Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hotspot Worksheet
Uploaded by
Andres BereznevOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hotspot Worksheet
Uploaded by
Andres BereznevCopyright:
Available Formats
Year 11 Pre-Diploma Biology
BIODIVERSITY HOTSPOTS
We tried to define biodiversity write down here what you now understand by the word BIODIVERSITY. Biological diversity is the variety and variability among the organisms and ecology. t divides into community diversity! species diversity! and genetic diversity. "enetic diversity is about genetic differences in two populations of the same species. #pecies diversity is about the amount of different species in a fi$ed area. %omunity diversity is about different ecosystems and habitats.
&round the world are various biodiversity '()*#P)*#+. What do you understand by this term! 'hotspot, A biodiversity hotspot is a biogeographic region with a significant reservoir of biodiversity that is under threat from humans.
-ist some of the more famous biodiversity hotspots! and beside each! very briefly say what ma.es it a hotspot or why it is determined or conserved as a hotspot. 1. MADAGASCAR & THE INDIAN OCEAN ISLANDS Eight plant families, four bird families, and five primate families that live nowhere else on Earth. 2. GUINEAN FORESTS OF WEST AFRICA
The lowland forests of West Africa are home to more than a quarter of Africa's mammals, including more than 20 species of primates. ogging is endangering this ecosystem.
3. CAUCASUS
The deserts, savannas, arid woodlands, and forests that comprise the !aucasus hotspot contain a large number of endemic plant species.
4. HIMALAYA
The hotspot is home to important populations of numerous large birds and mammals, including vultures, tigers, elephants, rhinos and wild water buffalo.
5. JAPAN
About a quarter of the vertebrate species occurring in this hotspot are endemic, including the !ritically "ndangered #$inawa woodpec$er and the %apanese macaque, the famous &snow mon$eys' that are the most northerly(living non(human primates in the world.
6. MEDITERRANEAN BASIN
The flora of the )editerranean *asin is dramatic. +ts 22,,00 endemic vascular plant species are more than four times the number found in all the rest of "urope- the hotspot also supports many endemic reptile species.
7. CARIBBEAN ISLANDS
The !aribbean +slands support e.ceptionally diverse ecosystems, ranging from montane cloud forests to cactus scrublands, which have been devastated by deforestation and encroachment
. MADREAN PINE!OA" WOODLANDS
A quarter of all )e.ico's plant species are found here, many of them found nowhere else on "arth.
#. ATLANTIC FOREST
The Atlantic /orest of tropical 0outh America boasts 20,000 plant species, 10 percent of which are endemic. 2et, less than 30 percent of the forest remains.
1$. TROPICAL ANDES
#ne of the richest and most diverse regions on "arth, about ,4 of all vascular plant species are endemic to the Tropical Andes region.
/ow go to www.biodiversityhotspots.org. (ere you will find some useful definitions and some 0uite detailed descriptions of the world+s hotspots. #elect any one of the hotspots from the drop-down menu and ma.e a written summary1
WALLACEA
This hotspot is located in the Islands of Indonesia. The Flora and Fauna there is so varied that protected areas are needed to conserve it. Wallacea has bird endemism which is only in 2 hotspots in the Tropical Andes. It also has the komodo dragon which is the largest lizard in the world. ther important species present are flowers! "adar and #inca. Alfred 5ussel Wallace, An "nglish e.plorer,
discovered in the 36th century the importance of Wallacea7s /lora and /auna. Wallacea is conserved by the +ndonesian government.
