Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 3: Redox, and Oxidation
Uploaded by
SeanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 3: Redox, and Oxidation
Uploaded by
SeanCopyright:
Available Formats
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
41
Carbon Compounds / Sebatian Karbon
1 Carbon compounds are compounds that contain the element carbon. These compounds can be classified into two groups:
/ Sebatian karbon adalah sebatian yang mengandungi unsur karbon. Sebatian ini boleh dikelaskan kepada dua kumpulan:
a. Organic compounds / Sebatian organik
b. Inorganic compounds / Sebatian tak organik
2 Organic compounds are carbon compounds that are obtained from living things such as sugar, starch, protein, vitamin,
enzym etc. They are obtained from plants and animals. / Sebatian organik adalah sebatian yang diperoleh daripada benda
hidup seperti gula, kanji, protein, vitamin, enzim dan lain-lain. Bahan-bahan ini diperoleh daripada tumbuhan dan binatang.
3 Inorganic compounds are carbon compounds that usually do not contain carbon to carbon bonds such as carbon dioxide
(CO
2
), carbon monoxide (CO), calcium carbonate (CaCO
3
) etc. / Sebatian tak organik adalah sebatian karbon yang biasanya
tidak mengandungi karbon dan ikatan karbon seperti karbon dioksida(CO
2
), karbon monoksida(CO), kalsium karbonat(CaCO
3
) dan
lain-lain.
4 Most organic compounds contain the element carbon and hydrogen. Complete combustion of organic compounds
produces carbon dioxide and water. / Kebanyakan sebatian organik mengandungi unsur karbon dan hidrogen. Pembakaran
lengkap sebatian organik menghasilkan karbon dioksida dan air.
Hydrocarbon / Hidrokarbon
1 Hydrocarbons are organic compounds that contain only carbon, C and hydrogen, H. / Hidrokarbon adalah sebatian
organik yang hanya mengandungi karbon, C dan hidrogen, H sahaja.
2 Hydrocarbons are classified into two groups: / Hidrokarbon boleh dikelaskan kepada dua kumpulan:
Saturated hydrocarbons / Hidrokarbon tepu Unsaturated hydrocarbons / Hidrokarbon tak tepu
Definition
Definasi
Hydrocarbon that contain only single
covalent bonds between carbon atoms.
Hidrokarbon yang mengandungi ikatan kovalen
tunggal
sahaja di antara atom kabon.
Hydrocarbon that contain at least one double
or
triple
covalent bond between carbon atoms.
Hidrokarbon yang mengandungi sekurang-kurangnya
satu ikatan kovalen
ganda dua
atau
ganda tiga
di antara atom karbon.
Example of
*structural
formula
Contoh
*formula
struktur
H H H
H C C C H
H H H
Single
covalent bond between carbon atoms.
Ikatan kovalen
tunggal
sahaja di antara karbon.
H H H H
H C C C C
H H H
Double
covalent bond between carbon atoms.
Ikatan kovalen
ganda dua
di antara karbon.
*Homologous
series
*Siri Homolog
Alkane / Alkana Alkene / Alkena
* Homologous series are carbon compounds that have the certain general characteristics.
* Siri homolog adalah sebatian karbon yang mempunyai sifat-sifat am yang tertentu.
* Structural formula is a chemical formula that shows how atoms are bonded to each other covalently in a molecule.
* Formula struktur ialah formula kimia yang menunjukkan bagaimana atom terikat di antara satu sama lain secara kovalen dalam suatu
molekul.
3 The main source of hydrocarbons is petroleum. It is formed as a result of decomposition of plants and animals that died
million years ago. / Sumber utama hidrokarbon ialah petroleum. Ia terbentuk daripada penguraian tumbuhan dan binatang yang
telah mati sejak berjuta-juta tahun dahulu.
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
42
4 Petroleum is a mixture of different molecular size hydrocarbons. These hydrocarbons can be separated using fractional
distillation of petroleum at different temperature. This process separates
hydrocarbons
______________ with different molecular
size (petroleum gas, petrol, naphta, kerosene, diesel and lubricating oil). / Petroleum ialah campuran molekul hidrokarbon
yang berlainan saiz. Hidrokarbon ini boleh diasingkan melalui penyulingan berperingkat petroleum pada suhu yang berlainan.
Proses ini mengasingkan hidrokarbon yang mempunyai saiz molekul yang berlainan (gas petroleum, petrol, nafta, kerosin, diesel
dan minyak pelincir).
Alkane / Alkana
1 Alkanes are hydrocarbons with general formula
C
n
H
2n + 2
, where n = 1, 2, 3, / Alkana adalah hidrokarbon yang
mempunyai formula am C
n
H
2n + 2
, di mana n = 1, 2, 3, ...
2 Each carbon atom is bonded to four other atoms by single
covalent bonds that is C C or C H. It is classified as
saturated
hydrocarbons. (A saturated
hydrocarbon contains only single covalent bonds between carbon atoms).
/ Setiap atom karbon terikat kepada empat atom lain oleh ikatan kovalen tunggal
iaitu C C atau C H. Ia dikelaskan
sebagai hidrokarbon tepu
. (Hidrokarbon tepu
mengandungi ikatan kovalen tunggal sahaja di antara atom
karbon).
Example / Contoh:
a. Methane / Metana, CH
4
H
H H
H
C
Electron arrangement in methane molecule, CH
4
Susunan elektron dalam molekul metana, CH
4
H
H C H
H
Represents (one pair of
electrons is shared to form a
single covalent bond)
Mewakili (Sepasang elektron
dikongsi untuk membentuk ikatan
kovalen tunggal)
Structural formula of methane, CH
4
Formula struktur metana, CH
4
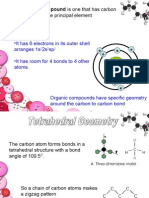
3 Each carbon atom in the structural formula must have a total of four pairs of electrons shared with another carbon and
hydrogen atom to achieve octet electron arrangement. (Each carbon atom must have four in the structural formula).
Setiap atom karbon dalam formula struktur mesti mempunyai empat pasang elektron yang dikongsi dengan atom karbon dan hidrogen
yang lain untuk mencapai susunan elektron oktet. (Setiap atom karbon mesti mempunyai empat dalam formula strukturnya).
4 Each hydrogen atom in the structural formula must have one pair of electrons shared with carbon to achieve duplet
electron arrangement. (Each hydrogen atom must have one in the structural formula).
Setiap atom hidrogen dalam formula struktur mesti mempunyai satu pasang elektron yang dikongsi dengan karbon untuk mencapai
susunan atom duplet (Setiap hidrogen mesti mempunyai satu dalam formula strukturnya).
5 Naming of alkanes / Penamaan alkana
a. The name of straight chain alkanes (all the carbon atoms are joined in a continuous chain) are made up of two
component parts. / Nama bagi alkana berantai lurus (semua atom karbon yang bergabung dalam rantai yang berterusan)
terdiri daripada dua komponen:
i. Stem/root: indicates the number of carbon atoms in the longest continuous carbon chain. The name of stems for
the first ten straight alkanes are: / Awalan/induk: menunjukkan bilangan atom karbon dalam rantai karbon berterusan
yang paling panjang. Nama awalan bagi sepuluh alkana pertama adalah:
Number of carbon, C
Bilangan karbon, C
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Stem / Awalan
Meth
Met
Eth
Et
Prop
Prop
But
But
Pent
Pent
Hex
Heks
Hept
Hept
Oct
Okt
Non
Non
Dec
Dek
ii. Suffix/ending: indicates the group of the compound. For alkane, the suffix is ane because it belongs to the
alkane group. / Akhiran: menunjukkan kumpulan sebatian. Bagi alkana, akhiran adalah ana kerana ia adalah dalam
kumpulan alkana.
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
43
b. Complete the table below. / Lengkapkan jadual berikut:
Number of
carbon atoms
Bilangan atom
karbon
Molecular formula C
n
H
2n + 2
Formula molekul
C
n
H
2n + 2
Structural formula
Formula struktur
Name of
alkane
Nama
alkana
1
(meth / met)
CH
4
H
H C H
H
Methane
2
(eth / et)
C
2
H
6
H H
H C C H
H H
Ethane
3
(prop / prop)
C
3
H
8
H H H
H C C C H
H H H
Propane
4
(but / but)
C
4
H
10
H H H H
H C C C C H
H H H H
Butane
5
(pent / pent)
C
5
H
12
H H H H H
H C C C C C H
H H H H H
Pentane
6
(hex / heks)
C
6
H
14
H H H H H H
H C C C C C C H
H H H H H H
Hexane
7
(hept / hept)
C
7
H
16
H H H H H H H
H C C C C C C C H
H H H H H H H
Heptane
8
(oct / okt)
C
8
H
18
H H H H H H H H
H C C C C C C C C H
H H H H H H H H
Octane
9
(non / non)
C
9
H
20
H H H H H H H H H
H C C C C C C C C C H
H H H H H H H H H
Nonane
10
(dec / dek)
C
10
H
22
H H H H H H H H H H
H C C C C C C C C C C H
H H H H H H H H H H
Decane
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
44
Chemical Properties of Alkane / Sifat-sifat Fizikal Alkana
1 Alkanes are covalent compounds which consist of
molecules
, the atoms are bonded together by a
strong
covalent bond. These
molecules
are held together by
weak
Van der Waals forces (intermolecular forces).
Alkana adalah sebatian kovalen yang terdiri daripada molekul
, atom-atom terikat bersama oleh ikatan kovalen yang kuat.
Molekul-molekul
ini ditarik bersama oleh daya Van der Waals yang lemah (daya antara molekul).
2 Alkanes have physical properties similar to covalent compounds. Alkanes are
insoluble
in water but dissolve in
organic solvents, cannot conduct electricity, low melting/boiling points and less dense than water. / Alkana mempunyai sifat
fizikal yang sama dengan sebatian kovalen. Alkana tidak larut
dalam air tetapi larut dalam pelarut organik, tidak
boleh mengalirkan arus elektrik, takat lebur/didih yang rendah dan kurang tumpat berbanding air.
3 Complete the following table: / Lengkapkan jadual berikut:
Name of
members
Nama ahli-ahli
Molecular
formula
Formula
molekul
Melting point/ C
Takat lebur/ C
Boiling point/C
Takat didih/C
Molar mass/ g mol
-1
Jisim molar/g mol
1
Physical
state at room
temperature
Keadaan fizikal
pada suhu bilik
Methane
Metana
CH
4
182 162 16 Gas
Ethane
Etana
C
2
H
6
183 89 30 Gas
Propane
Propana
C
3
H
8
188 42 44 Gas
Butane
Butana
C
4
H
10
138 0.5 58 Gas
Pentane
Pentana
C
5
H
12
130 36 72 Liquid
Hexane
Heksana
C
6
H
14
95 69 86 Liquid
Heptane
Heptana
C
7
H
16
91 98 100 Liquid
Octane
Oktana
C
8
H
18
57 126 114 Liquid
Nonane
Nonana
C
9
H
20
54 153 128 Liquid
Decane
Dekana
C
10
H
22
30 174 142 Liquid
The physical state of alkane is determined by its melting and boiling points. / Sifat fizikal alkana ditentukan oleh takat lebur dan didihnya.
The alkane is in gas form if its melting and boiling points are below room temperature. / Alkana adalah dalam bentuk gas jika takat lebur dan
didihnya di bawah suhu bilik.
The alkane is in liquid form if its melting point is below room temperature and its boiling is higher than room temperature. Alkana adalah
dalam bentuk cecair jika takat leburnya di bawah suhu bilik dan takat didihnya lebih tinggi dari suhu bilik.
4 The first
four
members of alkanes exist as
gas
at room temperature. Pentane to decane are
liquid
.
Empat
ahli pertama alkana wujud sebagai gas
pada suhu bilik. Pentana hingga dekana adalah cecair
.
5 As the number of carbon atoms in a molecule of alkane increases: / Apabila bilangan atom karbon dalam satu molekul alkana
meningkat:
a. The molecular size of alkane
increase
, the
Van der Waals
forces between molecules (intermolecular
forces)
increases
, more
heat
energy is needed to
overcome
this force, the melting and boiling points
increase
. / Saiz molekul alkana bertambah
, daya Van der Waals
(daya antara molekul) bertambah kuat
,
semakin banyak tenaga haba
diperlukan untuk mengatasi
daya ini, takat lebur dan takat didih bertambah
.
b. The viscosity and density of alkane
increase
. / Kelikatan dan ketumpatan alkana
bertambah
.
c. The alkane becomes less
flammable
, harder to ignite. / Alkana semakin susah untuk
terbakar
dan dinyalakan.
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
45
Chemical Properties of Alkanes / Sifat-sifat Kimia Alkana
1 Alkanes are
saturated
hydrocarbon which only have single covalent bonds, C C and C H. They are not reactive
because the strong C C and C H bonds in the molecules need a lot of energy to break. / Alkana adalah hidrokarbon
tepu
yang hanya mempunyai ikatan kovalen tunggal, C C dan C H. Ia tidak reaktif kerana ikatan C C dan C H yang kuat
dalam molekul memerlukan tenaga yang banyak untuk diputuskan.
2 Two chemical reaction of alkanes: / Dua tindak balas kimia bagi alkana adalah:
a. Combustion. / Pembakaran.
b. Substitution reaction. / Tindak balas penukargantian.
3 Combustion of alkane / Pembakaran alkana
a. Alkanes undergo complete combustion in the presence of sufficient oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water only.
Alkana mengalami pembakaran lengkap dengan kehadiran oksigen yang secukupnya untuk membentuk karbon dioksida dan
air sahaja.
Alkane + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + Water / Alkana + Oksigen Karbon dioksida + Air
b. Balance the equations: / Seimbangkan persamaan berikut:
CH
4
+
2
O
2
CO
2
+
2
H
2
O
C
2
H
6
+
7
O
2
2
CO
2
+
3
H
2
O
C
3
H
8
+
5
O
2
3
CO
2
+
4
H
2
O
Balancing the equations: / Mengimbangkan persamaan:
Step 1: Balance C / Langkah 1: Seimbangkan C
Step 2: Balance H / Langkah 2: Seimbangkan H
Step 3: Balance O, can use fraction / Langkah 3: Seimbangkan O,
dan boleh gunakan pecahan
c. Alkanes undergo incomplete combustion when there is insufficient oxygen to form carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide,
carbon (in the form of soot) and water. / Alkana melalui pembakaran yang tak lengkap apabila tiada oksigen yang mencukupi
untuk membentuk karbon dioksida, karbon monoksida, karbon(dalam bentuk jelaga) dan air.
Example / Contoh:
2CH
4
(g) + 3O
2
(g) C(s) + CO
2
(g) + 4H
2
O(g)
or / atau
6CH
4
(g) + 9O
2
(g) 2C(s) + 2CO + 2CO
2
(g) + 12H
2
O(g)
d. When alkanes are burnt, large quantities of heat are released. This makes alkanes suitable for use as a fuel. / Apabila
alkana dibakar, kuantiti haba yang banyak dibebaskan. Ini menjadikan alkana sesuai untuk dijadikan bahan api.
4 Substitution reaction: / Tindak balas penukargantian:
a. Occurs when an alkane is mixed with a halogen in the presence of
sunlight
(ultraviolet light). / Berlaku apabila
suatu alkana dicampurkan dengan halogen dengan kehadiran
cahaya matahari
(sinaran ultraungu).
b. In this reaction, each hydrogen atom in the alkane molecule is substituted one by one by another atom, usually
halogen atoms. The sunlight or UV light is needed to break covalent bond in halogen and alkane molecules to
produce hydrogen and chlorine atom. / Dalam tindak balas ini, setiap atom hidrogen dalam molekul alkana digantikan
satu demi satu oleh atom yang lain, biasanya atom halogen. Cahaya matahari atau sinaran UV diperlukan untuk memutuskan
ikatan kovalen dalam molekul halogen dan alkana untuk menghasilkan atom hidrogen dan klorin.
c. For example, when methane reacts with chlorine gas in the presence of ultraviolet light, a variety of substituted
products are formed: / Contohnya, apabila metana bertindak balas dengan gas klorin dalam kehadiran sinaran ultraungu,
pelbagai hasil yang bertukarganti terbentuk:
H
H C H
H
H
H C H
Cl
+ Cl Cl
UV
Cl atom substitutes H in CH
4
Atom Cl menggantikan H dalam CH
4
H atom substitutes Cl in Cl
2
Atom H menggantikan Cl dalam Cl
2
+ H Cl
CH
4
+ Cl
2
UV
CH
3
Cl + HCl
(chloromethane / klorometana)
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
46
Further substitution of chlorine atoms in the chloromethane molecule produces dichloromethane, trichloromethane
and tetrachloromethane. Complete the following substitution reaction.
Penukargantian yang seterusnya bagi atom klorin dalam molekul klorometana menghasilkan diklorometana, triklorometana
dan tetraklorometana. Lengkapkan tindak balas penukargantian berikut:
CH
3
Cl + Cl
2
UV
CH2Cl2
(dichloromethane / diklorometana)
+ HCl
CH
2
Cl
2
+ Cl
2
UV
CHCl3
(trichloromethane / triklorometana)
+ HCl
CHCl
3
+ Cl
2
UV
CCl4
(tetrachloromethane / tetraklorometana)
+ HCl
5 The effect of methane in everyday life: / Kesan metana dalam kehidupan seharian:
i. Methane is the major component in natural gas (gas found together with petroleum).
Metana adalah komponen utama dalam gas asli (gas yang dijumpai bersama petroleum).
ii. Methane gas is produced when waste organic matter decompose in the absence of oxygen. As methane is a
combustible gas, it can cause fire in landfills and peat swamps.
Gas metana terhasil apabila bahan buangan organik terurai tanpa kehadiran oksigen. Oleh kerana metana boleh terbakar, ia
boleh menyebabkan kebakaran di tempat buangan sampah dan paya gambut.
Alkene / Alkena
1 Alkenes are hydrocarbons with the general formula C
n
H
2n
, where n = 2, 3,
Alkena adalah hidrokarbon dengan formula am C
n
H
2n
, di mana n = 2, 3,
2 Every alkene has a carbon-carbon double covalent bond, C = C in its molecule. It is classified as
unsaturated
hydrocarbons. (An
unsaturated
hydrocarbon contains at least one
double
covalent bond between
carbon atoms). / Setiap alkena mempunyai satu ikatan ganda dua karbon-karbon, C = C dalam molekulnya. Ia boleh dikelaskan
sebagai hidrokarbon tidak tepu
. (Hidrokarbon tidak tepu
mengandungi sekurang-kurangnya satu ikatan kovalen ganda dua
di antara atom-atom karbon)
Example / Contoh:
a. Ethene / Etena, C
2
H
4
H
H C C H
H
H H
H C C H
Electron arrangement in ethene molecule, C
2
H
4
Susunan elektron dalam molekul etena, C
2
H
4
Structural formula for ethene, C
2
H
4
Formula struktur bagi etena, C
2
H
4
3 The first member of alkenes has two carbon atoms in a molecule because
double covalent bond
is
formed between two carbon atoms. / Ahli pertama alkena mempunyai dua atom karbon dalam satu molekul kerana
ikatan kovalen ganda dua
terbentuk di antara dua atom karbon.
4 Naming of alkenes / Penamaan alkena
a. The name of straight chain alkenes are also made up of two component parts.
Nama bagi rantai lurus alkena juga terdiri daripada dua komponen.
i. Stem/root: / Awalan:
Indicates the number of carbon atoms in the longest continuous carbon chain. The name of the stems for the first
nine straight alkanes are eth, prop, but, pent, hex, hept, oct, non and dec.
Menunjukkan bilangan atom karbon dalam rantai karbon yang terpanjang. Nama awalan bagi sembilan alkena lurus
pertama adalah et, prop, but, pent, heks, hept, okt, non dan dek.
ii. Suffix/ending: / Akhiran:
Indicates the group of the compound. For alkene, the suffix is ene because it belongs to the alkene group.
Menunjukkan kumpulan bagi sebatian. Bagi alkena, akhiran adalah ena kerana ia tergolong dalam kumpulan alkena.
b. Naming the straight chain alkene: / Menamakan rantai lurus alkena:
i. Determine the longest carbon chain containing double bond give the stem name according to the number
of carbon atoms i.e eth, prop, but, pent, hex, hept, oct, non and dec.
Tentukan rantai karbon terpanjang yang mengandungi ikatan ganda dua memberikan nama awalan berdasarkan
bilangan atom karbon iaitu et, prop, but, pent, heks, hept, okt, non dan dek.
ii. Add the suffix ene at the end of the name. / Tambahkan akhiran ena pada setiap penghujung nama.
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
47
c. Complete the table below: / Lengkapkan jadual berikut:
Number of
carbon atoms
Bilangan atom
karbon
Molecular
formula
Formula
molekul
Structural formula
Formula struktur
Name
Nama
2 C
2
H
4
H H
C C
H H
Ethene
3 C
3
H
6
H H H
H C C C H
H
Propene
4 C
4
H
8
H H H H
H C C C C H
H H
Butene
5 C
5
H
10
H H H H H
H C C C C C H
H H H
Pentene
6 C
6
H
12
H H H H H H
H C C C C C C H
H H H H
Hexene
7 C
7
H
14
H H H H H H H
H C C C C C C C H
H H H H H
Heptene
8 C
8
H
16
H H H H H H H H
H C C C C C C C C H
H H H H H H
Octene
9 C
9
H
18
H H H H H H H H H
H C C C C C C C C C H
H H H H H H H
Nonene
10 C
10
H
20
H H H H H H H H H H
H C C C C C C C C C C H
H H H H H H H H
Decene
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
48
Physical Properties of Alkenes / Sifat-Sifat Fizikal Alkena
1 Physical properties of alkenes are similar to alkanes. Alkenes are covalent compounds which consist of
molecules
. The atoms
are bonded together by a
strong
covalent bond. These
molecules
are held together by
weak
Van
der Waals forces (intermolecular forces). / Sifat-sifat fizikal alkena adalah menyerupai alkana. Alkena adalah sebatian Kovalen
yang terdiri daripada molekul
, atom-atom terikat bersama oleh ikatan kovalen yang kuat
. Molekul-molekul
ini ditarik
bersama oleh daya Van der Waals yang lemah
(daya antara molekul).
2 Alkenes have physical properties similar to covalent compounds. Alkene are
insoluble
in water but dissolve in
organic solvents, cannot conduct electricity, low melting/boiling points and less dense than water. / Alkena mempunyai sifat-
sifat fizikal yang sama dengan sebatian kovalen. Alkena tak larut
di dalam air tetapi larut dalam pelarut organik, tidak boleh
mengalirkan arus elektrik, takat lebur/didih yang rendah dan kurang tumpat daripada air.
