Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Important Statistics Formulas
Uploaded by
Rakesh YadavOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Important Statistics Formulas
Uploaded by
Rakesh YadavCopyright:
Available Formats
Important Statistics Formulas
This web page presents statistics formulas described in the Stat Trek tutorials. Each formula links to a web page that explains how to use the formula.
Parameters
Population mean = = ! "i # $ %
Population standard de&iation = ' = s(rt ) ! "i * #+ $ % ,
Population &ariance = '+ = ! "i * #+ $ %
-ariance of population proportion = 'P+ = P. $ n
Standardi/ed score = 0 = " * # $ '
Population correlation coefficient = 1 = ) 2 $ % , 3 ! 4 ) "i * "# $ 'x , 3 ) 5i * 5# $ '6 , 7
Statistics
8nless otherwise noted9 these formulas assume simple random sampling.
Sample mean = x = ! xi # $ n
Sample standard de&iation = s = s(rt ) ! xi * x #+ $ n * 2 # ,
Sample &ariance = s+ = ! xi * x #+ $ n * 2 #
-ariance of sample proportion = sp+ = p( $ n * 2#
Pooled sample proportion = p = p2 3 n2 : p+ 3 n+# $ n2 : n+#
Pooled sample standard de&iation = sp = s(rt ) n2 * 2# 3 s2+ : n+ * 2# 3 s++ , $ n2 : n+ * +# ,
Sample correlation coefficient = r = ) 2 $ n * 2# , 3 ! 4 ) x i * x# $ sx , 3 ) 6i * 6# $ s6 , 7
;orrelation
Pearson product*moment correlation = r = ! x6# $ s(rt ) ! x + # 3 ! 6+ # ,
<inear correlation sample data# = r = ) 2 $ n * 2# , 3 ! 4 ) x i * x# $ sx , 3 ) 6i * 6# $ s6 , 7
<inear correlation population data# = 1 = ) 2 $ % , 3 ! 4 ) " i * "# $ 'x , 3 ) 5i * 5# $ '6 , 7
Simple <inear =egression
Simple linear regression line> ? = b@ : b2x
=egression coefficient = b2 = ! ) xi * x# 6i * 6# , $ ! ) xi * x#+,
=egression slope intercept = b@ = 6 * b2 3 x
=egression coefficient = b2 = r 3 s6 $ sx#
Standard error of regression slope = sb2 = s(rt ) ! 6i * ?i#+ $ n * +# , $ s(rt ) ! xi * x#+ ,
;ounting
n factorial> nA = n 3 n*2# 3 n * +# 3 . . . 3 B 3 + 3 2. C6 con&ention9 @A = 2.
Permutations of n things9 taken r at a time> nPr = nA $ n * r#A
;ombinations of n things9 taken r at a time> n;r = nA $ rA n * r#A = nPr $ rA
Probabilit6
=ule of addition> P D C# = P D# : P C# * P D C#
=ule of multiplication> P D C# = P D# P CED#
=ule of subtraction> P DF# = 2 * P D#
=andom -ariables
In the following formulas9 X and Y are random &ariables9 and a and b are constants.