$ohn sborne 2ebruary 3415
You might also like
- Hotspot Worksheet.Document2 pagesHotspot Worksheet.Maria Caridad GarzonNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and ConservationDocument7 pagesBiodiversity and ConservationAnshul VermaNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity HotspotsDocument6 pagesBiodiversity Hotspotsok cheemsNo ratings yet
- Hotspot WorksheetDocument2 pagesHotspot WorksheetMartín EcheverriaNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument8 pagesBiodiversityapi-423260675No ratings yet
- 25 Hot SpotsDocument3 pages25 Hot Spotsx5trawb3rriNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity 1Document22 pagesBiodiversity 1Krish BagNo ratings yet
- Evs Assignment-Biodiversity: NAME: G - SURYA TEJA REG - NO. 11199D014 B.E. MechanicalDocument11 pagesEvs Assignment-Biodiversity: NAME: G - SURYA TEJA REG - NO. 11199D014 B.E. MechanicalnNo ratings yet
- Hotspot WorksheetDocument3 pagesHotspot Worksheetali7167No ratings yet
- Peruvian Amazonia and Its BiodiversityDocument13 pagesPeruvian Amazonia and Its BiodiversityGerard PalaciosNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument5 pagesBiodiversityArgha senguptaNo ratings yet
- BIODIVERSITY AND CONSERVATION NewDocument6 pagesBIODIVERSITY AND CONSERVATION Newkanishk17295No ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument3 pagesBiodiversityshodhan shettyNo ratings yet
- 36 Recognized Biodiversity HotspotsDocument5 pages36 Recognized Biodiversity HotspotsSachin ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- A Catalogue For Endemic Birds of Ethiopia: January 2016Document26 pagesA Catalogue For Endemic Birds of Ethiopia: January 2016Alexis CrossNo ratings yet
- Definition of SpeciesDocument35 pagesDefinition of Speciesmastermind20130% (1)
- Biodiversity HotspotsDocument11 pagesBiodiversity HotspotsChaitrali ChawareNo ratings yet
- Indonesia S Forests: What Is at Stake?: 1.1 100 Million Hectares of Tropical ForestDocument6 pagesIndonesia S Forests: What Is at Stake?: 1.1 100 Million Hectares of Tropical ForestNahrowi Al MahardikaNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument12 pagesBiodiversityThanushree.SNo ratings yet
- SBIO - Introduction To BiodiversityDocument66 pagesSBIO - Introduction To BiodiversitymmballesterosNo ratings yet
- CONSERVATION of Floura and FaunnaDocument21 pagesCONSERVATION of Floura and FaunnaAnonymous D5g37JjpGBNo ratings yet
- Atlantic Forest - Brazil, Paraguay, Argentina, UruguayDocument6 pagesAtlantic Forest - Brazil, Paraguay, Argentina, Uruguaythe Kong of theNo ratings yet
- Hotspot Biodiversity WorksheetDocument2 pagesHotspot Biodiversity WorksheetCarlos Andres Andrade100% (1)
- Biodiversity at Global LevelDocument23 pagesBiodiversity at Global LevelShantanu Sharma67% (3)
- Flora Fauna Biodiversity Conservation of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesFlora Fauna Biodiversity Conservation of The PhilippinesBhea Lyn SomblingoNo ratings yet
- Hiba Firoos Roll No.13. S4 B BatchDocument11 pagesHiba Firoos Roll No.13. S4 B BatchHiba 111No ratings yet
- BIODIVERSITY: Understanding Species, Ecosystems & Genetic DiversityDocument27 pagesBIODIVERSITY: Understanding Species, Ecosystems & Genetic DiversityJemimah Anne Santos FerrerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Biodiversity and ConservationDocument31 pagesChapter 15 Biodiversity and ConservationGillu SinghNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and ConservationDocument2 pagesBiodiversity and Conservationsrk.abhinandhanNo ratings yet
- C3 - Biodiversity at The Species LevelDocument27 pagesC3 - Biodiversity at The Species LevelShawn BlueNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Investigatory ProjectDocument18 pagesBiodiversity Investigatory Projectpiu77% (52)
- Yz ThineDocument19 pagesYz ThineMhel ChieeNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity:: Biodiversity, A Contraction of "Biological Diversity," Generally Refers To TheDocument6 pagesBiodiversity:: Biodiversity, A Contraction of "Biological Diversity," Generally Refers To ThePrajwala GmathNo ratings yet
- L-4 Indian Flora and FaunaDocument9 pagesL-4 Indian Flora and FaunaKhushi KotwaniNo ratings yet
- The Biodiversity and The Ecosystem 4TH FEMS 5Document4 pagesThe Biodiversity and The Ecosystem 4TH FEMS 5mark.mendozaNo ratings yet
- IE2 Course Pack: Essential Reading MaterialDocument15 pagesIE2 Course Pack: Essential Reading MaterialKim Hoang TaNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity HotspotsDocument2 pagesBiodiversity HotspotsTommy MorteboyNo ratings yet
- Notes - On Environment ScienceDocument8 pagesNotes - On Environment Sciencegaurdian12574No ratings yet
- Two New Species Discovered, Bolster Case For Philippine ConservationDocument47 pagesTwo New Species Discovered, Bolster Case For Philippine Conservationallanlopez_2009No ratings yet
- Biodiversityconservation 140413102641 Phpapp02Document37 pagesBiodiversityconservation 140413102641 Phpapp02Anita Arora100% (1)
