Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quantum 91
Uploaded by
NeoHoodaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quantum 91
Uploaded by
NeoHoodaCopyright:
Available Formats
76
SCATTERING
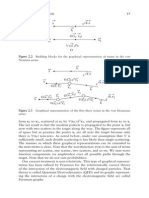
interesting results. To evaluate Equation (2.103) we must specify (k) and (k ), keeping in mind that they are perpendicular to the respective photon momenta k and k . We choose the z-axis along k, the direction of the incident photon. Therefore we choose 1 (k) along the x-axis and 2 (k) along the y-axis and obtain a right-handed triplet of unit vectors 1 (k), 2 (k), k/k . We characterize k in spherical coordinates as k = k (sin cos , sin sin , cos ). We choose 1 (k ) to be real and to be in the x, y-plane perpendicular to k . Thus 1 (k ) = (a, b, 0) with a and b to be determined such that a2 + b2 = 1. The requirement that 1 (k ) is perpendicular to k gives a sin cos + b sin sin = 0. These two relations between a and b give a = sin and b = cos or a = sin and b = cos . We choose the rst solution so 1 (k ) = (sin , cos , 0), independent of . We dene 2 (k ) to be real as well and given by 2 (k ) = (k / ) 1 (k ) where the order of the vectors in the cross product has been chosen such that we obtain a right-handed triplet of unit vectors 1 (k ), 2 (k ), k /k . We nd that 2 (k ) = (cos cos , cos sin , sin ). With these expressions for the polarization vectors we nd 1 (k) 1 (k ) = sin 1 (k) 2 (k ) = cos cos 2 (k) 1 (k ) = cos 2 (k) 2 (k ) = cos sin (2.104)
If we assume that the incident photon is unpolarized we must average over its two possible polarizations, that is sum over and divide by 2. If we assume that the polarization of the outgoing photon is not measured we must sum over its two possible polarizations, that is sum over . Note that we must calculate the sum of squared terms and not the square of the sum. We get 2 d 2 1 (k) (k ) = r2 e 2 d , =1
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 =1 2 re (sin + cos cos + cos + cos sin ) 2 2 = 1 2 re (1 + cos )
(2.105)
This result exhibits an interesting angular dependence of the cross section: it is maximum for = 0 or , that is, for outgoing photons along the incident photons direction or in the opposite direction. It is minimal at directions perpendicular to the incident photons direction. There is no dependence as expected because there is no direction dened transverse to the incident photons direction for unpolarized incident photons. The total cross section is obtained by integrating Equation (2.106) over = 8 2 r 3 e (2.106)
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Symmetries and Conservation LawsDocument1 pageSymmetries and Conservation LawsNeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- Quantum 85Document1 pageQuantum 85NeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- Quantum 100Document1 pageQuantum 100NeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- 3.2.1 Translations: 3.2 Continuous Symmetry OperatorsDocument1 page3.2.1 Translations: 3.2 Continuous Symmetry OperatorsNeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- Quantum 83Document1 pageQuantum 83NeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- ω d σ d m A A A I I A A E A I I ωDocument1 pageω d σ d m A A A I I A A E A I I ωNeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- Quantum 94Document1 pageQuantum 94NeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- Quantum 97Document1 pageQuantum 97NeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Symmetries and Conservation LawsDocument1 page3.1 Symmetries and Conservation LawsNeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- Quantum 88Document1 pageQuantum 88NeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- Quantum 92Document1 pageQuantum 92NeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- λ and dividing the result λ we chose the z-axis parallel to kDocument1 pageλ and dividing the result λ we chose the z-axis parallel to kNeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- Problems: a. Use the Born θ, φ) where θ, φ are the scatterDocument1 pageProblems: a. Use the Born θ, φ) where θ, φ are the scatterNeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- ω cancel I I d σ d m ω A A A I I E: Photon ScatteringDocument1 pageω cancel I I d σ d m ω A A A I I E: Photon ScatteringNeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- Quantum 87Document1 pageQuantum 87NeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- λt λ > 0. λ → 0. This procedure damps the rapid: Photon ScatteringDocument1 pageλt λ > 0. λ → 0. This procedure damps the rapid: Photon ScatteringNeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- λ a θ/2 1 for hard scattering can be /2 to get E E E a E E m α) Z αm E EDocument1 pageλ a θ/2 1 for hard scattering can be /2 to get E E E a E E m α) Z αm E ENeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- Quantum 81Document1 pageQuantum 81NeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- H e m e m: λ k λ ikx λ λ λDocument1 pageH e m e