Expected &alue of " = E "# = x = ! ) xi 3 P xi# ,
-ariance of " = -ar "# = '+ = ! ) xi * E x# ,+ 3 P xi# = ! ) xi * x ,+ 3 P xi#
%ormal random &ariable = /*score = / = " * #$'
;hi*s(uare statistic = G+ = ) n * 2 # 3 s+ , $ '+
f statistic = f = ) s2+$'2+ , $ ) s++$'++ ,
Expected &alue of sum of random &ariables = E " : 5# = E "# : E 5#
Expected &alue of difference between random &ariables = E " * 5# = E "# * E 5#
-ariance of the sum of independent random &ariables = -ar " : 5# = -ar "# : -ar 5#
-ariance of the difference between independent random &ariables = -ar " * 5# = -ar "# : -ar 5#
Sampling Histributions
Iean of sampling distribution of the mean = x =
Iean of sampling distribution of the proportion = p = P
Standard de&iation of proportion = 'p = s(rt) P 3 2 * P#$n , = s(rt P. $ n #
Standard de&iation of the mean = 'x = '$s(rt n#
Standard de&iation of difference of sample means = 'd = s(rt) '2+ $ n2# : '++ $ n+# ,
Standard de&iation of difference of sample proportions = ' d = s(rt4 )P2 2 * P2# $ n2, : )P+ 2 * P+# $ n+, 7
Standard Error
Standard error of proportion = SEp = sp = s(rt) p 3 2 * p#$n , = s(rt p( $ n #
Standard error of difference for proportions = SE p = sp = s(rt4 p 3 2 * p # 3 ) 2$n2# : 2$n+# , 7
Standard error of the mean = SEx = sx = s$s(rt n#
Standard error of difference of sample means = SE d = sd = s(rt) s2+ $ n2# : s++ $ n+# ,
Standard error of difference of paired sample means = SE d = sd = 4 s(rt ) ! di * d#+ $ n * 2# , 7 $ s(rt n#
Pooled sample standard error = spooled = s(rt ) n2 * 2# 3 s2+ : n+ * 2# 3 s++ , $ n2 : n+ * +# ,
Standard error of difference of sample proportions = s d = s(rt4 )p2 2 * p2# $ n2, : )p+ 2 * p+# $ n+, 7
Hiscrete Probabilit6 Histributions
Cinomial formula> P " = x# = b xJ n, P# = n;x 3 Px 3 2 * P#n * x = n;x 3 Px 3 .n * x
Iean of binomial distribution = x = n 3 P
-ariance of binomial distribution = 'x+ = n 3 P 3 2 * P #
%egati&e Cinomial formula> P " = x# = b3 xJ r, P# =
x*2;r*2
3 Pr 3 2 * P#x * r
Iean of negati&e binomial distribution = x = r. $ P
-ariance of negati&e binomial distribution = 'x+ = r 3 . $ P+
Keometric formula> P " = x# = g xJ P# = P 3 .x * 2
Iean of geometric distribution = x = . $ P
-ariance of geometric distribution = 'x+ = . $ P+
L6pergeometric formula> P " = x# = h xJ N9 n9 k# = ) k;x , )
%*k;n*x
, $ ) % ;n ,
Iean of h6pergeometric distribution = x = n 3 k $ %
-ariance of h6pergeometric distribution = 'x+ = n 3 k 3 % * k # 3 % * n # $ ) %+ 3 % * 2 # ,
Poisson formula> P x; # = e*# x# $ xA
Iean of Poisson distribution = x =
-ariance of Poisson distribution = 'x+ =
Iultinomial formula> P = ) nA $ n2A 3 n+A 3 ... nkA # , 3 p2n2 3 p+n+ 3 . . . 3 pknk #
<inear Transformations
For the following formulas9 assume that 5 is a linear transformation of the random &ariable "9 defined b6 the e(uation> 5 = a" : b.
Iean of a linear transformation = E 5# = 5 = a" : b.
-ariance of a linear transformation = -ar 5# = a + 3 -ar "#.
Standardi/ed score = / = x * x# $ 'x.
t*score = t = x * x# $ ) s$s(rt n# ,.
Estimation
;onfidence inter&al> Sample statistic : ;ritical &alue 3 Standard error of statistic
Iargin of error = ;ritical &alue# 3 Standard de&iation of statistic#
Iargin of error = ;ritical &alue# 3 Standard error of statistic#
L6pothesis Testing
Standardi/ed test statistic = Statistic * Parameter# $ Standard de&iation of statistic#
Mne*sample /*test for proportions> /*score = / = p * P@# $ s(rt p 3 ( $ n #
Two*sample /*test for proportions> /*score = / = / = ) p 2 * p+# * d , $ SE
Mne*sample t*test for means> t*score = t = x * # $ SE
Two*sample t*test for means> t*score = t = ) x2 * x+# * d , $ SE
Iatched*sample t*test for means> t*score = t = ) x2 * x+# * H , $ SE = d * H# $ SE
;hi*s(uare test statistic = G+ = !) Mbser&ed * Expected#+ $ Expected ,
Hegrees of Freedom
The correct formula for degrees of freedom HF# depends on the situation the nature of the test statistic9 the number of samples9 underl6ing assumptions9 etc.#.
