Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Compressed Air Safety
Uploaded by
gshdavidCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Compressed Air Safety
Uploaded by
gshdavidCopyright:
Available Formats
Compressed Air Safety GM-11-031-22
This is a Controlled Document that complies with CSBP Limited formatting and Quality Control guidelines. Please check that this is the latest available version before use. Title: Number: Owner: Authoriser: Version Details:
COMPRESSED AIR SAFETY GM-11-031-22
Steve Jones Mick McGrath Owner changed to Steve Jones. McGrath. Authoriser changed to Mick
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION ................................................................................................................................ 2 1. 2. GENERAL................................................................................................................................. 2 TOOLS, FITTINGS AND EQUIPMENT............................................................................... 2 NO PLANT AIR IS TO BE USED ON ANY PROCESS ASSOCIATED WITH ABRASIVE BLASTING OR INDUSTRIAL COATING (BREATHING, BLASTING OR PAINTING)................................ 2 3. 3.1 3.2 3.3 4. PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT (PPE) AND CLOTHING............................... 4 EYES ..................................................................................................................................... 4 HANDS ................................................................................................................................. 4 BODY.................................................................................................................................... 4 SAFE USE OF COMPRESSED AIR ...................................................................................... 4
Version No. 10.0 Document last modified: 16 May 2007. PDF Created: 30 July 2007.
Page 1 of 5
Compressed Air Safety GM-11-031-22
INTRODUCTION
This guide manual provides information on the safe use and protection of personnel when using compressed air.
1.
GENERAL
Compressed air is a powerful energy source, used throughout industry for various purposes. As an energy source it must be treated with the same respect as electricity, if it is not used correctly it can be fatal. Compressed air may be stored in cylinders and air receivers or generated by compressors. Air under pressure is delivered via a regulator, air line and air hose to air tools and equipment. The tool or equipment is driven by the energy contained in the compressed air.
2.
TOOLS, FITTINGS AND EQUIPMENT
WARNING
NO PLANT AIR IS TO BE USED ON ANY PROCESS ASSOCIATED WITH ABRASIVE BLASTING OR INDUSTRIAL COATING (BREATHING, BLASTING OR PAINTING) Observe the following precautions when using compressed air: Select equipment suitable for the pressure being used. Select air hoses according to Australian Standards 2554 - Hose and Hose Assemblies for Air. Ensure that air hoses and connectors are in good condition. Secure all fittings in the approved manner e.g. use safety clips in all snap coupling joints, attach chains to screw coupling. Before use check all couplings for damage that might prevent a connection or proper seal.
CAUTION
Do not use damaged or worn fittings and equipment. Ensure the trigger or operating valve works properly. If it is faulty, repairs shall be undertaken by a competent person before the equipment is used.
Version No. 10.0 Document last modified: 16 May 2007. PDF Created: 30 July 2007.
Page 2 of 5
Compressed Air Safety GM-11-031-22
Use an Out of Service Tag to tag out any faulty equipment. Report the fault to your team leader or the person responsible for the equipment to have it repaired. Before disconnecting tools, depressurise the airline by isolating at the main air supply valve and operating the connected tool until all the air is expelled. Always isolate the air supply at the main air valve when not in use, and depressurise airlines. Always drain water traps or reservoirs before using airlines or compressors. Never kink a hose to stop the air supply, close the valve. Air break (excess flow) valves should be considered for installation in main compressed air line supply to air hoses. If an air break valve has not been installed, secure the hose to prevent whipping in the event of failure. Airline outlets shall be positioned to prevent any person being exposed to a direct blast of air. Isolate and bleed all compressed air equipment before dismantling, Always point air guns away from the user and NEVER directly at anyone else. Never use compressed air to pressurise a vessel (unless the vessel is specifically designed for that purpose). For example, do not use compressed air to empty oil from gear boxes. They are not designed to withstand high internal pressures.
WARNING
ACCIDENTS HAVE HAPPENED IN WHICH PERSONNEL WERE KILLED BECAUSE GEAR BOXES EXPLODED UNDER PRESSURE. Do not dry bearings using compressed air.
CAUTION
There have been incidents where bearings have exploded because of the excessive speed of rotation caused by drying with compressed air. Compressed airlines shall be labelled in accordance with the AS 1345 - Identification of the Contents of Piping, Conduits and Ducts.
Version No. 10.0 Document last modified: 16 May 2007. PDF Created: 30 July 2007.
Page 3 of 5
Compressed Air Safety GM-11-031-22
3.
PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT (PPE) AND CLOTHING
Wearing appropriate personal protective equipment and clothing can reduce compressed air injuries.