3 Complete the following table: / Lengkapkan jadual berikut:
Name of
members
Nama ahli
Molecular
formula
Formula molekul
Melting point/ C
Takat lebur/ C
Boiling point/C
Takat didih/C
Molar mass/
g mol
1
Jisim molar
g mol
1
Physical
state at room
temperature
Sifat fizikal pada
suhu bilik
Ethene / Etena C
2
H
4
169 104 28 Gas
Propene / Propena C
3
H
6
185 47 42 Gas
Butene / Butena C
4
H
8
185 6 56 Gas
Pentene / Pentena C
5
H
10
165 30 70 Liquid
Hexene / Heksena C
6
H
12
140 63 84 Liquid
Heptene / Heptena C
7
H
14
119 93 98 Liquid
Octene / Oktena C
8
H
16
104 122 112 Liquid
Nonene / Nonena C
9
H
18
94 146 126 Liquid
Decene / Dekena C
10
H
20
87 171 140 Liquid
4 Physical state at room temperature: ethene, propene and butene are
gases
. Pentene to decene are
liquid
.
Sifat fizikal pada suhu bilik: etena, propena dan butena adalah gas
. Pentena hingga dekene adalah cecair
.
5 Alkenes have
low
melting and boiling points because the
weak
Van der Waals forces (intermolecular
forces) between small molecules need
less
heat energy to overcome.
Alkena mempunyai takat lebur dan didih yang rendah
kerana daya Van der Waals (daya antara molekul) yang lemah
di
antara molekul kecil memerlukan tenaga haba yang rendah
untuk diatasi.
6 As the number of carbon atoms per molecule of alkene increases, the molecular size of alkene
increases
, the Van der
Waals or inter molecular forces
increases
between molecules, more
heat
energy is needed to
overcome
this forces, the melting and boiling points
increase
.
Apabila bilangan atom karbon dalam setiap molekul alkena meningkat, saiz molekul alkena meningkat
, daya Van der Waals atau
daya antara molekul juga meningkat
, semakin banyak tenaga haba
diperlukan untuk mengatasi
daya ini, takat lebur dan
takat didih juga meningkat
.
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
49
Chemical Properties of Alkenes / Sifat-Sifat Kimia Alkena
1 Alkenes are chemically more
reactive
than alkanes because of the existence of covalent double bond between two
carbon atoms. Almost all of the chemical reactions of alkene occur at the double bond.
Alkena adalah secara kimia lebih reaktif
berbanding alkana kerana kewujudan ikatan kovalen ganda dua di antara dua atom
karbon. Hampir semua tindak balas kimia alkena berlaku di ikatan ganda dua.
2 The chemical reactions of alkenes are: / Tindak balas kimia alkena adalah:
a. combustion / pembakaran
b. addition reaction / tindak balas penambahan
3 Combustion of alkenes / Pembakaran alkena
a. Alkene burns completely in the excess oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water:
Alkena terbakar dengan lengkap dalam keadaan oksigen berlebihan untuk menghasilkan karbon dioksida dan air:
Alkene + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + Water / Alkena + Oksigen Karbon dioksida + Air
b. Balance the following equations: / Seimbangkan persamaan berikut:
i. C
2
H
4
+
3
O
2
2
CO
2
+
2
H
2
O
ii. C
3
H
6
+
9
O
2
3
CO
2
+
3
H
2
O
iii. C
4
H
8
+
6
O
2
4
CO
2
+
4
H
2
O
Balancing the equations: / Mengimbangkan persamaan:
Step 1: Balance C / Langkah 1: Seimbangkan C
Step 2: Balance H / Langkah 2: Seimbangkan H
Step 3: Balance O, and can use fraction
Langkah 3: Seimbangkan O, dan boleh gunakan pecahan
c. Alkene burns incompletely in limited supply of oxygen to form carbon monoxide, carbon (in the form of soot)
and water. / Alkena terbakar dengan tidak lengkap dalam keadaan bekalan oksigen yang terhad untuk membentuk karbon
monoksida, karbon (dalam bentuk jelaga) dan air.
Example / Contoh:
C
2
H
4
(g) + O
2
(g) 2C(s) + 2H
2
O(g)
or / atau
C
2
H
4
(g) + 2O
2
(g) 2CO(g) + 2H
2
O (g)
d. Combustion of alkene will produce more sooty flame compared with their corresponding alkane. This is due to
higher percentage of carbon (by mass) in alkene than its corresponding alkane (the percentage of carbon for the
same number of carbon atom per molecule of alkane and alkene is higher in alkene).
Pembakaran alkena akan menghasilkan nyalaan yang lebih berjelaga berbanding alkana. Ini kerana peratus karbon mengikut
jisim yang lebih tinggi dalam alkena berbanding alkana (Peratusan karbon bagi bilangan atom per molekul yang sama bagi
alkena dan alkana adalah lebih tinggi dalam alkena).
Example / Contoh:
Corresponding hydrocarbon
Hidrokarbon yang selaras
Propane
Propana, C
3
H
8
Propene
Propena, C
3
H
6
Percentage of carbon
by mass
Peratusan karbon berdasarkan
jisim
Percentage of carbon / Peratusan karbon
=
12 3
12 3 + 8 1
100%
= 81.81%
Percentage of carbon / Peratusan karbon
=
12 3
12 3 + 6 1
100%
= 85.7%
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
50
4 Addition reaction / Tindak balas penambahan
a. As alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbon, they undergo addition reaction. An addition reaction is a reaction in
which other atoms are added to each carbon atom of the
double
bond, C=C to form
single
covalent
bond product CC. / Oleh kerana alkena adalah hidrokarbon tak tepu, ia melalui tindak balas penambahan. Tindak balas
penambahan ialah tindak balas di mana atom lain ditambah kepada setiap atom karbon pada ikatan ganda dua
, C=C
untuk membentuk hasil ikatan kovalen tunggal
CC.
H H
C C
Y X
H H
C C
+ X Y
Unsaturated / Tak tepu Saturated / Tepu
b. Five of addition reaction in alkenes that will be studied in this topic are: / Lima tindak balas penambahan yang akan
dipelajari dalam topik ini ialah:
i. Addition of hydrogen (hydrogenation) / Penambahan hidrogen (penghidrogenan)
ii. Addition halogen (halogenation) / Penambahan halogen (penghalogenan)
iii. Addition of hydrogen halide / Penambahan hidrogen halida
iv. Addition of water (hydration) / Penambahan air (penghidratan)
v. Addition of acidified potassium manganate(VII), KMnO
4
solution
Penambahan larutan kalium manganat(VII) berasid, KMnO
4
vi. Addition polymerisation / Pempolimeran penambahan
c. Addition of Hydrogen (Hydrogenation) / Penambahan Hidrogen (Penghidrogenan)
i. Alkenes react with hydrogen at 180C in the presence of nickel/platinum as a
catalyst
to produce
alkanes
. / Alkena bertindak balas dengan hidrogen pada suhu 180C dengan kehadiran nikel/platinum sebagai
mangkin
untuk menghasilkan alkana
.
ii. Hydrogenation is used to prepare an
alkane
(saturated compound) from an
alkene
(unsaturated
compound) in industry. / Penghidrogenan digunakan untuk menyediakan alkana
(sebatian tepu) daripada
alkena
(sebatian tak tepu) dalam industri.
iii. Example / Contoh:
H H H H
Ni
180
H C C H + H
2
H C C H
H H
CH
4
+ H
2
Ni
180
C
2
H
6
iv. Complete the following: / Lengkapkan yang berikut:
C
3
H
6
Propene / Propena
+ H
2
Ni
180
C
3
H
8
Propane / Propana
C
4
H
8
Butene / Butena
+ H
2
Ni
180
C
4
H
10
Butane / Butana
CnH
2n
Alkene / Alkena
+ H
2
Ni
180
C
n
H
2n+2
Alkane / Alkana
Hydrogenation of an
alkene
with the present of nickel as a
catalyst
will produce
alkane
.
Penghidrogenan alkena
dengan kehadiran nikel sebagai mangkin
akan menghasilkan alkana
.
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
51
d. Addition of Halogen (Halogenation) / Penambahan Halogen (Penghalogenan)
i. Alkenes react with halogens such as chlorine and bromine at room conditions (no catalyst or ultraviolet needed)
Alkena bertindak balas dengan halogen seperti klorin dan bromin pada keadaan bilik (tanpa mangkin atau sinaran ultraungu
yang diperlukan)
ii. Example / Contoh:
H H H H
H C C H + Br
2
H C C H
Br Br
Ethene
Etena
Bromine water
Air bromin
1, 2-dibromoethane
1, 2-dibromoetana
C
2
H
4
+ Br
2
C
2
H
4
Br
2
When ethene gas is passed through bromine water,
brown
colour of bromine water is
decolourised
. This
reaction is used to
distinguish
a saturated hydrocarbon and unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Apabila gas etena dilalukan pada air bromin, warna perang
air bromin menjadi luntur
. Tindak balas ini digunakan
untuk membezakan
hidrokarbon tepu dan hidrokaron tak tepu.
e. Addition of Hydrogen Halide / Penambahan Hidrogen Halida
i. Alkenes react with hydrogen halide such as hydrogen chloride or hydrogen bromide at room temperature to
form haloalkane. / Alkena bertindak balas dengan hidrogen halida seperti hidrogen klorida atau hidrogen bromida pada
suhu bilik untuk membentuk haloalkana.
ii. Example / Contoh:
C
2
H
4
(g)
+
HCl(g) C
2
H
5
Cl (g)
Ethene Hydrogen chloride Chloroethane
Etena Hidrogen klorida Kloroetana
Complete the following equation. / Lengkapkan persamaan berikut.
H H H H
H C C H + HCl H C C H
H Cl
f. Addition of Acidified Potassium Manganate(VII), KMnO
4
Solution
Penambahan Larutan Kalium Manganat(VII) Berasid, KMnO
4
i. In this reaction, two hydroxyl, -OH groups are added to the carbon-carbon
double bond
in an alkene
molecule. / Dalam tindak balas ini, dua hidroksil kumpulan -OH ditambah kepada ikatan ganda dua
karbon-
karbon dalam molekul alkena.
ii. An alkene
decolourised
the
purple
solution of acidified potassium manganate(VII). This reaction
is used to
distinguish
a
saturated
hydrocarbon and
unsaturated
hydrocarbon. / Alkena
melunturkan
warna ungu
larutan kalium manganat(VII) berasid. Tindak balas ini digunakan untuk
membezakan hidrokarbon tepu
dan hidrokarbon tak tepu
.
Example / Contoh:
H H H H
H C C H + H
2
O(l) + [O] H C C H
OH OH
Ethene / Etena
Ethane-1, 2-diol
Etana-1, 2-diol
C
2
H
4
(g) + H
2
O(l) + [O] C
2
H
4
(OH)
2
(l)
Complete the following equation. / Lengkapkan persamaan berikut.
C
3
H
6
(g) + H
2
O(l) + [O] C
3
H
6
(OH)
2
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
52
g. Addition of Water (Hydration Reaction) / Penambahan Air (Tindak balas Penghidratan)
i. Alkenes react with water (in the form of steam) at high temperature and pressure in the presence of phosphoric
acid as a catalyst to produce alcohols. / Alkena bertindak balas dengan air (dalam bentuk stim) pada suhu dan tekanan
yang tinggi dalam kehadiran asid fosforik sebagai mangkin untuk menghasilkan alkohol.
Example / Contoh:
H H H H
H
3
PO
4
300C/60 atm
C C C H + H
2
O(g) H C C H
H OH
Ethene / Etena Ethanol / Etanol
C
2
H
4
(g) + H
2
O(g) C
2
H
5
OH(l)
ii. Complete the following equations. / Lengkapkan persamaan berikut.
H H H H H H H H H
H
3
PO
4
300C/60 atm
or
atau
H C C C H + H
2
O(g) H C C C H H C C C H
H H H OH H OH H
Propene / Propena Propan-1-o1 Propan-2-o1
C
3
H
6
(g) H
2
O(g)
H
3
PO
4
300C/60 atm
+ C
3
H
7
OH
C
4
H
8
(g) H
2
O(g)
H
3
PO
4
300C/60 atm
+ C
4
H
9
OH
C
n
H
2n
H
2
O(g)
H
3
PO
4
300C/60 atm
+ C
n
H
2n + 1
OH
Alkene
Alkena
Alcohol
Alkohol
Addition of steam to alkene is a method to manufacture alcohol in industry.
Penambahan stim kepada alkena adalah satu cara untuk menghasilkan alkohol dalam industri.
h. Addition Polymerisation Reaction / Pempolimeran Penambahan
i. In this reaction, small alkene molecules undergo addition reaction at a high pressure of 1 000 atm and temperature
of 200C. Thousands of alkene molecule join together to form a long chain giant molecules called
polymer
.
Dalam tindak balas ini, molekul alkena yang kecil melalui tindak balas penambahan pada tekanan yang tinggi iaitu 1 000 atm
dan suhu 200C. Beribu-ribu molekul alkena bergabung untuk membentuk rantai panjang molekul besar yang dipanggil
polimer
.
ii. The small repeating units of molecules that join together to form polymer are called
monomers
.
Unit kecil molekul-molekul yang berulang bergabung untuk membentuk polimer dipanggil monomer
.
iii. Example / Contoh:
Polymerisation of ethene: / Pempolimeran etena:
H H
n C C
H H
H H
C C
H H n
n is large number up to a
few thousands
n ialah nombor yang besar
sehingga beberapa ribu
Ethene / Etena Polythene / Polietena
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
53
Polymerisation of propene: / Pempolimeran propena:
Propene / Propena
Polypropene / Polipropena
H CH
3
C C
H H n
H CH
3
n C C
H H
5 Conclusion of Addition Reaction of Alkene / Kesimpulan Tindak Balas Penambahan bagi Alkena
Alkene
Alkena, C
n
H
2n
Addition of Halogen
Penambahan halogen, X
2
C
n
H
2n
X
2
Addition of water
Penambahan air, H
2
O
H
3
PO
4
300C/60 atm
Alcohol / Alkohol, C
n
H
2n + 1
OH
Addition of acidified KMnO
4
Penambahan KMnO
4
berasid
C
n
H
2n
(OH)
2
Addition of hydrogen halide
Penambahan hidrogen halida,
HX
C
n
H
2n + 1
X
Addition of hydrogen
Penambahan hidrogen, H
2
Ni, 180C
Alkane / Alkana, C
n
H
2n + 2
Addition Polymerisation
Penambahan pempolimeran
(C
n
H
2n
)
n
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
54
Comparing Properties of Alkane with Alkene (Using hexane and hexene in the laboratory)
Membanding Sifat-sifat Alkana dengan Alkena (Menggunakan heksana dan heksena di dalam makmal)
Chemical
Properties
Sifat kimia
Procedure / Prosedur
Observation / Pemerhatian
Explanation/Chemical
Equation for Reaction
Penerangan/ Persamaaan
kimia untuk tindak balas
Hexane
Heksana
Hexene
Heksena
Sootiness of
flame
Kejelagaan
nyalaan api
Porcelein dish
Mangkuk penyejat
Hexane
Heksana
Hexene
Heksena
F ilter paper / Kertas turas
1.
2 cm
3
of hexane and hexene
are poured into two separated
porcelain dishes
.
Sebanyak 2 cm
3
heksana dan
heksena dituang ke dalam dua
mangkuk penyejat
berbeza.
2. A
lighted wooden splinter
is
used to light up the two liquids.
Kayu uji menyala
digunakan
untuk menyalakan kedua-dua cecair.
3. When the burning occurs, a
piece of
filter paper
is held
above each flame as shown in the
diagram.
Semasa pembakaran berlaku, sehelai
kertas turas
dipegang di atas
setiap nyalaan dalam kedua-dua
piring seperti ditunjukkan dalam
rajah.
4. The flame is observed for its
sootiness
and the amount of
soot
collected on the
two pieces of
filter paper
is
recorded.
Nyalaan tersebut diperhatikan untuk
kejelagaannya
dan kuantiti
jelaga
yang terkumpul pada
dua helai kertas turas
dicatat.
Hexane
burns with
a yellow
sooty flame.
Less soot
collected
on the filter
paper.
Hexene
burns with a
yellow and
very sooty
flame.
More soot
collected
on the filter
paper.
1. Combustion of hexene in
air produces
more
soot compared to hexane.
Pembakaran heksena
dalam udara menghasilkan
lebih
jelaga
berbanding heksana.
2. Percentage of carbon in
hexane, C
6
H
14
Peratusan karbon dalam
heksana, C
6
H
14
=
6(12)
6(12) + 14(1)
100%
= 83.72%
3. Percentage of carbon in
hexene, C
6
H
12
Peratusan karbon dalam
heksena, C
6
H
12
=
6(12)
6(12) + 12(1)
100%
= 85.71%
4. Hexene contains
higher
percentage
of carbon by mass than
hexane.
Heksena mengandungi
persatusan karbon yang lebih
tinggi
berbanding
heksana.
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
55
Reaction with
bromine water
Tindak balas
dengan air
bromin
Bromine water
Air bromin
Hexane
Heksana
1.
2 cm
3
of hexane is poured
into a
test tube
.
Sebanyak 2 cm
3
heksana dituang
ke dalam tabung uji
.
2.
2 3 drops
of bromine water are
added to the hexane.
2 3 titik
air bromin ditambah
ke dalam heksana.
3. The mixture is
shaken
.
Campuran digoncang
.
4. All changes that occur are
recorded.
Semua perubahan yang berlaku
direkodkan.
5. Steps 1 to 4 are repeated using
hexene to replace hexane.
Langkah 1 hingga 4 diulangi
menggunakan heksena untuk
menggantikan heksana.
Brown colour
of bromine
water remains
unchanged.
Brown
colour of
bromine water
decolourised.
1. Hexane
does not
react
with bromine water because
it is an alkane which is
saturated
hydrocarbon.
Heksana tidak
bertindak
balas dengan air bromin
kerana ia adalah hidrokarbon
yang merupakan hidrokarbon
tepu
.
2. Hexene is
unsaturated
hydrocarbon that contains
double
covalent
bond between carbon
atoms, C=C.
Heksena ialah hidrokarbon
tak tepu
yang
mengandungi ikatan kovalen
ganda dua
di antara
atom-atom karbon, C=C.
3.
Addition
reaction
occurs when bromine water
is added to hexene to form
dibromohexane.
Tindak balas penambahan
berlaku apabila air bromin
ditambah kepada heksena,
untuk membentuk
dibromoheksana.
4. Balanced equation:
Persamaan seimbang:
C
6
H
12
+ Br
2
C
6
H
12
Br
2
Hexene 1, 2-dibromohexane
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
56
Reaction with
acidified
potassium
manganate(VII)
solution
Tindak balas
dengan larutan
kalium
manganat(VII)
berasid
Acidified potassium
manganate(VII)
solution
Larutan kalium
manganat(VII) berasid
Hexane
Heksana
1. Pour
2 cm
3
of hexane into
a
test tube
.
Sebanyak 2 cm
3
heksana
dituang ke dalam tabung uji
.
2.
2 3 drops
of acidified
potassium manganate(VII)
solution are added to the hexane.
2 3 titik
larutan kalium
manganat(VII) berasid ditambah ke
dalam heksana.
3. The mixture is
shaken
.
Campuran digoncangkan
.
4. All changes that occur are
recorded.
Semua perubahan yang berlaku
direkodkan.
5. Steps 1 to 4 are repeated using
hexene to replace hexane.
Langkah 1 hingga 4 diulangi
menggunakan heksena untuk
menggantikan heksana.
No change Purple colour
of acidified
potassium
manganate(VII)
solution
decolourised.
1. Hexane
does not react
with acidified potassium
manganate(VII) solution
because it is
saturated
hydrocarbon.
Heksana
tidak bertindak balas
dengan larutan kalium
manganat(VII) berasid
kerana ia adalah hidrokarbon
tepu
.
2. Hexene is
unsaturated
hydrocarbon that contains
double
covalent
bond between carbon
atoms, C=C.
Heksena ialah hidrokarbon
tak tepu
yang
mengandungi ikatan kovalen
ganda dua
di antara
atom-atom karbon, C=C.
3.
Addition
reaction
occurs when acidified
potassium manganate(VII)
solution is added to
hexene to form hexanediol.
Tindak balas penambahan
berlaku apabila larutan
kalium manganat(VII)
berasid ditambah kepada
heksena untuk membentuk
heksanadiol.
4. Balanced equation:
Persamaan seimbang:
C
6
H
12
+ H
2
O + [O] C
6
H
12
(OH)
2
Hexene Hexan-1, 2-diol
Conclusion: / Kesimpulan:
i. Alkane and alkene have
different
chemical properties.
Alkana dan alkena mempunyai sifat-sifat kimia yang berbeza
.
ii. Alkene produces
more
soot than alkane when it is
burnt
in the air.
Alkena menghasilkan lebih banyak
jelaga berbanding alkana apabila dibakar
dalam udara.
iii. Alkene
decolourises
brown colour of bromine water but
alkane
does not.
Alkena melunturkan
warna perang air bromin tetapi alkana
tidak.
iv. Alkene
decolourises
purple colour of acidified potassium manganate(VII) solution but
alkane
does not.
Alkena melunturkan
warna ungu larutan kalium manganat(VII) berasid tetapi alkana tidak
.
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
57
Homologous Series / Siri Homolog
1 Homologous series are groups of carbon compounds that have the following general characteristics:
Siri homolog ialah kumpulan sebatian karbon yang mempunyai sifat-sifat berikut:
a. Members having the same
chemical
properties have the same
functional group
(group that
takes part in a reaction). / Ahli-ahli mempunyai sifat-sifat kimia
yang sama kerana ahli-ahli tersebut mempunyai
kumpulan berfungsi
(kumpulan yang mengambil bahagian dalam tindak balas) yang sama.
b. Members of the series can be represented by a
general
formula.
Ahli-ahli siri boleh diwakili oleh satu formula am
.
c. Members of the series can be prepared by the
same method
.
Ahli-ahli siri boleh disediakan dengan kaedah yang sama
.
d. Two consecutive members in the series are different in relative atomic mass of 14
/ a difference of CH
2
.
Dua ahli yang berturutan dalam siri homolog mempunyai perbezaan jisim atom relatif sebanyak 14
/ perbezaan CH
2
.
e. Members of the series have physical properties that change
gradually as the number of carbon atoms in a
molecule increases
. / Ahli-ahli siri mempunyai sifat fizikal yang berubah
beransur-ansur apabila bilangan atom karbon
dalam molekul meningkat
.