Mne*sample t*test> HF = n * 2
Two*sample t*test> HF = s2+$n2 : s++$n+#+ $ 4 ) s2+ $ n2#+ $ n2 * 2# , : ) s++ $ n+#+ $ n+ * 2# , 7
Two*sample t*test9 pooled standard error> HF = n2 : n+ * +
Simple linear regression9 test slope> HF = n * +
;hi*s(uare goodness of fit test> HF = k * 2
;hi*s(uare test for homogeneit6> HF = r * 2# 3 c * 2#
;hi*s(uare test for independence> HF = r * 2# 3 c * 2#
Sample Si/e
Celow9 the first two formulas find the smallest sample si/es re(uired to achie&e a fixed margin of error9 using simple random sampling. The third formula assigns sample to strata9 based on a proportionate design. The fourth formula9 %e6man allocation9 uses stratified sampling to minimi/e &ariance9 gi&en a fixed sample si/e. Dnd the last formula9 optimum allocation9 uses stratified sampling to minimi/e &ariance9 gi&en a fixed budget.
Iean simple random sampling#> n = 4 /+ 3 '+ 3 ) % $ % * 2# , 7 $ 4 IE+ : ) /+ 3 '+ $ % * 2# , 7
Proportion simple random sampling#> n = ) /+ 3 p 3 ( # : IE+ , $ ) IE+ : /+ 3 p 3 ( $ % ,
Proportionate stratified sampling> nh = %h $ % # 3 n
%e6man allocation stratified sampling#> nh = n 3 %h 3 'h # $ ) ! %i 3 'i # ,
Mptimum allocation stratified sampling#> nh = n 3 ) %h 3 'h # $ s(rt ch # , $ ) ! %i 3 'i # $ s(rt ci # ,
You might also like
- Introduction To Econometrics - Stock & Watson - CH 4 SlidesDocument84 pagesIntroduction To Econometrics - Stock & Watson - CH 4 SlidesAntonio Alvino100% (2)
- Nota Pendek MatematikDocument10 pagesNota Pendek Matematikzakry80No ratings yet
- Handout 6 (Chapter 6) : Point Estimation: Unbiased Estimator: A Point EstimatorDocument9 pagesHandout 6 (Chapter 6) : Point Estimation: Unbiased Estimator: A Point EstimatoradditionalpylozNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument5 pagesAnswer All Questions in This SectionSathia KdmsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document23 pagesChapter 9Avishka PriyanjanaNo ratings yet
- Information Technology: Cybersecurity: Program OverviewDocument1 pageInformation Technology: Cybersecurity: Program OverviewMicheal AkpanNo ratings yet
- Binomial Theorem 2012Document10 pagesBinomial Theorem 2012Razia KhanNo ratings yet
- Standard Form 1.1 Significant Figures (S.F) : A B Ab A B Ab A B Ab A A B BDocument4 pagesStandard Form 1.1 Significant Figures (S.F) : A B Ab A B Ab A B Ab A A B BZaweyah SulaimanNo ratings yet
- StringDocument3 pagesStringharriselNo ratings yet
- 06 SequencesDocument23 pages06 SequencesmeheheheNo ratings yet
- Tips Cemerlang Addmath SPMDocument105 pagesTips Cemerlang Addmath SPMZeZe ZeZeNo ratings yet
- Calculate Spearman's Rank Correlation CoefficientDocument4 pagesCalculate Spearman's Rank Correlation CoefficientAli SajjadNo ratings yet
- A.sqrt (X+y) B.pow (X, (Y+7) ) F.abs (X-Y) : Area Ss As Bs C S A B CDocument6 pagesA.sqrt (X+y) B.pow (X, (Y+7) ) F.abs (X-Y) : Area Ss As Bs C S A B CJhon Carlo PadillaNo ratings yet
- Coordinate GeometryDocument11 pagesCoordinate GeometryksganNo ratings yet
- Reference Textbooks: Networking Concepts ExplainedDocument54 pagesReference Textbooks: Networking Concepts ExplainedJay RathodNo ratings yet
- PRF192 Workshop 4Document16 pagesPRF192 Workshop 427-11 Lí - Mait xuân ThắngNo ratings yet
- 1'') 2&/3#-0#4!#") 25/6#7.-5' 89 7':# - ) /6,) - +3/&-# ?#@+/'-) 0&' Abc#d-'Document1 page1'') 2&/3#-0#4!#") 25/6#7.-5' 89 7':# - ) /6,) - +3/&-# ?#@+/'-) 0&' Abc#d-'MikeNo ratings yet
- ! "#$%&'& %# +#$,-. /0. 123$45%. MarkovDocument24 pages! "#$%&'& %# +#$,-. /0. 123$45%. MarkovΔέσποινα ΜιχάλογλουNo ratings yet
- Mathematical SymbolsDocument20 pagesMathematical SymbolsDo Minh NamNo ratings yet
- Design of Line, Circle & Ellipse AlgorithmsDocument21 pagesDesign of Line, Circle & Ellipse AlgorithmsAshish GuptaNo ratings yet
