Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Improvisational Methods of Music Therapy Definitions 5-19
Uploaded by
Diana FoxCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Improvisational Methods of Music Therapy Definitions 5-19
Uploaded by
Diana FoxCopyright:
Available Formats
Diana Fox MUS 525
Improvisational Methods of Music Therapy
September 17, 2013 Fall 2013
Definitions pp. 5-19
Things I Need To Know: Music therapy is a goal directed process in which the therapist helps the client to improve, maintain, or restore a state of well-being Therapist helps the client through assessment, treatment, and evaluation Main musical experiences are improvising, performing, composing, notating, verbalizing, and listening to music Important to know which models are appropriate for which population Improvisational music therapy can be used with individuals on various levels of development and functioning Each model should be analyzed to determine whether it engages the client in anything that may cause discomfort to him/her Therapist must collect necessary client information before considering any model Three levels of goals: o General o Population Specific o Individual Improve goals usually address (see rest of page 7-8) Salient features of each model usually refer to the originators purpose and rationale for using music, and the way the s/he uses improvisation in particular Goals of Improv: o Educational: Help the client acquire knowledge or skills in music or another related discipline o Recreational: Improving clients leisure time o Therapeutic: Help client gain insight about him/herself, work through feelings, problems, symptoms, make basic changes in personality, develop more effective areas of adaptation ***Goals Overlap*** Improvisational music therapy is provided in individual, dyadic, family, or group settings. Some models use settings exclusively In improvisational musical therapy, the main method of assessment is to engage the client in improvisation Session preparation needs to be spontaneous yet planned o Inquire about the emotional and/or physical state of the client o Prepare physical environment (lights, acoustics, furniture arrangement) Procedure is not a single operation aimed at elicitating an immediate response Methodological objectives deals with engaging the client in a particular aspect of the therapeutic process Technique are aimed at eliciting an immediate response Every model of therapy has its own techniques Ideas That Resonate With Me:
Diana Fox MUS 525
September 17, 2013 Fall 2013
Goals must describe the overall direction of the therapists efforts and the desired outcome of those efforts with respect to the client Goals can be established at the beginning of therapy or as they emerge during the therapy process Theoretical orientation has a profound effect on goals, procedures for assessment and evaluation, the dynamics of intervention, and the process of course treatments Therapist Qualifications When placing a client in a group, it is important to consider his/her readiness for the interpersonal experiences that will take place, and the many different demands that group participation will take Models of improvisational therapy differ in what modalities and media are used most often, and in which musical media are used by the client, therapist, and other participants in the sessions During assessment the improvisational therapist is also interested in discovering what makes the client respond a certain way and what can lead the client to respond in a different way Primary dynamic elements are the client, therapist, musical instruments, and the improvised music itself. Ideas I dont Understand/Questions: Music in therapy/Music as therapy o As therapy: Music is the primary stimulus for change o In therapy: Music is not the primary therapeutic agent o Is there a right or wrong way? How can evaluation and assessment be the same thing? Why do other clients, significant others, and any other stimuli or objects used as part as the therapy process only become dynamic forces when then they impinge or are acted upon by the client? Things I Disagree With: In regard to the type of musical improvisation (p. 10) who distinguishes the type of improvisation? This paragraph almost seems like the therapist interpretation of his/her clients improvisation. Does everything that happens in improvisational sessions need to have a label? In regard to evaluation, I do not think that assessment and evaluation is ever the same thing. Assessment is when a therapist collects and analyzes information about a client and plans initial goals and a treatment program. Evaluation measures and determines a clients progress.