- Biodiversity and Its ConservationDocument23 pagesBiodiversity and Its ConservationAkanksha BarnawalNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument21 pagesIntroductionsachinagsNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument17 pagesBiodiversityswainananta336No ratings yet
- EVSDocument28 pagesEVSH8000100% (1)
- BiodiversityDocument19 pagesBiodiversityGill0% (1)
- _Biodiversity -1 (1)Document73 pages_Biodiversity -1 (1)aakaankshaagupta20No ratings yet
- Libro RaddaDocument162 pagesLibro RaddaPablo MirandaNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Its ConservationDocument7 pagesBiodiversity and Its ConservationPaul KirubainathanNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian Wetlands & Bird BiodiversityDocument6 pagesEthiopian Wetlands & Bird BiodiversityYilma Dellelegn AbebeNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Book English PDFDocument90 pagesBiodiversity Book English PDFsarora_usNo ratings yet
- Collage EcuadorDocument5 pagesCollage EcuadorGaby MaizaNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument8 pagesBiodiversityCLASH OF DARKNo ratings yet
- EBS 42L - Lesson 1 - 2019-2020Document99 pagesEBS 42L - Lesson 1 - 2019-2020Chel SyNo ratings yet
- Project Report For Environmental Studies PaperDocument6 pagesProject Report For Environmental Studies PaperNuman KabirNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity NotesDocument6 pagesBiodiversity Notesraushankumar05072No ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Conservation: Ms. Jannet Broas Ms. Celeste Desingaño Ms. Gladys Guirre Ms. Jenalyn SampangDocument55 pagesBiodiversity and Conservation: Ms. Jannet Broas Ms. Celeste Desingaño Ms. Gladys Guirre Ms. Jenalyn SampangKaye SolanoyNo ratings yet
- Going, Going, Gone: 100 animals and plants on the verge of extinctionFrom EverandGoing, Going, Gone: 100 animals and plants on the verge of extinctionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Wildlife Conservation As Done By Experts - Animal Book Age 10 | Children's Animal BooksFrom EverandWildlife Conservation As Done By Experts - Animal Book Age 10 | Children's Animal BooksNo ratings yet
- Copa Savanna! Is There Such a Word? Earth Science Book Grade 3 | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandCopa Savanna! Is There Such a Word? Earth Science Book Grade 3 | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Planning Q1: Which Activities Do You Plan To Participate in This Quimester?Document3 pagesPlanning Q1: Which Activities Do You Plan To Participate in This Quimester?Andres BereznevNo ratings yet
- Self-Review and Personal GoalsDocument4 pagesSelf-Review and Personal GoalsAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
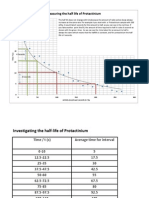
- Andres Bereznev Half Life of ProtactiniumDocument6 pagesAndres Bereznev Half Life of ProtactiniumAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- Biological HierarchyDocument2 pagesBiological HierarchyAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- BinomialDocument16 pagesBinomialGuille PazNo ratings yet
- Prediction TestingDocument2 pagesPrediction TestingAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- Interspecific RelationshipsDocument4 pagesInterspecific RelationshipsAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- Andrés Nichrome Investigation CorrectedDocument14 pagesAndrés Nichrome Investigation CorrectedAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- Geography Essay FinishedDocument7 pagesGeography Essay FinishedAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- Factors Andres BereznevDocument4 pagesFactors Andres BereznevAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- Genetics Harry PotterDocument29 pagesGenetics Harry PotterGuille PazNo ratings yet
- The King CobraDocument2 pagesThe King CobraAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- Analysing StatisticsDocument13 pagesAnalysing StatisticsAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- Classification TimelineDocument1 pageClassification TimelineAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- Dichotomous KeyDocument3 pagesDichotomous KeyAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- Sources Table FinishedDocument3 pagesSources Table FinishedDevon BassNo ratings yet
- Effects of ICT On Society: Computer Usage Within Businesses Has Increased Massively Over The Last 30 YearsDocument4 pagesEffects of ICT On Society: Computer Usage Within Businesses Has Increased Massively Over The Last 30 YearsAndres Bereznev100% (1)
- Animalfamiliescharacteristics TommyJoseAndresDocument5 pagesAnimalfamiliescharacteristics TommyJoseAndresAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- Andres PPT PhotoshopDocument2 pagesAndres PPT PhotoshopAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- Hybridisation QuestionsDocument2 pagesHybridisation QuestionsAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- Andres Research EssayDocument29 pagesAndres Research EssayAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- Effects of ICT On Society Andres CarlosDocument8 pagesEffects of ICT On Society Andres CarlosAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- Burger DeforestationDocument9 pagesBurger DeforestationAndres Bereznev100% (2)