- D06A Prog Logice Devices (GALs)Document13 pagesD06A Prog Logice Devices (GALs)P_leeNo ratings yet
- Math Final 2010 Form2 PAPER 2Document8 pagesMath Final 2010 Form2 PAPER 2Liew Kok YeeNo ratings yet
- One-Way ANOVA Example From Introductory Notes: D E F 3 4 2 5 10 8 10 - Sum 18 14 10 N 3 2 2Document5 pagesOne-Way ANOVA Example From Introductory Notes: D E F 3 4 2 5 10 8 10 - Sum 18 14 10 N 3 2 2Rosendo BernabeNo ratings yet
- Panel 2Document26 pagesPanel 2tilfaniNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme June 2007 6665 Core Mathematics C3Document9 pagesMark Scheme June 2007 6665 Core Mathematics C3zainabpetalNo ratings yet
- SI for Managers - Probability, Distributions, Hypothesis TestingDocument4 pagesSI for Managers - Probability, Distributions, Hypothesis TestingZainab Abizer MerchantNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Laboratory Activity #1: Polynomials, Linear Algebraic Equations, and Partial Fraction ExpansionDocument14 pagesMATLAB Laboratory Activity #1: Polynomials, Linear Algebraic Equations, and Partial Fraction ExpansionEdiIkawNaNo ratings yet
- Coeb223 Formula Sheet For Final ExamDocument9 pagesCoeb223 Formula Sheet For Final ExamGautham Raavo PainaiduNo ratings yet
- Csec Mathematics Past Paper Solution - Jan 2008: Cxcdirect InstituteDocument12 pagesCsec Mathematics Past Paper Solution - Jan 2008: Cxcdirect Institutestyles_2980No ratings yet
- Matlab:: #$: ! Input:) 1: (Document13 pagesMatlab:: #$: ! Input:) 1: (Tupáč OoNo ratings yet
- Problemas Redes MalladasDocument19 pagesProblemas Redes MalladasPedroIgnacioGaeteValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- University SyllabusDocument129 pagesUniversity SyllabusHari NarayananNo ratings yet
- Cheat-Sheet - Boas Mathematical Methods in The Physical SciencesDocument4 pagesCheat-Sheet - Boas Mathematical Methods in The Physical Sciencesakkarbakkarbambepor67% (3)
- Algebra Logarithm and Exponential Functions TestDocument3 pagesAlgebra Logarithm and Exponential Functions TestRenee Edwards McKnightNo ratings yet
- Pointer in CDocument29 pagesPointer in CRutvik ShethNo ratings yet
- C' Questions: Visit - For More Downloads!Document56 pagesC' Questions: Visit - For More Downloads!Samarth DarganNo ratings yet
- PARABOLIC GRAPHS: SOLUTIONS FOR PROJECT WORK 2014Document10 pagesPARABOLIC GRAPHS: SOLUTIONS FOR PROJECT WORK 2014Ravendran MunianNo ratings yet
- LINEARDocument49 pagesLINEARTanapat LapanunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Numerical Descriptive Measures - LesssonDocument53 pagesChapter 3 Numerical Descriptive Measures - LesssonClarence Omalay-AgnesNo ratings yet
- Modul 3 Fungsi KuadratikDocument14 pagesModul 3 Fungsi Kuadratikadik5967No ratings yet
- Rangkuman Model Jaringan - Dicoding IndonesiaDocument9 pagesRangkuman Model Jaringan - Dicoding IndonesiaRizki MarchellNo ratings yet
- Science, Technology, and Engineering Program (STEP) : Iligan City National High SchoolDocument9 pagesScience, Technology, and Engineering Program (STEP) : Iligan City National High SchoolKate NamindangNo ratings yet
- Indices and Logarithms: V T y X XyDocument1 pageIndices and Logarithms: V T y X XySamion AwaldinNo ratings yet
- MIT6 0002F16 Lec7Document37 pagesMIT6 0002F16 Lec7scribd100% (1)
- Unit 4- Extensions - handinDocument13 pagesUnit 4- Extensions - handinAllisonNo ratings yet
- INTI Intl Un CollegeDocument2 pagesINTI Intl Un CollegejekannNo ratings yet
- F: X (X - P) (X - Q) .: (Total 4 Marks)Document18 pagesF: X (X - P) (X - Q) .: (Total 4 Marks)JacmNo ratings yet
- Discrete Random Variables: IntegralDocument7 pagesDiscrete Random Variables: IntegralKanchana RandallNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document24 pagesCH 4kishorkumarn8212No ratings yet