2 Example of homologous series: / Contoh siri homolog:
Homologous series
Siri homolog
General formula / Formula am
Functional group
Kumpulan berfungsi
Type of carbon compound
Jenis sebatian karbon
Alkane
Alkana
C
n
H
2n + 2
, n = 1, 2, 3, CC
Saturated hydrocarbon
Hidrokarbon tepu
Alkene
Alkena
C
n
H
2n
, n = 2, 3, C=C
Unsaturated hydrocarbon
Hidrokarbon tak tepu
Alcohol
Alkohol
C
n
H
2n + 1
OH, n = 1, 2, 3, OH
Non-hydrocarbon
Bukan hidrokarbon
Carboxylic acid
Asid karboksilik
C
n
H
2n + 1
COOH, n = 0, 1, 2, 3, COOH
Non-hydrocarbon
Bukan hidrokarbon
Ester
Ester
C
n
H
2n + 1
COO C
n
H
2n + 1
n = 0, 1, 2, 3, n = 1, 2, 3
COO
Non-hydrocarbon
Bukan hidrokarbon
Naming Alkane and Alkene Using IUPAC Nomenclature / Menamakan Alkana dan Alkena Menggunakan Sistem
Penamaan IUPAC
1 Three parts in the naming of alkane and alkene / Tiga bahagian dalam penamaan alkana dan alkena
a. Prefix : Shows the branch group alkyl group with general formula C
n
H
2n + 1
, attached to the longest carbon chain:
Imbuhan: Menunjukkan kumpulan cabang kumpulan alkil dengan formula am C
n
H
2n + 1
, tercantum dengan rantai karbon
terpanjang:
H H
H C C
H H
ethyl / etil
H
H C H
methyl
metil
b. Stem/root shows the number of carbon atom in the longest carbon chain.
Nama induk/awalan menunjukkan bilangan atom karbon dalam rantai karbon terpanjang.
c. Suffix/ending shows the homologous series: / Akhiran menunjukkan siri homolog:
i. Alkane ane / Alkana ana iii. Alcohol ol / Alkohol ol
ii. Alkene ene / Alkena ena iv. Carboxylic acid oic / Asid karboksilik oik
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
58
2 Steps in naming alkanes and alkenes: / Langkah-langkah penamaan alkana dan alkena:
Step 1: Identify the longest carbon chain, the number of carbon atoms in the longest carbon chain gives the name of the
stem e.g prop, but, pent...
Langkah 1: Kenal pasti rantai karbon terpanjang, bilangan atom karbon dalam rantai karbon terpanjang memberikan nama induk
contohnya prop, but, pent.
Step 2: Identify the branch chain. Determine the prefix and number of carbon atom in the longest carbon chain beginning
with the end of the chain nearer to the branch chain (Number of carbon atom in the longest carbon chain
provided the branch gets the smallest number). The name for the branch chain ends with yl. For alkenes, the
smallest number is given to the carbon with the double bond.
Langkah 2: Kenal pasti rantai cabang. Tentukan imbuhan dan bilangan atom karbon dalam rantai karbon terpanjang bermula dengan
hujung rantai yang berdekatan dengan rantai cabang (Bilangan atom karbon dalam rantai karbon terpanjang dengan
cabang mendapat nombor yang paling kecil). Nama rantai cabang berakhir dengan il. Bagi alkena, nombor terkecil
diberi kepada karbon yang mempunyai ikatan ganda dua.
Step 3: Identify the suffix i.e the functional group or homologous series of the compound.
Langkah 3: Kenal pasti akhiran iaitu kumpulan berfungsi atau siri homolog sebatian.
i. Alkane ane / Alkana ana ii. Alkene ene / Alkena ena
3 Method of writing the IUPAC name: / Kaedah menulis nama IUPAC:
Prefix (Branch)
Imbuhan (Cabang)
Stem (number of carbon atoms in the longest
carbon chain)
Nama induk/awalan (bilangan atom karbon dalam
rantai karbon terpanjang)*
Suffix (functional group/ homologous series)
Akhiran (kumpulan berfungsi/ siri homolog)
- Name and name write close together / Nama dan nama ditulis rapat
- Number and name, write - / Nombor dan nama, tulis -
- Number and number, write , / Nombor dan nombor, tulis ,
4 Example / Contoh:
a. Draw structural formula for the following molecule: / Lukis formula struktur bagi molekul-molekul berikut:
PREFIX (Branches): Methyl branches,
CH
3
are at carbon number 2 and 3. The
numbering of carbon in the longest
carbon is made from the left to give the
smallest number to methyl.
Imbuhan (Cabang): Cabang metil, CH
3
berada pada karbon 2 dan 3. Pernomboran
karbon dalam rantai karbon terpanjang
dibuat daripada kiri untuk memberi nombor
terkecil kepada metil.
STEM (Number of carbon atom
in the longest carbon chain is 5
because the stem is pent).
NAMA INDUK (Bilangan atom
karbon dalam rantai karbon terpanjang
ialah 5 kerana nama induk ialah
pent).
SUFFIX (Homologous series): Suffix
ane indicates homologous series
alkane, longest carbon chain consists of
single covalent bond between carbon
atoms.
AKHIRAN (Siri homolog): Akhiran ana
menandakan siri homolog alkana, rantai
karbon terpanjang yang terdiri daripada
ikatan kovalen tunggal di antara atom-atom
karbon.
2, 3-dimetylpentane
Structural formula: / Formula struktur:
H
H C H
H H H H
H
1
C
2
C
3
C
4
C
5
C H
H H H H
H C H
H
Branches are two methyl, CH
3
at
carbon number 2 and 3
Cabang ada dua metil, CH
3
pada karbon
nombor 2 dan 3
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
59
b. Name the following structural formula using IUPAC system:
Namakan formula struktur berikut menggunakan sistem IUPAC:
i.
STEP 2: Identify branch. It is methyl, CH
3
attached to
carbon number 2. PREFIX is 2-methyl. The numbering
of carbon in the longest carbon is made from the right to
give the smallest number to methyl.
LANGKAH 2: Kenal pasti cabang. Ianya adalah metil, CH
3
terikat pada karbon ke-2. IMBUHAN adalah 2-metil.
Pernomboran karbon pada rantai karbon terpanjang dibuat
dari kanan supaya metil mendapat nombor paling rendah.
STEP 3: Identify homologous series. It is alkane.
SUFFIX is ane.
LANGKAH 3: kenal pasti siri homolog. Ianya adalah
alkana. AKHIRAN adalah ana.
H
H C H
H H H H
H
5
C
4
C
3
C
2
C
1
C H
H H H H H
STEP 1: Identify the longest
carbon chain. It consists of 5
carbons. STEM is pent.
LANGKAH 1: Kenal pasti
ranatai karbon paling panjang.
Ia mengandunngi 5 karbon.
AWALAN adalah pent.
IUPAC name: 2-methylpentane / Nama IUPAC: 2-metilpentana
ii.
STEP 2: Identify branch. Methyl, CH
3
is attached to
carbon number 4. PREFIX is 4-methyl.
LANGKAH 2: Kenal pasti cabang. Ianya adalah metil,
CH
3
terikat pada karbon ke 4. IMBUHAN adalah 4-metil.
STEP 3: Identify the homologous series. It is
alkene, SUFFIX is 2-ene because smallest number is
given to the carbon with double bond.
LANGKAH 3: Kenal pasti siri homolog. Ianya adalah
alkena. AKHIRAN adalah 2-ena kerana nombor paling
kecil diberikan kepada karbon dengan ikatan ganda dua.
H
H C H
H H H H
H
5
C
4
C
3
C
2
C
1
C H
H H H
STEP 1: Identify the
longest carbon chain. It
consists of 5 carbons.
STEM is pent.
LANGKAH 1: Kenal pasti
rantai karbon paling panjang.
Ia mengandunngi 5 karbon.
AWALAN adalah pent.
IUPAC name: 4-methylpent-2-ene / Nama IUPAC: 4-metilpent-2-ena
c. Draw structural formulae for the following molecules: / Lukiskan formula struktur bagi molekul-molekul berikut:
PREFIX (Branches):
Methyl branches, CH
3
are at carbon number
2 and 3
IMBUHAN (Cabang):
Cabang metil, CH
3
adalah pada karbon
nombor 2 dan 3
SUFFIX
(Homologous series):
Suffix ene indicates
homologous series
alkene: double bond
is at carbon number 1
AKHIRAN (Siri
homolog): Akhiran
ena menandakan siri
homolog alkena: ikatan
ganda dua pada karbon
nombor 1
2, 3-dimetylbut-1-ene
STEM (Number of
carbon atom in the
longest carbon chain
is 4 because the stem
is but)
NAMA INDUK
(Bilangan atom karbon
dakam rantai karbon
terpanjang adalah 4
kerana nama induk ialah
but)
Structural formula: / Formula struktur:
H
H C H
H H
H C C C C
H H H
H C H
H
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
60
EXERCISE / LATIHAN
Name the following compounds. / Namakan sebatian-sebatian berikut.
i.
H H H H H
H C C C C C H
H H H H
H C H
H
2-metylpentane
ii.
H
H C H
H H H H H
H C C C C C C H
H H H H H
H C H
H
2, 3-dimetylhexane
iii.
H
H H C H
H C H
H H H H
H C C C C C C H
H H H H H
H C H
H
2, 3, 4-trimetylhexane
iv.
H
H C H
H H H H
H C C C C C H
H H H
4-metylpent-2-ene
v.
H
H C H
H H H H H
H C C C C C C H
H H H
H C H
H
4, 5-dimetylhex-2-ene
vi.
H
H C H
H C H
H H H H H H
H C C C C C C C H
H H H H H
3-ethylhept-2-ene
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
61
Isomerism / Keisomeran
1 Atoms in organic compound can be bonded or arranged in different ways:
Atom-atom dalam sebatian organik boleh terikat atau tersusun dalam pelbagai cara:
a.
Molecular
formula shows the type and number of atoms in a molecular compound.
Formula molekul
menunjukkan jenis dan bilangan atom dalam sebatian molekul.
b.
Structural
formula shows the type and number of atoms for each element, and how the atoms are bonded to
one and another in a compound. / Formula struktur
menunjukkan jenis dan bilangan atom dalam setiap unsur, dan
bagaimana atom-atom terikat di antara satu sama lain dalam suatu sebatian.
Example / Contoh:
Molecular formula for propane:
Formula molekul bagi propana:
Structural formula for propane:
Formula struktur bagi propana:
C
3
H
7
H H H
H C C C H
H H H
2 Isomerism is the phenomenon where a compound has the
same
molecular formula but
different
structural
formula. / Keisomeran ialah fenomena di mana suatu sebatian mempunyai formula molekul yang sama
tetapi formula
struktur yang berbeza
.
3 The carbon atoms in a structural formula can be joined in a straight chain or branched chain.
Atom-atom karbon dalam formula struktur boleh digabungkan dalam rantai lurus atau rantai bercabang.
4 Complete the following table by constructing the structural formulae for alkanes in a straight chain or any possible
branched chain structural formulae. Name each structural formula using IUPAC system, based on the number of
structural for each of molecular formula, determine whether the molecule has isomers or no isomer. / Lengkapkan jadual
berikut dengan membina formula struktur bagi alkana dalam rantai lurus atau formula struktur bagi rantai bercabang yang mungkin.
Namakan formula struktur menggunakan sistem IUPAC, berdasarkan bilangan struktur bagi setiap formula molekul, tentukan sama
ada molekul tersebut mempunyai isomer atau tidak.
Molecular
formula
Formula
molekul
Structural formula and IUPAC name
Formula struktur dan nama IUPAC
Number of structural
formulae
Bilangan formula
struktur
Number of
isomers
Bilangan isomer
CH
4
H
H C H methane
H
1 No isomer
C
2
H
6
H H
H C C H ethane
H H
1 No isomer
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
62
C
3
H
8
H H H
H C C C H propane
H H H
1 No isomer
C
4
H
10
H H H H
H C C C C H
H H H H
H H H
H C C C H
H H
H C H
H
2 2 isomers
n-butane 2-methylpropane
C
5
H
12
H H H H H
H C C C C C H
H H H H H
n-pentane
H H H H
H C C C C H
H H H
H C H
H
2-methylbutane
3 3 isomers
H
H C H
H H
H C C C H
H H
H C H
H
2, 2-dimethylpropane
5 The first
three
members of alkane
do not have
isomers because each molecule has only
one
structural
formula. /
Tiga
ahli pertama alkana
tidak mempunyai
isomer kerana setiap molekul mempunyai
satu
formula struktur
sahaja.
6 Isomerism in alkane starts from
butane, C
4
H
10
. / Keisomeran dalam alkana bermula daripada
butana, C
4
H
10
.
7 Complete the following table by constructing the structural formulae for alkenes in a straight chain or any possible
branched chain structural formulae. Name each structural formula using IUPAC system, based on the number of
structural formulae for each of molecular formula, determine whether the molecule has isomers or no isomer.
Lengkapkan jadual berikut dengan membina formula struktur bagi alkena dalam rantai lurus atau formula struktur bagi rantai
bercabang yang mungkin. Namakan setiap formula struktur menggunakan sistem IUPAC, berdasarkan bilangan formula struktur
bagi setiap formula molekul, tentukan sama ada molekul tersebut mempunyai isomer atau tidak.
Molecular
formula
Formula
molekul
Structural formula and IUPAC name
Formula struktur dan nama IUPAC
Number of structural
formulae
Bilangan formula
struktur
Number of
isomers
Bilangan isomer
C
2
H
4
H H
C C
H H
ethene
1 No isomer
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
63
C
3
H
6
H H H
H C C C H
H
propene
1 No isomer
C
4
H
8
H H H H
H C C C C H
H H H H
n-but-1-ene
H H H H
H C C C C H
H H
n-but-2-ene
H
H C H
H H
H C C C H
H
2-methylprop-1-ene
3 3 isomers
8 The isomers have
similar
chemical properties but
different
in physical properties such as melting and boiling
points. / Isomer-isomer mempunyai sifat-sifat kimia yang
sama
tetapi sifat-sifat fizikal yang
berbeza
seperti takat lebur
dan didih.
9 Isomerism in alkene starts from
butene, C
4
H
8
. / Keisomeran dalam alkana bermula daripada
butena, C
4
H
8
.
10 The number of isomers increases as the number atom per molecule increases.
Bilangan isomer meningkat apabila bilangan atom per molekul meningkat.
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
64
NON-HYDROCARBON / BUKAN HIDROKARBON
ANALYSING ALCOHOL / MENGANALISIS ALKOHOL
Write the general formula of alcohols, identify the functional group, list the names and molecular formulae, draw structural
formulae and name isomers using IUPAC nomenclature.
Menulis formula am alkohol, mengenal pasti kumpulan berfungsi, menyenaraikan nama dan formula molekul, melukis formula
struktur dan menamakan isomer menggunakan sistem IUPAC.
Describe the preparation of ethanol in the laboratory and industrial production of alcohol.
Menghuraikan penyediaan etanol di dalam makmal dan penghasilan alkohol dalam industri.
State the physical properties of ethanol. / Menyatakan sifat-sifat fzikal etanol.
Describe an activity to investigate chemical properties of ethanol in terms of combustion, oxidation and dehydration.
Menghuraikan aktiviti untuk mengkaji sifat-sifat kimia etanol dari segi pembakaran, pengoksidaan dan pendehidratan.
Predict the chemical properties of other members of alcohol. / Meramal sifat-sifat kimia bagi ahli-ahli alkohol yang lain.
Explain with example on the use of alcohol in everyday life.
Menerangkan kegunaan alkohol dalam kehidupan seharian berserta dengan contoh.
Explain the effects of misuse and abuse of alcohol. / Menerangkan kesan-kesan penyalahgunaan alkohol.
ANALYSING CARBOXYLIC ACID / MENGANALISIS ASID KARBOKSILIK
State the general formulae, identify the functional group, list the names and molecular formulae of the frst four
members, draw structural formulae and name using IUPAC nomenclature.
Menyatakan formula am, mengenal pasti kumpulan berfungsi, menyenaraikan nama dan formula molekul bagi empat ahli
pertama dan menamakan menggunakan sistem penamaan IUPAC.
Describe the preparation of carboxylic acid by oxidation of alcohol.
Menghuraikan penyediaan asid karboksilik dengan cara pengoksidaan alkohol.
State the physical properties of carboxylic acid. / Menyatakan sifat-sifat fzikal asid karboksilik.
Describe the activities to investigate chemical properties of ethanoic acid through:
Menghuraikan aktiviti untuk menyiasat sifat-sifat kimia asid etanoik melalui:
i. Reaction with metal, metal carbonates and metal oxides (acidic properties).
Tindak balas dengan logam, logam karbonat dan logam oksida (sifat-sifat berasid).
ii. Esterifcation reactions with alcohol and naming of esters.
Tindak balas pengesteran dengan alkohol dan penamaan ester.
Predict the chemical properties for other member of carboxylic acid.
Meramal sifat-sifat kimia bagi ahli asid karboksilik yang lain.
Explain with examples the uses of carboxylic acids in everyday life.
Menerangkan dengan contoh kegunaan asid karboksilik dalam kehidupan seharian.
ANALYSING ESTERS / MENGANALISIS ESTER
Carry out an activity to derive general formulae of esters and identify the functional group, draw structural formulae,
name them using the IUPAC nomenclature and write equations for esterifcation reaction.
Menjalankan aktiviti untuk memperoleh formula am bagi ester dan mengenal pasti kumpulan berfungsi, melukis formula
struktur, menamakan ester menggunakan sistem IUPAC dan menulis persamaan untuk tindak balas pengesteran.
Describe the preparation of ester in the laboratory.
Menerangkan penyediaan ester di dalam makmal.
State the physical properties of ester. / Menyatakan sifat-sifat fzik ester.
Collect data on natural sources of ester and uses of ester in everyday life.
Mengumpulkan data mengenai sumber semula jadi ester dan kegunaannya dalam kehidupan seharian.
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
65
Alcohol / Alkohol
1 Alcohols are organic compounds that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms (Non-hydrocarbon). The general
formula for alcohol is C
n
H
2n + 1
OH in which n is 1, 2, 3 / Alkohol ialah sebatian organik yang mengandungi atom karbon,
hidrogen dan oksigen (bukan hidrokarbon). Formula am bagi alkohol ialah C
n
H
2n + 1
OH di mana n ialah 1, 2, 3
2 Each member of alcohol series contains hydroxyl functional group (OH) which is covalently bonded to the carbon
atom, / Setiap ahli siri alkohol mengandungi kumpulan berfungsi hidroksil (OH) yang terikat secara kovalen dengan atom
karbon,
C OH
3 Naming alcohol using IUPAC nomenclature: / Menamakan alkohol menggunakan sistem IUPAC:
Step 1 : Determine the number of carbon atoms in the longest carbon chain which contains the hydroxyl group OH.
obtain the name of alkane with the same number of carbon atom as alcohol.
Langkah 1 : Tentukan bilangan atom karbon dalam rantai karbon terpanjang yang mengandungi kumpulan hidroksil OH.
dapatkan nama alkana yang mengandungi bilangan atom karbon yang sama dengan alkohol.
Step 2 : Replace the ending e from the name of alkane with ol.
(e.g: Methane methanol, Propane propanol)
Langkah 2 : Gantikan akhiran a daripada nama alkana dengan ol.
(cth: Metana metanol, Propana propanol)
Step 3 : Number the carbon atom in the longest carbon chain which is joined to the hydroxyl group OH with
the smallest number.
the number is placed in front of the ol to indicate which carbon atom the hydroxyl group is attached to.
Langkah 3 : Nomborkan bilangan atom karbon dalam rantai karbon terpanjang yang terikat dengan kumpulan hidroksil, OH
dengan nombor terkecil.
nombor diletakkan di hadapan ol untuk menandakan atom karbon yang terikat dengan kumpulan hidroksil.
EVALUATING FATS / MENGANALISIS LEMAK
State what oils, fats, saturated and unsaturated fats are, and the differences between fats and oils.
Menyatakan maksud minyak, lemak, lemak tepu dan lemak tak tepu, dan perbezaan di antara lemak dan minyak.
Compare and contrast between saturated and unsaturated fats and the process of changing unsaturated fats to saturated
fats. / Membanding dan membezakan di antara lemak tepu dengan lemak tak tepu dan proses penukaran lemak tak tepu kepada
lemak tepu.
State the importance of oils and fats for body processes and the sources of fats and oils.
Menyatakan kepentingan minyak dan lemak untuk proses badan dan sumber lemak dan minyak.
Describe the effect of eating food high in fats and oils.
Menghuraikan kesan memakan makanan yang tinggi dengan lemak dan minyak.
Describe the industrial extraction of palm oil. / Menghuraikan proses industri dalam penghasilan minyak sawit.
ANALYSING NATURAL RUBBER / MENGANALISIS GETAH SEMULA JADI
List the example of natural polymers and their monomers. / Menyenaraikan contoh polimer semula jadi dan monomernya.
Write the structural formulae of natural rubber (monomer and polymer).
Menulis struktur formula getah semula jadi (monomer dan polimer).
State the properties of natural rubber and its uses. / Menyatakan sifat-sifat getah semula jadi dan kegunaannya.
Describe the coagulation process of latex and method used to prevent latex from coagulating.
Menghuraikan proses penggumpalan lateks dan kaedah yang digunakan untuk mencegah lateks daripada menggumpal.
Describe the vulcanisation of rubber and how the presence of sulphur atoms changes the properties of vulcanised
rubber. / Menghuraikan pemvulkanan getah dan bagaimana kehadiran atom sulfur mengubah sifat-sifat getah tervulkan.
Compare and contrast the properties of vulcanised and unvulcanised rubber.
Membanding dan membezakan sifat-sifat getah tervulkan dan tak tervulkan.
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
66
Example / Contoh:
Butan-2-ol the OH is attached at the second carbon from the end. / Butan-2-ol OH terikat dengan karbon kedua
daripada hujung.
The structural formula: / Formula struktur:
H H H H
H C C C C H
H H H OH
Step 4 : For alcohols with branches, write the names of all the branches as prefix.
Langkah 4 : Bagi alkohol-alkohol yang bercabang, tulis nama semua cabang sebagai Imbuhan.
PREFIX is methyl, CH3. It is attached to
carbon 3. The numbering of carbon in the longest
carbon is made from the right to give the smallest
number to the carbon with hydroxyl, OH.
IMBUHAN ialah metil, CH
3
. Ia bersambung
dengan karbon 3. Pernomboran karbon dalam
rantai karbon terpanjang dibuat daripada kanan
untuk memberi nombor terkecil kepada karbon
yang bersambung dengan hidroksil, OH.