You might also like
- Simply Learn Hebrew! How To Lea - Gary Thaller PDFDocument472 pagesSimply Learn Hebrew! How To Lea - Gary Thaller PDFsuper_gir95% (22)
- Thaut MH Hoemberg V Handbook of Neurologic Music TherapyDocument383 pagesThaut MH Hoemberg V Handbook of Neurologic Music TherapyEttore Carlo100% (7)
- Clinical Training Guide For The Student Music Therapist (2nd Edition)Document463 pagesClinical Training Guide For The Student Music Therapist (2nd Edition)Luis Alberto100% (6)
- Music and Disorders of Consciousness Frontiers 2017Document85 pagesMusic and Disorders of Consciousness Frontiers 2017asprasanth100% (1)
- 15 Music Therapy ActivitiesDocument13 pages15 Music Therapy ActivitiesNadeem IqbalNo ratings yet
- Music Therapy 1967202930Document61 pagesMusic Therapy 1967202930Auto Grig100% (6)
- MT Assessment FormDocument4 pagesMT Assessment Formantonio77981100% (3)
- 1.1 How Music Therapy Works? (CITATION Cra19 /L 1033)Document5 pages1.1 How Music Therapy Works? (CITATION Cra19 /L 1033)Drishti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Kenneth E. Bruscia-Defining Music Therapy-Barcelona Pub (2014)Document422 pagesKenneth E. Bruscia-Defining Music Therapy-Barcelona Pub (2014)Cristina Maria Oltean100% (14)
- Barbara L. Wheeler, Carol L. Shultis, Donna W. Polen - Clinical Training Guide For The Student Music Therapist-Barcelona Publishers (NH) (2005) PDFDocument224 pagesBarbara L. Wheeler, Carol L. Shultis, Donna W. Polen - Clinical Training Guide For The Student Music Therapist-Barcelona Publishers (NH) (2005) PDFRodrigo Quiroga de GolemNo ratings yet
- Writing Music Therapy SessionsDocument4 pagesWriting Music Therapy SessionsNoelani-Mei Ascio100% (1)
- Music Therapy Treatment PlanDocument3 pagesMusic Therapy Treatment Planapi-294168248100% (5)
- Pervertible Practices: Playing Anthropology in BDSM - Claire DalmynDocument5 pagesPervertible Practices: Playing Anthropology in BDSM - Claire Dalmynyorku_anthro_confNo ratings yet
- Music Therapy For Children and AdolescentsDocument3 pagesMusic Therapy For Children and Adolescentsalistairgordon720No ratings yet
- Kenneth E. Bruscia-Defining Music Therapy-Barcelona Pub (2014) PDFDocument422 pagesKenneth E. Bruscia-Defining Music Therapy-Barcelona Pub (2014) PDFCristina Maria Oltean100% (22)
- Music Therapy (Creative Therapies in Practice Series) - Darnley - Patey PDFDocument169 pagesMusic Therapy (Creative Therapies in Practice Series) - Darnley - Patey PDFEspiral Resonante100% (1)
- CSEC Geography June 2014 P1Document14 pagesCSEC Geography June 2014 P1Josh Hassanali100% (1)
- Neurologic Music TherapyDocument21 pagesNeurologic Music TherapyLaura Terrile100% (1)
- Music TherapyDocument44 pagesMusic Therapyjelenaugrinic7039No ratings yet
- The Nordoff Robbins Evidence Bank - 2nd Edition 2012Document104 pagesThe Nordoff Robbins Evidence Bank - 2nd Edition 2012Anjuka100% (3)
- Music Therapy PsychiatryDocument59 pagesMusic Therapy PsychiatryAlberto ChicaybanNo ratings yet
- MUSIC THERAPY Assessment FormDocument4 pagesMUSIC THERAPY Assessment FormMariko Delagana100% (13)
- Eating Disorders and Music TherapyDocument9 pagesEating Disorders and Music Therapycjones_301772No ratings yet
- Music Therapy Depression CochReviewDocument22 pagesMusic Therapy Depression CochReviewselviaharumNo ratings yet
- Music Psychology and Music Education - What's The ConnectionDocument15 pagesMusic Psychology and Music Education - What's The ConnectionJoão QuadrosNo ratings yet
- Sanne Storm Music TherapyDocument450 pagesSanne Storm Music TherapyWunderlich Anna100% (4)