- 1 (A) Find The Capital of The Company. (B) Find The Profit of The Previous YearDocument13 pages1 (A) Find The Capital of The Company. (B) Find The Profit of The Previous YearjiashengroxNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Challenge ProblemsDocument5 pagesUnit 2 Challenge Problemsjc1264No ratings yet
- JUJ07 ModulDocument125 pagesJUJ07 Moduladib1606No ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document6 pagesAssignment 2soniamtech2014No ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Bangalore Institute of TechnologyDocument115 pagesAssignment 1: Bangalore Institute of TechnologyShantanu PrasharNo ratings yet
- 115 Cor UpdateDocument19 pages115 Cor Updateshantap5520No ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - Graphs P2 PDFDocument59 pagesLecture 12 - Graphs P2 PDFminhthang_hanuNo ratings yet
- Method One of Reading:-: Standard Costing - IDocument9 pagesMethod One of Reading:-: Standard Costing - IRana HaiderNo ratings yet
- Divided States: Strategic Divisions in EU-Russia RelationsFrom EverandDivided States: Strategic Divisions in EU-Russia RelationsNo ratings yet
- The Crystals of DestinyDocument3 pagesThe Crystals of DestinyRakesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Colours and CodesDocument5 pagesColours and CodesRakesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Transfer Text One Frame To Another Frame Text Area or Text Box or LableDocument8 pagesTransfer Text One Frame To Another Frame Text Area or Text Box or LableRakesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Working Capital Requirements Form Ii - Operating Statement Sanoj Kumar Potdar Amounts in Rs. LacsDocument34 pagesAssessment of Working Capital Requirements Form Ii - Operating Statement Sanoj Kumar Potdar Amounts in Rs. LacsRakesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Readme PDFDocument1 pageReadme PDFmicrounNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Working Capital Requirements Form Ii - Operating Statement Sanoj Kumar Potdar Amounts in Rs. LacsDocument34 pagesAssessment of Working Capital Requirements Form Ii - Operating Statement Sanoj Kumar Potdar Amounts in Rs. LacsRakesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Transfer Text One Frame To Another Frame Text Area or Text Box or Lable 05.05.20Document5 pagesTransfer Text One Frame To Another Frame Text Area or Text Box or Lable 05.05.20Rakesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Codig For Text AreaDocument2 pagesCodig For Text AreaRakesh YadavNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument1 pageReadmeTI IgsoftecNo ratings yet
- Equations of Motion by Graphical Method - PhysicsDocument3 pagesEquations of Motion by Graphical Method - PhysicsRakesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions - 2018120585816 PMDocument41 pagesPractice Questions - 2018120585816 PMRakesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Equations of Motion by Graphical Method - PhysicsDocument3 pagesEquations of Motion by Graphical Method - PhysicsRakesh YadavNo ratings yet
- TheoryDocument3 pagesTheoryRakesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Exer 9Document4 pagesExer 9Rakesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Probability Using Words: Exercise 3.1Document12 pagesProbability Using Words: Exercise 3.1Rakesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Probability Using Words: Exercise 3.1Document12 pagesProbability Using Words: Exercise 3.1Rakesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Probability Using Words: Exercise 3.1Document12 pagesProbability Using Words: Exercise 3.1Rakesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Thesis Hardware and SoftwareDocument4 pagesThesis Hardware and Softwaregbxm8h7g100% (1)