3-methylbutan-2-ol
Longest carbon chain consists of 4 carbon with the presence of
hydroxyl at carbon number 2. STEM is butan. Homologous series
is alcohol, SUFFIX is '2ol', number 2 is to indicate the position of
hydroxyl,
OH in the longest carbon chain.
Rantai karbon terpanjang terdiri daripada 4 karbon dengan
kehadiran hidroksil pada karbon nombor 2. NAMA INDUK ialah
butan. Siri homolog ialah alkohol, AKHIRAN ialah 2ol,
nombor 2 adalah untuk menandakan kedudukan hidroksil, OH
dalam rantai karbon terpanjang.
H
H C H
H H H
H
4
C
3
C
2
C
1
C H
H H H OH
Name the following compound using IUPAC nomenclature: / Namakan sebatian berikut mengikut sistem penamaan IUPAC:
H
H C H
H H H H
H C C C C C H
H H OH H
H C H
H C H
H
IUPAC name / Nama IUPAC: 2, 4-dimetylhexan-2-ol
4 Isomerism in alcohol: / Keisomeran dalam alkohol:
a. Isomers are molecules that have same molecular formulae but different structural formula.
Isomer ialah molekul-molekul yang mempunyai formula molekul yang sama tetapi formula struktur yang berbeza.
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
67
b. Complete the following table: / Lengkapkan jadual berikut:
Alcohol
Alkohol
Molecular
formula
Formula
molekul
Structural formula and IUPAC name
Formula struktur dan nama IUPAC
Number of
isomers
Bilangan isomer
Methanol
Metanol
CH
3
OH
H
H C OH Methanol
H
No isomer
Ethanol
Etanol
C
2
H
5
OH
H H
H C C OH Ethanol
H H
No isomer
Propanol
Propanol
C
3
H
7
OH
H H H
H C C C OH Propan-1-ol
H H H
H H H
H C C C H Propan-2-ol
H OH H
2 isomers
Butanol
Butanol
C
4
H
9
OH
H H H H
H C C C C H
H H H OH
n-butan-1-ol
H
H C H
H H
H C C C OH
H H H
2-methylpropan-1-ol
4 isomers
H H H H
H C C C C H
H H OH H
n-butan-2-ol
H
H C H
H H
H C C C H
H OH H
2-methylpropan-2-ol
c.
Methanol
and
ethanol
do not have isomers because each molecule only has
one
structural formula.
Metanol
dan
etanol
tidak mempunyai isomer kerana setiap molekul mempunyai
satu
formula struktur sahaja.
d. Isomerism in alcohol begins with
propanol
. / Keisomeran dalam alkohol bermula dengan
propanol
.
5 Two methods in preparing ethanol: / Dua kaedah penyediaan etanol:
a. Preparation of ethanol, C
2
H
5
OH in the laboratory (Fermentation of glucose).
Penyediaan etanol, C
2
H
5
OH di dalam makmal (Penapaian glukosa).
b. Industrial production of ethanol, C
2
H
5
OH (Hydration of ethene).
Penghasilan etanol, C
2
H
5
OH dalam industri (Penghidratan etena).
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
68
6 Preparation of ethanol, C
2
H
5
OH in the laboratory (Fermentation of glucose)
Penyediaan etanol, C
2
H
5
OH di dalam makmal (Penapaian glukosa)
a. Fermentation is a process in which microorganism such as yeast acts on carbohydrates (sugar or starch) to produce
ethanol and carbon dioxide.
Penapaian ialah suatu proses di mana mikroorganisma seperti yis bertindak ke atas karbohidrat (gula atau kanji) untuk
menghasilkan etanol dan karbon dioksida.
b. Yeast is added to glucose solution (or fruit juices such as grape/pineapple juice) and left in a warm place for a three
days in the absence of oxygen. Yeast contains enzyme which breaks down the sugar/starches into glucose and then
to ethanol and carbohydrate. / Yis ditambah ke dalam larutan glukosa (atau jus buah seperti jus anggur/nanas) dan dibiarkan
dalam tempat yang hangat untuk tiga hari tanpa kehadiran oksigen. Yis mengandungi enzim yang memecahkan gula/kanji
kepada glukosa dan kemudiannya kepada etanol dan karbohidrat.
Fermentation equation: / Persamaan penapaian:
C
6
H
12
O
6 Yeast / Yis
2C
2
H
5
OH(aq)
+ 2CO
2
(g)
Glucose / Glukosa Ethanol / Etanol
c. The ethanol is purified by fractional distillation. / Etanol ditulenkan melalui penyulingan berperingkat.
7 Industrial production of ethanol, C
2
H
5
OH (Hydration of ethene):
Penghasilan etanol, C
2
H
5
OH dalam industri (Penghidratan etena):
Alkene is reacted with steam (H
2
O) at 300C and 60 atm pressure in the presence of phosphoric acid as a catalyst.
(refer to chemical properties of alkene): / Alkena ditindak balaskan dengan stim (H
2
O) pada 300C dan tekanan 60 atm dalam
kehadiran asid fosforik sebagai mangkin. (rujuk sifat-sifat kimia alkena):
C
2
H
4
(g)
+
H
2
O(g)
H
3
PO
4
300C/60 atm
C
2
H
6
OH(l)
Ethanol / Etanol Ethene / Etena Steam / Stim
8 Physical Properties of Alcohol: / Sifat-sifat Fizikal Alkohol:
a. Alcohols with one to eleven carbon atoms per molecule exist as liquids.
Alkohol yang mengandungi satu hingga sebelas atom karbon per molekul wujud sebagai cecair.
b. Methanol
, ethanol
and propanol
mix with water in all proportions. Solubility in water decreases
with increasing of molecular size. /
Metanol
,
etanol
dan
propanol
bercampur dengan air dalam semua kadar.
Keterlarutan dalam air berkurang dengan peningkatan saiz molekul.
c. Ethanol is a colourless liquid, mixes with water in all proportions. It is less dense than water and its boiling point is
78C at 1 atm. / Etanol ialah cecair tanpa warna, bercampur dengan air dalam semua kadar, kurang tumpat daripada air dan
takat didihnya ialah 78C pada 1 atm.
d. Alcohols have low boiling points. The boiling points of alcohols increase with the increasing in the number of carbon
atoms in a molecule. / Alkohol mempunyai takat didih yang rendah. Takat didih alkohol meningkat dengan peningkatan
atom-atom karbon dalam molekul.
9 Chemical Properties of Alcohol: / Sifat-sifat Kimia Alkohol:
a. All alcohols have similar chemical properties due to the presence of the hydroxyl group, OH as a functional group.
Semua alkohol mempunyai sifat-sifat kimia yang sama kerana kehadiran kumpulan hidroksil, OH sebagai kumpulan berfungsi.
Chemical reaction of alcohols are: / Tindak balas kimia bagi alkohol adalah:
i. Combustion of alcohol / Pembakaran alkohol
ii. Oxidation of alcohol / Pengoksidaan alkohol
iii. Dehydration of alcohol / Pendehidratan alkohol
10 Combustion of Alcohol / Pembakaran alkohol
a. Alcohol burns in excess supply of oxygen to produce water
and carbon dioxide
. Alcohols burn easily
with a blue flame and without producing soot
.
Alkohol terbakar dalam bekalan oksigen yang berlebihan untuk menghasilkan
air
dan
karbon dioksida
.
Alkohol membakar dengan senang, dengan nyalaan biru dan tidak menghasilkan
jelaga
.
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
69
Example / Contoh: Combustion of ethanol / Pembakaran etanol
C
2
H
5
OH + 3O
2
2CO
2
+ 3H
2
O
Combustion of ethanol releases large amount of heat (ethanol is suitable for use as a fuel).
Pembakaran etanol membebaskan kuantiti haba yang besar (etanol sesuai digunakan sebagai bahan bakar).
b. Balance the following equation: / Seimbangkan persamaan berikut:
C
3
H
7
OH +
9 __
2
O
2
3
CO
2
+
4
H
2
O
Balancing the equations:
Mengimbangkan persamaan:
Step 1: Balance C / Langkah 1: Seimbangkan C
Step 2: Balance H / Langkah 2: Seimbangkan H
Step 3: Balance O, can use fraction.
Langkah 3: Seimbangkan O, gunakan pecahan
C
4
H
9
OH +
6
O
2
4
CO
2
+
5
H
2
O
C
5
H
11
OH +
15 __
2
O
2
5
CO
2
+
6
H
2
O
C
6
H
13
OH +
9
O
2
6
CO
2
+
7
H
2
O
11 Oxidation of Alcohol / Pengoksidaan Alkohol
a. Alcohols are oxidised to form carboxylic acid with presence of a suitable oxidising agent.
Alkohol dioksidakan untuk membentuk asid karboksilik dalam kehadiran agen pengoksidaan yang sesuai.
The common oxidizing agent used in the oxidation of alcohols are: / Agen pengoksidaan yang biasa digunakan adalah:
i. Acidified potassium manganate(VII) solution / Larutan kalium manganat(VII) berasid
ii. Acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution / Larutan kalium dikromat(VI) berasid
b. Both agents are represented as 2[O] in the chemical equation. One oxygen atom joins the alcohol molecule to
form C=O and the other oxygen atom joins to the two hydrogen atoms that are removed from the alcohol to
form H
2
O. / Kedua-dua agen ini diwakili sebagai 2[O] dalam persamaan kimia. Satu atom oksigen bergabung dengan
molekul alkohol untuk membentuk C=O dan atom oksigen yang lain bergabung dengan dua atom hidrogen yang terkeluar
daripada alkohol untuk membentuk H
2
O.
c. Oxidation of alcohol is the process where an alcohol molecule loses two H atoms and receives one O atom. / Pengoksidaan
alkohol ialah proses di mana satu molekul alkohol hilang dua atom H dan menerima satu atom O.
Example Oxidation of ethanol / Contoh Pengoksidaan etanol, C
2
H
5
OH:
H H
H C C H
H OH
Two hydrogen atoms are removed and
replaced by one oxygen atom
Dua atom hidrogen dibuang dan
digantikan dengan satu atom oksigen
H O
H C C
H OH
+
H
2
O
Water / Air
+ 2[O]
CH
3
CH
2
OH + 2[O] CH
3
COOH +
H
2
O
Water / Air
or / atau
C
2
H
5
OH
Ethanol / Etanol
+ 2[O]
CH
3
COOH
Ethannoic acid
Asid etanoik
+
H
2
O
Water / Air
d. Complete the following equations for oxidation of various alcohol:
Lengkapkan persamaan berikut bagi pengoksidaan pelbagai jenis alkohol:
i. Oxidation of propanol / Pengoksidaan propanol:
CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
OH + 2[O]
CH
3
CH
2
COOH + H
2
O
or / atau
C
3
H
7
OH + 2[O]
C
2
H
5
COOH + H
2
O
Propanol / Propanol Propanoic acid / Asid propanoik
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
70
ii. Oxidation of butanol / Pengoksidaan butanol:
CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
OH + 2[O]
CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
COOH + H
2
O
or / atau
C
4
H
9
OH + 2[O]
C
3
H
7
COOH + H
2
O
Butanol / Butanol Butanoic acid / Asid butanoik
e. Alcohol undergoes oxidation to produce carboxylic acid (Oxidation of alcohol is used to prepare carboxylic
acid). / Alkohol mengalami pengoksidaan untuk menghasilkan asid karboksilik (Pengoksidaan alkohol digunakan untuk
menyediakan asid karboksilik).
C
n
H
2n+1
OH + 2[O] C
n
H
2n+1
COOH + H
2
O
n = 1, 2, 3 n = 0, 1, 2, 3.
EXERCISE / LATIHAN
Describe how ethanol can be oxidised in the laboratory with different oxidising agent. In your answer, include all the
observations. / Huraikan bagaimana etanol boleh dioksidakan di dalam makmal dengan agen pengoksidaan yang berbeza. Dalam
jawapan anda, sertakan semua pemerhatian.
Set-up of apparatus:/ Susunan radas:
Boiling tube / Tabung didih Delivery tube / Salur penghantar
Acidified potassium manganate(VII), KM
n
O
4
solution and ethanol, C
2
H
5
OH
Larutan kalium manganate(VII), KM
n
O
4
berasid dan etanol, C
2
H
5
OH Heat
Panaskan
Bikar
Beaker
Cold water
Air sejuk
Test tube
Tabung uji
Hasil sulingan
Distillate
Procedure: / Kaedah:
i. Pour 2 cm
3
of potassium manganate(VII) solution into a boiling tube.
Tuangkan
2 cm
3
larutan kalium manganate(VII) ke dalam tabung didih.
ii. Add 10 drops of concentrated sulphuric acid. / Tambahkan 10 titik asid sulfurik pekat.
iii. Heat
the solution gently. /
Panaskan
larutan tersebut perlahan-lahan.
iv. Add 1 cm
3
of ethanol
drop by drop into the boiling tube.
Tambahkan 1 cm
3
etanol
titik demi titik ke dalam tabung didih.
v. Delivery tube is connected to the boiling tube as shown in the diagram. The mixture is heated until it boils
.
Salur penghantar disambung kepada tabung didih seperti yang ditunjukkan di dalam rajah. Campuran dipanaskan sehingga
mendidih
.
vi. The distillate
is collected in a test tube and it is tested with a blue
litmus paper. / Hasil
sulingan
dikumpulkan di dalam tabung uji dan diuji dengan kertas litmus
biru
.
vii. Steps 1 6 are repeated by replacing acidified potassium(VII) with acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution.
Langkah 1 6 diulangi dengan menggantikan larutan kalium manganat(VII) berasid dengan larutan kalium dikormat(VI)
berasid.
Observation / Pemerhatian:
i. The purple
colour of acidified potassium manganate(VII) solution turns colourless
. / Warna
purple
larutan kalium manganat(VII) berasid bertukar menjadi
tanpa warna
.
ii. The orange
colour of acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution turns green
. / Warna
jingga
larutan kalium dikromat(VI) bertukar menjadi
hijau
.
iii. The distillate smells like a vinegar
. / Hasil sulingan berbau seperti
cuka
.
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
71
iv. The distillate
turns blue
litmus paper to red
.
Hasil
sulingan
menukar warna kertas litmus
biru
kepada
merah
.
Conclusion / Kesimpulan:
Oxidation of ethanol with oxidising agents
such as acidified potassium manganate(VII) solution or acidified
potassium dichromate(VI) solution produces ethanoic acid. / Pengoksidaan etanol dengan
agen pengoksidaan
seperti
larutan kalium manganat(VII) berasid atau larutan kalium dikromat(VI) berasid menghasilkan asid etanoik.
C
2
H
5
OH
Ethanol / Etanol
+ 2[O]
CH
3
COOH
Ethanoic acid / Asid etanoik
+
H
2
O
Water / Air
12 Dehydration of Alcohol / Pendehidratan Alkohol
a. Dehydration of an alcohol involves the removal of water molecule from each of alcohol molecule to produce
corresponding alkene. / Pendehidratan alkohol melibatkan penyingkiran molekul air daripada setiap molekul alkohol untuk
menghasilkan alkena yang setara.
b. Water molecule from the alcohol molecule is removed by a heated catalyst such as:
Molekul air daripada molekul alkohol disingkir oleh mangkin yang telah dipanaskan dengan kuat seperti:
i. Porcelain chips / Serpihan porselin
ii. Aluminium oxide / Aluminium oksida
iii. Concentrated sulphuric acid at 180C / Asid sulfurik pekat pada 180C
iv. Concentrated phosphoric acid at 210C / Asid fosforik pekat pada 210C
c. The removal of water molecule from alcohol results in the formation of C=C.
Penyingkirann molekul air daripada alkohol menyebabkan pembetukan C=C.
Example / Contoh: Dehydration of ethanol / Pendehidratan etanol, C
2
H
5
OH
H H
H C C H
H OH
Porcelain chips / Serpihan porselin
Porcelain chips / Serpihan porselin
H H
H C C H
+ H
2
O
Hydroxyl group is removed together with a hydrogen atom from an adjacent carbon
atom to form water, H
2
O / Kumpulan hidroksil dibuang bersama dengan atom hidrogen
daripada atom karbon bersebelahan untuk membentuk air, H
2
O
C
2
H
4
+
H
2
O
Ethene / Etena Water / Air
C
2
H
5
OH
Ethanol / Etanol
d. Complete the following equations: / Lengkapkan persamaan-persamaan berikut:
i. Dehydration of propanol / Pendehidratan propanol
C
3
H
7
OH
Propanol / Propanol
Porcelain chips / Serpihan porselin
C
3
H
6
+
H
2
O
Propene / Propena Water / Air
ii. Dehydration butanol / Pendehidratan butanol
C
3
H
7
OH
Butanol / Butanol
Porcelain chips / Serpihan porselin
C
4
H
8
+
H
2
O
Butene / Butena Water / Air
e. Dehydration of alcohol produces alkene
. / Pendehidratan alkohol menghasilkan
alkena
.
C
n
H
2n + 1
OH
n = 2, 3 .......
Porcelain chips / Serpihan porselin
C
n
H
2n
+
H
2
O
n = 2, 3, 4 .... Water / Air
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
72
EXERCISE / LATIHAN
Describe an experiment to prepare ethene from ethanol in the laboratory. In your answer, include the apparatus set-up for the
experiments, procedure and all the observations. / Huraikan eksperimen untuk menyediakan etena daripada etanol di dalam makmal.
Dalam jawapan anda, sertakan susunan alat radas untuk eksperimen ini, prosedur dan semua pemerhatian.
Set-up of apparatus: / Susunan alat radas:
Glass wool
soaked with
ethanol
Porcelein chips
Heat
Gas
Water
Procedure: / Prosedur:
i. Place some glass wool
in a boiling tube
. / Letakkan
kapas kaca
di dalam
tabung didih
.
ii. Pour 2 cm
3
of ethanol into the boiling tube to soak the glass wool.
Tuangkan
2 cm
3
etanol ke dalam tabung didih untuk membasahkan kapas kaca.
iii. Some porcelain chips
are placed in the middle of section of the boiling tube
as shown in the diagram.
Sebahagian
serpihan porselin
diletakkan di bahagian tengah
tabung didih
seperti ditunjukkan dalam rajah.
iv. The porcelain chips
are heated strongly
. The glass wool is then warm
gently so that ethanol
vaporises and the vapour is passed through the heated porcelain chips
.
Serpihan porselin
dipanaskan dengan
kuat
. Kapas kaca tersebut kemudiaanya
dipanaskan
perlahan-lahan supaya
etanol menyejat dan wap tersebut melalui
serpihan porselin
yang dipanaskan itu.
v. Collect the gas released in two test tubes as shown in the diagram.
Kumpulkan gas yang dibebaskan dalam dua tabung uji seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam rajah di atas.
vi. Test the gas with: / Uji gas tersebut dengan:
a. a lighted wooden splinter. / kayu uji menyala.
b. bromine water. / air bromin.
Observation: / Pemerhatian:
i. A colourless
gas is collected in the test tube. / Gas
tanpa warna
terkumpul dalam tabung uji.
ii. The gas burns with yellow sooty
flame. / Gas tersebut membakar dengan nyalaan
kuning berjelaga
.
iii. The gas changed the brown
colour of bromine water to colourless
. / Gas tersebut menukar warna
perang
air bromin kepada
tanpa warna
.
Conclusion: / Kesimpulan:
The product is an alkene. Dehydration of ethanol produces ethene: / Hasil ialah alkena. Pendehidratan etanol menghasilkan
etana:
C
2
H
5
OH
Ethanol / Etanol
Porcelain chips / Serpihan porselin
C
2
H
4
+ H
2
O
Butene / Etena Water / Air
13 Uses of alcohol / Kegunaan alkohol
a. As a fuel because combustion of alcohol produces water and carbon dioxide. It releases a lot of heat energy
(exothermic). / Sebagai bahan bakar kerana pembakaran alkohol menghasilkan air dan karbon dioksida dan membebaskan
tenaga haba yang banyak (eksotermik).
b. As a solvent to dissolve many organic compounds such as paint, varnish, lacquer and perfume. / Sebagai pelarut untuk
melarutkan sebatian organik seperti cat, varnis dan minyak wangi.
c. In medical field, alcohol is used as a solvent for the preparation of certain medicines. Ethanol for example is used
as an antiseptic and an ingredient in cough mixtures. / Dalam bidang perubatan, alkohol digunakan untuk menyediakan
ubat yang tertentu. Sebagai contoh etanol digunakan sebagai antiseptik dan ramuan untuk ubat batuk.
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
73
d. In the production of cosmetics, alcohol is used as the main component in production of cosmetics, creams, lotions,
soaps and others. / Dalam penghasilan kosmetik, alkohol digunakan sebagai bahan utama dalam penghasilan kosmetik, krim,
losen, sabun dan lain-lain.
14 Alcohol misuse and abuse / Penyalahgunaan alkohol
a. Used in alcoholic beverages. Excessive drinking of alcoholic beverages causes drunk driving and accidents on
the road. / Digunakan dalam minuman beralkohol. Minum secara berlebihan menyebabkan pemanduan secara mabuk dan
kemalangan jalan raya.
b. Excessive drinking can be fatal due to poisoning.
Minum secara berlebihan adalah merbahaya kerana kemungkinan untuk keracunan.
c. Alcoholism affects the well being of an individual and the family concerned.
Ketagihan dengan alkohol memberi kesan terhadap kesihatan seorang individu dan juga keluarga.
EXERCISE / LATIHAN
Complete the following chart: / Lengkapkan carta berikut:
GLUCOSE / GLUKOSA
Fermentation
Penapaian
Ethanol
Addition of water
Penambahan air, H
2
O
H
3
PO
4
300C/60 atm
Ethene
Etena
Carbon dioxide
and
water
Combustion in excess oxygen
Pembakaran dalam oksigen berlebihan
Ethanoic acid
and
water
Ethene
and
water
Oxidation by an
oxidising agent
Pengoksidaan oleh
agen pengoksidaan
Dehydration by a dehydrating agent
Pendehidratan oleh agen pendehidratan
Carboxylic Acid / Asid Karboksilik
1 Carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen (non-hydrocarbon). The general
formula for carboxylic acid is C
n
H
2n + 1
COOH, n = 0, 1, 2, 3.... / Asid karboksilik ialah sebatian organik yang mengandungi
karbon, hidrogen dan oksigen (bukan hidrokarbon). Formula am bagi asid karboksilik adalah C
n
H
2n + 1
COOH, n = 0, 1, 2, 3.....