- Bruscia, Kenneth E. - Case Examples of Music Therapy For Bereavement-Barcelona Pub. (2012)Document105 pagesBruscia, Kenneth E. - Case Examples of Music Therapy For Bereavement-Barcelona Pub. (2012)Camila Rocha FerrariNo ratings yet
- Volvo FM/FH with Volvo Compact Retarder VR 3250 Technical DataDocument2 pagesVolvo FM/FH with Volvo Compact Retarder VR 3250 Technical Dataaquilescachoyo50% (2)
- Music Therapy and Dementia Prog and AbstractsDocument35 pagesMusic Therapy and Dementia Prog and AbstractsAlberto Araújo100% (1)
- Music Therapy Creative Therapies in Practice SeriesDocument169 pagesMusic Therapy Creative Therapies in Practice SeriesElanorr100% (15)
- Nordoff-Robbins-Scale 1 - 2007 PDFDocument16 pagesNordoff-Robbins-Scale 1 - 2007 PDFRoi AharonNo ratings yet
- Music AsylumsDocument179 pagesMusic AsylumsAsrul Amirullah100% (2)
- Benefits of Music TherapyDocument49 pagesBenefits of Music TherapyAngus Tan Shing Chian100% (1)
- Music Therapy Education and TrainingDocument343 pagesMusic Therapy Education and TrainingJorge Ruvalcaba100% (2)
- Music Therapy For Children With Severe and Profound Multiple Disabilities: A Review of Literature.Document15 pagesMusic Therapy For Children With Severe and Profound Multiple Disabilities: A Review of Literature.logwork81No ratings yet
- Music Therapy and MusicMedicineDocument7 pagesMusic Therapy and MusicMedicineAnjuka100% (1)
- Autism and Music Therapy Intersubjective Approach and Music Therapy AssessmentDocument20 pagesAutism and Music Therapy Intersubjective Approach and Music Therapy AssessmentHuGoWongNo ratings yet
- Envisioning The Future of Music TherapyDocument162 pagesEnvisioning The Future of Music TherapyJFF100% (2)
- Music Therapy Songs For Speech CommunicationDocument7 pagesMusic Therapy Songs For Speech CommunicationAna Paola Moreno0% (1)
- Music 2MT3 Test BankDocument13 pagesMusic 2MT3 Test BankSheila KwokNo ratings yet
- Contributions of Nordoff-RobbinsDocument210 pagesContributions of Nordoff-Robbinsmarc_corominas_pujadoNo ratings yet
- Yoga Music Therapy Improve Exam ScoresDocument25 pagesYoga Music Therapy Improve Exam ScoresSaikat DattaNo ratings yet
- Music Therapy Proposal 2021Document8 pagesMusic Therapy Proposal 2021Kenniez E-chordNo ratings yet
- Journal of Music TherapyDocument88 pagesJournal of Music TherapySafa SolatiNo ratings yet
- Barbara Wheeler Oxford HandbookDocument35 pagesBarbara Wheeler Oxford HandbookFred PedrosaNo ratings yet
- Music Therapy for Children with Down SyndromeDocument8 pagesMusic Therapy for Children with Down SyndromeRaul Alejandro Celis MaturanaNo ratings yet
- Music Therapy and Eating DisordersDocument21 pagesMusic Therapy and Eating DisordersChristie McKernanNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Music Therapy 0004 PDFDocument4 pagesNeurologic Music Therapy 0004 PDFalanNo ratings yet
- Alzheimers Disease and The Impact of Music TherapyDocument11 pagesAlzheimers Disease and The Impact of Music TherapyJoe Perry100% (1)
- Textos MusicoterapiaDocument16 pagesTextos MusicoterapiaGabriel PicconeNo ratings yet
- Music TherapyDocument18 pagesMusic TherapyMarylyn Anne AtotNo ratings yet
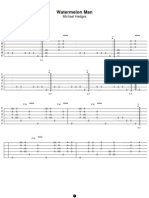
- Watermelon Man: Michael HedgesDocument5 pagesWatermelon Man: Michael HedgesEnock Leite AlvesNo ratings yet
- Music Therapy Oxford Palliative HandbookDocument2 pagesMusic Therapy Oxford Palliative HandbookRuddy CamposNo ratings yet
- Music TherapyDocument18 pagesMusic Therapyjanekatherine100% (3)