m: λ k λ ikx λ λ λNeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- ρ (r) normalized to 1; remember: ScatteringDocument1 pageρ (r) normalized to 1; remember: ScatteringNeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- Quantum 84Document1 pageQuantum 84NeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- xd p p: ε · k = 0 in the Coulomb gauge. When we useDocument1 pagexd p p: ε · k = 0 in the Coulomb gauge. When we useNeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- Quantum 76Document1 pageQuantum 76NeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- f (θ, φ) = π Ze d ρ: ScatteringDocument1 pagef (θ, φ) = π Ze d ρ: ScatteringNeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- 2.2.5 Electron-Atom Scattering: Born ApproximationDocument1 page2.2.5 Electron-Atom Scattering: Born ApproximationNeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- 2.2.4 Born Approximation: X X X X X X XDocument1 page2.2.4 Born Approximation: X X X X X X XNeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- Quantum 72Document1 pageQuantum 72NeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- 2.2.3 Solution of The SCHR Odinger Equation: Born ApproximationDocument1 page2.2.3 Solution of The SCHR Odinger Equation: Born ApproximationNeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- ψ (x π d G (x ψ (x ψ (x: ScatteringDocument1 pageψ (x π d G (x ψ (x ψ (x: ScatteringNeoHoodaNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Heat Exchanger Design CHE 311 Final Project MSUDocument15 pagesHeat Exchanger Design CHE 311 Final Project MSUnefoussiNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Flow in Plastic Injection MoldingDocument9 pagesOptimizing Flow in Plastic Injection MoldingThang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics ChapterDocument42 pagesThermodynamics ChapterBuild AteddyNo ratings yet
- 05 - Beams and FramesDocument10 pages05 - Beams and FramesOn Fan ChowNo ratings yet
- Leo Esaki - The Superlattice Story With The Esaki Tunnel DiodeDocument54 pagesLeo Esaki - The Superlattice Story With The Esaki Tunnel DiodeKonnasderNo ratings yet
- Analytical Methods For The Stress Concentration Analysis of Multilayered Anisotropic Composites With Pin-Loaded HolesDocument2 pagesAnalytical Methods For The Stress Concentration Analysis of Multilayered Anisotropic Composites With Pin-Loaded Holesredmod79No ratings yet
- Power Consumption and Mixing Time in an Agitated Vessel with Double ImpellerDocument6 pagesPower Consumption and Mixing Time in an Agitated Vessel with Double ImpellerJose Davi Rodrigues Silva UFCNo ratings yet
- Signals, Continuous Time and Discrete TimeDocument27 pagesSignals, Continuous Time and Discrete TimeSukanta ParidaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Transmission (Winter)Document20 pagesThermal Transmission (Winter)Robin Charles SamuelNo ratings yet
- Pump Calc ExampleDocument21 pagesPump Calc ExampleMohammad Usman HabibNo ratings yet
- Physics Internal AssessmentDocument14 pagesPhysics Internal AssessmentRachitNo ratings yet
- Inertia FormulasDocument4 pagesInertia FormulasLoysa Agtarap MataNo ratings yet
- Physical Pharmacy I States of MatterDocument24 pagesPhysical Pharmacy I States of MatterJayrine MonteroNo ratings yet
- Maglev Wind Mill ReportDocument24 pagesMaglev Wind Mill ReportBalu MahendarNo ratings yet
- Earth Spin Sun OrbitDocument4 pagesEarth Spin Sun Orbitmrshong5bNo ratings yet
- LTB Part2 F14 OptDocument15 pagesLTB Part2 F14 OptNejib GhazouaniNo ratings yet
- Motion in PlaneDocument1 pageMotion in Planerina85293No ratings yet
- Conductance ManualDocument12 pagesConductance ManualhannibalmrNo ratings yet
- PHY 504 - Advanced Mechanics Assignment 2: (Dated: August 28, 2020)Document2 pagesPHY 504 - Advanced Mechanics Assignment 2: (Dated: August 28, 2020)santosh thapaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions March2 For Cbse Class 7 Science Chapter 14Document6 pagesNcert Solutions March2 For Cbse Class 7 Science Chapter 14VimalaNo ratings yet
- SOLA2060 Introduction To Electronic Devices Semester 1, 2019Document43 pagesSOLA2060 Introduction To Electronic Devices Semester 1, 2019Marquee BrandNo ratings yet
- Introduction 2Document30 pagesIntroduction 2niteshNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Elctricity and Electronics Week 1Document10 pagesFundamentals of Elctricity and Electronics Week 1richie cuizonNo ratings yet
- On FACTSDocument33 pagesOn FACTSAravind Babu100% (1)
- Swing Angle CalculationDocument4 pagesSwing Angle CalculationRajas Alshi100% (1)
- Super Space or 1001 Lessons in SupersymmetryDocument568 pagesSuper Space or 1001 Lessons in SupersymmetryNelly MoralesNo ratings yet
- Mga Sagot Ni Ashe Montage (Gen. Physics)Document4 pagesMga Sagot Ni Ashe Montage (Gen. Physics)John Michael Cañero MaonNo ratings yet
- Midas Gen Structural Analysis (Basic)Document308 pagesMidas Gen Structural Analysis (Basic)Pornjad Pongmanee75% (4)
- Reheat Factor - Mollier DiiagramDocument40 pagesReheat Factor - Mollier DiiagramTanmay MajhiNo ratings yet