3.1
EYES
Wear goggles when using compressed air. Wear a face shield where there is a risk of flying particles.
CAUTION
Safety glasses worn beneath a face shield do not provide adequate eye protection goggles must be worn.
3.2
HANDS
Wear gloves that the compressed air cannot penetrate, such as rubber or leather.
3.3
BODY
Use leather or PVC aprons where there is a risk of contact with compressed air.
CAUTION
Cotton clothing is not a barrier to compressed air.
4.
SAFE USE OF COMPRESSED AIR
WARNING
DO NOT PLAY PRACTICAL JOKES WITH COMPRESSED AIR - IT CAN BE FATAL. Observe the following precautions when using compressed air: Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment and clothing (refer to section 3 PPE and Clothing).
Version No. 10.0 Document last modified: 16 May 2007. PDF Created: 30 July 2007.
Page 4 of 5
Compressed Air Safety GM-11-031-22
Never use compressed air to dust off clothing. There is a risk of injury to eyes, perforation of the eardrums, and penetration of the skin, leading to bubbles in the blood stream and possible embolism, causing death. Do not use compressed air to clean up your work area. This can create airborne particles that will put you and others at risk of injury, Where it is considered that compressed air must be used to blow-down or clean hard to get at places etc, and it is impractical to use some other, safer, means such as vacuum cleaning, compressed air maybe used provided compressed outlet air pressure does not exceed 200 kPa and strict precautions are taken to protect the user and persons in the vicinity.
Note:
Do not try to stop a whipping hose. The force of the hose can break bones. Isolate the air at the main valve and wait for hose to settle. Do not create trip hazards with air hoses. Suspend or guard hoses with boards. Isolate and bleed all air lines and hoses before disconnecting. To disconnect air lines under pressure is hazardous. Use compressed air only for the work it is provided for. It is an energy source and must be treated as such.
Version No. 10.0 Document last modified: 16 May 2007. PDF Created: 30 July 2007.
Page 5 of 5
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- BS en Iso 3037 2013 (Ect)Document20 pagesBS en Iso 3037 2013 (Ect)rob100% (1)
- PAUT General Work ProceduresDocument16 pagesPAUT General Work Proceduresdiaccessltd_1717296188% (8)
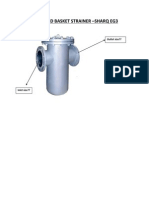
- Basket Strainer Intro PDFDocument4 pagesBasket Strainer Intro PDFgshdavidNo ratings yet
- Inspection and Testing of Piping Systems ES-14-602-02Document44 pagesInspection and Testing of Piping Systems ES-14-602-02Edmund MoraldeNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil Properties (Laboratory)Document15 pagesCrude Oil Properties (Laboratory)gshdavidNo ratings yet
- P&ID SymbolDocument18 pagesP&ID SymbolBagus Okti100% (1)
- Worksafe Bulletin: Safe Procedures For Vacuum Truck OperationsDocument2 pagesWorksafe Bulletin: Safe Procedures For Vacuum Truck OperationsgshdavidNo ratings yet
- Hot Tapping: Typical Hot Tap ApplicationDocument1 pageHot Tapping: Typical Hot Tap ApplicationgshdavidNo ratings yet
- 007 UTube CleaningDocument2 pages007 UTube CleaninggshdavidNo ratings yet
- Catalyst in Refining PetrochemicalsDocument5 pagesCatalyst in Refining PetrochemicalsgshdavidNo ratings yet
- Hot Tapping GuideDocument3 pagesHot Tapping GuidegshdavidNo ratings yet
- Code Pid PDFDocument6 pagesCode Pid PDFMejdi Sylas ToudjiNo ratings yet
- Hot Tap ProcedureDocument21 pagesHot Tap ProcedureImanuel Sitepu100% (1)
- Mesh Size EquivalentsDocument2 pagesMesh Size EquivalentsFrancisco Chavez ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Portable 8X8X10: Command ContainerDocument9 pagesPortable 8X8X10: Command ContainergshdavidNo ratings yet
- Proposed Basket StrainerDocument1 pageProposed Basket StrainergshdavidNo ratings yet