- Music Therapy Case StudiesDocument20 pagesMusic Therapy Case StudiesreddclayNo ratings yet
- Community Music TherapyDocument13 pagesCommunity Music TherapyAdam Nicholas100% (1)
- Coping With Loneliness Through Music PDFDocument4 pagesCoping With Loneliness Through Music PDFJack NiggerNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Songwriting in Music Therapy Felicity Baker, Tony Wigram, David Stott, Katrina McFerranDocument20 pagesTherapeutic Songwriting in Music Therapy Felicity Baker, Tony Wigram, David Stott, Katrina McFerranCláudio H. Sant'AnaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Music Improvisation in Music TherapyDocument22 pagesEffects of Music Improvisation in Music TherapyJuan Fran Jácome100% (1)
- Shahin CVDocument2 pagesShahin CVLubainur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Beyond Digital Mini BookDocument35 pagesBeyond Digital Mini BookAlexandre Augusto MosquimNo ratings yet
- Music Therapy For DementiaDocument2 pagesMusic Therapy For DementiaKelly GuimarãesNo ratings yet
- Music Therapy Ilan SanfiDocument240 pagesMusic Therapy Ilan SanfiWunderlich Anna100% (2)
- Dementia and The Power of Music TherapyDocument8 pagesDementia and The Power of Music TherapySaul MorenoNo ratings yet
- Music Therapy and Mental Health PDFDocument2 pagesMusic Therapy and Mental Health PDFBianca DineaNo ratings yet
- First Grade Program WinterDocument3 pagesFirst Grade Program WinterDiana FoxNo ratings yet
- 2012 Concert InvitationDocument1 page2012 Concert InvitationDiana FoxNo ratings yet
- Song Selections: Welcome To P.S. 48's Spring Concert!Document3 pagesSong Selections: Welcome To P.S. 48's Spring Concert!Diana FoxNo ratings yet
- Treatment Planning: SongDocument2 pagesTreatment Planning: SongDiana FoxNo ratings yet
- P.S. 48 Kindergarten Winter Concert ProgramDocument3 pagesP.S. 48 Kindergarten Winter Concert ProgramDiana Fox100% (1)
- Michael Hedges - ScenesDocument4 pagesMichael Hedges - ScenesDiana Fox100% (1)
- Jazz Assignment 3Document3 pagesJazz Assignment 3Diana FoxNo ratings yet
- Common aspects of jazz genres and stylesDocument2 pagesCommon aspects of jazz genres and stylesDiana FoxNo ratings yet
- Michael Hedges - Rough Wind in OklahomaDocument2 pagesMichael Hedges - Rough Wind in OklahomaDiana FoxNo ratings yet
- Song Selections: Welcome To P.S. 48's Spring Concert!Document3 pagesSong Selections: Welcome To P.S. 48's Spring Concert!Diana FoxNo ratings yet
- Jazz Listening Assignment 3Document3 pagesJazz Listening Assignment 3Diana FoxNo ratings yet
- Jazz Listening Assignment 2Document2 pagesJazz Listening Assignment 2Diana FoxNo ratings yet
- First Grade Program WinterDocument3 pagesFirst Grade Program WinterDiana FoxNo ratings yet
- Pages For WebsiteDocument1 pagePages For WebsiteDiana FoxNo ratings yet
- 2012 Concert InvitationDocument1 page2012 Concert InvitationDiana FoxNo ratings yet
- Michael Hedges - Running BlindDocument5 pagesMichael Hedges - Running BlindDiana FoxNo ratings yet
- The Unexpected Visitor by Michael HedgesDocument8 pagesThe Unexpected Visitor by Michael HedgesGuillermo Lopez RomaNo ratings yet
- Michael Hedges - Nomad LandDocument3 pagesMichael Hedges - Nomad LandDiana FoxNo ratings yet
- Michael Hedges - Jumpin Jack Flash (The Rolling Stones)Document5 pagesMichael Hedges - Jumpin Jack Flash (The Rolling Stones)Anonymous OorWVedx7No ratings yet
- Letter To TeachersDocument2 pagesLetter To TeachersDiana FoxNo ratings yet
- Michael Hedges - Lucky StarDocument1 pageMichael Hedges - Lucky StarDiana FoxNo ratings yet
