204 Power ElectronicsDocument1 pageR5310204 Power ElectronicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A14503 Principles of Machine DesignDocument8 pages9A14503 Principles of Machine DesignsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A23501 Heat Transfer in BioprocessesDocument4 pages9A23501 Heat Transfer in BioprocessessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A04504 Digital IC ApplicationsDocument4 pages9A04504 Digital IC ApplicationssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignDocument8 pages9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A03505 Heat TransferDocument4 pages9A03505 Heat TransfersivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A05505 Operating SystemsDocument4 pages9A05505 Operating SystemssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A02505 Electrical Machines-IIIDocument4 pages9A02505 Electrical Machines-IIIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Scour Protection at Bridge PiersDocument10 pagesScour Protection at Bridge PiersAlexDeLacRuzNo ratings yet
- Naval Hydrodynamics, Resistance & PropulsionDocument3 pagesNaval Hydrodynamics, Resistance & PropulsionDanevNo ratings yet
- 10 21 0030 - MPFDocument20 pages10 21 0030 - MPFdavid leeNo ratings yet
- 3 ArtificialliftsystemsDocument29 pages3 Artificialliftsystemsstephaniebritosuare2No ratings yet
- PIP PCEFL001 Flow Measurement GuidelinesDocument28 pagesPIP PCEFL001 Flow Measurement GuidelinesMax AdamsonNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Gas DynamicsDocument32 pagesFundamentals of Gas DynamicsRahul SuganaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Hydraulics 2Document5 pagesSyllabus Hydraulics 2acurvz2005No ratings yet
- Fluids 1 Toricelli ExperimentDocument7 pagesFluids 1 Toricelli ExperimentKiasha ChettyNo ratings yet
- Crosswind Action On Rail Vehicles: Wind Tunnel Experimental AnalysesDocument27 pagesCrosswind Action On Rail Vehicles: Wind Tunnel Experimental AnalysesDoicielNo ratings yet
- Flushing Hydraulic System (Rexroth)Document3 pagesFlushing Hydraulic System (Rexroth)Eric CNo ratings yet
- Group No.5 CFD in VD ReportDocument24 pagesGroup No.5 CFD in VD ReportAnonymous kDWBJdNo ratings yet
- CANNON Viscosity & Flash Point Standards BrochureDocument12 pagesCANNON Viscosity & Flash Point Standards BrochureLuis Xarlos GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics of Solar CarsDocument4 pagesAerodynamics of Solar CarsNeil WuNo ratings yet
- ORIFICE DISCHARGE EXPERIMENTDocument12 pagesORIFICE DISCHARGE EXPERIMENTgongweejieNo ratings yet
- Pyrolysis Gasoline Flowmeter SizingDocument4 pagesPyrolysis Gasoline Flowmeter SizingahmedNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Aerodynamics With SolvingDocument180 pagesFundamentals of Aerodynamics With SolvingaerorenNo ratings yet
- Lec 12Document15 pagesLec 12Muhammad SulemanNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument3 pagesFluid MechanicsHelloNo ratings yet
- Cengel Heat Transfer Errata SheetDocument2 pagesCengel Heat Transfer Errata SheetBharath VrNo ratings yet
- Dinamica de Fluido Sucker Rod PumpDocument26 pagesDinamica de Fluido Sucker Rod PumpyeralhNo ratings yet
- Removal of Air From Water Lines by Hydraulic Means (P.E. Wisner) (1975)Document16 pagesRemoval of Air From Water Lines by Hydraulic Means (P.E. Wisner) (1975)Alex0% (1)
- Ldo Storage Tank Calculation 170Document24 pagesLdo Storage Tank Calculation 170NARENDRA PATELNo ratings yet
- Em - 1110 2 1601 PDFDocument183 pagesEm - 1110 2 1601 PDFrgscribd61No ratings yet
- Sauer Danfoss PV PumpDocument11 pagesSauer Danfoss PV PumpCristian100% (2)
- WTC2019 SchoesserStraesserThewes Fullpaper REV01Document11 pagesWTC2019 SchoesserStraesserThewes Fullpaper REV01Federico MalteseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction TurbomachinesDocument9 pagesLecture 1 Introduction TurbomachinesYash KalaNo ratings yet
- 9.0 Stability of Floating BodiesDocument12 pages9.0 Stability of Floating BodiesAcharaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of fluid mechanicsDocument1 pageFundamentals of fluid mechanicsJASONNo ratings yet
- Automatic Recirculation ValveDocument4 pagesAutomatic Recirculation ValveHeri Fadli SinagaNo ratings yet
- ME8694 Hydraulics and PneumaticsDocument4 pagesME8694 Hydraulics and PneumaticsHarry HarryNo ratings yet