2 The functional group is the carboxyl group, COOH, / Kumpulan berfungsi ialah kumpulan karboksil, COOH,
O
C OH
3 Carboxylic acids are organic acid that comes from an organic source such as ethanoic acid in vinegar, citric acid in
lemon and methanoic acid from ants. / Asid karboksilik ialah asid organik yang berasal daripada sumber organik seperti asid
etanoik dalam cuka, asid sitrik dalam limau dan asid metanoik daripada semut.
4 Naming carboxylic acid IUPAC nomenclature: / Menamakan asid karboksilik mengikut sistem penamaan IUPAC:
Step 1 : Determine the number of carbon atoms, obtain the name of the corresponding alkane.
Langkah 1 : Tentukan bilangan atom karbon, dapatkan nama alkana yang setara.
Step 2 : Replace the ending ane from the name of alkane with -oic acid.
Langkah 2 : Gantikan akhiran ana daripada nama alkana dengan -oik
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
74
Example: / Contoh:
a. Molecular formula: HCOOH
Formula molekul: HCOOH
Number of carbon atom is 1.
Bilangan atom karbon ialah 1.
Name of corresponding alkane is methane.
Nama alkana yang selaras ialah metana.
Name of HCOOH is methanoic acid.
Nama HCOOH ialah asid metanoik.
b. Molecular formula: CH
3
COOH
Formula molekul: CH
3
COOH
Number of carbon atom is 2.
Bilangan atom karbon ialah 2.
Name of corresponding alkane is ethane.
Nama alkana yang selaras ialah etana.
Name of CH
3
COOH is ethanoic acid.
Nama CH
3
OOH ialah asid etanoik.
5 Complete the following table: / Lengkapkan jadual berikut:
n
Molecular formula,
Formula molekul,
C
n
H
2n + 1
COOH
Number of
carbon atoms
Bilangan atom
karbon
Structural formula / Formula struktur Name / Nama
0 HCOOH 1
O
H C OH
Methanoic acid
1 CH
3
COOH 2
H O
H C C OH
H
Ethanoic acid
2 C
2
H
5
COOH 3
H H O
H C C C OH
H H
Propanoic acid
3 C
3
H
7
COOH 4
H H H O
H C C C C OH
H H H
Butanoic acid
6 The naming for branched chain carboxylic acid molecule is similar to the naming of alcohol. / Penamaan molekul asid
karboksilik bercabang adalah sama dengan penamaan alkohol.
a. The name and position of the branched group is written as prefix. / Nama dan kedudukan kumpulan yang bercabang
ditulis sebagai awalan.
b. The smallest number is given to the carbon atom that is joined to the functional carboxyl group, COOH. Carboxyl group,
COOH will always at the beginning or end of carbon chain. The number of the carbon atom in the longest carbon
chain which is joined to the carboxyl group COOH is always 1. The suffix is oic. Nombor terkecil diberi kepada atom
karbon yang bergabung dengan kumpulan berfungsi karboksil, COOH. Kumpulan karboksil, COOH sentiasa berada pada
permulaan atau pada hujung rantai karbon. Bilangan atom karbon dalam rantai karbon terpanjang yang bersambung dengan
kumpulan karboksil COOH sentiasa 1. Akhiran ialah oik.
Example / Contoh:
H H H O
H
4
C
3
C
2
C
1
C OH
H H CH
3
2-methylbutanoic acid
Asid 2-metilbutanoik
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
75
7 Preparation of ethanoic acid: / Penyediaan asid etanoik:
a. Ethanoic acid is prepared when ethanol is oxidised by oxidising agents such as acidified potassium manganate(VII)
solution or acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution: / Asid etanoik disediakan apabila etanol dioksidakan oleh agen
pengoksidaan seperti larutan kalium manganat(VII) berasid atau larutan kalium dikromat(VI) berasid:
H H
H C C H
H OH
+ 2[O]
H O
H C C OH
H
+ H
2
O
Ethanol / Etanol Ethanoic acid / Asid etanoik Water / Air
b. Oxidation of ethanol to ethanoic acid is conducted by reflux method. The round bottom flask is fitted with an upright
condenser to prevent ethanol loss from vaporisation. / Pengoksidaan etanol kepada asid etanoik dilakukan melalui kaedah
refluks. Kelalang dasar bulat dipasang tegak bersama kondenser untuk mengelakkan alkohol meruap keluar.
Heat
Haba
Boiling chips
Batu didih
Water / Air
Ethanol + excess acidified K
2
Cr
2
O
7
/ H
+
Etanol + K
2
Cr
2
O
7
/ H
+
berasid berlebihan
Beaker / Bikar
Condenser (as a reflux)
Kondenser (sebagai refluks)
Water in / Air masuk
Water out / Air keluar
Round-bottomed flask
Kelalang dasar bulat
8 Physical Properties of Carboxylic Acid / Sifat-sifat Fizikal Asid Karboksilik
a. Small molecules of carboxylic acid are soluble in water and ionise partially in water to form weak acid. As the
number of carbon atom per molecule increases, the carboxylic acid becomes less soluble.
Molekul kecil asid karboksilik larut dalam air dan mengion separa dalam air untuk membentuk asid lemah. Apabila bilangan
atom karbon per molekul meningkat, asid karboksilik menjadi kurang larut.
b. The boiling points and density of carboxylic acid increases as the number of carbon atom per molecule increases. / Takat didih
dan ketumpatan asid karboksilik meningkat apabila bilangan atom karbon dalam satu molekul meningkat.
9 Chemical Properties of Carboxylic Acid / Sifat-sifat Kimia Asid Karboksilik
All carboxylic acids have similar chemical properties due to the presence of the carboxyl group, COOH as a functional
group. / Semua asid karboksilik mempunyai sifat-sifat kimia yang sama kerana kehadiran kumpulan karboksil, COOH sebagai
kumpulan berfungsi.
Chemical reactions of carboxylic acid are: / Tindak balas kimia asid karboksilik adalah:
a. Carboxylic acid + Metal Carboxylate salt + Hydrogen
Asid karboksilik + Logam Garam karboksilat + Hidrogen
b. Carboxylic acid + Base/alkali Carboxylate salt + Water
Asid karboksilik + Bes/alkali Garam karboksilat + Air
c Carboxylic acid + Metal carbonate Carboxylate salt + Water + Carbon dioxide
Asid karboksilik + Logam karbonat Garam karboksilat + Air + Karbon dioksida
d. Reaction with alcohol to produce ester and water.
Tindak balas dengan alkohol untuk menghasilkan ester dan air.
Chemical properties
of acid
Sifat-sifat kimia asid
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
76
10 Complete the following equation to show that carboxylic acids show similar chemical properties as other acid.
Lengkapkan persamaan berikut untuk menunjukkan asid karboksilik mempunyai sifat-sifat kimia yang sama dengan asid lain.
i.
2CH
3
COOH
Ethanoic acid
Asid etanoik
+
CaCO
3
Calcium carbonate
Kalsium karbonat
(CH
3
COO)
2
Ca + H
2
O + CO
2
Calcium ethanoate
Kalsium etanoat
Water
Air
Carbon dioxide
Karbon dioksida
ii.
C
3
H
5
COOH
Propanoic acid
Asid propanoik
+
NaOH
Sodium hydroxide
Natrium hidroksida
C
2
H
5
COONa + H
2
O
Sodium propanoate
Natrium propanoat
Water
Air
iii.
2HCOOH
Methanoic acid
Asid metanoik
+
Mg
Magnesium
Magnesium
(HCOO)
2
Mg + H
2
Magnesium methanoate
Magnesium metanoat
Hydrogen
Hidrogen
11 Reaction with alcohol to produce ester and water. / Tindak balas dengan alkohol untuk menghasilkan ester dan air.
a. Carboxylic acid reacts with alcohol to produce ester and water with the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid as a
catalyst (esterification reaction). The removal of water occurs at the functional carboxyl, COOH in carboxylic acid
and hydroxyl, OH in alcohol. To form water (HOH) , OH is removed from carboxylic acid and H is removed from
alcohol. / Asid karboksilik bertindak balas dengan alkohol untuk menghasilkan ester dan air dengan kehadiran asid sulfurik
pekat sebagai mangkin (tindak balas pengesteran). Penyingkiran air berlaku pada kumpulan berfungsi karboksil, COOH
dalam asid karboksilik dan hidroksil, OH dalam alkohol. Untuk membentuk air (HOH), OH disingkirkan daripada asid
karboksilik dan H disingkirkan daripada alkohol.
C
n
H
2n + 1
COOH
Carboxylic acid
Asid karboksilik
+
C
n
H
2n+1
OH
Alcohol
Alkohol
H
2
SO
4
C
n
H
2n + 1
COOC
n
H
2n + 1
Ester
Ester
+
H
2
O
Water
Air
b. Water molecule is removed from carboxylic acid and alcohol as shown in chemical equation below:
Molekul air disingkirkan daripada asid karboksilik dan alkohol seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam persamaan kimia di bawah:
H O
H C C OH
H
+
H H
HO C C H
H H
H
2
SO
4
H O H H
H C C O C C H
H H H
+ HOH
CH
3
COOH
Ethanoic acid
Asid etanoik
+
C
2
H
5
OH
Alcohol
Alkohol
H
2
SO
4
CH
3
CO OC
2
H
5
Ester
Ester
+
H
2
O
Water
Air
c. Naming of an ester: / Penamaan ester:
i. Name of ester is derived from alcohol and carboxylic acid and it consists of two parts.
Nama ester diterbitkan daripada alkohol dan asid karboksilik dan ia terdiri daripada dua bahagian.
ii. The first part is from the name of alcohol component and the second part is from the name of carboxylic
acid component. / Bahagian pertama adalah daripada nama komponen alkohol dan bahagian kedua adalah daripada
nama komponen asid karboksilik.
iii. Replace the ending name of alcohol with yl and ending oic from the name of carboxylic acid with oate.
Gantikan akhiran nama alkohol dengan il dan akhiran oik daripada nama asid karboksilik dengan oat.
Methanol Methyl, Methanoic acid Methanoate / Metanol Metil, Asid etanoik Metanoat
Ethanol Ethyl, Ethanoic acid Ethanoate / Etanol Etil, Asid etanoik Etanoat
Propanol Propyl, Propanoic acid Propanoate / Propanol Propil, Asid propanoik Propanoat
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
77
Example: / Contoh:
Name the ester from its structural formula. / Namakan ester daripada formula strukturnya:
Ethyl ethanoate
Etil etanoat
Structural formula
Formula struktur
H O H H
H C C O C C H
H H H
Molecular formula
Formula molekul
CH
3
CO OC
2
H
5
From ethanoic acid / Dari asid etanoik
CH
3
COOH
From ethanol / Dari etanol
C
2
H
5
OH
Name of ester
Nama ester
12 Uses of carboxylic acid / Kegunaan asid karboksilik
Example of the uses: / Contoh kegunaan-kegunaan:
Carboxylic acid / Asid karboksilik Uses / Kegunaan
Ethanoic acid / Asid etanoik
As food flavour and preservative / Sebagai perasa makanan dan pengawet
Manufacture of drugs like aspirin / Pembuatan ubat seperti aspirin
Methanoic acid / Asid metanoik
To coagulate latex / Untuk menggumpalkan lateks
Manufacture of dyes, synthetic leather and insecticide
Pembuatan pewarna rambut, kulit buatan dan racun serangga
Citric acid / Asid sitrik
Flavouring in soft drinks and antioxidant in cakes and biscuits
Perasa dalam minuman bergas dan antioksidan dalam kek dan biskut
Fatty acid (Long carbon chain
carboxylic acid) / Asid lemak
(Asid karboksilik rantai karbon panjang)
Making soap / Membuat sabun
EXERCISE / LATIHAN
1 Name the following esters: / Namakan ester berikut:
Structural formula of ester
Formula struktur ester
Molecular formula / Formula molekul Name / Nama
H O H H H
H C C O C C C H
H H H H
Molecular formula of ester:
Formula molekul ester:
CH
3
COOC
3
H
7
Molecular formula of alcohol part:
Formula molekul bahagian alkohol:
C
3
H
7
OH
Molecular formula of carboxylic acid part:
Formula molekul bahagian asid karboksilik:
CH
3
COOH
Name of alcohol:
Nama alkohol:
Propanol
Name of carboxylic acid:
Nama asid karboksilik:
Ethanoic acid
Name of ester:
Nama ester:
Propyl ethanoate
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
78
H H O H H
H C C C O C C H
H H H H
Molecular formula of ester:
Formula molekul ester:
C
2
H
5
COOC
2
H
5
Molecular formula of alcohol part:
Formula molekul bahagian alkohol:
C
2
H
5
OH
Molecular formula of carboxylic acid part:
Formula molekul bahagian asid karboksilik:
C
2
H
5
COOH
Name of alcohol:
Nama alkohol:
Ethanol
Name of carboxylic acid:
Nama asid karboksilik:
Propanoic acid
Name of ester:
Nama ester:
Ethyl propanoate
H H O H
H C C C O C H
H H H
Molecular formula of ester:
Formula molekul ester:
C
2
H
5
COOCH
3
Molecular formula of alcohol part:
Formula molekul bahagian alkohol:
CH
3
OH
Molecular formula of carboxylic acid part:
Formula molekul bahagian asid karboksilik:
C
2
H
5
COOH
Name of alcohol:
Nama alkohol:
Methanol
Name of carboxylic acid:
Nama asid karboksilik:
Propanoic acid
Name of ester:
Nama ester:
Methyl propanoate
2 Describe an experiment to prepare ethyl ethanoate in the laboratory. In your answer, include the procedure, observations
and conclusion. / Huraikan eksperimen untuk menyediakan etil etanoat di dalam makmal. Dalam jawapan anda, sertakan kaedah,
pemerhatian dan kesimpulan.
Procedure: / Kaedah:
i. 2 cm
3
glacial
ethonoic acid is poured into a boiling tube. / 2 cm
3
asid etanoik
glasial
dituang ke dalam tabung didih.
ii. 4 cm
3
of ethanol
is added to the glacial
ethanoic acid. / 4 cm
3
etanol
ditambah ke dalam asid etanoik glasial.
iii. Five drops of concentrated
sulphuric acid are added to the mixture with a dropper
. The boiling tube is
shaken
. / Lima titik asid sulfurik
pekat
dimasukkan ke dalam campuran menggunakan
penitis
. Tabung didih
digoncangkan
.
iv. The mixture is then heated gently
over a small flame until it boils
for two to three minutes. / Campuran
dipanaskan secara
perlahan-lahan
di atas nyalaan yang kecil sehingga
mendidih
untuk dua hingga tiga minit.
v. The content of the boiling tube is poured in a beaker half filled with water
. / Kandungan tabung didih dituang
ke dalam bikar yang telah diisi separuh dengan
air
.
vi. The odour, colour and solubility of the product are recorded. / Bau, warna dan keterlarutan hasil direkodkan.
Observation: / Pemerhatian:
i. Colourless liquid with sweet
smell is formed. / Cecair tanpa warna dengan bau yang
wangi
terbentuk.
ii. The liquid is insoluble
in water. / Cecair tersebut
tak larut
dalam air.
iii. The liquid is less
dense than water (layer of liquid floats on water).
Cecair tersebut adalah
kurang
tumpat daripada air (lapisan cecair terapung di atas air).
Conclusion / Kesimpulan:
i. Ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol to form ester: / Asid etanoik bertindak balas dengan etanol untuk membentuk ester:
CH
3
COOH + C
2
H
5
OH CH
3
COOC
2
H
5
+ H
2
O
ii. Concentrated sulphuric acid is the catalyst
for the reaction. / Asid sulfurik pekat ialah
mangkin
bagi tindak balas ini.
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
79
Esters / Ester
1 Esters are non-hydrocarbon organic compounds containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen formed when a carboxylic
acid reacts with an alcohol. / Ester ialah sebatian organik bukan hidrokarbon yang mengandungi karbon, hidrogen dan oksigen
yang terbentuk apabila asid karboksilik bertindak balas dengan alkohol.
2 General formula of ester: / Formula am ester:
O
R C O R or / atau C
n
H
2n + 1
COO C
n
H
2n + 1
R O
:
Derived from alcohol, name ending with yl. R is alkyl group with general formula C
n
H
2n + 1
where
n = 1, 2, 3
Diperoleh daripada alkohol, namanya berakhir dengan il. R ialah kumpulan alkil dengan formula am C
n
H
2n + 1
di mana n=1, 2, 3
O
R C
:
Derived from carboxylic acid, name ending with oate. R is alkyl group with general formula C
n
H
2n + 1
where n = 0, 1, 2, 3 / Diperoleh daripada asid karboksilik, namanya berakhir dengan oat. R ialah kumpulan
alkohol dengan formula am C
n
H
2n + 1
di mana n = 0, 1, 2, 3
3 The functional group for ester is carboxylate group, COO:
Kumpulan berfungsi bagi ester ialah kumpulan karboksilat, COO:
O
C O
4 Formation of esters: / Pembentukan ester:
a. Esters are produced when carboxylic acid reacts with alcohol in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid as a
catalyst (esterification reaction): / Ester terhasil apabila asid karboksilik bertindak balas dengan alkohol dalam kehadiran
asid sulfurik pekat sebagai mangkin (tindak balas pengesteran):
O
R C O H
H
+ H O R
O
R C O R + HOH
Carboxylic acid
Asid karboksilik
Alcohol
Alkohol
Ester
Ester
Water
Air
5 Naming of esters: / Penamaan ester:
Name for esters are first read from the alcohol component followed by the carboxylic acid component.
Nama bagi ester dibaca daripada komponen alkohol dahulu diikuti dengan komponen asid karboksilik.
Example: / Contoh:
From ethanoic acid
Dari asid etanoik
From propanol
Dari propanol
CH
3
COOH + C
3
H
7
OH
H
2
SO
4
CH
3
CO OC
3
H
7
+ H
2
O
Ethanoic acid
Asid etanoik
Propanol
Propanol
Propyl ethanoate
Propil etanoat
6 Complete the following equations: / Lengkapkan persamaan-persamaan berikut:
i.
H H H O
H C C C C OH
H H H
+
H H H H H
H O C C C C C H
H H H H H
H
2
SO
4
H H H O H H H H H
H C C C C O C C C C C H
H H H H H H H H
+ HOH
Butanoic acid
Pentanol
Pentyl butanoate
Water
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
80
ii.
HCOOH
Methanoic acid
+
C
2
H
5
OH
Ethanol
H
2
SO
4
HCOOC
2
H
5
Ethyl methanoate
+
H
2
O
Water
iii.
C
3
H
7
OH
Propanol
+
C
4
H
9
COOH
Pentanoic acid
H
2
SO
4
C
4
H
9
COOC
3
H
7
Propyl pentanoate
+
H
2
O
Water
iv.
C
3
H
7
COOH
Butanoic acid
+
C
2
H
5
OH
Etanol
H
2
SO
4
C
3
H
7
COOC
2
H
5
Ethyl butanoate
+
H
2
O
Water / Air
7 Physical Properties of Esters: / Sifat-sifat Fizikal Ester:
i. Ester is a neutral compound with a sweet
smell. / Ester ialah sebatian neutral dengan bau yang
wangi
.
ii. Esters have low density, less
dense than water. / Ester mempunyai ketumpatan yang rendah,
kurang
tumpat
berbanding air.
iii. Simple esters are colourless liquid at room temperature. / Ester yang ringkas adalah cecair tanpa warna pada suhu bilik.
iv. Simple esters are very volatile
and evaporate easily at room temperature.
Ester yang ringkas adalah sangat
tidak stabil
dan meruap dengan mudah pada suhu bilik.
v. Esters are covalent compound which is insoluble
in water.
Ester adalah sebatian kovalen yang
tidak larut
dalam air.
8 Uses of esters: / Kegunaan ester:
i. Most simple esters are found naturally in fruits and flowers. The fragrance of flowers and fruits is due to thepresence
of esters. / Kebanyakan ester dijumpai secara semula jadi dalam buah-buahan dan bunga-bungaan. Bau wangi buah-buahan
dan bunga-bungaan adalah disebabkan kehadiran ester.
Example: / Contoh:
Ester / Ester Name / Nama Naturel source / Sumber semula jadi
C
3
H
7
COOC
2
H
5
Ethyl butanoate Pineapple / Nanas
C
3
H
7
COOCH
3
Methyl butanoate Apple / Epal
CH
3
COOC
5
H
11
Pentyl ethanoate Banana / Pisang
ii. Used in the preparation of cosmetics and perfumes.
Digunakan dalam penyediaan barang kosmetik dan minyak wangi.
iii. As artificial flavour in processed food and drinks.
Sebagai perasa tiruan dalam makanan dan minuman yang diproses.
iv. Used in the production of polyester (synthetic fibers for making textiles).
Digunakan dalam penghasilan poliester (gentian sintetik untuk pembuatan tekstil).
v. Natural fats are esters which react with alkalis to produce soap.
Lemak semula jadi ialah ester yang bertindak balas dengan alkali untuk menghasilkan sabun.
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
81
C
O
N
C
L
U
S
I
O
N
F
O
R
T
H
E
C
H
E
M
I
C
A
L
P
R
O
P
E
R
T
I
E
S
O
F
A
L
K
A
N
E
,
A
L
K
E
N
E
,
A
L
C
O
H
O
L
,
C
A
R
B
O
X
Y
L
I
C
A
C
I
D
A
N
D
E
S
T
E
R
G
L
U
C
O
S
E
C
6
H
1
2
O
6
*
F
e
r
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
A
L
K
A
N
E
C
n
H
2
n
+
2
,
n
=
1
,
2
,
3
#
C
r
a
c
k
i
n
g
*
H
y
d
r
o
g
e
n
a
t
i
o
n
A
L
K
E
N
E
C
n
H
2
n
,
n
=
2
,
3
,
4
#
H
y
d
r
a
t
i
o
n
*
D
e
h
y
d
r
a
t
i
o
n
A
L
C
O
H
O
L
C
n
H
2
n
+
1
O
H
,
=
n
=
1
,
2
,
3
*
O
x
i
d
a
t
i
o
n
C
A
R
B
O
X
Y
L
I
C
A
C
I
D
C
n
H
2
n
+
1
C
O
O
H
,
n
=
0
,
1
,
2
,
3
S
A
T
U
R
A
T
E
D
H
Y
D
R
O
C
A
R
B
O
N
C
h
e
m
i
c
a
l
r
e
a
c
t
i
o
n
1
.
S
u
b
s
t
i
t
u
t
i
o
n
r
e
a
c
t
i
o
n
w
i
t
h
h
a
l
o
g
e
n
s
u
c
h
a
s
c
h
l
o
r
i
n
e
,
C
l
2
a
n
d
b
r
o
m
i
n
e
,
B
r
2
w
i
t
h
p
r
e
s
e
n
t
o
f
s
u
n
l
i
g
h
t
.