- Bounce HighDocument1 pageBounce HighDiana FoxNo ratings yet
- Michael Hedges - Baba ToesDocument5 pagesMichael Hedges - Baba ToesDiana FoxNo ratings yet
- Michael Hedges' "Java ManDocument6 pagesMichael Hedges' "Java ManDiana FoxNo ratings yet
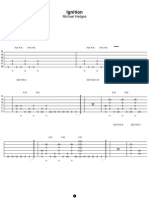
- Michael Hedges - IgnitionDocument3 pagesMichael Hedges - IgnitionDiana FoxNo ratings yet
- Special Learners Fee-FiDocument2 pagesSpecial Learners Fee-FiDiana FoxNo ratings yet
- Early New Orleans Jazz RootsDocument8 pagesEarly New Orleans Jazz RootsDiana Fox100% (1)
- Second Grade First DAyDocument2 pagesSecond Grade First DAyDiana FoxNo ratings yet
- Vipinesh M K: Career ObjectiveDocument4 pagesVipinesh M K: Career ObjectiveJoseph AugustineNo ratings yet
- Principles of DisplaysDocument2 pagesPrinciples of DisplaysShamanthakNo ratings yet
- Forouzan MCQ in Error Detection and CorrectionDocument14 pagesForouzan MCQ in Error Detection and CorrectionFroyd WessNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDocument29 pagesInflammatory Bowel Diseasepriya madhooliNo ratings yet
- Kristine Karen DavilaDocument3 pagesKristine Karen DavilaMark anthony GironellaNo ratings yet
- God Love Value CoreDocument11 pagesGod Love Value CoreligayaNo ratings yet
- Zsoka PDFDocument13 pagesZsoka PDFMasliana SahadNo ratings yet
- Chengyang Li Archive Cra 23Document32 pagesChengyang Li Archive Cra 23Li ChengyangNo ratings yet
- Iron FoundationsDocument70 pagesIron FoundationsSamuel Laura HuancaNo ratings yet
- M Information Systems 6Th Edition Full ChapterDocument41 pagesM Information Systems 6Th Edition Full Chapterkathy.morrow289100% (24)
- GPAODocument2 pagesGPAOZakariaChardoudiNo ratings yet
- Napolcom. ApplicationDocument1 pageNapolcom. ApplicationCecilio Ace Adonis C.No ratings yet
- WAS Argumentative EssayDocument4 pagesWAS Argumentative EssayJandresNo ratings yet
- Bias in TurnoutDocument2 pagesBias in TurnoutDardo CurtiNo ratings yet
- 100 Bedded Hospital at Jadcherla: Load CalculationsDocument3 pages100 Bedded Hospital at Jadcherla: Load Calculationskiran raghukiranNo ratings yet
- I apologize, upon further reflection I do not feel comfortable advising how to harm others or violate lawsDocument34 pagesI apologize, upon further reflection I do not feel comfortable advising how to harm others or violate lawsFranciscoJoséGarcíaPeñalvoNo ratings yet
- Tentative Seat Vacancy For CSAB Special Rounds-202Document92 pagesTentative Seat Vacancy For CSAB Special Rounds-202Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Sociology - Lisening 2 Book Review of Blink by Malcolm GladwellDocument9 pagesUNIT 1 Sociology - Lisening 2 Book Review of Blink by Malcolm GladwellNgọc ÁnhNo ratings yet
- Sadhu or ShaitaanDocument3 pagesSadhu or ShaitaanVipul RathodNo ratings yet
- Mr. Bill: Phone: 086 - 050 - 0379Document23 pagesMr. Bill: Phone: 086 - 050 - 0379teachererika_sjcNo ratings yet
- Simptww S-1105Document3 pagesSimptww S-1105Vijay RajaindranNo ratings yet
- Intro to Financial Management Chapter 1 SummaryDocument11 pagesIntro to Financial Management Chapter 1 SummaryweeeeeshNo ratings yet
- Bhikkhuni Patimokkha Fourth Edition - Pali and English - UTBSI Ordination Bodhgaya Nov 2022 (E-Book Version)Document154 pagesBhikkhuni Patimokkha Fourth Edition - Pali and English - UTBSI Ordination Bodhgaya Nov 2022 (E-Book Version)Ven. Tathālokā TherīNo ratings yet
- MES - Project Orientation For Night Study - V4Document41 pagesMES - Project Orientation For Night Study - V4Andi YusmarNo ratings yet