- Working With Adobe PhotoshopDocument1 pageWorking With Adobe PhotoshopAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- Dotty Squares Investigation AndresDocument4 pagesDotty Squares Investigation AndresAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- Sources Table FinishedDocument3 pagesSources Table FinishedDevon BassNo ratings yet
- Surrealist Collage Project ReviewDocument1 pageSurrealist Collage Project ReviewAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- UNMIK Management Finished GroupDocument6 pagesUNMIK Management Finished GroupAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- UNMIK Management Finished GroupDocument6 pagesUNMIK Management Finished GroupAndres BereznevNo ratings yet
- 2nd Grading Science ReviewerDocument10 pages2nd Grading Science ReviewerEn CyNo ratings yet
- enviroWORKS Vol 1 07 Feb 2007 1332007131850 465Document32 pagesenviroWORKS Vol 1 07 Feb 2007 1332007131850 465winstonNo ratings yet
- Science Notes Year 6Document7 pagesScience Notes Year 6esther1phanNo ratings yet
- National Geographic IELTS BOOK WRITING MATERIALDocument14 pagesNational Geographic IELTS BOOK WRITING MATERIALharshit4421No ratings yet
- Effects of Climate Change What Does It Mean? How Is This Caused by Climate Change? What Are The Consequences?Document3 pagesEffects of Climate Change What Does It Mean? How Is This Caused by Climate Change? What Are The Consequences?Reymark Alciso EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Musakhel BalochistanDocument51 pagesMusakhel BalochistanMohammad Yahya Musakhel100% (3)
- Ippkh and PPTKHDocument24 pagesIppkh and PPTKHBudsNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Evil QuartetDocument5 pagesBiodiversity Evil QuartetMohd Amirul Firdhaus Mohd RidhwanNo ratings yet
- PassifloraDocument23 pagesPassifloraFernandoNo ratings yet
- Stream and Riparian Ecology: Chapter 3Document20 pagesStream and Riparian Ecology: Chapter 3Dragana SekulicNo ratings yet
- Evolution and Biodiversity: Species Diversity, Genetic Variation, and Natural SelectionDocument22 pagesEvolution and Biodiversity: Species Diversity, Genetic Variation, and Natural SelectionJonnel VillasordaNo ratings yet
- Wilderness in A NutshellDocument2 pagesWilderness in A NutshellCraig GlatthaarNo ratings yet
- Villaflor, Jesus Jr. O 2019-30506Document5 pagesVillaflor, Jesus Jr. O 2019-30506Jesus Villaflor Jr.No ratings yet
- REACTION PAPER Tree PlantingDocument11 pagesREACTION PAPER Tree PlantingErrol TortolaNo ratings yet
- Simcz Write-UpDocument10 pagesSimcz Write-Upapi-529788294No ratings yet
- Consequences of Deforestation and Climate Change On BiodiversityDocument27 pagesConsequences of Deforestation and Climate Change On Biodiversitydokifi6985nonicamy.comNo ratings yet
- Simpson's Diversity Index ExplainedDocument5 pagesSimpson's Diversity Index ExplainedGISSANo ratings yet
- Ang Huling Gubat Sa MaynilaDocument3 pagesAng Huling Gubat Sa MaynilaRay John Mark Alcovendas67% (3)
- 2010 Annual Report Yellowstone River Conservation District CouncilDocument23 pages2010 Annual Report Yellowstone River Conservation District CouncilYellowstone River Conservation District CouncilNo ratings yet
- Coed Cymerau Isaf - Cattle GrazingDocument2 pagesCoed Cymerau Isaf - Cattle GrazingwoodlandtrustNo ratings yet
- Wild Animals 12Document2 pagesWild Animals 12anonimas anoninaminaviciusNo ratings yet
- Medicinal and Aromatic Plants, in SE EuropeDocument201 pagesMedicinal and Aromatic Plants, in SE EuropeOana Sidor100% (1)
- Crisis in Culture and Livelihood of The Zay: An Islander Community of Lake Zeway Islands, EthiopiaDocument72 pagesCrisis in Culture and Livelihood of The Zay: An Islander Community of Lake Zeway Islands, EthiopiadoffanazNo ratings yet
- 52 National Annual Science Conference MAVIPA - ScheduleDocument4 pages52 National Annual Science Conference MAVIPA - ScheduleVasundhara SindhudurgNo ratings yet
- Endemic Orchids of Western Ghats PDFDocument190 pagesEndemic Orchids of Western Ghats PDFSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Chapter Summarizes Key Concepts Like Genetic, Species & Ecosystem DiversityDocument25 pagesBiodiversity Chapter Summarizes Key Concepts Like Genetic, Species & Ecosystem DiversitysushmitaNo ratings yet
- Departmental Schedule 2nd Semester 2018-2019Document76 pagesDepartmental Schedule 2nd Semester 2018-2019visayasstateuNo ratings yet
- Biology Coursework STPM 2020 Experiment 16 Title: Ecological Study of A Terrestrial Habitat ObjectiveDocument8 pagesBiology Coursework STPM 2020 Experiment 16 Title: Ecological Study of A Terrestrial Habitat ObjectiveEcikkNo ratings yet
- Mangroves Forests in PakistanDocument18 pagesMangroves Forests in PakistanaquayeeNo ratings yet
- National Integrated Protected Areas System Act of 1992Document25 pagesNational Integrated Protected Areas System Act of 1992Danny Castillo100% (1)