- Environmental Temperature Prediction Using A Data Analysis and Neural Networks Methodological ApproachDocument6 pagesEnvironmental Temperature Prediction Using A Data Analysis and Neural Networks Methodological ApproachEvaluaciones UTNNo ratings yet
- UPCAT 2019 ReviewerDocument4 pagesUPCAT 2019 ReviewerCarl William YabutNo ratings yet
- T-test AnalysisDocument6 pagesT-test AnalysisReno PhillipNo ratings yet
- Data AnalystDocument12 pagesData Analystsolomonjackson218No ratings yet
- Frequency Distribution, Cross-Tabulation, and Hypothesis TestingDocument17 pagesFrequency Distribution, Cross-Tabulation, and Hypothesis TestingMelissaNo ratings yet
- CPSP Dissertation Experience ProformaDocument5 pagesCPSP Dissertation Experience ProformaDoMyPaperForMoneyDesMoines100% (1)
- Table 8. Fisher-ADF Unit Root Tests: EroareDocument2 pagesTable 8. Fisher-ADF Unit Root Tests: EroareCorovei EmiliaNo ratings yet
- Bro ibaDAQ-x enDocument12 pagesBro ibaDAQ-x ennesxius IndonesiaNo ratings yet
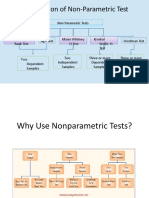
- Chapter 6 Non-Parametric and Robust TestDocument43 pagesChapter 6 Non-Parametric and Robust TestgirmaNo ratings yet
- University of The Punjab, LahoreDocument3 pagesUniversity of The Punjab, LahoreZerlishamaarNo ratings yet
- ASTM D2992-06 Standard Practice For Obtaining Hydrostatic Pressure Design Basis For Fiberglass Pipe & FittingsDocument11 pagesASTM D2992-06 Standard Practice For Obtaining Hydrostatic Pressure Design Basis For Fiberglass Pipe & FittingsKlich77No ratings yet
- Erbacher Vita 2010Document5 pagesErbacher Vita 2010HuntMNo ratings yet
- Patient AttendanceNo-Show PredictionDocument10 pagesPatient AttendanceNo-Show PredictionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Msds Iu GermanyDocument37 pagesMsds Iu GermanyShwetNo ratings yet
- What is Quantitative Research? Methods & ExamplesDocument30 pagesWhat is Quantitative Research? Methods & Examplesfrincess quezonNo ratings yet
- Document 3Document13 pagesDocument 3Drick BarcenasNo ratings yet
- Employee Motivation and Performance Appraisal in Textile IndustryDocument85 pagesEmployee Motivation and Performance Appraisal in Textile IndustryAkhil Anil Kumar75% (4)
- Marketing InsightsDocument44 pagesMarketing InsightsdanielsancaromeroNo ratings yet
- Summer Research Internship Flyer 2024Document2 pagesSummer Research Internship Flyer 2024Nicole Swenarton100% (1)
- Assessing Credit Management Practices at Commercial Bank of EthiopiaDocument36 pagesAssessing Credit Management Practices at Commercial Bank of Ethiopiapadm100% (6)
- Introduction To Geological Field MappingDocument152 pagesIntroduction To Geological Field MappingSrikanth JutruNo ratings yet
- Chap 012Document79 pagesChap 012Bruno MarinsNo ratings yet
- Multilinear RegressionDocument140 pagesMultilinear RegressiontemkimleangNo ratings yet
- Forecasting Techniques: Dr. C. Lightner Fayetteville State University 1Document46 pagesForecasting Techniques: Dr. C. Lightner Fayetteville State University 1Ali DandamunNo ratings yet
- FIN'22 Business Statistics Assignment QuestionsDocument3 pagesFIN'22 Business Statistics Assignment Questionsfaith olaNo ratings yet
- BRM - Marketing Research Project ToothpasteDocument81 pagesBRM - Marketing Research Project ToothpasteNishant KrNo ratings yet
- Topics in Time Series EconometricsDocument157 pagesTopics in Time Series EconometricsDrDeepti Ji67% (3)
- Leaflet Easy and Smart Control en PDFDocument12 pagesLeaflet Easy and Smart Control en PDFjad oussamaNo ratings yet
- Data Surfer Clastic RasioDocument8 pagesData Surfer Clastic RasioAmriansyahNo ratings yet