2
.
C
o
m
b
u
s
t
i
o
n
t
o
p
r
o
d
u
c
e
c
a
r
b
o
n
d
i
o
x
i
d
e
a
n
d
w
a
t
e
r
w
i
t
h
l
e
s
s
s
o
o
t
.
U
N
S
A
T
U
R
A
T
E
D
H
Y
D
R
O
C
A
R
B
O
N
C
h
e
m
i
c
a
l
r
e
a
c
t
i
o
n
1
.
A
d
d
i
t
i
o
n
r
e
a
c
t
i
o
n
w
i
t
h
:
a
.
H
y
d
r
o
g
e
n
,
H
2
(
H
y
d
r
o
g
e
n
a
t
i
o
n
)
b
.
W
a
t
e
r
,
H
2
O
(
H
y
d
r
a
t
i
o
n
)
c
.
H
a
l
o
g
e
n
s
u
c
h
a
s
b
r
o
m
i
n
e
,
B
r
2
d
.
A
c
i
d
i
f
i
e
d
p
o
t
a
s
s
i
u
m
m
a
n
g
a
n
a
t
e
(
V
I
I
)
,
K
M
n
O
4
2
.
A
d
d
i
t
i
o
n
p
o
l
y
m
e
r
i
s
a
t
i
o
n
3
.
C
o
m
b
u
s
t
i
o
n
t
o
p
r
o
d
u
c
e
c
a
r
b
o
n
d
i
o
x
i
d
e
a
n
d
w
a
t
e
r
w
i
t
h
m
o
r
e
s
o
o
t
.
N
O
N
-
H
Y
D
R
O
C
A
R
B
O
N
C
h
e
m
i
c
a
l
r
e
a
c
t
i
o
n
1
.
D
e
h
y
d
r
a
t
i
o
n
2
.
O
x
i
d
a
t
i
o
n
3
.
C
o
m
b
u
s
t
i
o
n
t
o
p
r
o
d
u
c
e
c
a
r
b
o
n
d
i
o
x
i
d
e
a
n
d
w
a
t
e
r
w
i
t
h
n
o
s
o
o
t
.
N
O
N
-
H
Y
D
R
O
C
A
R
B
O
N
C
h
e
m
i
c
a
l
r
e
a
c
t
i
o
n
1
.
S
h
o
w
t
h
e
c
h
e
m
i
c
a
l
p
r
o
p
r
e
t
i
e
s
o
f
a
c
i
d
:
i
.
A
c
i
d
+
M
e
t
a
l
S
a
l
t
+
H
y
d
r
o
g
e
n
i
i
.
A
c
i
d
+
M
e
t
a
l
+
C
a
r
b
o
n
a
t
e
S
a
l
t
+
W
a
t
e
r
+
C
a
r
b
o
n
d
i
o
x
i
d
e
i
i
i
.
A
c
i
d
+
B
a
s
e
/
a
l
k
a
l
i
S
a
l
t
+
W
a
t
e
r
2
.
E
s
t
e
r
i
f
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
E
S
T
E
R
,
R
C
O
O
R
R
i
s
C
n
H
2
n
+
1
,
n
=
0
,
1
,
2
,
3
.
.
.
.
a
n
d
R
i
s
C
n
H
2
n
+
1
,
n
=
1
,
2
,
3
.
.
.
.
C
o
m
p
l
e
t
e
t
h
e
f
o
l
l
o
w
i
n
g
.
1
.
C
o
m
b
u
s
t
i
o
n
o
f
a
l
k
a
n
e
a
n
d
a
l
k
e
n
e
p
r
o
d
u
c
e
d
i
f
f
e
r
e
n
t
a
m
o
u
n
t
o
f
s
o
o
t
.
C
o
m
b
u
s
t
i
o
n
i
s
u
s
e
d
t
o
d
i
f
f
e
r
e
n
t
i
a
t
e
a
l
k
a
n
e
a
n
d
a
l
k
e
n
e
.
2
.
A
d
d
i
t
i
o
n
r
e
a
c
t
i
o
n
o
f
a
l
k
e
n
e
w
i
t
h
b
r
o
m
i
n
e
w
a
t
e
r
c
h
a
n
g
e
b
r
o
w
n
c
o
l
o
u
r
o
f
b
r
o
m
i
n
e
w
a
t
e
r
t
o
c
o
l
o
u
r
l
e
s
s
.
T
h
i
s
r
e
a
c
t
i
o
n
d
o
e
s
n
o
t
o
c
c
u
r
i
n
a
l
k
a
n
e
.
A
l
k
a
n
e
a
n
d
a
l
k
e
n
e
c
a
n
b
e
d
i
f
f
e
r
e
n
t
i
a
t
e
d
b
y
u
s
i
n
g
b
r
o
m
i
n
e
w
a
t
e
r
.
3
.
A
d
d
i
t
i
o
n
r
e
a
c
t
i
o
n
o
f
a
l
k
e
n
e
w
i
t
h
a
c
i
d
i
f
i
e
d
p
o
t
a
s
s
i
u
m
m
a
n
g
a
n
a
t
e
(
V
I
I
)
c
h
a
n
g
e
p
u
r
p
l
e
c
o
l
o
u
r
o
f
a
c
i
d
i
f
i
e
d
p
o
t
a
s
s
i
u
m
m
a
n
g
a
n
a
t
e
(
V
I
I
)
t
o
c
o
l
o
u
r
l
e
s
s
.
T
h
i
s
r
e
a
c
t
i
o
n
d
o
e
s
n
o
t
o
c
c
u
r
i
n
a
l
k
a
n
e
.
A
l
k
a
n
e
a
n
d
a
l
k
e
n
e
c
a
n
a
l
s
o
b
e
d
i
f
f
e
r
e
n
t
i
a
t
e
d
b
y
u
s
i
n
g
a
c
i
d
i
f
i
e
d
p
o
t
a
s
s
i
u
m
m
a
n
n
g
a
n
a
t
e
(
V
I
I
)
.
4
.
A
d
d
i
t
i
o
n
r
e
a
c
t
i
o
n
o
f
a
l
k
e
n
e
w
i
t
h
h
y
d
r
o
g
e
n
(
h
y
d
r
o
g
e
n
a
t
i
o
n
)
h
a
s
c
h
a
n
g
e
d
a
l
k
e
n
e
t
o
a
l
k
a
n
e
.
5
.
A
d
d
i
t
i
o
n
r
e
a
c
t
i
o
n
o
f
a
l
k
e
n
e
w
i
t
h
w
a
t
e
r
(
h
y
d
r
a
t
i
o
n
)
h
a
s
c
h
a
n
g
e
d
a
l
k
e
n
e
t
o
a
l
c
o
h
o
l
.
6
.
D
e
h
y
d
r
a
t
i
o
n
o
f
a
l
c
o
h
o
l
h
a
s
c
h
a
n
g
e
d
a
l
c
o
h
o
l
t
o
a
l
k
e
n
e
.
7
.
O
x
i
d
a
t
i
o
n
o
f
a
l
c
o
h
o
l
h
a
s
c
h
a
n
g
e
d
a
l
c
o
h
o
l
t
o
c
a
r
b
o
x
y
l
i
c
a
c
i
d
.
8
.
E
s
t
e
r
i
f
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
o
f
a
l
c
o
h
o
l
a
n
d
c
a
r
b
o
x
y
l
i
c
a
c
i
d
p
r
o
d
u
c
e
s
e
s
t
e
r
.
*
Esterification
K
e
y
:
R
e
a
c
t
i
o
n
s
m
a
r
k
e
d
w
i
t
h
a
r
e
i
n
d
u
s
t
r
i
a
l
p
r
o
c
e
s
s
e
s
R
e
a
c
t
i
o
n
s
m
a
r
k
e
d
w
i
t
h
a
r
e
c
o
n
d
u
c
t
e
d
i
n
t
h
e
l
a
b
o
r
a
t
o
r
y
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
82
K
E
S
I
M
P
U
L
A
N
U
N
T
U
K
S
I
F
A
T
-
S
I
F
A
T
K
I
M
I
A
A
L
K
A
N
A
,
A
L
K
E
N
A
,
A
L
K
O
H
O
L
,
A
S
I
D
K
A
R
B
O
K
S
I
L
I
K
D
A
N
E
S
T
E
R
G
L
U
K
O
S
A
C
6
H
1
2
O
6
*
P
e
n
a
p
a
i
a
n
A
L
K
A
N
A
C
n
H
2
n
+
2
,
n
=
1
,
2
,
3
#
P
e
r
e
t
a
k
a
n
*
P
e
n
g
h
i
d
r
o
g
e
n
a
n
A
L
K
E
N
A
C
n
H
2
n
,
n
=
2
,
3
,
4
#
P
e
n
g
h
i
d
r
a
t
a
n
*
P
e
n
d
e
h
i
d
r
a
t
a
n
A
L
K
O
H
O
L
C
n
H
2
n
+
1
O
H
,
=
n
=
1
,
2
,
3
*
P
e
n
g
o
k
s
i
d
a
a
n
A
S
I
D
K
A
R
B
O
K
S
I
L
I
K
C
n
H
2
n
+
1
C
O
O
H
,
n
=
0
,
1
,
2
,
3
H
I
D
R
O
K
A
R
B
O
N
T
E
P
U
T
i
n
d
a
k
b
a
l
a
s
k
i
m
i
a
1
.
T
i
n
d
a
k
b
a
l
a
s
p
e
n
u
k
a
r
g
a
n
t
i
a
n
d
e
n
g
a
n
h
a
l
o
g
e
n
s
e
p
e
r
t
i
k
l
o
r
i
n
,
C
l
2
d
a
n
b
r
o
m
i
n
,
B
r
2
d
e
n
g
a
n
k
e
h
a
d
i
r
a
n
c
a
h
a
y
a
m
a
t
a
h
a
r
i
.
2
.
P
e
m
b
a
k
a
r
a
n
u
n
t
u
k
m
e
n
g
h
a
s
i
l
k
a
n
k
a
r
b
o
n
d
i
o
k
s
i
d
a
d
a
n
a
i
r
d
e
n
g
a
n
k
u
r
a
n
g
j
e
l
a
g
a
.
H
I
D
R
O
K
A
R
B
O
N
T
A
K
T
E
P
U
T
i
n
d
a
k
b
a
l
a
s
k
i
m
i
a
1
.
T
i
n
d
a
k
b
a
l
a
s
p
e
n
a
m
b
a
h
a
n
d
e
n
g
a
n
:
a
.
H
i
d
r
o
g
e
n
,
H
2
(
P
e
n
g
h
i
d
r
o
g
e
n
a
n
)
b
.
A
i
r
,
H
2
O
(
P
e
n
g
h
i
d
r
a
t
a
n
)
c
.
H
a
l
o
g
e
n
s
e
p
e
r
t
i
b
r
o
m
i
n
,
B
r
2
d
.
K
a
l
i
u
m
m
a
n
g
a
n
a
t
(
V
I
I
)
b
e
r
a
s
i
d
K
M
n
O
4
2
.
P
e
m
p
o
l
i
m
e
r
a
n
p
e
n
a
m
b
a
h
a
n
3
.
P
e
m
b
a
k
a
r
a
n
u
n
t
u
k
m
e
n
g
h
a
s
i
l
k
a
n
k
a
r
b
o
n
d
i
o
k
s
i
d
a
d
a
n
a
i
r
d
e
n
g
a
n
l
e
b
i
h
j
e
l
a
g
a
.
B
U
K
A
N
H
I
D
R
O
K
A
R
B
O
N
T
i
n
d
a
k
b
a
l
a
s
k
i
m
i
a
1
.
P
e
n
d
e
h
i
d
r
a
t
a
n
2
.
P
e
n
g
o
k
s
i
d
a
a
n
3
.
P
e
m
b
a
k
a
r
a
n
u
n
t
u
k
m
e
n
g
h
a
s
i
l
k
a
n
k
a
r
b
o
n
d
i
o
k
s
i
d
a
d
a
n
a
i
r
d
e
n
g
a
n
t
i
a
d
a
j
e
l
a
g
a
.
B
U
K
A
N
H
I
D
R
O
K
A
R
B
O
N
T
i
n
d
a
k
b
a
l
a
s
k
i
m
i
a
1
.
M
e
n
u
n
j
u
k
k
a
n
s
i
f
a
t
-
s
i
f
a
t
k
i
m
i
a
a
s
i
d
:
i
.
A
s
i
d
+
L
o
g
a
m
G
a
r
a
m
+
H
i
d
r
o
g
e
n
i
i
.
A
s
i
d
+
L
o
g
a
m
K
a
r
b
o
n
a
t
G
a
r
a
m
+
A
i
r
+
K
a
r
b
o
n
d
i
o
k
s
i
d
a
i
i
i
.
A
s
i
d
+
B
e
s
/
a
l
k
a
l
i
G
a
r
a
m
+
A
i
r
2
.
P
e
n
g
e
s
t
e
r
a
n
E
S
T
E
R
,
R
C
O
O
R
R
i
s
C
n
H
2
n
+
1
,
n
=
0
,
1
,
2
,
3
.
.
.
.
d
a
n
R
i
s
C
n
H
2
n
+
1
,
n
=
1
,
2
,
3
.
.
.
.
L
e
n
g
k
a
p
k
a
n
y
a
n
g
b
e
r
i
k
u
t
:
1
.
P
e
m
b
a
k
a
r
a
n
a
l
k
a
n
a
d
a
n
a
l
k
e
n
a
m
e
n
g
h
a
s
i
l
k
a
n
k
u
a
n
t
i
t
i
j
e
l
a
g
a
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
y
a
n
g
b
e
r
b
e
z
a
.
P
e
m
b
a
k
a
r
a
n
d
i
g
u
n
a
k
a
n
u
n
t
u
k
m
e
m
b
e
z
a
k
a
n
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
a
l
k
a
n
a
d
a
n
a
l
k
e
n
a
.
2
.
T
i
n
d
a
k
b
a
l
a
s
p
e
n
a
m
b
a
h
a
n
a
l
k
e
n
a
d
e
n
g
a
n
a
i
r
b
r
o
m
i
n
m
e
n
g
u
b
a
h
w
a
r
n
a
p
e
r
a
n
g
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
a
i
r
b
r
o
m
i
n
k
e
p
a
d
a
t
a
n
p
a
w
a
r
n
a
.
T
i
n
d
a
k
b
a
l
a
s
i
n
i
t
i
d
a
k
b
e
r
l
a
k
u
d
a
l
a
m
a
l
k
a
n
a
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
.
A
l
k
a
n
a
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
d
a
n
a
l
k
e
n
a
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
b
o
l
e
h
d
i
b
e
z
a
k
a
n
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
m
e
n
g
g
u
n
a
k
a
n
a
i
r
b
r
o
m
i
n
.
3
.
T
i
n
d
a
k
b
a
l
a
s
p
e
n
a
m
b
a
h
a
n
a
l
k
e
n
a
d
e
n
g
a
n
k
a
l
i
u
m
m
a
n
g
a
n
a
t
(
V
I
I
)
b
e
r
a
s
i
d
m
e
n
g
u
b
a
h
w
a
r
n
a
u
n
g
u
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
k
a
l
i
u
m
m
a
n
g
a
n
a
t
(
V
I
I
)
b
e
r
a
s
i
d
k
e
p
a
d
a
t
a
n
p
a
w
a
r
n
a
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
.
T
i
n
d
a
k
b
a
l
a
s
i
n
i
t
i
d
a
k
b
e
r
l
a
k
u
d
a
l
a
m
a
l
k
a
n
a
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
.
A
l
k
a
n
a
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
d
a
n
a
l
k
e
n
a
j
u
g
a
b
o
l
e
h
d
i
b
e
z
a
k
a
n
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
m
e
n
g
g
u
n
a
k
a
n
k
a
l
i
u
m
m
a
n
g
a
n
a
t
(
V
I
I
)
b
e
r
a
s
i
d
.
4
.
T
i
n
d
a
k
b
a
l
a
s
p
e
n
a
m
b
a
h
a
n
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
a
l
k
e
n
a
d
e
n
g
a
n
h
i
d
r
o
g
e
n
(
p
e
n
g
h
i
d
r
o
g
e
n
a
n
)
m
e
n
g
u
b
a
h
a
l
k
e
n
a
k
e
p
a
d
a
a
l
k
a
n
a
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
.
5
.
T
i
n
d
a
k
b
a
l
a
s
p
e
n
a
m
b
a
h
a
n
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
a
l
k
e
n
a
d
e
n
g
a
n
a
i
r
(
p
e
n
g
h
i
d
r
a
t
a
n
)
m
e
n
g
u
b
a
h
a
l
k
e
n
a
k
e
p
a
d
a
a
l
k
o
h
o
l
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
.
6
.
P
e
n
d
e
h
i
d
r
a
t
a
n
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
a
l
k
o
h
o
l
m
e
n
g
u
b
a
h
a
l
k
o
h
o
l
k
e
p
a
d
a
a
l
k
e
n
a
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
.
7
.
P
e
n
g
o
k
s
i
d
a
a
n
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
a
l
k
o
h
o
l
m
e
n
g
u
b
a
h
a
l
k
o
h
o
l
k
e
p
a
d
a
a
s
i
d
k
a
r
b
o
k
s
i
l
i
k
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
.
8
.
P
e
n
g
e
s
t
e
r
a
n
a
l
k
o
h
o
l
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
d
a
n
a
s
i
d
k
a
r
b
o
k
s
i
l
i
k
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
m
e
n
g
h
a
s
i
l
k
a
n
e
s
t
e
r
.
*
Pengesteran
P
e
t
u
n
j
u
k
:
T
i
n
d
a
k
b
a
l
a
s
d
e
n
g
a
n
t
a
n
d
a
a
d
a
l
a
h
p
r
o
s
e
s
d
a
l
a
m
i
n
d
u
s
t
r
i
T
i
n
d
a
k
b
a
l
a
s
d
e
n
g
a
n
t
a
n
d
a
d
i
l
a
k
u
k
a
n
d
i
d
a
l
a
m
m
a
k
m
a
l
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
83
EXERCISE / LATIHAN
1 The table below shows the formulae of three organic compounds.
Jadual berikut menunjukkan formula bagi tiga sebatian organik.
Organic compound / Sebatian organik P Q R
Formula / Formula C
4
H
8
C
4
H
9
OH CH
3
COOH
a. i. What is meant by unsaturated hydrocarbon? / Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan hidrokarbon tak tepu?
Compounds that contain element carbon and hydrogen only with at least one double covalent bond between
carbon atoms
ii. Which of the organic compound in the table above is unsaturated hydrocarbon?
Antara sebatian organik dalam jadual di atas, yang manakah merupakan hidrokarbon tak tepu?
P // C
4
H
8
b. i. State the homologous series for compounds P and Q. / Nyatakan siri homolog bagi sebatian P dan Q.
Compound P / Sebatian P: Alkene
Compound Q / Sebatian Q: Alcohol
c. Compound P can be produced from compound Q through a chemical reaction.
Sebatian P boleh dihasilkan daripada sebatian Q melalui suatu tindak balas kimia.
i. What is the name of the reaction? / Apakah nama bagi tindak balas tersebut?
Dehydration
ii. Write the chemical equation for the reaction. / Tuliskan persamaan kimia bagi tindak balas tersebut.
C
4
H
9
OH
Porcelain chips
C
4
H
8
+ H
2
O
iii. Draw the set-up of apparatus for the reaction in (c)(ii). / Lukiskan susunan alat radas bagi tindak balas di (c)(ii).
Glass wool
soaked with
ethanol
Porcelain chips
Heat
Gas
Water
d. Draw the structural formula for compound R, circle the functional group.
Lukiskan formula struktur bagi sebatian R, bulatkan kumpulan berfungsi.
H O
H C C OH
H
i. State the general formula for compound R. / Tuliskan formula am bagi sebatian R.
C
n
H
2n + 1
COOH
ii. Another compound, S, is in the same homologous series as R. S has five carbon atoms. Write the molecular
formula for S. / Sebatian lain, S adalah dalam siri homolog yang sama dengan R. S mempunyai lima atom karbon.
Tuliskan formula molekul bagi S.
C
4
H
9
COOH
e. i. What is meant by isomerism? / Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan keisomeran?
Isomerism is the phenomenon where a compound has the same molecular formula but different structural
formulae.
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
84
ii. Draw the structural formula for compound P. Name all the isomers using IUPAC nomenclature.
Lukiskan formula struktur bagi sebatian P. Namakan semua isomer menggunakan sistem penamaan IUPAC.
H H H H H H H H H
H C C C C H H C C C C H H C H
H H
H H H H
H C C C
H H
n-but-1-ene n-but-2-ene 2-metylprop-1-ene
f. When compound Q is added into a test tube containing acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution and heated for
a few minutes, a chemical reaction occurs. / Apabila sebatian Q ditambah ke dalam tabung uji yang mengandungi larutan
kalium dikromat(VI) berasid dan dipanaskan untuk beberapa minit, tindak balas kimia berlaku.
i. Name the type of reaction that occurs. / Namakan jenis tindak balas yang berlaku.
Oxidation
ii. State one observation for this experiment. / Nyatakan satu pemerhatian dalam eksperimen ini.
The orange colour of acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution turns green.
iii. Write a chemical equation for the reaction. / Tuliskan persamaan kimia bagi tindak balas ini.
C
4
H
9
OH + 2[O] C
3
H
7
COOH + H
2
O
g. Compound Q undergoes complete combustion in excess oxygen. / Sebatian Q terbakar dengan lengkap dalam oksigen
berlebihan.
i. Write chemical equation for the complete combustion of Q. / Tuliskan persamaan kimia bagi pembakaran lengkap Q.
C
4
H
9
OH + 6O
2
4CO
2
+ 5H
2
O
ii. 7.4 g of compound undergoes complete combustion at room conditions. Calculate the volume of carbon dioxide
gas released. [1 mol of gas occupies 24 dm
3
at room conditions, Relative atomic mass: H, 1; C, 12]
7.4 g sebatian Q terbakar dengan lengkap pada suhu bilik. Hitung isi padu gas karbon dioksida yang terbebas. [1 mol gas
memenuhi 24 dm
3
pada suhu bilik, Jisim atom relatif: H, 1; C, 12]
Number of mol of C
4
H
9
OH =
7.4
74
= 0.1 mol
From the equation, 1 mol of C
4
H
9
OH : 4 mol of CO
2
0.1 mol of C
4
H
9
OH : 0.4 mol of CO
2
Volume of CO
2
= 0.4 24 dm
3
= 9.6 dm
3
2 The diagram below shows series of reaction involving organic compound.
Rajah di bawah menunjukkan siri tindak balas yang melibatkan sebatian organik.