- Pages: 20-25 May, 2000: By: Bill RockwellDocument7 pagesPages: 20-25 May, 2000: By: Bill RockwellgshdavidNo ratings yet
- Tatoray ReacrorsDocument2 pagesTatoray ReacrorsgshdavidNo ratings yet
- Munters High Temp Psych ChartDocument2 pagesMunters High Temp Psych ChartaniruddhaskNo ratings yet
- Minimum Oil Circuit BreakerDocument4 pagesMinimum Oil Circuit BreakergshdavidNo ratings yet
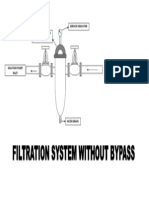
- Filtration System Without BypassDocument1 pageFiltration System Without BypassgshdavidNo ratings yet
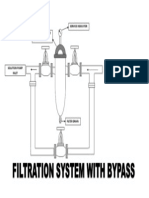
- Filtration System With BypassDocument1 pageFiltration System With BypassgshdavidNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Objective Type Questions Matls of ConstructionDocument14 pagesChemical Engineering Objective Type Questions Matls of ConstructiongshdavidNo ratings yet
- Pyrophoric Vessel HandlingDocument4 pagesPyrophoric Vessel HandlinggshdavidNo ratings yet
- BSC6910 Configuration Principle (Global) (V100R017C10 07) (PDF) - EN PDFDocument111 pagesBSC6910 Configuration Principle (Global) (V100R017C10 07) (PDF) - EN PDFMayra GarrettNo ratings yet
- Ups PDFDocument14 pagesUps PDFMiguelNo ratings yet
- Networking Course Week 1 RepsonsesDocument2 pagesNetworking Course Week 1 RepsonsesAndreThomasNo ratings yet
- MEC LPG Tank Valve GuideDocument12 pagesMEC LPG Tank Valve GuideSandro Aparecido CrianoNo ratings yet
- Knoop - Vicker 1202 WilsonHardnessREV3Document2 pagesKnoop - Vicker 1202 WilsonHardnessREV3Khoa Bui AnhNo ratings yet
- T4wilden Pump SpecDocument34 pagesT4wilden Pump SpecjsprtanNo ratings yet
- FLP Temperature IndicatorDocument2 pagesFLP Temperature IndicatorNiranjan BeheraNo ratings yet
- Brochure - Thermalia (R) Dual (55-140) Dual H (35-90) - ExA - 111016Document28 pagesBrochure - Thermalia (R) Dual (55-140) Dual H (35-90) - ExA - 111016Nur Rachman HardiantoNo ratings yet
- Create An SSH Tunnel For MySQL Remote AccessDocument4 pagesCreate An SSH Tunnel For MySQL Remote Accessleonard1971No ratings yet
- Openvswitch - Brezular's Technical BlogDocument48 pagesOpenvswitch - Brezular's Technical BlogbrandonNo ratings yet
- Acp CTPT AnaylserDocument18 pagesAcp CTPT AnaylserMusembiNo ratings yet
- SDADocument1 pageSDAFrans van der MerweNo ratings yet
- Fire Extinguisher OpsDocument51 pagesFire Extinguisher Opsdsn_sarmaNo ratings yet
- Gift From ElonDocument8 pagesGift From ElonAnonymous uPeo5Y0tNo ratings yet
- Tempconversion PDFDocument6 pagesTempconversion PDFPravat TiadiNo ratings yet
- Windows Server 2012R2 - PowerShellDocument35 pagesWindows Server 2012R2 - PowerShellTuấn BéoNo ratings yet
- 7 Steps To Calculate Measurement Uncertainty - IsobudgetsDocument17 pages7 Steps To Calculate Measurement Uncertainty - IsobudgetsJGlobex100% (1)
- Msds Aluminium FoilDocument7 pagesMsds Aluminium FoillatifahNo ratings yet
- IPA 48S User Manual V1.1Document50 pagesIPA 48S User Manual V1.1ivoroNo ratings yet
- Async Multistep Policy DatapowerDocument19 pagesAsync Multistep Policy DatapowerChinna VadyalamNo ratings yet
- Legend & Symbols: General Notes:: Vicinity MapDocument1 pageLegend & Symbols: General Notes:: Vicinity MapFranz AryanNo ratings yet
- Inter VXLAN RoutingDocument2 pagesInter VXLAN Routingsaqr8000No ratings yet
- Terasaki MV BreakersDocument20 pagesTerasaki MV BreakersnicholasleeNo ratings yet
- FLM 420 RLV1Document4 pagesFLM 420 RLV1Muhammad Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Binary SMSSFSFSDFSDFSDFSFSDFSDFSFSDFSDDocument4 pagesBinary SMSSFSFSDFSDFSDFSFSDFSDFSFSDFSDArun BabuNo ratings yet
- Dana Spicer DiffsDocument70 pagesDana Spicer DiffsPlymptonite100% (2)
- M700 M701 Unidrive Manual PDFDocument48 pagesM700 M701 Unidrive Manual PDFmecatronico87100% (1)
- BRC Packaging Document KitDocument8 pagesBRC Packaging Document KitRiky Hadi WibawaNo ratings yet