Heat gently with ethanoic acid and concentrated sulphuric acid
Panaskan perlahan-lahan dengan asid ettanoik dan asid sulfurik pekat
Acidified potassium
manganate(VII) solution
Larutan kalium manganat(VII)
berasid
IV
Y
Propane
Propana
I
Propene
Propena
II
Propanol
Propanol
III
X
a. i. Name the reaction I. / Namakan tindak balas I.
Hydrogenation.
ii. State the conditions for the reaction I. / Nyatakan keadaan bagi tindak balas I.
Temperature 180C in the presence of nickel/platinum as a catalyst.
b. i. Write the molecular formula for propane and propene. / Tuliskan formula molekul bagi propana dan propena.
Propane / Propana:
C
3
H
8
Propene / Propena:
C
3
H
6
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
85
ii. Combustion of propene produces more soot than propane. Explain why. [Given relative atomic mass: H; 1, C;
12]. Pembakaran propena menghasilkan lebih banyak jelaga berbanding propana. Terangkan mengapa. [Diberi jisim atom
relatif: H; 1, C; 12]
Percentage of carbon by mass in propane =
12 3
12 3 + 8 1
100%
= 81.8 %
Percentage of carbon by mass in propene =
12 3
12 3 + 6 1
100%
= 85.7 %
Percentage of carbon by mass in propene is higher than propane.
c. The table below shows the results of a test to differentiate between propane and propene.
Jadual di bawah menunjukkan keputusan suatu ujian untuk membezakan antara propana dengan propena.
Procedure / Kaedah Observation / Pemerhatian
Bromine water is added to propene.
Air bromin ditambah kepada propena.
Brown colour is decolourised.
Warna perang luntur.
Bromine water is added to propane.
Air bromin ditambah kepada propana.
Brown colour remains.
Warna perang tidak berubah.
Based on the table above, explain why there is a difference in these observations.
Berdasarkan jadual, terangkan mengapa terdapat perbezaan dalam pemerhatian.
Propene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon/has double bond between carbon atoms.
Addition reaction occurs.
C
3
H
6
+ Br
2
C
3
H
6
Br
2
Propane is a saturated hydrocarbon/has single bond between carbon atoms.
Addition reaction does not occur.
d. Compound X is produced when propanol heated gently in the reaction III. / Sebatian X terhasil apabila propanol
dipanaskan dengan perlahan-lahan dalam tindak balas III.
i. What is the observation in process III? / Apakah pemerhatian dalam proses III?
The purple colour of acidified potassium manganate(VII) solution turns colourless.
ii. Name and write the chemical formula for compound X. / Namakan dan tuliskan formula kimia bagi sebatian X.
Name / Nama: Propanoic acid
Chemical formula / Formula kimia:
C
2
H
5
COOH
iii. Compound X can react with magnesium. Write the chemical equation for the reaction. / Sebatian X boleh bertindak
balas dengan magnesium. Tuliskan persamaan kimia bagi tindak balas tersebut.
2C
2
H
5
COOH + Mg (C
2
H
5
COO)
2
Mg + H
2
e. Propanol reacts with ethanoic acid through reaction IV to form compound Y.
Propanol bertindak balas dengan asid etanoik dalam tindak balas IV untuk membentuk sebatian Y.
i. Name compound Y. / Namakan sebatian Y.
Propil ethanoate.
ii. Draw the structural formula for Y. / Lukiskan formula struktur bagi Y.
H O H H H
H C C O C C C H
H H H H
iii. State one special characteristic of compound Y. / Nyatakan satu sifat istimewa sebatian Y.
Sweet smell
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
86
3 The information below is regarding substance X. / Maklumat di bawah adalah mengenai bahan X.
Carbon / Karbon 85.70%
Hydrogen / Hidrogen 14.3%
Relative molecular mass / Jisim molekul relatif = 56
Determine the empirical formula and molecular formula of substance X. [Given that the relative atomic mass of C =
12 , H = 1] / Tentukan formula empirik dan formula molekul bagi bahan X. [Diberi jisim atom relatif bagi C = 12 , H = 1]
Element C H
Mass/g 85.70/12 14.30/1
Mol atom 7.14 14.3
Simplest Ratio 1 2
The empirical formula CH
2
.
(CH
2
)n = 56
[12 + 2(1)]n = 56
n = 56/14 = 4
The molecular formula C
4
H
8
.
Fats / Lemak
1 Fats and oils are esters. / Lemak dan minyak adalah ester.
a. Fat is a natural ester found in animal and human tissue (solid at room temperature). / Lemak ialah ester semula jadi
yang dijumpai dalam haiwan dan tisu manusia (pepejal pada suhu bilik).
b. Oil is a natural ester found in fish tissue and plants (liquid at room temperature). / Minyak ialah ester semula jadi yang
dijumpai dalam tisu ikan dan tumbuh-tumbuhan (cecair pada suhu bilik).
c. Formed by esterification of alcohol glycerol (alcohol with 3OH) with fatty acid. (organic acid with long carbon
chain, C
n
H
2n+1
COOH, n is about 10 to 20). / Terbentuk melalui pengesteran alkohol gliserol (alkohol dengan 3OH)
dengan asid lemak (asid organik dengan rantai karbon yang panjang, C
n
H
2n + 1
COOH, n adalah di antara 10 hingga 20).
d. Esterification reaction between glycerol and fatty acid: / Tindak balas pengesteran antara gliserol dengan asid lemak:
Glycerol / Gliserol + Fatty acid / Asid lemak Oil or fat / Minyak atau lemak + Water / Air
H O H H
H C O H + H O C R H C O C R
O O + 3 H O H
H C O H + H O C R' H C O C R'
O O
H C O H + H O C R'' H C O C R''
H H
1 mol of glycerol
1 mol gliserol
3 mol of fatty acid
3 mol asid lemak
1 mol of fat/oil
1 mol lemak/minyak
3 mol of water
3 mol air
e. Fats are triesters (triglyceride). Lemak ialah triester (trigliserida).
2 The importance of oils and fats: / Kepentingan minyak dan lemak:
a. Fats and oils provide energy for our bodies. / Lemak dan minyak membekalkan tenaga untuk badan kita.
b. Build membrane cell and certain hormones. / Membina sel membran dan hormon-hormon tertentu.
c. Dissolve certain vitamins for absorption. / Melarutkan vitamin-vitamin tertentu untuk penyerapan.
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
87
3 Source of fats and oils: / Sumber lemak dan minyak:
a. Fats found in animals like cows and goats, are solid
at room temperature. The example of animal fats are
butter, cheese and etc. / Lemak dijumpai dalam haiwan seperti lembu dan kambing, adalah
pepejal
pada suhu bilik.
Contoh lemak haiwan ialah mentega, keju dan lain-lain.
b. Fats from plants are liquid
at room temperature. They are called oils
. The example of oils are
peanut oil, soybean oil and corn oil. / Lemak daripada tumbuh-tumbuhan adalah
cecair
pada suhu bilik. Ia dipanggil
minyak
. Contoh minyak ialah minyak kacang, minyak kacang soya dan minyak jagung.
4 Saturated and unsaturated fat / Lemak tepu dan lemak tak tepu
a. Fat and oil molecules are made up of two parts i.e derived from glycerol
and fatty acid
. / Molekul lemak dan
minyak terdiri daripada dua bahagian iaitu diperoleh daripada
gliserol
dan diperoleh daripada
asid lemak
.
b. Saturated fats molecules are esters of saturated fatty acids. Saturated fatty acids contain single
carbon-
carbon ( C C ) covalent bonds. / Molekul lemak tepu adalah ester bagi asid lemak tepu. Asid lemak tepu mengandungi
ikatan kovalen karbon-karbon (CC)
tunggal
.
Example: / Contoh: Glyceryl tristearate / Gliseril tristearat
H O
H C O C (CH
2
)
16
CH
3
O
H C O C (CH
2
)
16
CH
3
O
H C O C (CH
2
)
16
CH
3
H
Derived from glycerol
Diperoleh daripada gliserol
Derived from fatty acid (hydrogen chains contain single
covalent bonds between carbon atoms)
Diperoleh daripada asid lemak (rantai karbon mengandungi
ikatan kovalen tunggal antara atom karbon)
c. Unsaturated fat molecules are esters of unsaturated fatty acids that contain single
and double
covalent
bonds between carbon atoms in their hydrocarbon chain. / Molekul lemak tak tepu ialah ester bagi asid lemak tak tepu
yang mengandungi ikatan kovalen
tunggal
atau
ganda dua
di antara atom-atom karbon dalam rantai hidrokarbonnya.
Example: / Contoh: Glycerol trilinolate / Gliseril trilinolat
H O
H C O C (CH
2
)
7
(CH
2
)
7
CH = CHCH
2
CH = CH(CH
2
)
4
CH
3
O
H C O C
(CH
2
)
16
(CH
2
)
7
CH = CHCH
2
CH = CH(CH
2
)
4
CH
3
O
H C O C
(CH
2
)
16
(CH
2
)
7
CH = CHCH
2
CH = CH(CH
2
)
4
CH
3
H
Hydrocarbon chains contain double covalent bonds between carbon atoms
Rantai hidrokarbon mengandungi ikatan kovalen ganda dua antara atom-atom karbon
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
88
d. The fats and oils are mixture of saturated and unsaturated fats molecules:
Lemak dan minyak ialah campuran molekul lemak tepu dan tak tepu:
i. An oil or fat is classified as saturated
if it has more saturated
fat molecules compared to
unsaturated
fat molecules, for example animal fats. / Suatu minyak atau lemak dikelaskan sebagai
tepu
jika ia mengandungi lebih banyak molekul lemak
tepu
berbanding molekul lemak
tak tepu
, contohnya lemak
haiwan.
ii. An oil or fat is classified as unsaturated
if it has more unsaturated
fat molecules compared
to saturated fat molecules, for example vegetable oils except coconut oil.
Suatu minyak atau lemak dikelaskan sebagai
tak tepu
jika ia mengandungi lebih banyak molekul lemak
tak tepu
berbanding molekul lemak tepu, contohnya minyak sayuran kecuali minyak kelapa.
5 Converting unsaturated fats to saturated fats / Menukar lemak tak tepu kepada lemak tepu
a. The double covalent bonds between carbon atoms in unsaturated
fats are easily oxidised. When this
happens, the fat turns rancid. / Ikatan kovalen ganda dua di antara atom-atom karbon dalam lemak
tak tepu
boleh
teroksida dengan mudah. Apabila ini terjadi, lemak menjadi tengik.
b. Unsaturated fats can be converted to saturated fats through hydrogenation
process such as in the manufacture
of margarine. Catalyst used is nickel at 180C: / Lemak tak tepu boleh ditukarkan kepada lemak tepu melalui proses
penghidrogenan
, contohnya dalam pembuatan marjerin. Mangkin yang digunakan ialah nikel pada 180C:
H H
~ C C ~ + H
2
Nickel / nikel
180C
H H
~ C C ~
H H
Unsaturated fat (liquid)
Lemak tak tepu (cecair)
Saturated fat (solid)
Lemak tepu (pepejal)
c. Sources of unsaturated fats are palm oil, soybean oil and corn oil. / Sumber bagi lemak tak tepu ialah minyak sawit,
minyak kacang soya dan minyak jagung.
6 The effect of fats on health / Kesan lemak ke atas kesihatan
a. There are two types of cholesterol, LDL cholesterol and HDL cholesterol: / Terdapat dua jenis kolestrol, kolestrol LDL
dan kolestrol HDL:
i. LDL cholesterol causes plaque
deposits on the walls of veins or arteries which will lead to heart attack
and stroke. / Kolestrol LDL menyebabkan pengenapan
plak
pada dinding salur darah vena atau arteri yang boleh
menyebabkan sakit jantung dan angin ahmar.
ii. HDL cholesterol reduces
deposits on the artery walls. / Kolestrol HDL
mengurangkan
pengenapan
pada dinding arteri.
b. Animal
fats (saturated fats) contain higher LDL cholesterol whereas vegetable
oils (unsaturated fats) contain
higher HDL cholesterol. / Lemak
haiwan
(lemak tepu) mengandungi kolestrol LDL yang lebih banyak manakala
minyak
sayuran
(lemak tak tepu) mengandungi lebih banyak kolestrol HDL.
c. Eating food high in animal fats increases the level of LDL
in blood.
Memakan makanan yang tinggi dengan lemak haiwan akan meningkatkan kandungan
LDL
dalam darah.
7 Palm oil / Minyak sawit
a. Palm oil is extracted from fresh oil palm fruits. / Minyak sawit diekstrak daripada buah sawit yang segar.
b Palm oil contains 49% of saturated fats and 51% of unsaturated fats. It is classified as unsaturated
fat. / Minyak
sawit mengandungi 49% lemak tepu dan 51% lemak tak tepu. Ia dikelaskan sebagai lemak
tak tepu
.
c. Palm oil is used in cooking and manufacture margarine and shortening, chocolate, cakes, ice creams and noodles.
Minyak sawit digunakan untuk memasak dan membuat marjerin dan coklat, kek, aiskrim dan mee.
d. The advantages of palm oil compared to other oil are: / Kelebihan minyak sawit berbanding minyak lain adalah:
i. rich in vitamin E which is a powerful antioxidant. / kaya dengan vitamin E yang merupakan antioksidan yang kuat.
ii. rich in beta-carotene which contains vitamin A. Vitamin A helps to strengthen the immune system.
kaya dengan beta-carotene yang mengandungi vitamin A. Vitamin A membantu menguatkan sistem imuniti.
iii. it is cholesterol free. / tiada kolestrol.
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
89
Natural Rubber / Getah Asli
1 Natural polymers are polymers that exist in nature and are not man-made.
Polimer semula jadi ialah polimer yang wujud secara semula jadi dan bukannya buatan manusia.
Example: / Contoh:
Natural polymer / Polimer semula jadi Monomer / Monomer
Protein / Protein Amino acid / Asid amino
Cabohydrate / Karbohidrat Glucose / Glukosa
Natural rubber / Getah semula jadi Isoprene / Isoprena
2 The structure of rubber / Struktur getah
a. Rubber is a natural polymer. It is formed from the monomer isoprene
. Molecular formula of isoprene
is
C
5
H
8
. / Getah ialah polimer asli. Ia terbentuk daripada monomer
isoprena
. Formula molekul
isoprena
ialah C
5
H
8
.
b. Isoprene molecules are joined together by addition polymerisation
process to form the polymer of natural
rubber, polyisoprene: / Molekul isoprena terikat bersama oleh proses
pempolimeran
penambahan untuk membentuk
polimer getah semula jadi, poliisoprena:
H H CH
3
H
n ( C C C C )
H H
H H CH
3
H
( C C C C )
H H
n
n is large numbers
n ialah nombor yang besar
Isoprene (2-methylbut-1, 3-diene)
Isoprena (2-metilbut-1, 3-diena)
Polyisoprene
Polimer getah
3 Coagulation of latex / Penggumpalan lateks
a. Latex is milk like liquid obtained from tapped rubber tree. Latex is a colloid
which contains suspension of
rubber particles in water. / Lateks ialah cecair seperti susu yang diperoleh daripada pokok getah yang ditoreh. Lateks ialah
koloid
yang mengandungi zarah-zarah getah yang tersebar dalam air.
b. The rubber particles are made up of long chain rubber polymers [(C
5
H
8
)
n
] surrounded by a
protein membrane
. The protein membrane
is negatively
charged. The forces of repulsion between
negatively charged particles prevent them from combining or coagulating. / Zarah-zarah getah terdiri daripada polimer
getah berantai panjang [(C
5
H
8
)
n
] yang dikelilingi
membran protein
.
Membran protein
adalah bercas
negatif
.
Daya tolakan di antara zarah-zarah bercas negatif menghalang zarah-zarah tersebut daripada bergabung atau bergumpal.
Negative charge
Rubber polymer
Water
Bercas negatif
Polimer getah
Air
Repulsion
Tolakan
c. Latex coagulates when: / Lateks tergumpal apabila:
i. acid is added to it such as methanoic acid (formic acid), ethanoic acid (acetic acid) or any other weak acids.
asid seperti asid metanoik (asid formik), asid etanoik (asid asetik) atau asid lemah lain ditambah ke dalamnya.
ii. Left aside for 1 2 days due to bacterial action on latex. Bacteria from the air enter latex. Activity of bacteria in
the latex produce lactic acid
that contains hydrogen ions (H
+
)
which causes coagulation of latex.
Coagulate latex is semi solid. / Dibiarkan selama 1 2 hari untuk tindakan bakteria ke atas lateks. Bakteria dari udara
masuk ke dalam lateks. Aktiviti bakteria di dalam lateks menghasilkan
acid
yang mengandungi
ion hidrogen (H
+
)
yang menyebabkan penggumpalan lateks. Menggumpal lateks adalah separa pepejal.
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
90
d. When acid is added to latex, coagulation of latex occurs:
Apabila asid ditambah kepada lateks, penggumpalan lateks berlaku:
i. Positively charged hydrogen ions from the acid neutralises
the negative charges on the surface of the protein
membrane. A neutral rubber particle
is formed. / Ion hidrogen bercas positif daripada asid
meneutralkan
cas-cas negatif pada permukaan membran protein.
Zarah
getah yang neutral terbentuk.
Collide
Perlanggaran
Breaking of protein membrane
Neutralised rubber particle
Membran protein pecah
Zarah getah yang neutral
H
+
H
+ H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+ H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+ H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+ H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+
Repulsion
Tolakan
ii. The neutral
particles no longer repel
each other. These neutral
particles collide
with
each other, causing the membrane to break
. The rubber polymers are freed and they coagulate
by
combining together to form large lump of rubber polymer. The latex has coagulated.
Zarah-zarah
neutral
tidak lagi
menolak
di antara satu sama lain. Zarah-zarah
neutral
ini
berlanggar
di
antara satu sama lain, menyebabkan membran
pecah
. Polimer getah terbebas dan
bergumpal
dengan bergabung
untuk membentuk gumpalan getah yang besar. Lateks telah tergumpal.
Broken protein membrane
Rubber polymers coagulate
Membran protein pecah
Polimer getah menggumpal
4 Coagulation of latex can be prevented by adding ammonia (alkali)
to it. The ammonia solution
(containing OH
ions) will neutralise any acids that may be produced by the bacteria. / Penggumpalan lateks boleh dihalang
dengan menambah
ammonia (alkali)
kepadanya. Larutan ammonia (mengandungi ion OH
) akan meneutralkan sebarang asid
yang dihasilkan oleh bakteria.
5 Describe how the presence of an alkali can prevent the coagulation process of latex: / Huraikan bagaimana alkali boleh
menghalang proses penggumpalan lateks:
a. Hydroxide ions, OH
from alkali neutralise
hydrogen ions, H
+
produced by acid
as a result of bacterial
attack on protein. / Ion hidroksida, OH
daripada alkali
meneutralkan
ion hidrogen, H
+
yang dihasilkan oleh
acid
disebabkan serangan bakteria ke atas protein.
b. The protein membrane remains negatively
charge because there is no hydrogen ions. / Membran protein kekal
bercas
negatif
kerana tiada ion-ion hidrogen.
c. The rubber particles repel
each other. / Zarah-zarah getah
menolak
di antara satu sama lain.
d. The rubber polymers cannot combine and coagulate
. / Polimer-polimer getah tidak boleh bergabung dan
menggumpal
.
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
91
6 Properties and uses of natural rubber / Sifat-sifat dan kegunaan getah asli
a. Properties of natural rubber / Sifat-sifat getah asli
Property
Sifat
Description / Penerangan Uses / Kegunaan
Elastic
Kekenyalan
When it is stretched
, it straighten out. It returns
back to
its original shape once the stretching
force is released. / Apabila
diregangkan
, ia menjadi lurus. Ia
kembali
kepada bentuk asal apabila
daya
regangan
dilepaskan.
Rubber tube, gloves,
rubber bands and shoe
soles. / Tiub getah, sarung
tangan, getah pengikat dan
tapak kasut.
Resistance to
oxidation
Ketahanan
terhadap
pengoksidaan
The natural rubber polymers are easily oxidised
due to the
presence of double bonds. / Polimer getah asli
teroksida
dengan
mudah kerana kehadiran ikatan ganda dua.
These properties make the
usage of natural rubber
limited. / Sifat-sifat ini
menjadikan kegunaan getah
asli terhad.
Effect of heat
Kesan haba
When it is heated, it is soften
and become sticky
.
Apabila dipanaskan, getah menjadi
lembut
dan menjadi
melekit
.
When it is cooled, it becomes hard
and brittle
.
Apabila disejukkan, ia menjadi
keras
dan
rapuh
.
Effect of
solvent
Kesan pelarut
Natural rubber is soluble
in organic, alkaline and acidic
solution.
Getah asli
larut
dalam larutan organik, beralkali dan berasid.
b. The properties of natural rubber can be improved through the vulcanisation process. / Sifat-sifat getah asli boleh
diperbaiki melalui proses pemvulkanan.
7 Vulcanisation of rubber: / Pemvulkanan getah:
a. Natural rubber is elastic (it will return to its original shape after stretching force is released). / Getah asli adalah kenyal
(ia akan kembali kepada bentuk asal apabila daya regangan dilepaskan).
b. When the rubber is over stretched, the rubber molecules do not return to their original positions. The rubber has lost
its elasticity. / Apabila getah diregang secara berlebihan, molekul getah tidak kembali kepada kedudukan asal. Getah telah
hilang sifat kekenyalannya.
c. Natural rubber becomes stronger and more elastic after vulcanisation:
Getah asli menjadi lebih kuat dan kenyal selepas pemvulkanan:
i. Sulphur is heated together with natural rubber. / Sulfur dipanaskan bersama dengan getah asli.
ii. Rubber stripe is soaked in sulphur monochloride solution in methylbenzene for a few hours, and then dried.
Jalur getah direndam dengan larutan sulfur monoklorida dalam metilbenzena untuk beberapa jam, dan kemudiannya
dikeringkan.
C
=
C
C
=
C
C
= C
C
=
C
C
= C
C
=
C
C = C
Pemvulkanan
Vulcanisation
C
S
S
C
C
S
S
C
C
C
S
S
C
Natural rubber / Getah asli Vulcanised rubber / Getah tervulkan
d. In vulcanised rubber / Dalam getah tervulkan
i. The sulphur atoms form cross-link between the long rubber molecule.
Atom-atom sulfur membentuk rangkai silang di antara molekul panjang getah.
ii. This reduces the ability of the polymers to slide over each other.
Ini mengurangkan kebolehan polimer untuk menggelongsor di antara satu sama lain.
iii. The rubber molecules return to their original positions after being stretched.
Molekul-molekul getah kembali kepada kedudukan asal selepas diregangkan.
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
92
e. Complete the table below: / Lengkapkan jadual di bawah:
Property / Sifat Natural rubber / Getah asli Vulcanised rubber / Getah tervulkan
Elasticity
Kekenyalan
Less
elastic because the polymer chain
of rubber can slide
over one another
easily.
Kurang
kenyal kerana rantai polimer getah
boleh
menggelongsor
di antara satu sama
lain dengan mudah.
More
elastic because the sulphur
cross-links prevents
the polymer chain
of rubber molecules slide
over one
another.
Lebih
kenyal kerana rangkai silang
sulfur
menghalang rantai polimer molekul
getah
menggelongsor
di antara satu sama
lain.
Strength and
hardness
Kekuatan dan
kekerasan
Weaker
and softer
. When it
is strectched
beyond the elastic limit,
the polymer chain will break
. Lebih
diregangkan
dan lebih
lembut
. Apabila
diregangkan
melebihi had kekenyalan, rantai
polimer akan
putus
.
Stronger
and harder
because the
presence of sulphur
cross-links between
the polymer.
Lebih
kuat
dan lebih
keras
kerana
kehadiran rangkai silang
sulfur
di antara
polimer.
Resistance to
heat
Ketahanan
terhadap haba
Cannot
withstand high temperature.
Easily melt
when heated.
Tidak tahan
haba.
Melebur
dengan mudah
apabila dipanaskan.
Can
withstand high temperature
because the presence of sulphur
cross-
links makes it more difficult to melt
.
Tahan
haba kerana kehadiran rangkai silang
sulfur
menjadikannya lebih susah untuk
melebur
.
Resistance to
oxidation
Ketahanan
terhadap
pengoksidaan
Easily oxidised by oxygen
because the
presence of many double bonds
in the
rubber polymer.
Teroksida dengan mudah oleh
oksigen
kerana
kehadiran banyak ikatan
ganda dua
dalam
polimer getah.
Not easily oxidised by oxygen because the
number of double bonds
is reduced.
Tidak teroksida oleh oksigen dengan mudah kerana
bilangan ikatan
ganda dua
berkurang.
FORM 5 Chemistry MODULE
N i l a m
P
u
b
l
i
c
a
t
io
n Sdn. B
h
d
.
93
1 The statement below is about organic compound X:
Pernyataan di bawah adalah berkenaan dengan sebatian organik X:
Organic compound X undergoes addition reaction.
Sebatian organik X mengalami tindak balas penambahan.
Which of the following represents the formula for
compound X?
Antara berikut, yang manakah mewakili formula untuk sebatian X?
A C
3
H
10
C C
3
H
7
OH
B C
3
H
6
D C
3
H
7
COOH
2 Which of the following are true about butane and butene?
Antara berikut, yang manakah benar tentang butana dan butena?
I Insoluble in water / Tidak larut di dalam air
II Exist as gas at room temperature
Wujud sebagai gas pada suhu bilik
III Decolourise acidified potassium manganate(VII)
solution / Melunturkan larutan kalium manganat(VII) berasid
IV Burn completely in air to produce carbon dioxide and
water / Terbakar lengkap di udara untuk menghasilkan karbon
dioksida dan air
A I and III only
I dan III sahaja
C I, II and IV only
I, II dan IV sahaja
B II and IV only
II dan IV sahaja
D I, II, III and IV
I, II, III, dan IV
3 The diagram below shows part of the structure of a polymer.
Rajah di bawah menunjukkan sebahagian daripada struktur polimer.
H H H H
~ C C C C ~
C1 H C1 H
Which of the following is its monomer?
Antara berikut, yang manakah monomer bagi polimer di atas?
A H C1
C C
H H
B
H H H
H C C C H
C1
C H C1
C C C H
H H
D H H H
C C C H
C1 C1
OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS / SOALAN OBJEKTIF
4 Which of the following hydrocarbons contains 81.82%
carbon by mass? [Relative atomic mass: H = 1, C = 12]
Hidrokarbon yang manakah mengandungi 81.82% karbon
berdasarkan jisim? [Jisim atom relatif: H = 1, C = 12]
A C
2
H
2
C C
3
H
6
B C
2
H
4
D C
3
H
8
5 The diagram below represents the structural formula of a
carbon compound.
Rajah di bawah menunjukkan formula struktur satu sebatian
karbon.
H H O H H H
H C C C O C C C H
H H H H H
What is the name of the compoud?
Apakah nama bagi sebatian di atas?
A Ethyl propanoate / Etil propanoat
B Propyl ethanoate / Propil etanoat
C Propyl propanoate / Propil propanoat
D Diethyl methanoate / Dietil metanoat
6 The diagram below shows the structural formula of carbon
compound J.
Rajah di bawah menunjukkan formula struktur sebatian karbon J.
H H O
H C C C
H H OH
Which of the following statements are true?
Antara pernyataan berikut, yang manakah benar?
I Compound J is unsaturated hydrocarbon
Sebatian J ialah hidrokarbon tak tepu
II Compound J reacts with sodium carbonate solution
Sebatian J bertindak dengan larutan natrium karbonat
III Oxidation of butanol will produce compound J
Pengoksidaan butanol akan menghasilkan sebatian J
IV Complete combustion of compound J produces carbon
dioxide gas and water / Pembakaran lengkap sebatian J
menghasilkan gas karbon dioksida and air
A II and III only
II dan III sahaja
B III and IV only
III dan IV sahaja
C I, II and III only
I, II dan III sahaja
D II, III and IV only
II, III dan IV sahaja
MODULE Chemistry FORM 5
N
i
la
m
Publica
t
io
n
S
d
n
. B
h
d .
94
7 The diagram below shows the structural formula of ethanoic
acid.
Rajah di bawah menunjukkan formula struktur bagi asid etanoik.
2
H O
1
H C C O
4
H
3
H
Which of the following hydrogen atoms will involve in a
chemical reaction? / Antara berikut, atom hidrogen yang manakah
akan terlibat dalam tindak balas kimia?
A
1
H C
3
H
B
2
H D
4
H
8 The diagram below show the conversion of ethanol into
compound P and subsequently into compound Q.
Rajah di bawah menunjukkan penukaran etanol kepada sebatian P
dan seterusnya kepada sebatian Q.
C
2
H
5
OH
Heat with / Panaskan dengan
K
2
Cr
2
O
7
Compound / Sebatian P
Heat with C
3
H
7
OH and
concentrated H
2
SO
4
Panaskan dengan C
3
H
7
OH
dan H
2
SO
4
pekat
Compound / Sebatian Q
Which of the following is compound Q?
Antara berikut, yang manakah sebatian Q?
A Ethyl propanoate / Etil propanoat
B Propyl ethanoate / Propil etanoat
C Propyl propanoate / Propil propanoat
D Ethyl ethanoate / Etil etanoat
9 The diagram below shows the structural formula of an organic
compound. / Rajah di bawah menunjukkan struktur formula satu
sebatian organik.
H
H C H
H H H H
H C C C C C H
H H H
H C H
H
What is the IUPAC name for the compound?
Apakah nama mengikut IUPAC bagi sebatian tersebut?
A 2, 4-dimethylpent-1-ene
2, 4-dimetilpent-1-ena
B 2, 4-dimethylpent-2-ene
2, 4-dimetilpent-2-ena
C 3, 4-dimethylpent-1-ene
3, 4-dimetilpent-1-ena
D 3, 4-dimethylpent-2-ene
3, 4-dimetilpent-2-ena
10 Which of the following fatty acids are unsaturated?
Antara berikut, asid lemak yang manakah tidak tepu?
I C
17
H
29
COOH
II C
17
H
31
COOH
III C
17
H
33
COOH
IV C
17
H
35
COOH
A I and III only
I dan III sahaja
C I, II and III only
I, II dan III sahaja
B II and IV only
II dan IV sahaja
D I, III and IV only
I, III dan IV sahaja
You might also like
- Organic Chemistry CurrentDocument48 pagesOrganic Chemistry CurrentBierzo JomarNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument10 pagesHydrocarbonsjoeNo ratings yet
- CARBON COMPOUNDS GUIDEDocument44 pagesCARBON COMPOUNDS GUIDECool VighneshNo ratings yet
- Section B-Arc Tutors Chemistry Crash Course Sources of Hydrocarbon CompoundsDocument38 pagesSection B-Arc Tutors Chemistry Crash Course Sources of Hydrocarbon CompoundsakeemNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemsitryDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemsitryRyanNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Organic Compounds and Carbon TerminologyDocument16 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Organic Compounds and Carbon Terminologyakusabrina2012No ratings yet
- Alkanes, Alkenes, AlkynesDocument7 pagesAlkanes, Alkenes, AlkynesMuhammad Hasnain AliNo ratings yet
- Carbon CompoundDocument48 pagesCarbon CompoundIlakiya Sharvinee KumarNo ratings yet
- IUPACDocument21 pagesIUPACMihir DhankarNo ratings yet
- Carbon CompoundDocument61 pagesCarbon CompoundhaslimiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - OrganicDocument50 pagesChemistry - Organicsgw67No ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Key Carbon Compounds ConceptsDocument9 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Key Carbon Compounds ConceptsSofiyyahOpieNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: The Scientific Study of Carbon CompoundsDocument14 pagesOrganic Chemistry: The Scientific Study of Carbon CompoundsidkNo ratings yet
- ORGANIC CHEMISTRY NOTEDocument7 pagesORGANIC CHEMISTRY NOTEmensahdelali73No ratings yet
- ORG CHEM (Add'l Notes)Document84 pagesORG CHEM (Add'l Notes)Myra Joy B MonteroNo ratings yet
- Carbon CompoundDocument78 pagesCarbon CompoundYRaj FimmNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Class 11.Document20 pagesOrganic Chemistry Class 11.asinriazNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds - NotesDocument18 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds - NotesFitfulNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ImprovedDocument47 pagesOrganic Chemistry ImprovedRachel Kieda100% (14)
- Hydrocarbon and PetroleumDocument38 pagesHydrocarbon and PetroleumVincentius Matthew YonathanNo ratings yet
- Lecture-10 (Organic Chemistry and Hidrocarbon) - 1Document75 pagesLecture-10 (Organic Chemistry and Hidrocarbon) - 1Permadi BagasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Carbon CompoundDocument50 pagesChapter 11 Carbon CompoundvaogerNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry BasicsDocument20 pagesOrganic Chemistry Basicsprashanth100% (1)
- Chemistry 3Document2 pagesChemistry 3sujana hossainNo ratings yet
- Carbon & Its CompoundsDocument64 pagesCarbon & Its Compoundssiya89308No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - 103 - Lecture 1Document41 pagesOrganic Chemistry - 103 - Lecture 1Abdus SubhanNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument17 pagesOrganic ChemistryesotericgraphicapparelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - HydrocarbonsDocument58 pagesChapter 3 - HydrocarbonsMarielle RumbaoaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry BasicsDocument107 pagesOrganic Chemistry Basics张浩天No ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - Docxnotes 1Document4 pagesINTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - Docxnotes 1Diane Jane SalomonNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Organic Chemistry OriginalDocument46 pagesIntroduction to Organic Chemistry OriginalJeneava ShirleyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SME Notes (Organic Chemmistry)Document14 pagesChemistry SME Notes (Organic Chemmistry)Sayeef MahdiNo ratings yet
- Tut Organic ChemistryDocument57 pagesTut Organic ChemistryThabelo NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument61 pagesOrganic ChemistryfuturainfermieraregistrataNo ratings yet
- Carbon Compounds: Standard/ Class/ Grade - 10 SSC, CBSE - 8 ICSEDocument53 pagesCarbon Compounds: Standard/ Class/ Grade - 10 SSC, CBSE - 8 ICSEsaintEmNo ratings yet
- Saturated Hydrocarbons ReviewerDocument15 pagesSaturated Hydrocarbons ReviewerViaBNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Fuels and Crude Oil Hydrocarbons Alcohols Organic AcidsDocument48 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Fuels and Crude Oil Hydrocarbons Alcohols Organic AcidsGideon CavidaNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument7 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsVijeyNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry EssentialsDocument18 pagesOrganic Chemistry EssentialsTrishaNo ratings yet
- OrganicNotes TolamateDocument36 pagesOrganicNotes Tolamateraghava123456No ratings yet
- The Saturated Hydrocarbons: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: Contrasts Between Organic and Inorganic MoleculesDocument9 pagesThe Saturated Hydrocarbons: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: Contrasts Between Organic and Inorganic MoleculesNaveenNo ratings yet
- Alkanes NotesDocument30 pagesAlkanes NotesSabina SabaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Rajendra01Document49 pagesOrganic Chemistry Rajendra01ecotechconsultantsNo ratings yet
- Part 2- Chapter 1Document14 pagesPart 2- Chapter 1Nguyen NhatNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Chem Notes Anil CH 12. Organic Chemistry Some Basic ConceptsDocument19 pagesHsslive Xi Chem Notes Anil CH 12. Organic Chemistry Some Basic ConceptsKrishnendu NairNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument76 pagesOrganic Chemistryapi-3738901100% (2)
- I CH 8 Chemistry Notes by AkDocument20 pagesI CH 8 Chemistry Notes by AkappugmenonNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Lectures on Alkanes, Cycloalkanes and AlkenesDocument32 pagesOrganic Chemistry Lectures on Alkanes, Cycloalkanes and AlkenesAbdulHameedNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and CycloalkanesDocument17 pagesAlkanes and CycloalkanesPeter ParkerNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem NotesDocument32 pagesOrganic Chem NotesSoleilNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Qt. 2 Week 5Document31 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Qt. 2 Week 5Nina Reca OmisolNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - 1Document14 pagesOrganic Chemistry - 1Habiba N. ElfrashNo ratings yet
- CH 22 Note Packet StudentDocument10 pagesCH 22 Note Packet StudentRENE N. RAMILONo ratings yet
- 1 Organic Compounds HydrocarbonsDocument29 pages1 Organic Compounds HydrocarbonsatNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ADocument113 pagesOrganic Chemistry AChelsea Kyrell TupasNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Review of Basic Organic CompoundsDocument18 pagesModule 5 Review of Basic Organic CompoundsBig BrotherNo ratings yet
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersNo ratings yet
- CAIE 9709 03 ComplexNumber M/J2008/Q5Document1 pageCAIE 9709 03 ComplexNumber M/J2008/Q5SeanNo ratings yet
- 2021 Kedah Fizik MPAT Paper 1Document5 pages2021 Kedah Fizik MPAT Paper 1SeanNo ratings yet
- 6093 - w18 - w21 - QP - 03 - Question 2Document18 pages6093 - w18 - w21 - QP - 03 - Question 2SeanNo ratings yet
- CH - 4 - Part IDocument12 pagesCH - 4 - Part IBAHARUDIN BURAHNo ratings yet
- UCSI University 33RD CONVOCATION CEREMONY YEAR 2021 - Convocation Details - 31.12.2020Document21 pagesUCSI University 33RD CONVOCATION CEREMONY YEAR 2021 - Convocation Details - 31.12.2020SeanNo ratings yet
- Challenge 2021 - Smart Car SystemDocument8 pagesChallenge 2021 - Smart Car SystemSeanNo ratings yet
- 964 QP 2 STPM Biology 2012 Section BDocument2 pages964 QP 2 STPM Biology 2012 Section BSeanNo ratings yet
- CH - 4 - Part IIIDocument19 pagesCH - 4 - Part IIIBAHARUDIN BURAHNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis: S14.1 Structure of The LiverDocument5 pagesHomeostasis: S14.1 Structure of The LiverSeanNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsDocument10 pagesSolution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsSeanNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsDocument5 pagesSolution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsSeanNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsDocument10 pagesSolution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsSeanNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsDocument6 pagesSolution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsSeanNo ratings yet
- CH - 4 - Part IIDocument16 pagesCH - 4 - Part IIBAHARUDIN BURAHNo ratings yet
- Co Co: U-Trac U-TracDocument25 pagesCo Co: U-Trac U-TracSeanNo ratings yet
- Co Co: U-Trac U-TracDocument18 pagesCo Co: U-Trac U-TracSeanNo ratings yet
- Physics H2 9749 Specimen P2Document24 pagesPhysics H2 9749 Specimen P2SeanNo ratings yet
- SPM KSSM Physics Form 4 Chapter 6Document53 pagesSPM KSSM Physics Form 4 Chapter 6Sean75% (4)
- Biologi K2 SPM 2019 PDFDocument34 pagesBiologi K2 SPM 2019 PDFfd bdbbn fjfbNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Lesson 7 Solution PDFDocument5 pagesTutorial - Lesson 7 Solution PDFSeanNo ratings yet
- Physics H2 9749 Specimen P3Document25 pagesPhysics H2 9749 Specimen P3SeanNo ratings yet
- 2017 Nov p11, 21Document73 pages2017 Nov p11, 21SeanNo ratings yet
- Physics H2 9749 Specimen P3Document25 pagesPhysics H2 9749 Specimen P3SeanNo ratings yet
- 4551 w19 QP 03Document16 pages4551 w19 QP 03SeanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Lesson 7 Solution PDFDocument5 pagesTutorial - Lesson 7 Solution PDFSeanNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 AnswersDocument4 pagesPaper 2 AnswersSean100% (1)
- Coll. - Success One HSC Physics 2017 (2017, Pascal Press)Document546 pagesColl. - Success One HSC Physics 2017 (2017, Pascal Press)Sean100% (2)
- Physics H2 9749 Specimen P2Document24 pagesPhysics H2 9749 Specimen P2SeanNo ratings yet
- Physics H2 9749 Specimen P1 MarkschemeDocument21 pagesPhysics H2 9749 Specimen P1 MarkschemeSeanNo ratings yet
- SPM KSSM Physics Form 4 Chapter 1Document22 pagesSPM KSSM Physics Form 4 Chapter 1Sean71% (7)
- Organic Important 2 by Pics Institute Pics Education SolutionsDocument3 pagesOrganic Important 2 by Pics Institute Pics Education SolutionsRamjee NelliNo ratings yet
- Che 176 Carboxylic Acids-2Document67 pagesChe 176 Carboxylic Acids-2BalogunNo ratings yet
- Phenol Preparation and Chemical ReactionsDocument13 pagesPhenol Preparation and Chemical Reactions36 : Tushar RajguruNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper - 01 Class - 12 Chemistry (Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids)Document6 pagesCbse Test Paper - 01 Class - 12 Chemistry (Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids)Tamil SelviNo ratings yet
- Organic Nitrogen Compounds Tutorial SolutionsDocument8 pagesOrganic Nitrogen Compounds Tutorial SolutionsDomNo ratings yet
- IISER BSMS Curriculum 2021Document162 pagesIISER BSMS Curriculum 2021ADWYTH GNAIRNo ratings yet
- Student Number: 201933674 Surname and Initials: Kabekwa BM Title of The Experiment: P-Bromo Acetanilide Date: 14 April 2021Document8 pagesStudent Number: 201933674 Surname and Initials: Kabekwa BM Title of The Experiment: P-Bromo Acetanilide Date: 14 April 2021bridgetteNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure and ProcessesDocument11 pagesElectronic Structure and ProcessesMark MercadoNo ratings yet
- Saturated vs Unsaturated Hydrocarbons TestDocument4 pagesSaturated vs Unsaturated Hydrocarbons TestgefegNo ratings yet
- Building Monomers of Macromolecules-Gummi BioregDocument7 pagesBuilding Monomers of Macromolecules-Gummi Bioregapi-267079239No ratings yet
- List of Organic ReactionsDocument16 pagesList of Organic ReactionsYourMotherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - StereochemistryDocument29 pagesChapter 5 - StereochemistryDenisdNo ratings yet
- Recent Developments in Crosslinking Technology For Coating ResinsDocument14 pagesRecent Developments in Crosslinking Technology For Coating ResinsblpjNo ratings yet
- KCet Chapter QuestionsDocument6 pagesKCet Chapter Questionslakashl14No ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides & Aryl Halides: Victor GrignardDocument50 pagesAlkyl Halides & Aryl Halides: Victor GrignardsarahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Functional GroupsDocument81 pagesChapter 23 Functional GroupsCarlos RochaNo ratings yet
- Short Review on Synthesis of Thiazolidinone and β-Lactam: KeywordsDocument28 pagesShort Review on Synthesis of Thiazolidinone and β-Lactam: KeywordsAmer KasidehNo ratings yet
- Glycerol Propylene. Reaction Scheme: EpichlorohydrinDocument3 pagesGlycerol Propylene. Reaction Scheme: EpichlorohydrinMUHAMMED BAQA ANWER100% (1)
- Different Functional Groups and Their Uses in Organic Compounds 2Document25 pagesDifferent Functional Groups and Their Uses in Organic Compounds 2Belaro JennyNo ratings yet
- GOC Chemistry Shots Notes Hack..Document8 pagesGOC Chemistry Shots Notes Hack..Vinayak ChiwadeNo ratings yet
- UV-Vis Spectroscopy Sample Problems Using Woodward-Fieser RulesDocument8 pagesUV-Vis Spectroscopy Sample Problems Using Woodward-Fieser RulesChris Mariam GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Study of Ethylene ProductionDocument6 pagesFeasibility Study of Ethylene ProductionIntratec SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proofs: Tetrahedron LettersDocument10 pagesJournal Pre-Proofs: Tetrahedron LettersMuhammad Syahrir PratamaNo ratings yet
- BenzeneDocument17 pagesBenzeneMitko100% (1)
- Proteins, amino acids and enzymesDocument6 pagesProteins, amino acids and enzymesChandrapal RathoreNo ratings yet
- 07 Chapter 11Document34 pages07 Chapter 11M Zia Dogar100% (2)
- Supelco Capillary GC ColumnsDocument36 pagesSupelco Capillary GC ColumnsluquisboNo ratings yet
- CA2004312C - Production of Allyl Chloride - Google PatentsDocument5 pagesCA2004312C - Production of Allyl Chloride - Google PatentsTeeTeeXdNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Catalysis. FOXIT - Not Different, Just Better NAT91 Sin ReferenciasDocument6 pagesEnzyme Catalysis. FOXIT - Not Different, Just Better NAT91 Sin Referenciaskiper.valNo ratings yet
- ZDHCDeclaration2020 (Rev 1 March 20th) 1Document2 pagesZDHCDeclaration2020 (Rev 1 March 20th) 1ZOUARINo ratings yet